Honors Bio: Evolution & Natural Selection
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
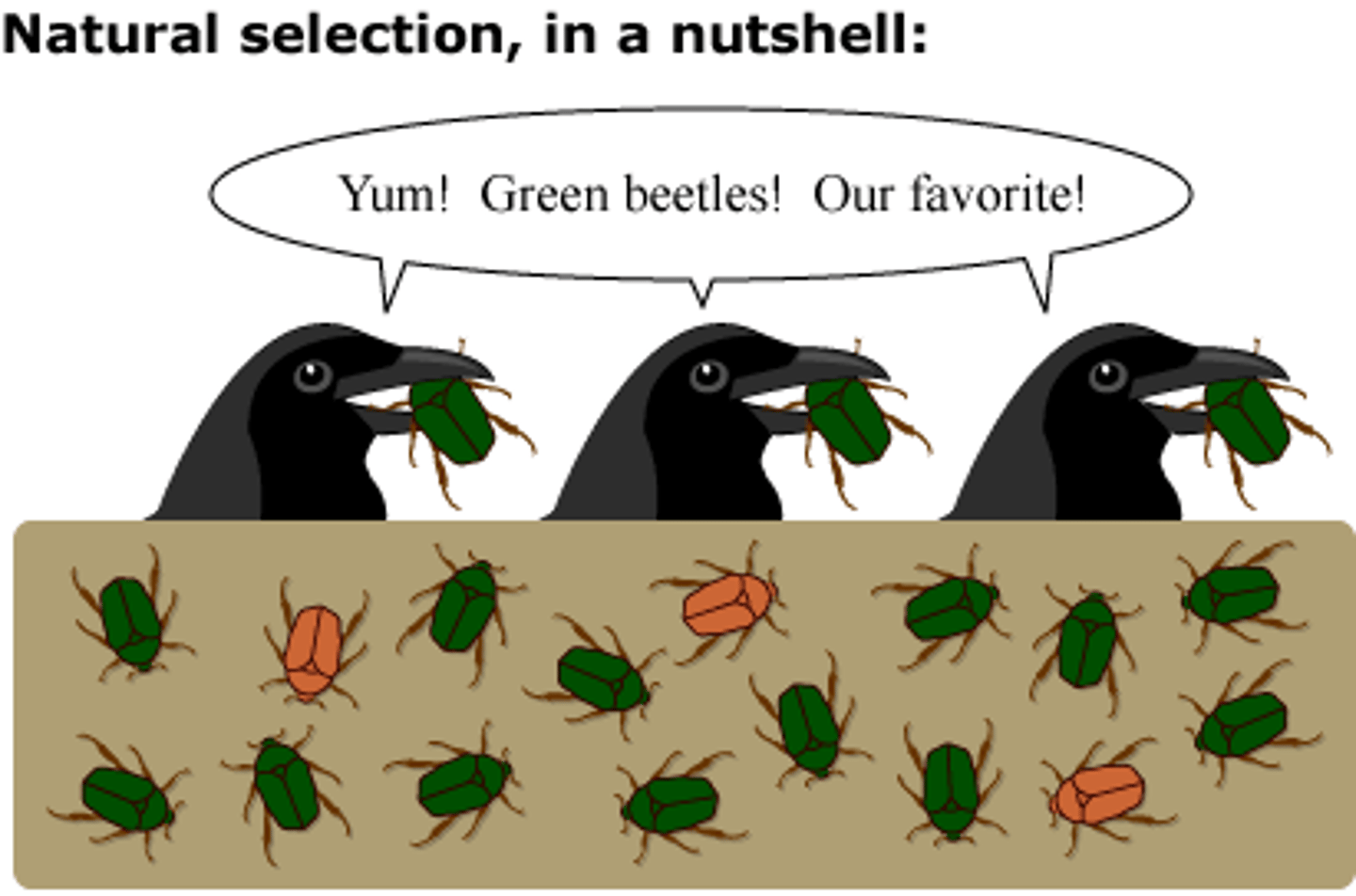
Natural Selection
"survival of the fittest"; the change in a population that occurs when organisms with favorable adaptations survive, reproduce, and pass these genes/traits to the next generation
Fitness
Reproductive success of an organism.

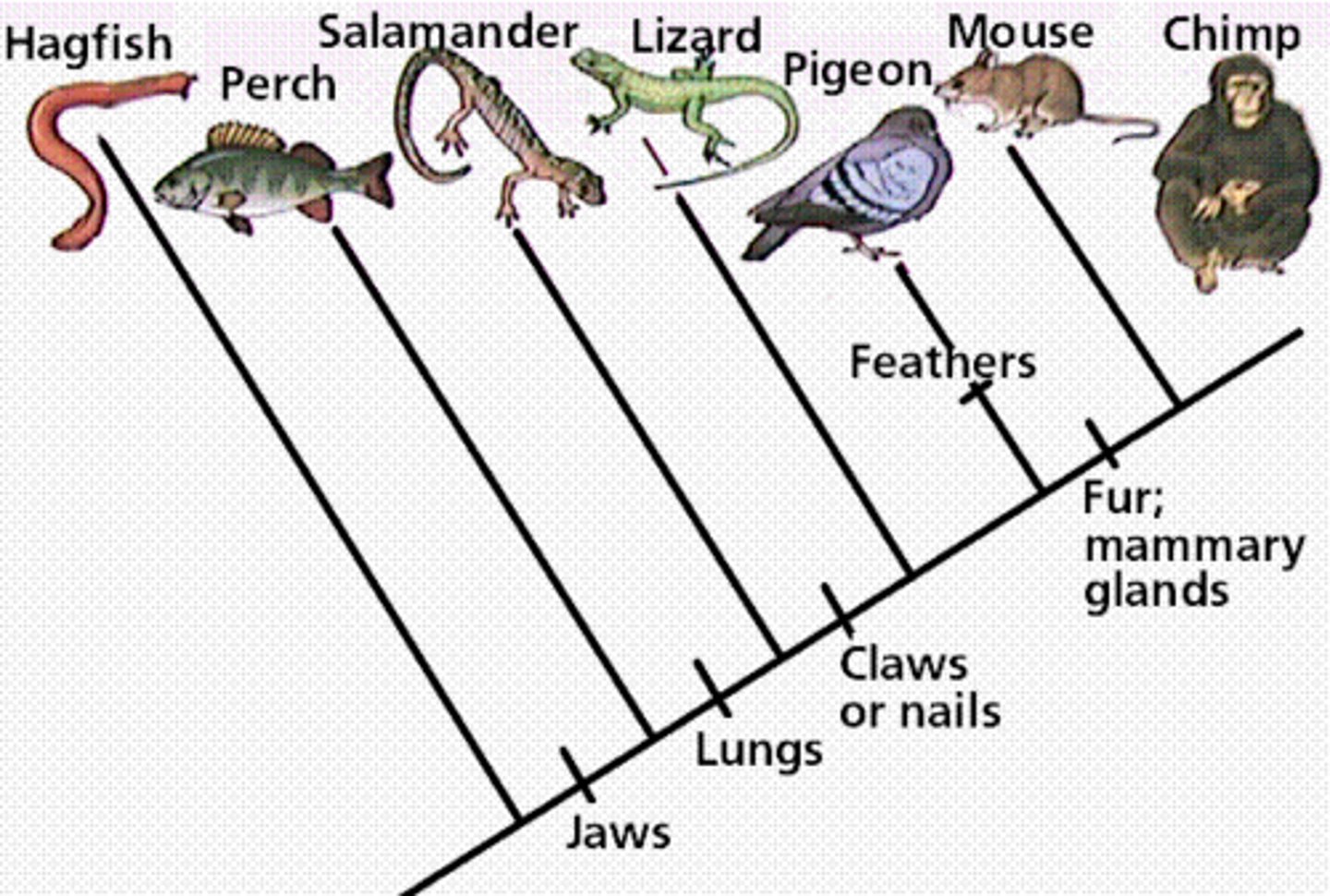
cladogram
a diagram which shows evolutionary relationships among organisms
Evolution
descent with modifications; genetic change in a species over time
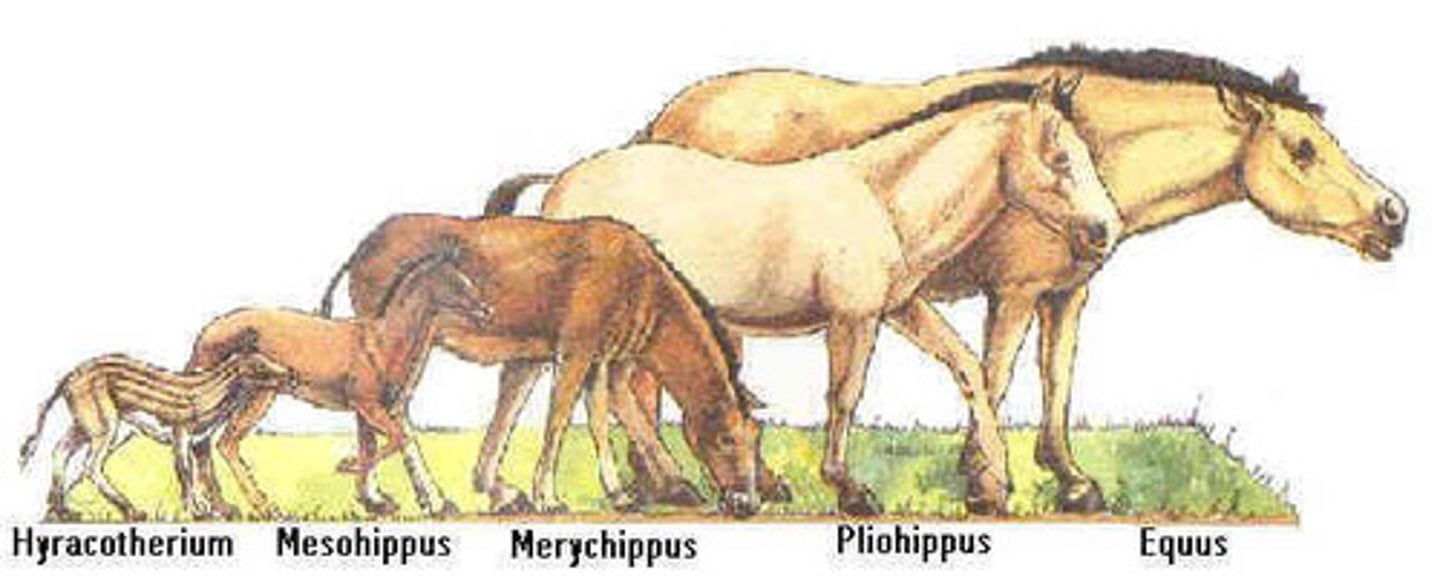
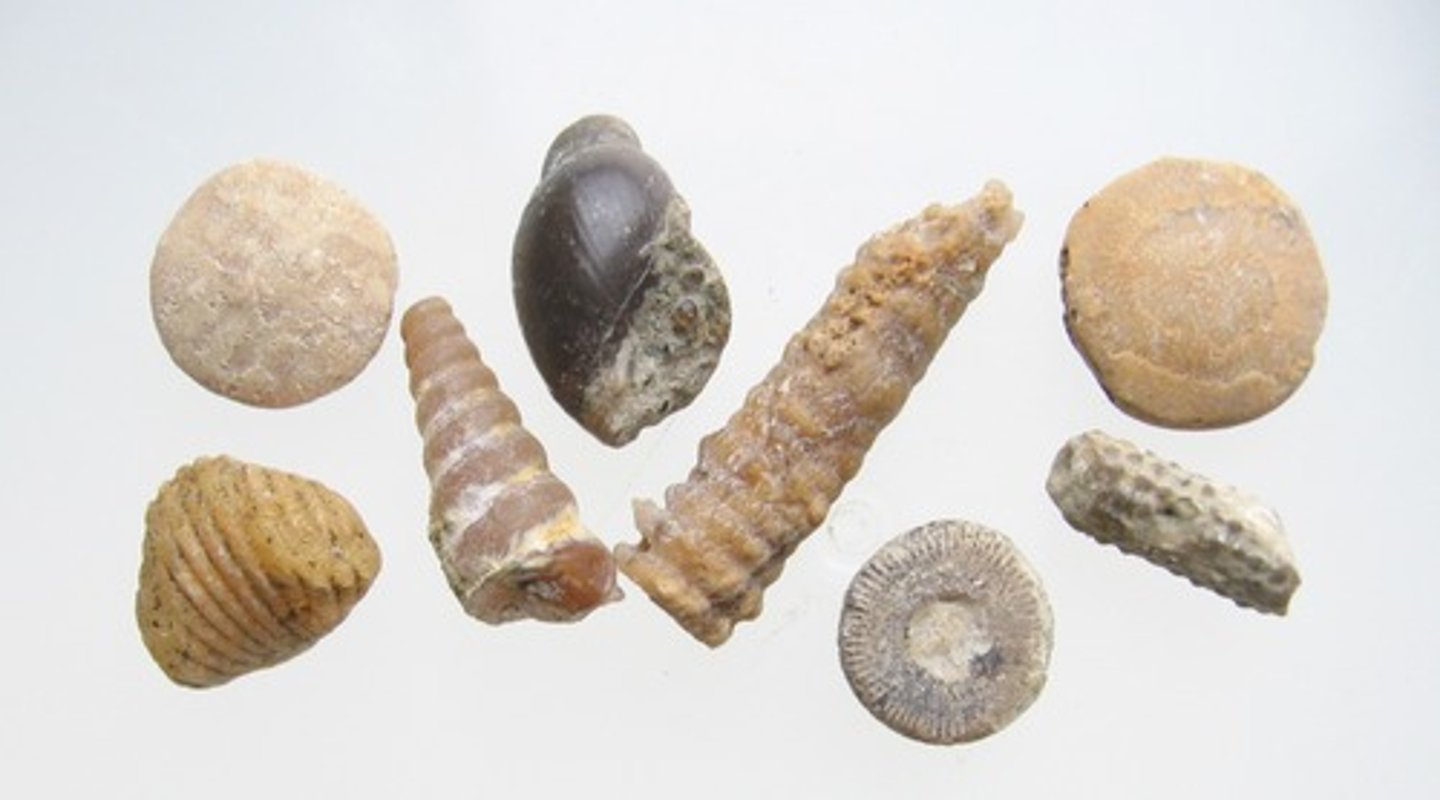
Fossil/ Fossil record
trace of once living organism; used as evidence of evolution. examples are foot imprints, molds, resin, teeth, and bones

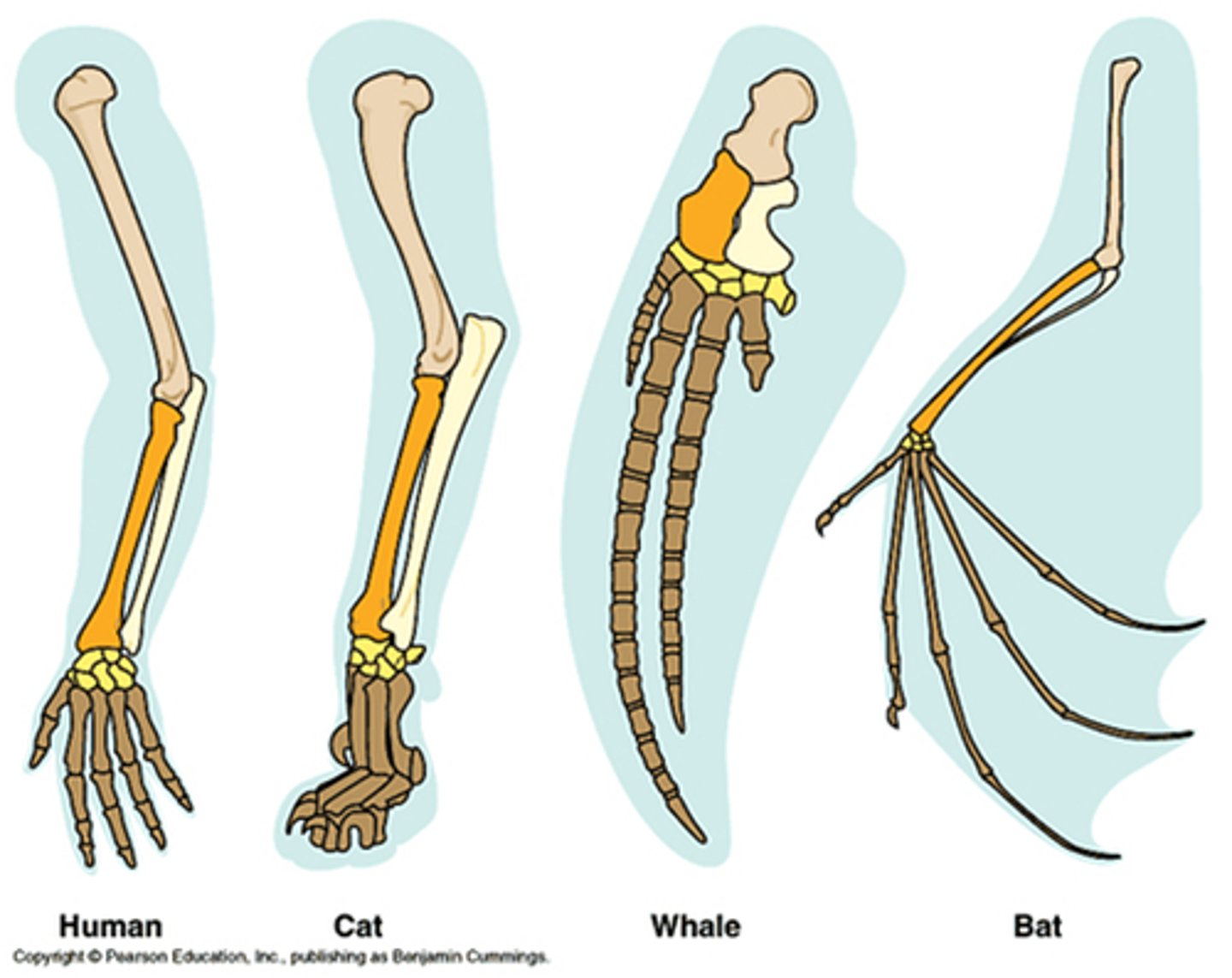
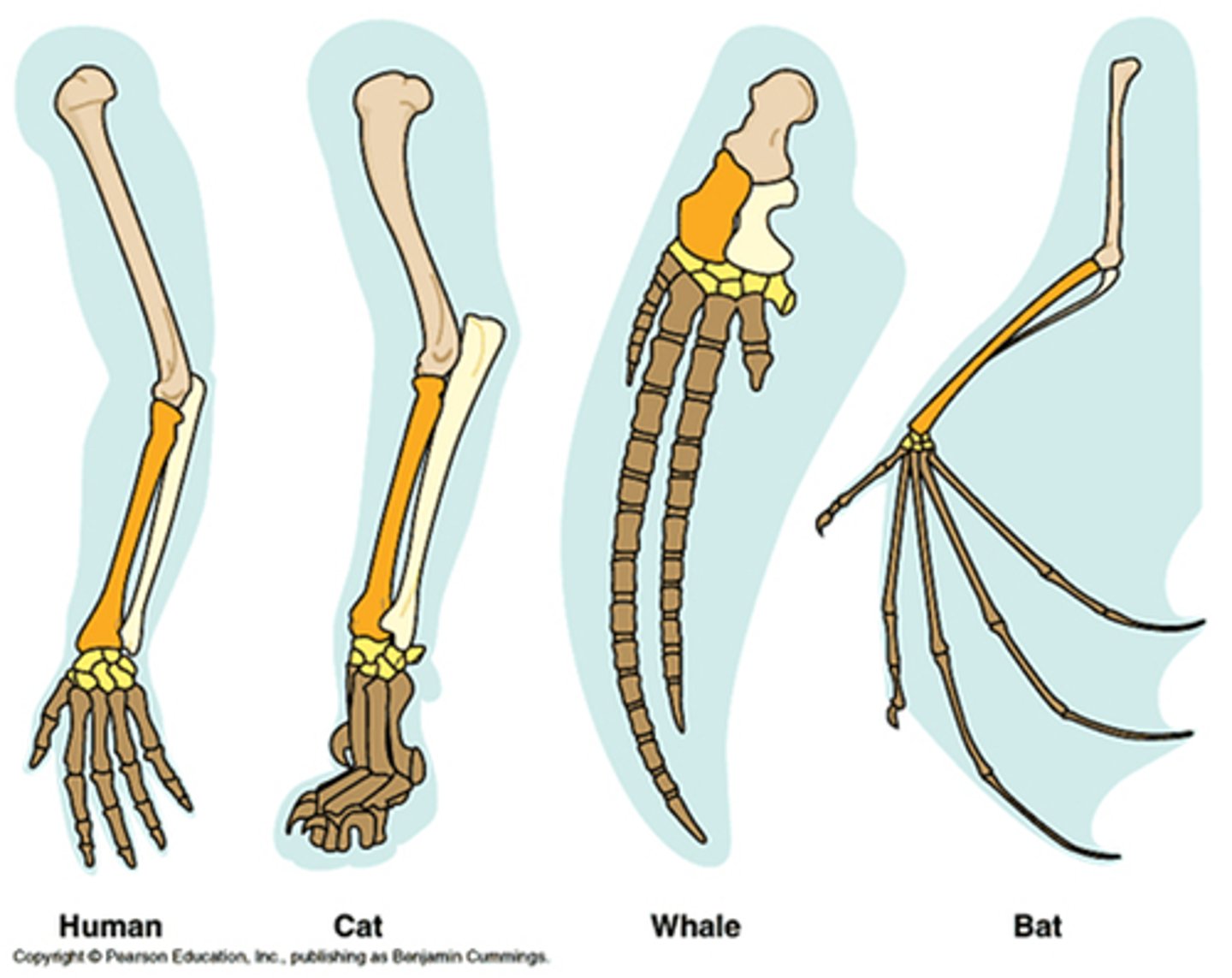
Homologous structures
structures that are similar in stucture due to common ancestry but possibly different in function; examples are the limbs of the human, cat, bat, whale
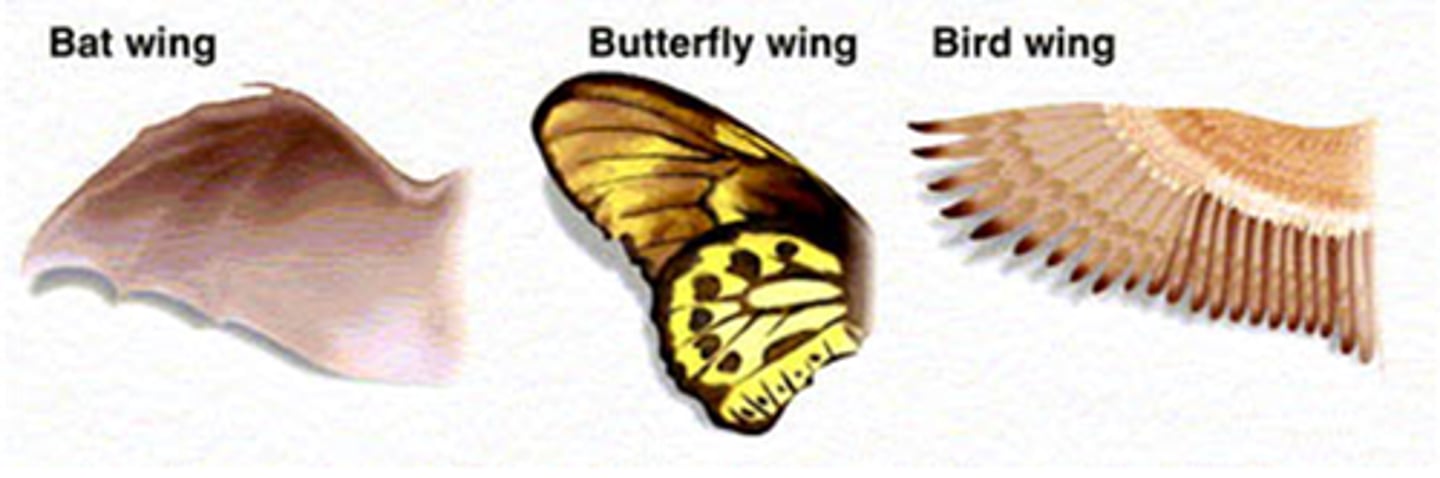
Analogous Structures
an organ or body part that is similar in function but different in structure; example: the wings of birds and butterflies
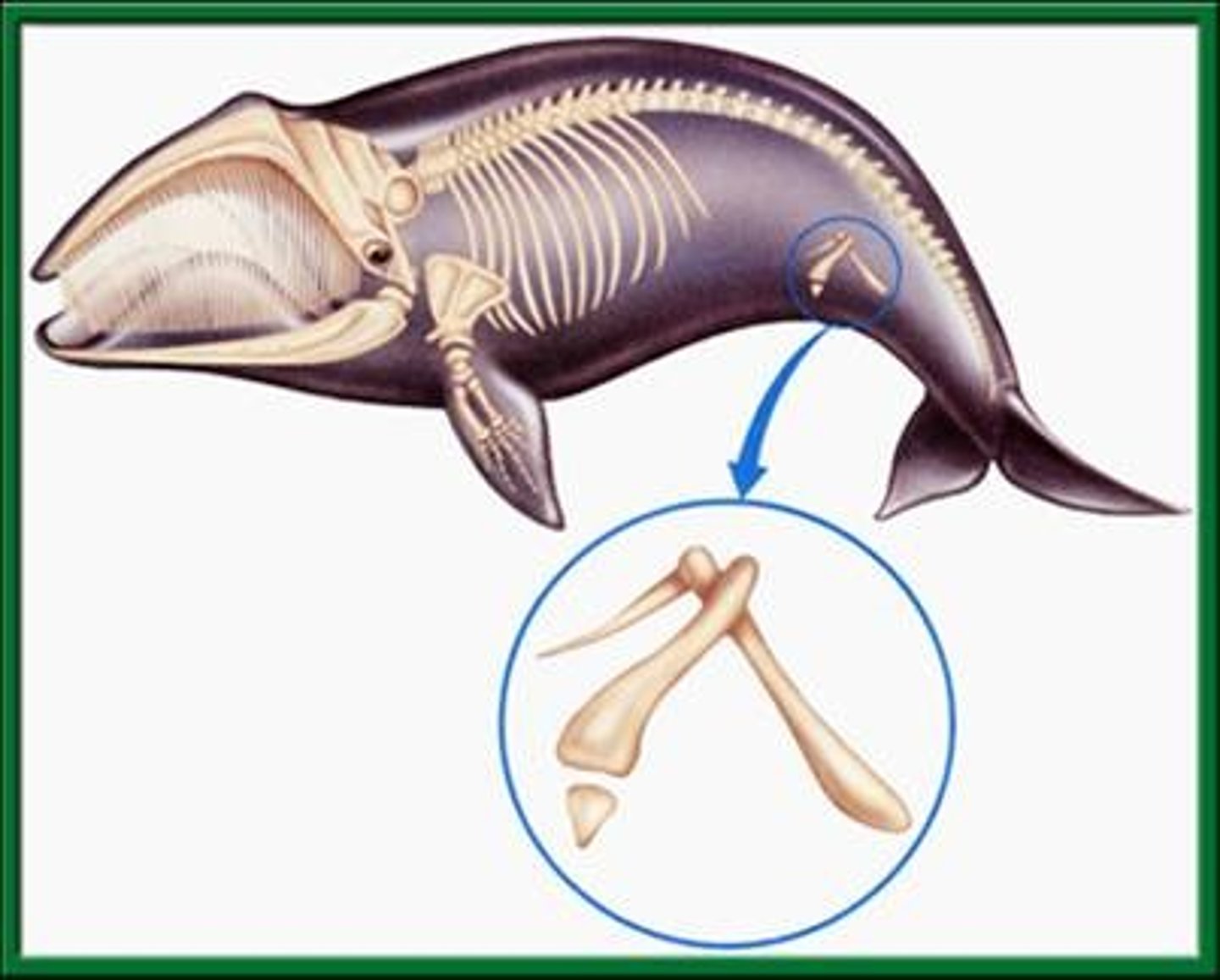
Vestigial Structures
a body part used by the ancestor but is reduced in function or no longer in use EX. human appendix, pelvic bone in whales and some snakes, some genes
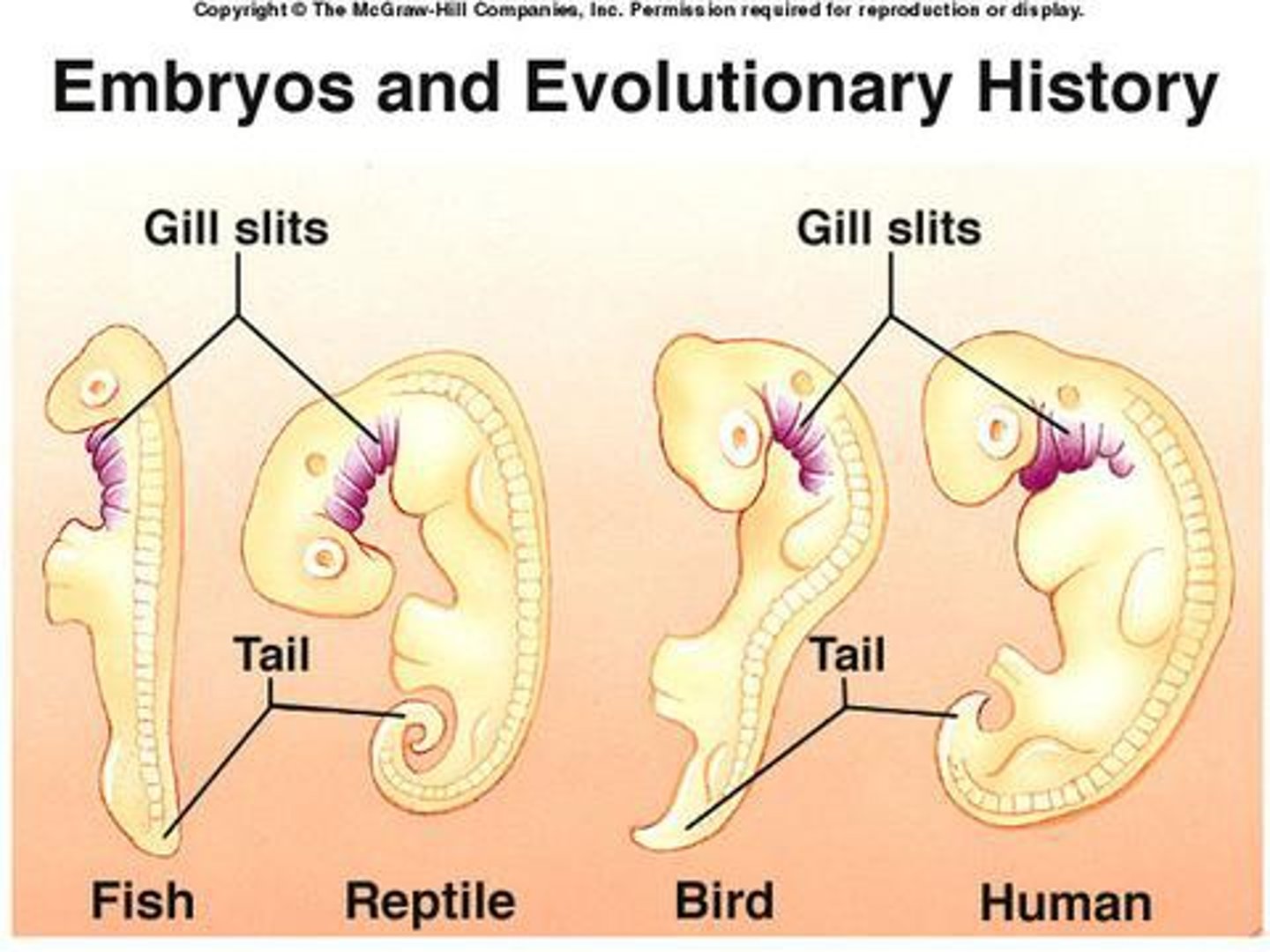
Embryology
the study of embryos and their development.; many different species have embryos which develop in similar ways Ex. Fish, chicken, turtles, and mammal embryos look similar in early stages
Genetic Comparisons / DNA
Most reliable evidence of evolution; the sequences of nucleotides can tell how closely related species are
Evidences for Evolution
Fossil/ Fossil record
Homologous Structures
Molecular Homologies
Developmental Homologies
Biogeography
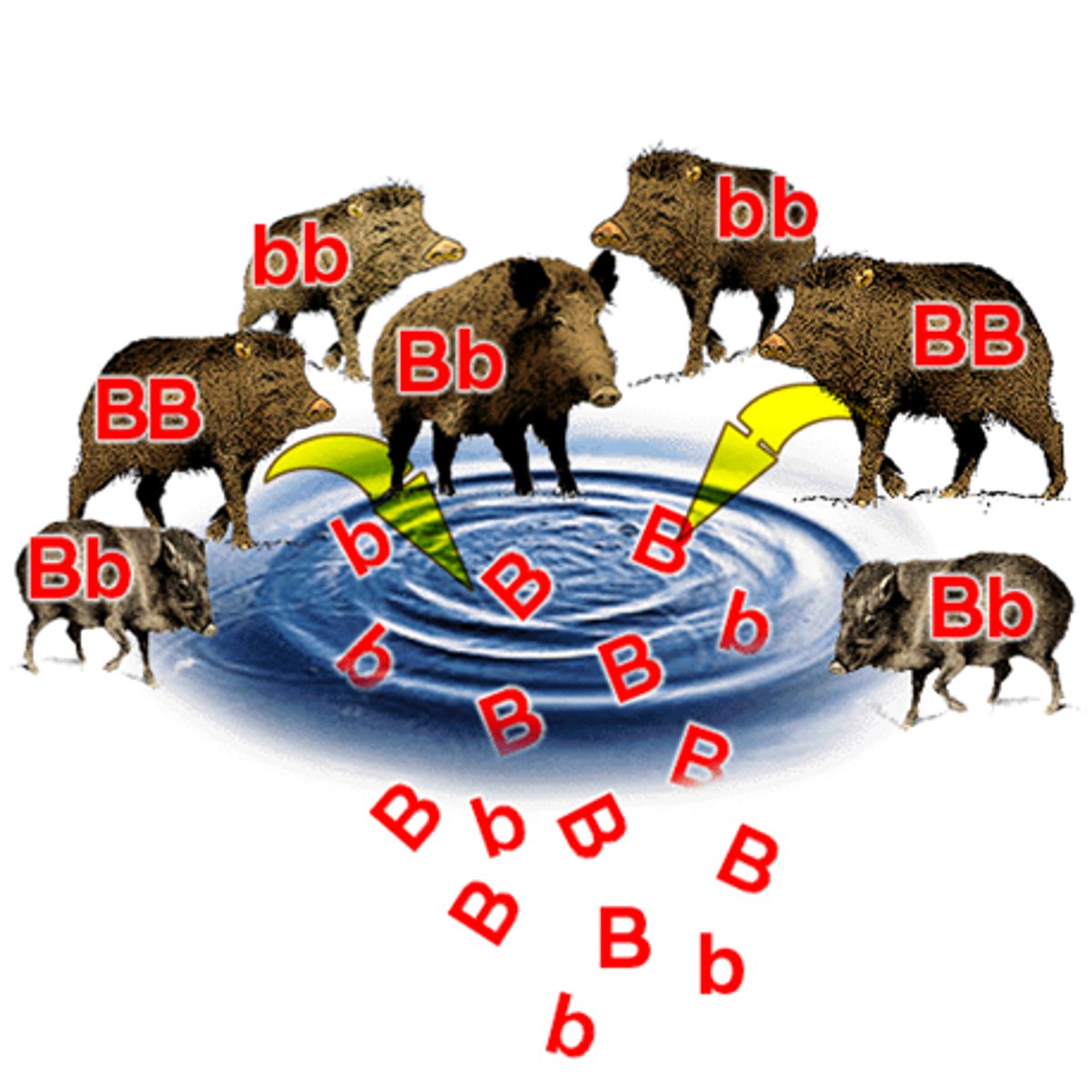
Gene Pool
all of the genes present in a population
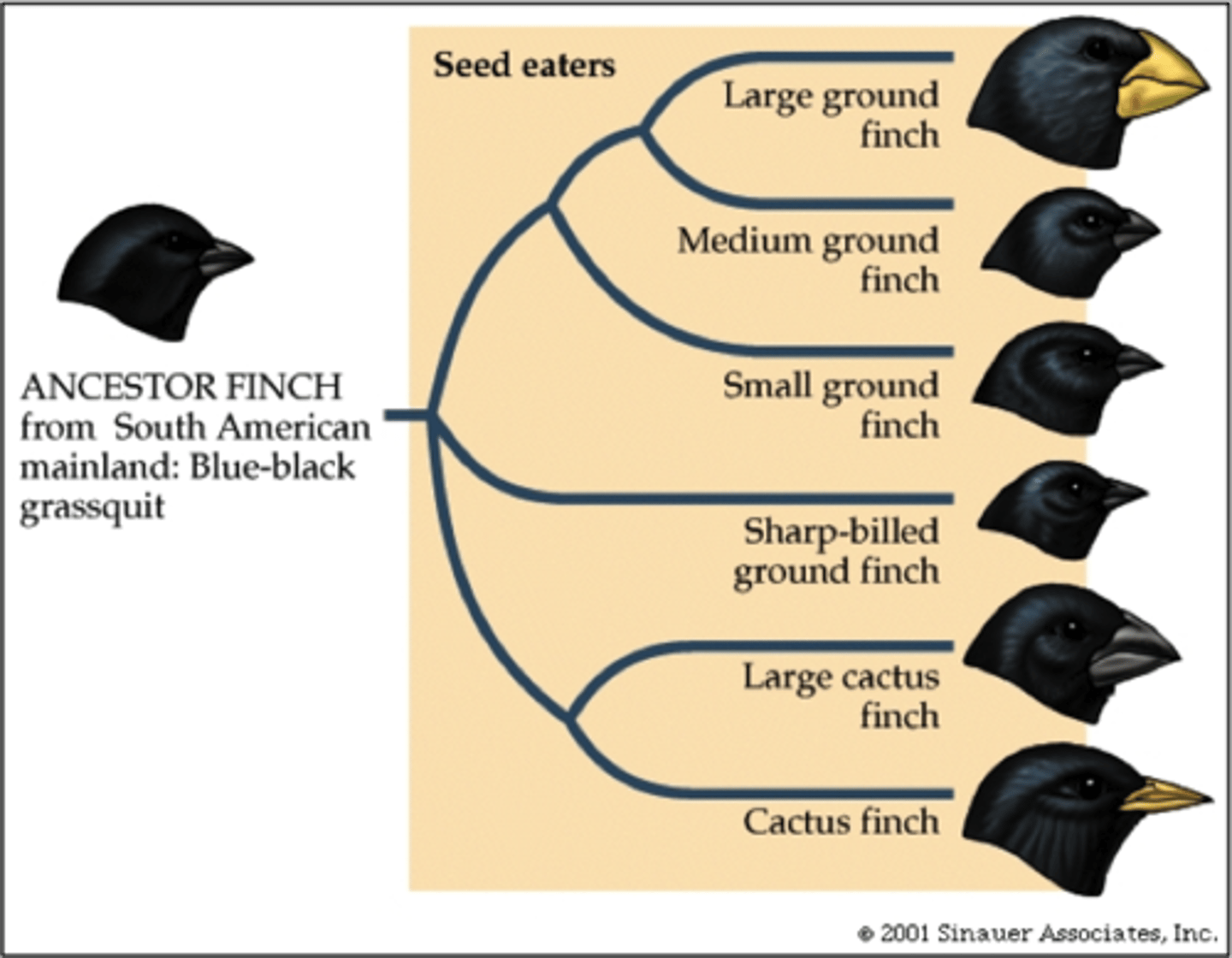
speciation
the evolutionary process by which new biological species develop because of reproductive isolation
competition
in the struggle for existence, all organisms compete for food, water, shelter, space, and a mate
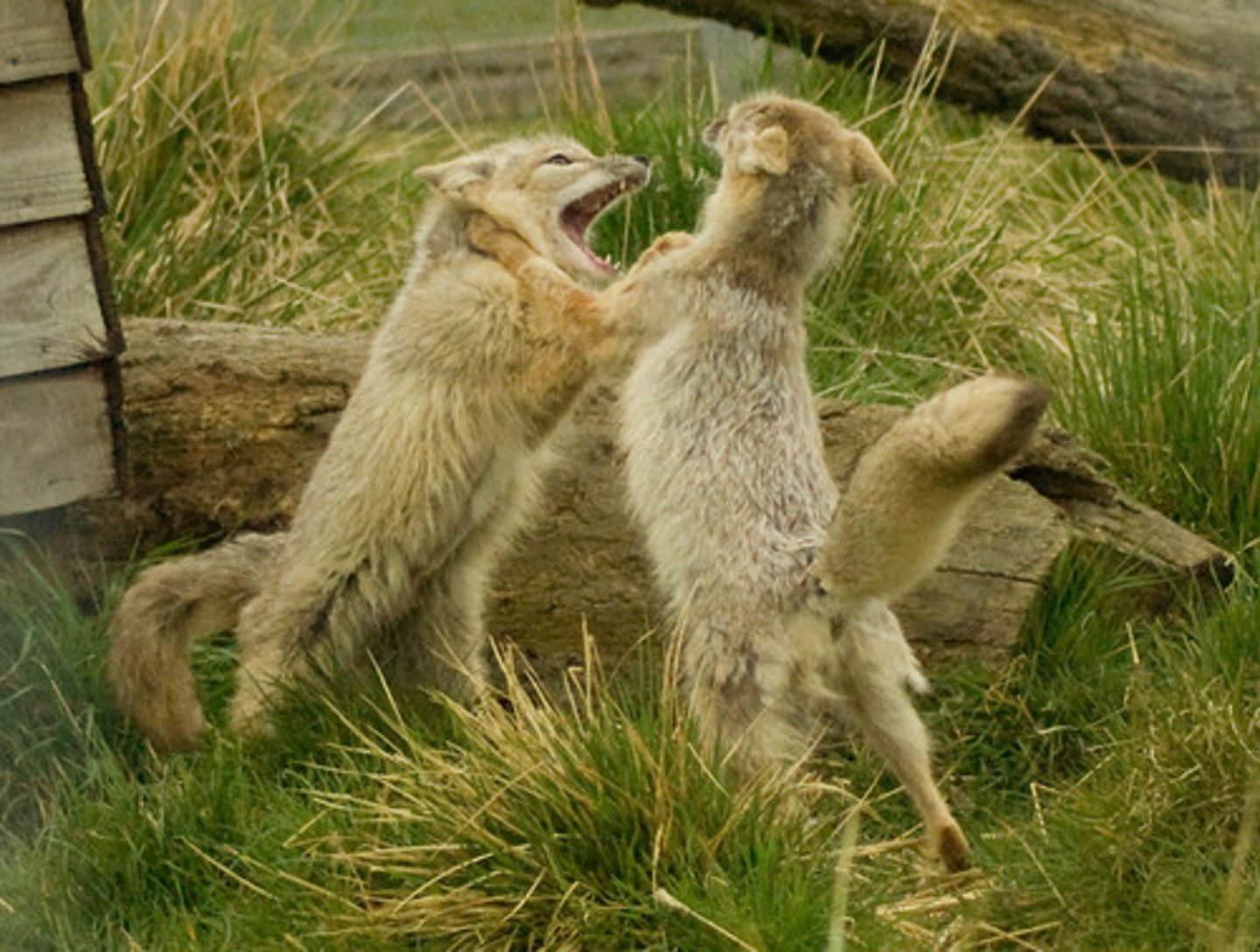

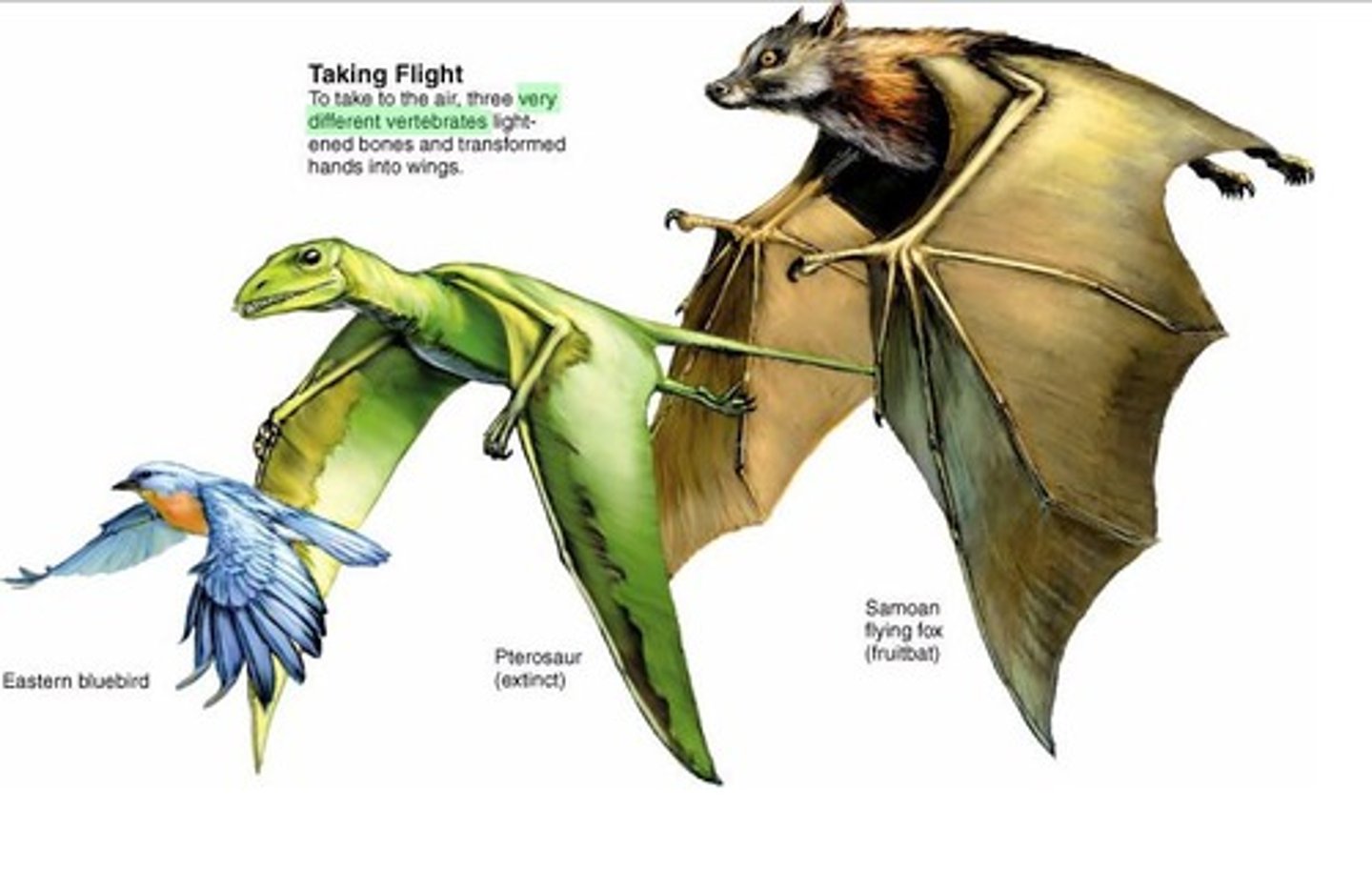
Convergent Evolution
process in which organisms not closely related (like birds and butterflies), independently evolve similar (analogous) traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological conditions.
Divergent evolution
the accumulation of differences between populations which can lead to the formation of new species, usually a result of isolated environments
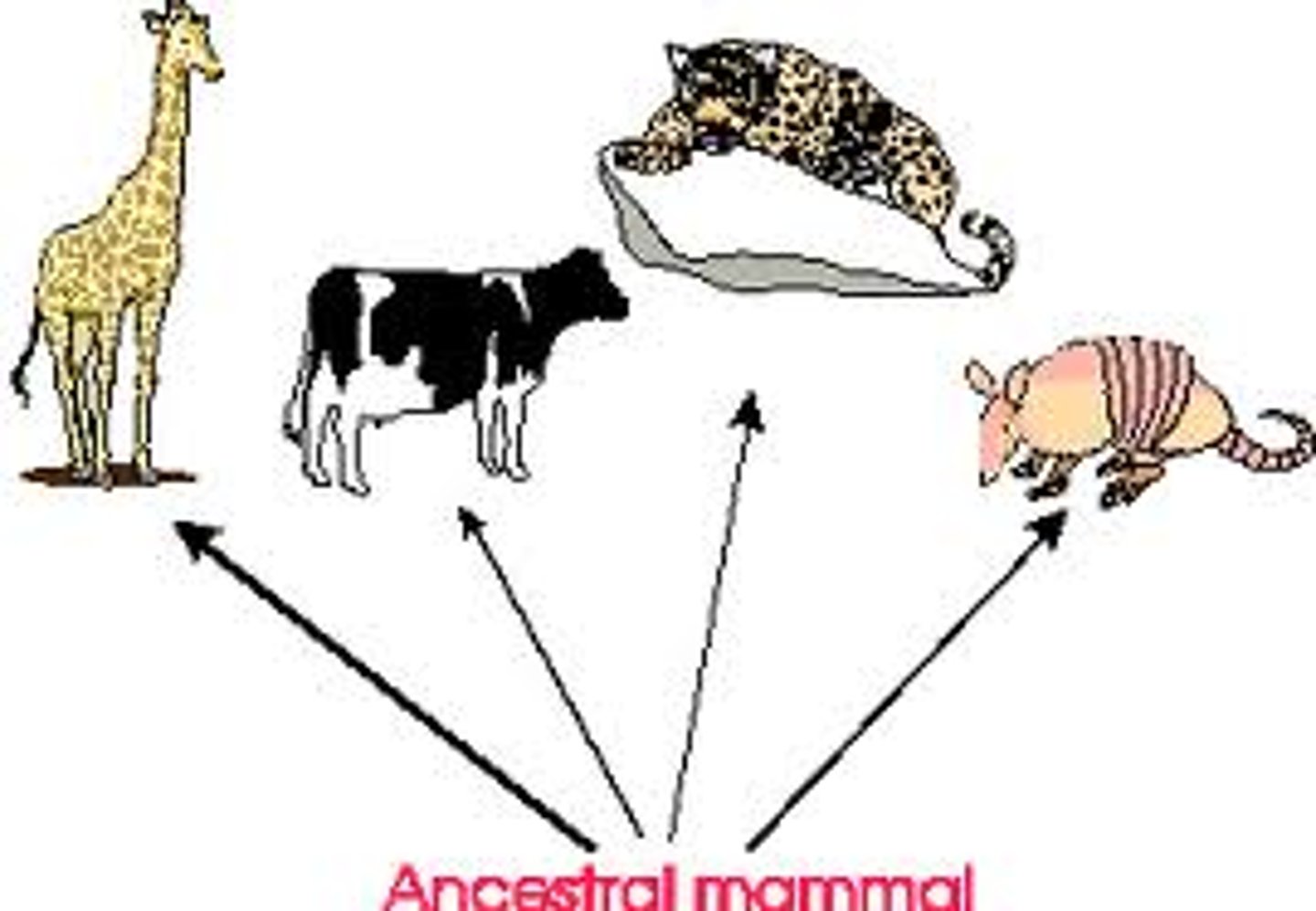
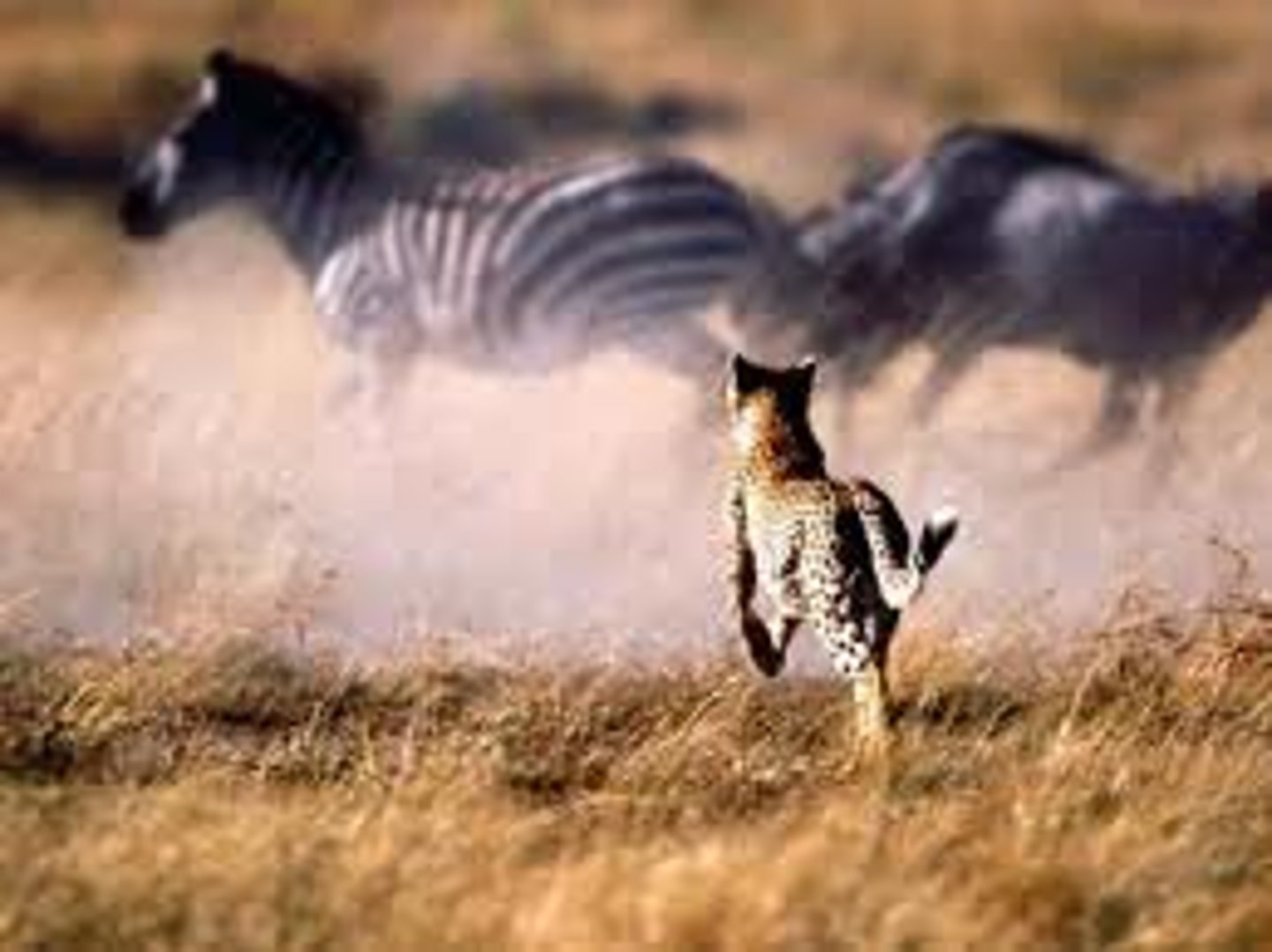
adaptation
a trait that is common in a population because it provides some improved function or contributes to survival; it is produced by natural selection

gene flow
is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another (also known as gene migration)
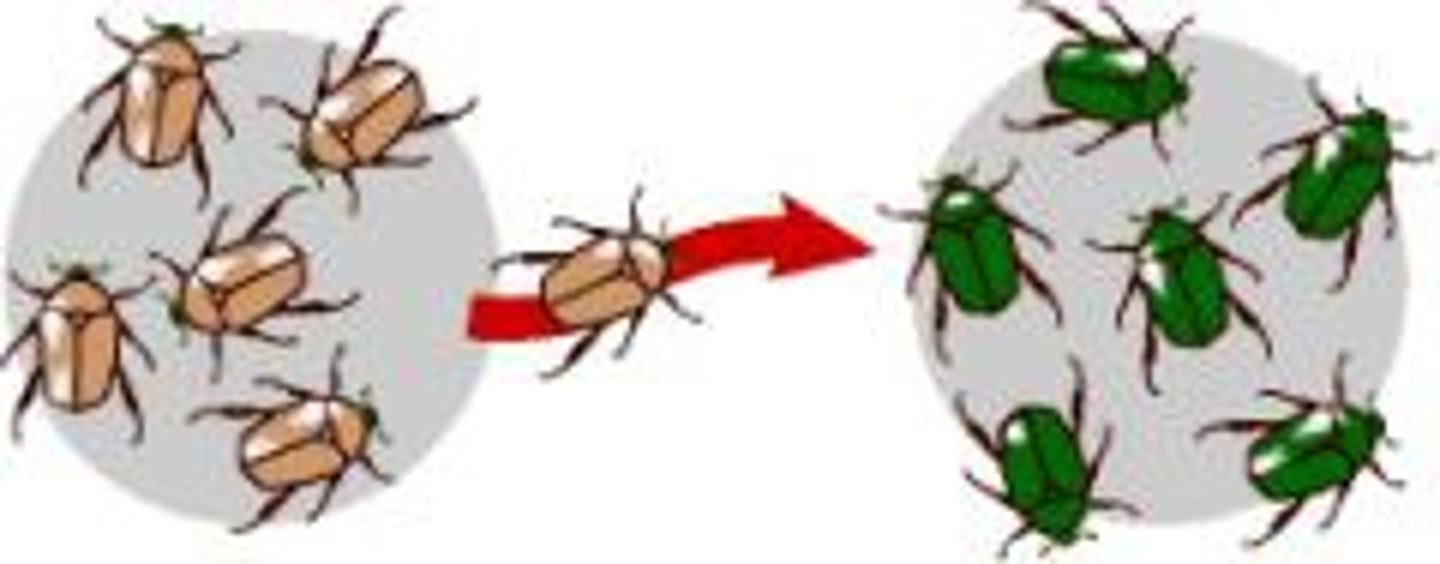
genetic drift
the change in the frequency of a gene (allele) in a population due to chance, not natural selection
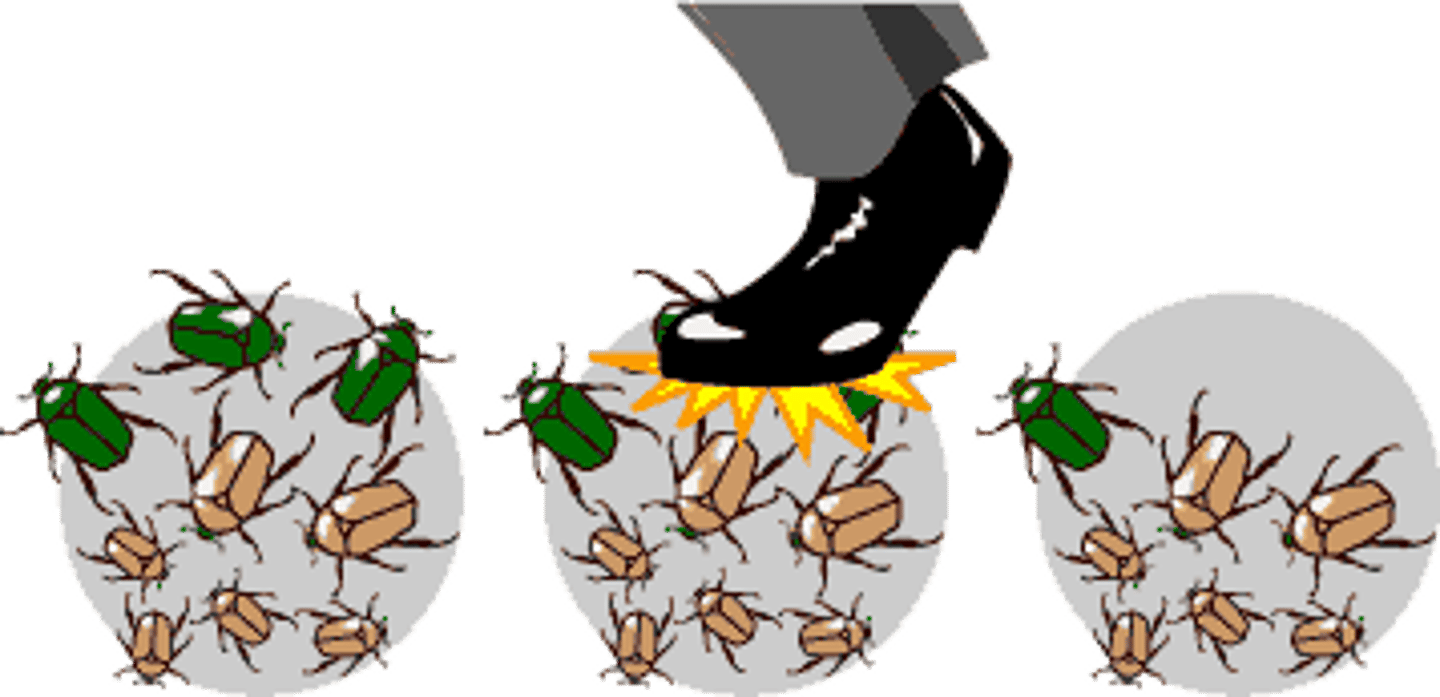

mutation
a change in the DNA sequence; occurs naturally or by some environmental factor such as x-rays or UV radiation from the sun
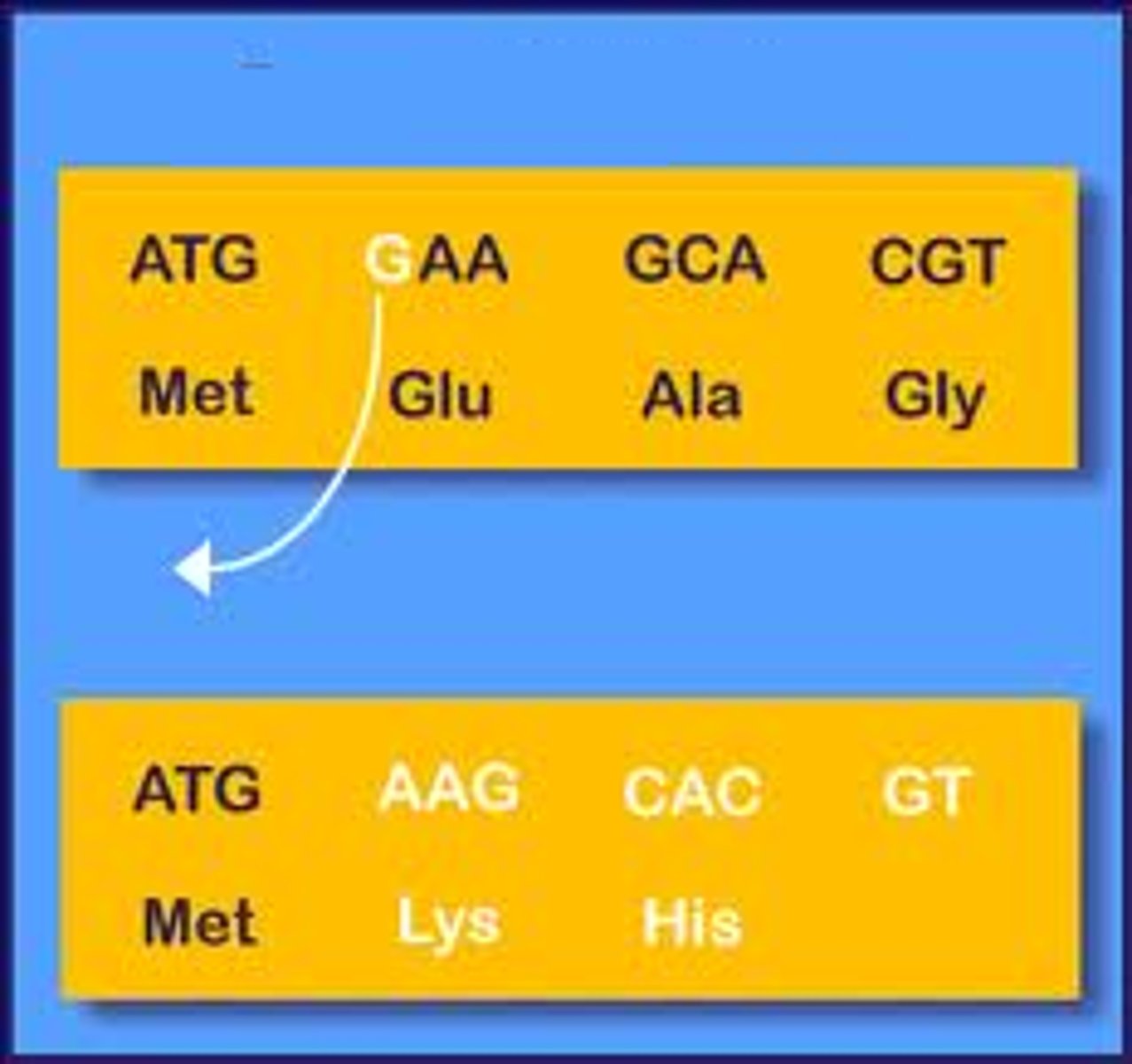
stasis
a long time period of little or no evolutionary change in a species
punctuated equilibrium
a theory which proposes that most species will exhibit little evolutionary change for most of their geological history, remaining in an extended state of stasis, and when significant evolutionary change occurs, rapid (on a geologic time scale) speciation takes place
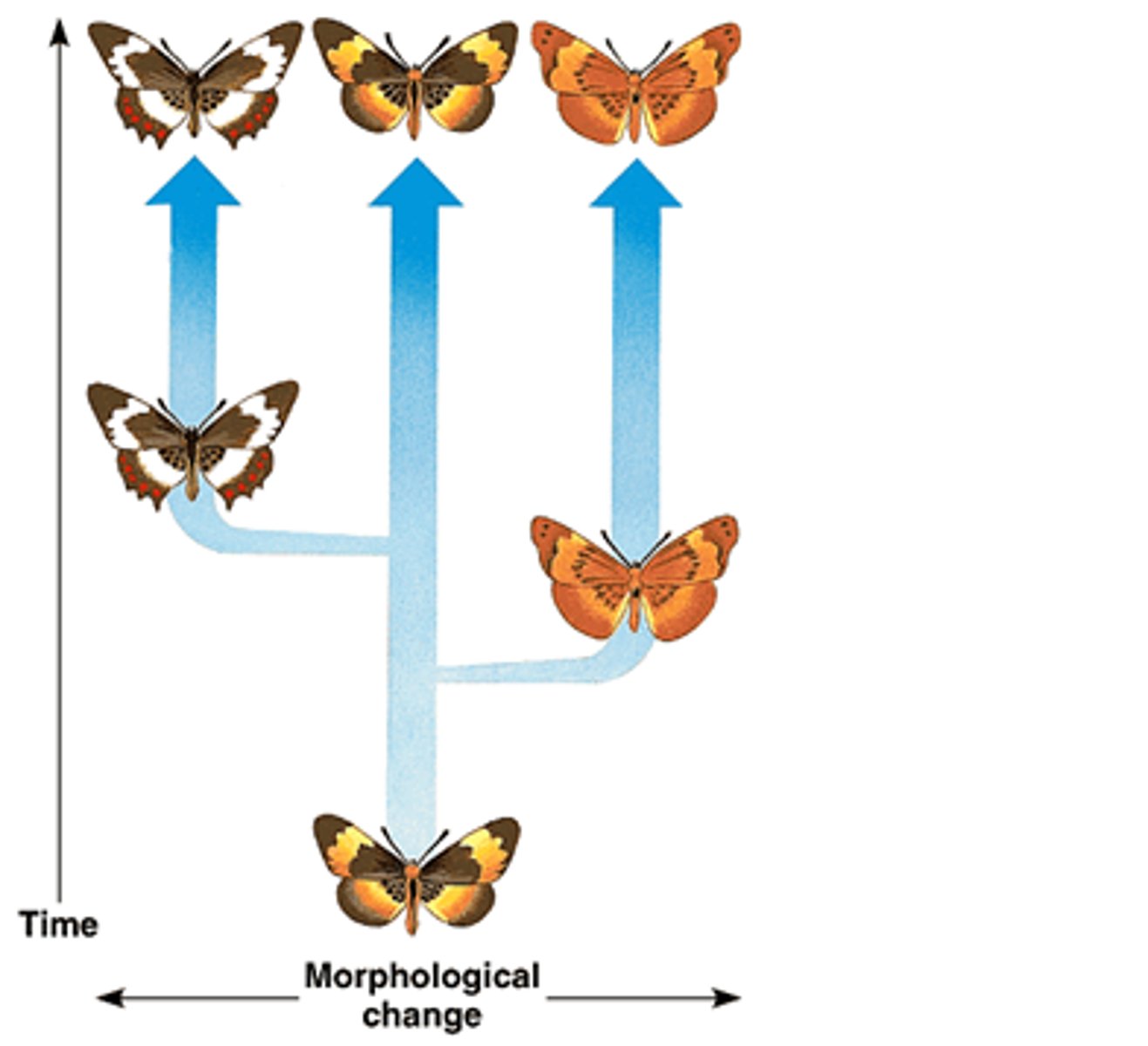
gradualism
a theory which proposes that profound change in a species (evolution) is the cumulative product of slow but gradual changes
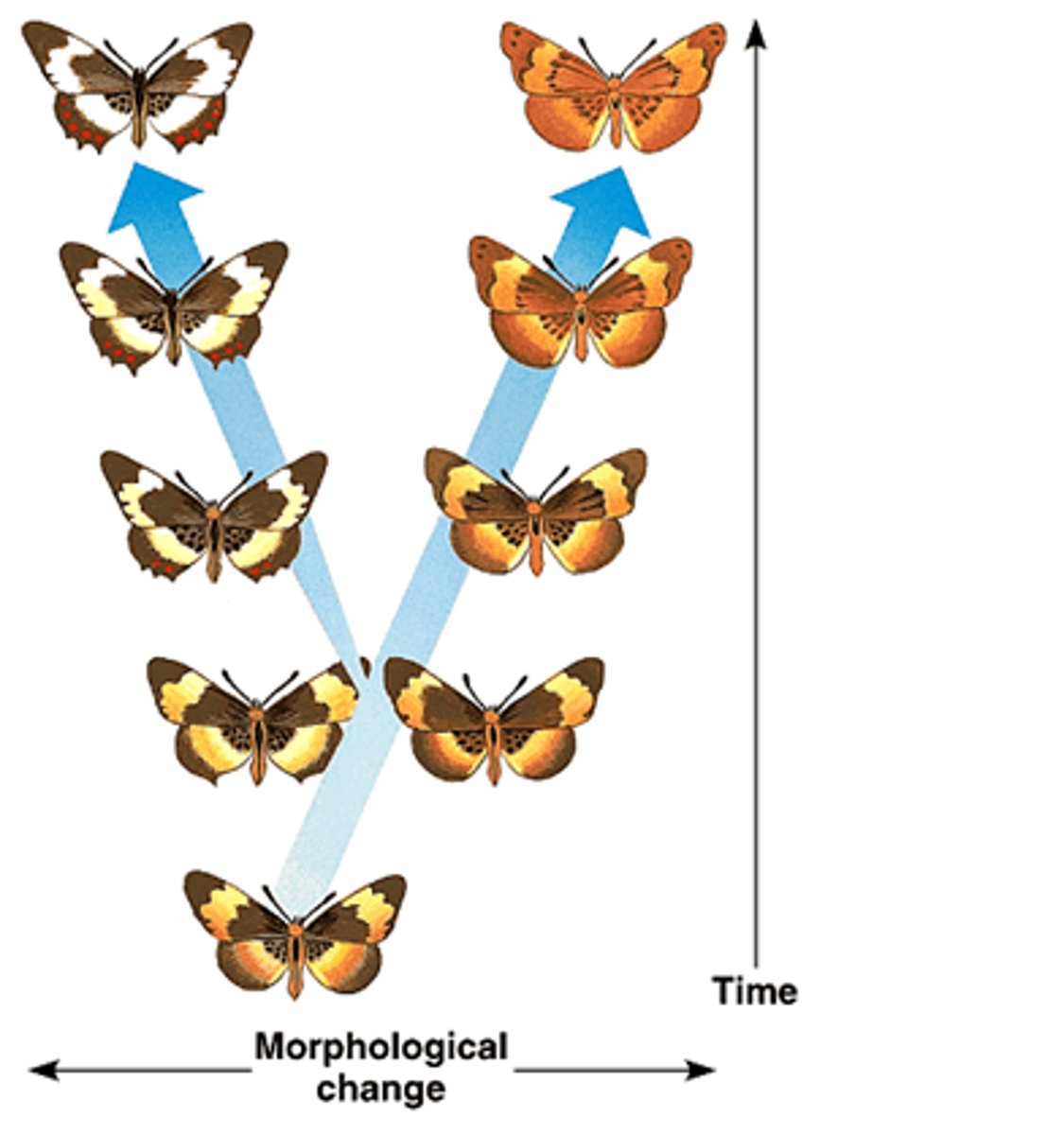
descent with modification
Charles Darwin's definition for the evolution of a species; offspring are always genetically unique from their parents and over time these genetic changes accumulate in a population
variation
a genetic difference among organisms in the same species; for example, some horses have very long legs and some have shorter legs.
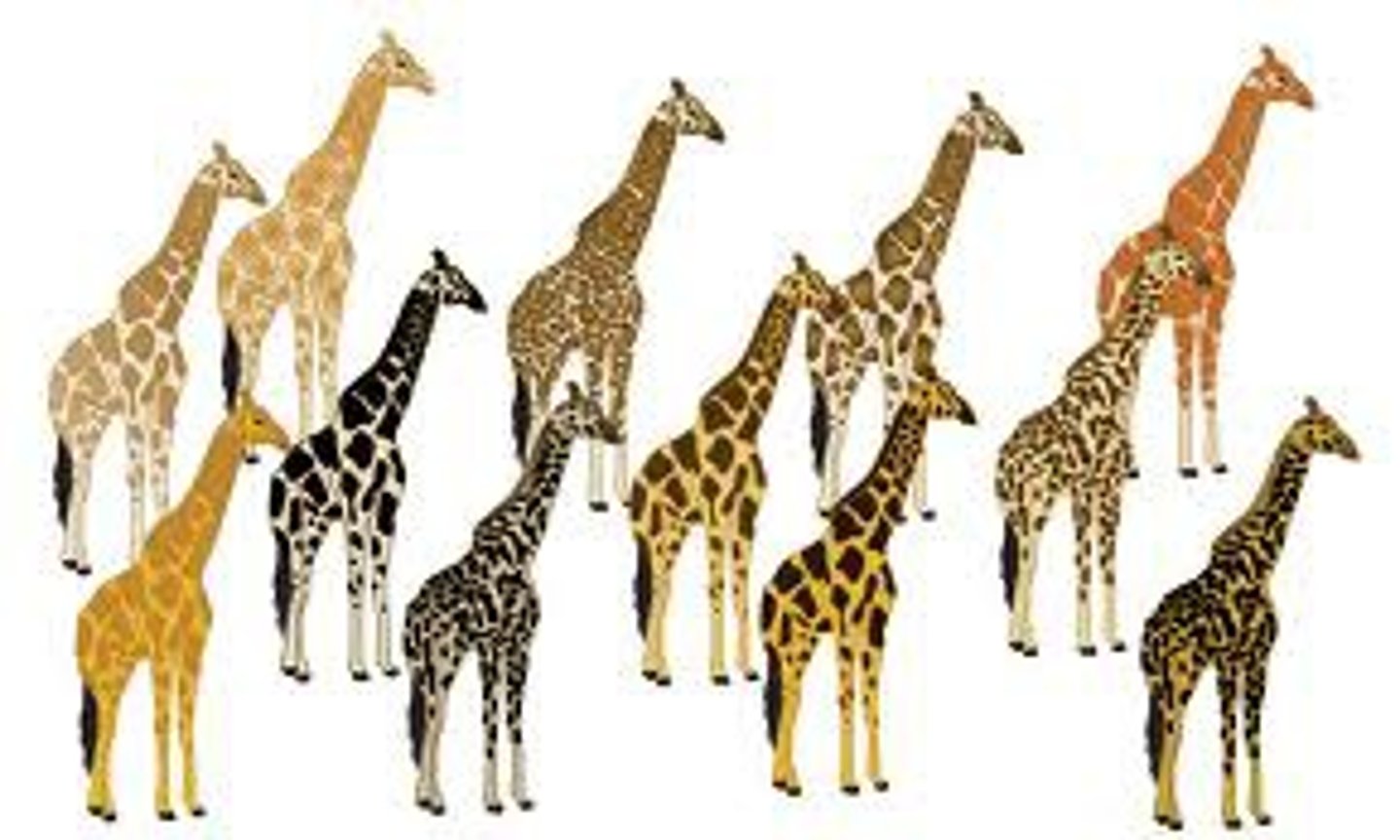

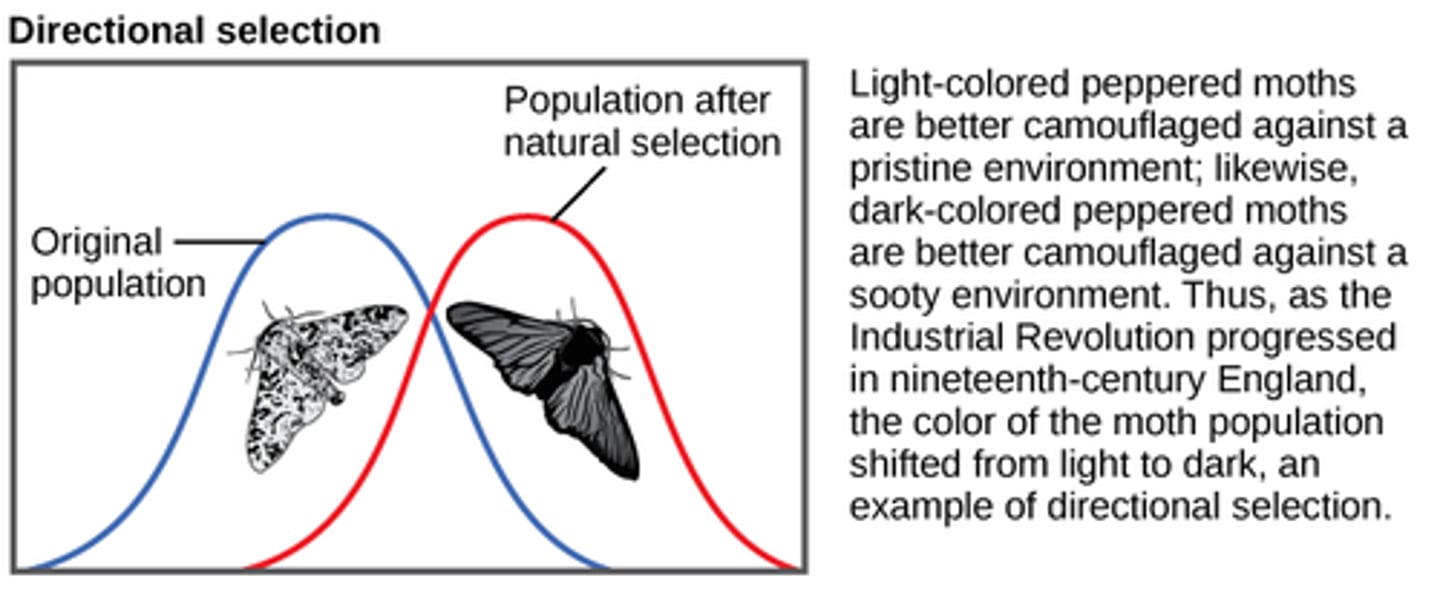
Directional selection
a mode (type) of natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype.
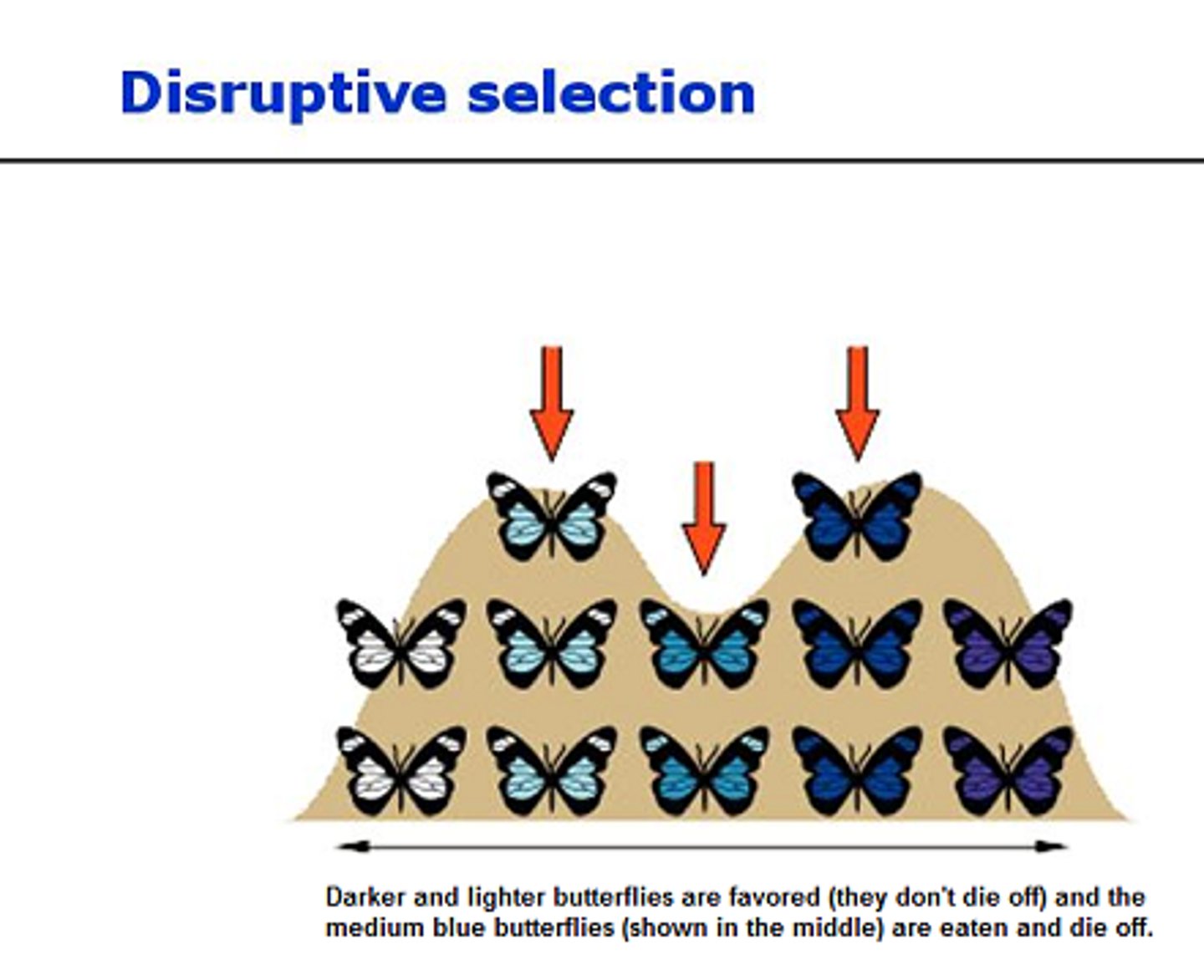
Disruptive selection
changes in population genetics in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values. In this case, the variance of the trait increases and the population is divided into two distinct groups.
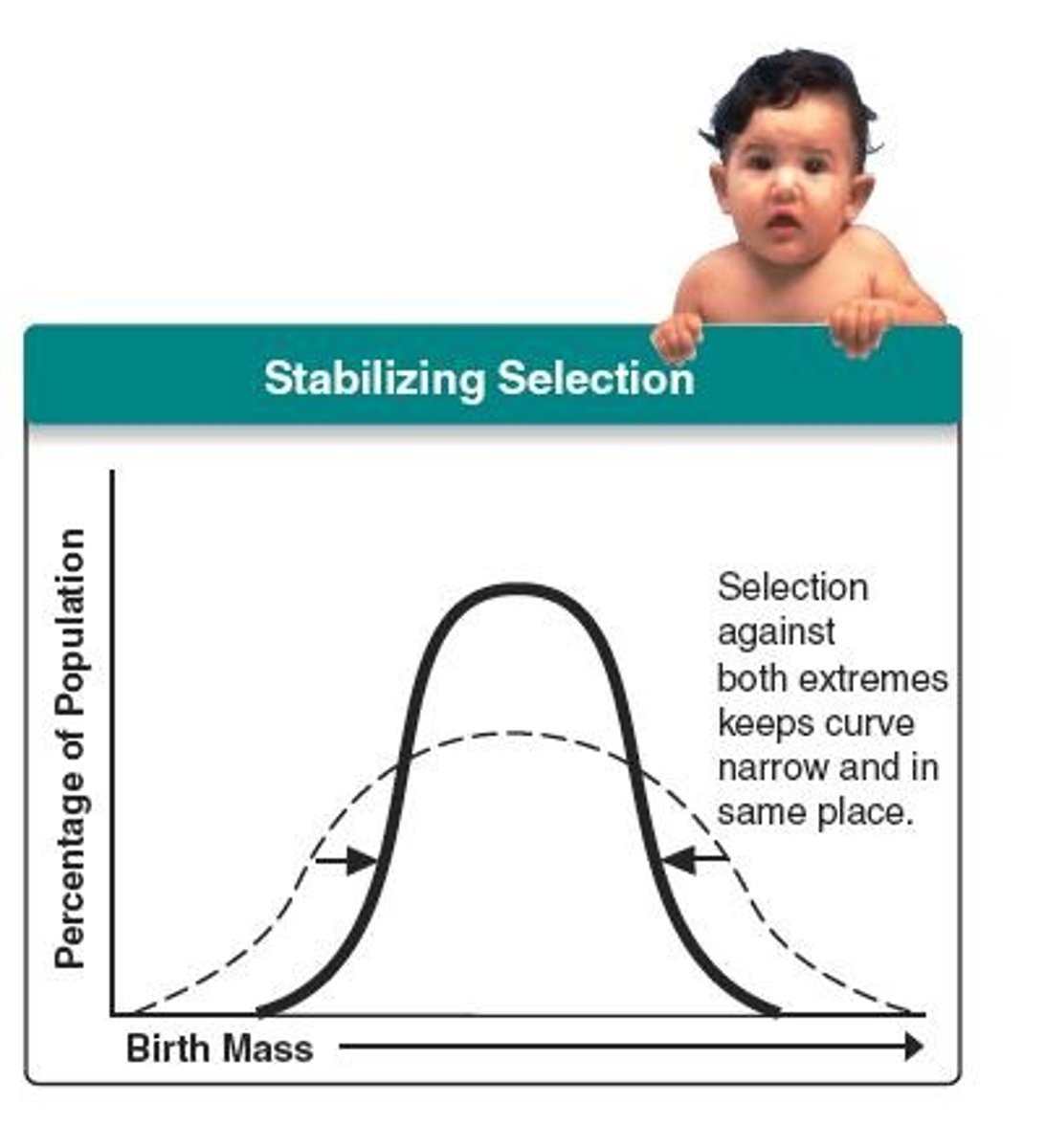
Stabilizing selection
the opposite of disruptive selection, stabilizing selection favors the intermediate variants. It reduces phenotypic variation and maintains the status quo.
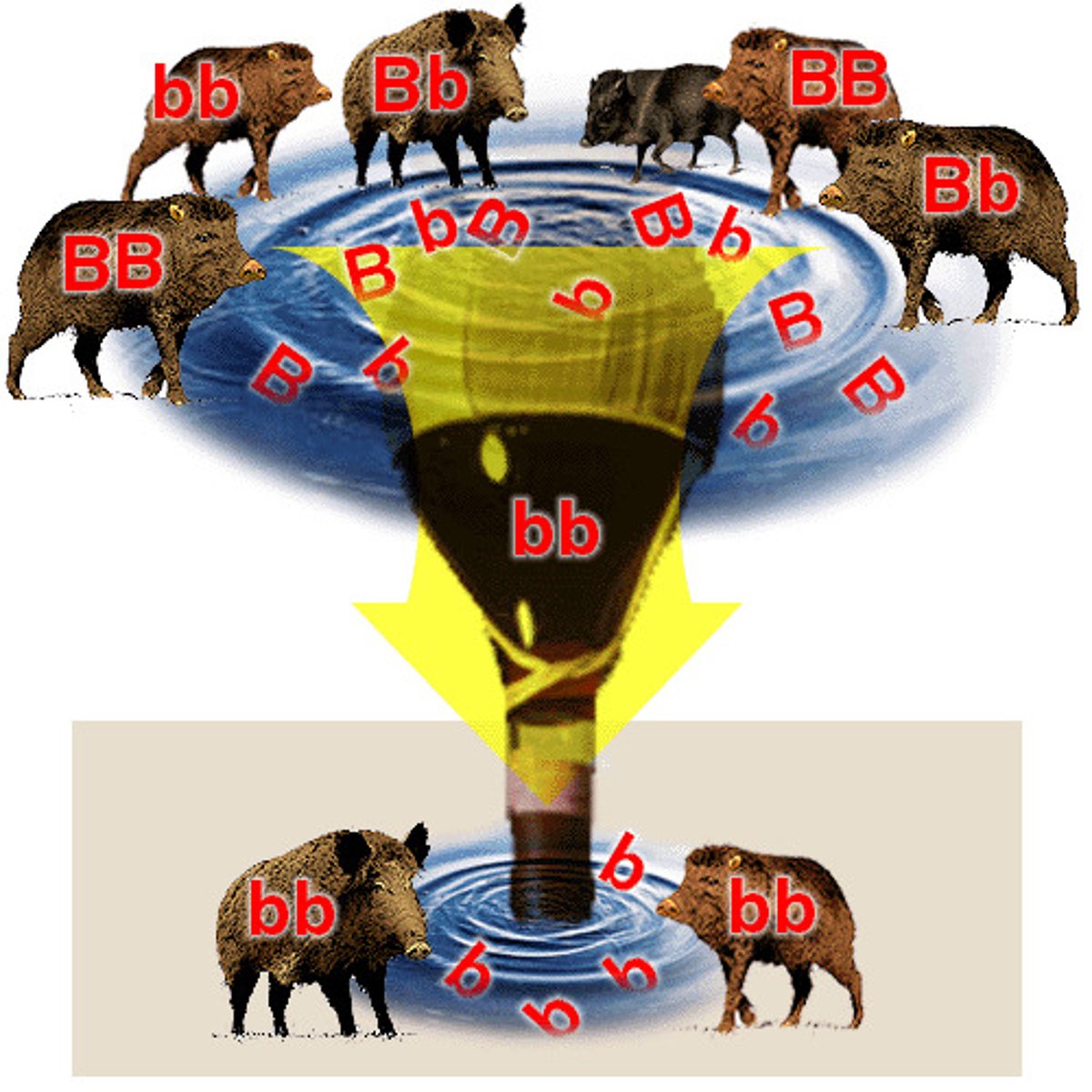
bottleneck effect (genetic drift)
a sudden reduction in population size due to a random change in the environment
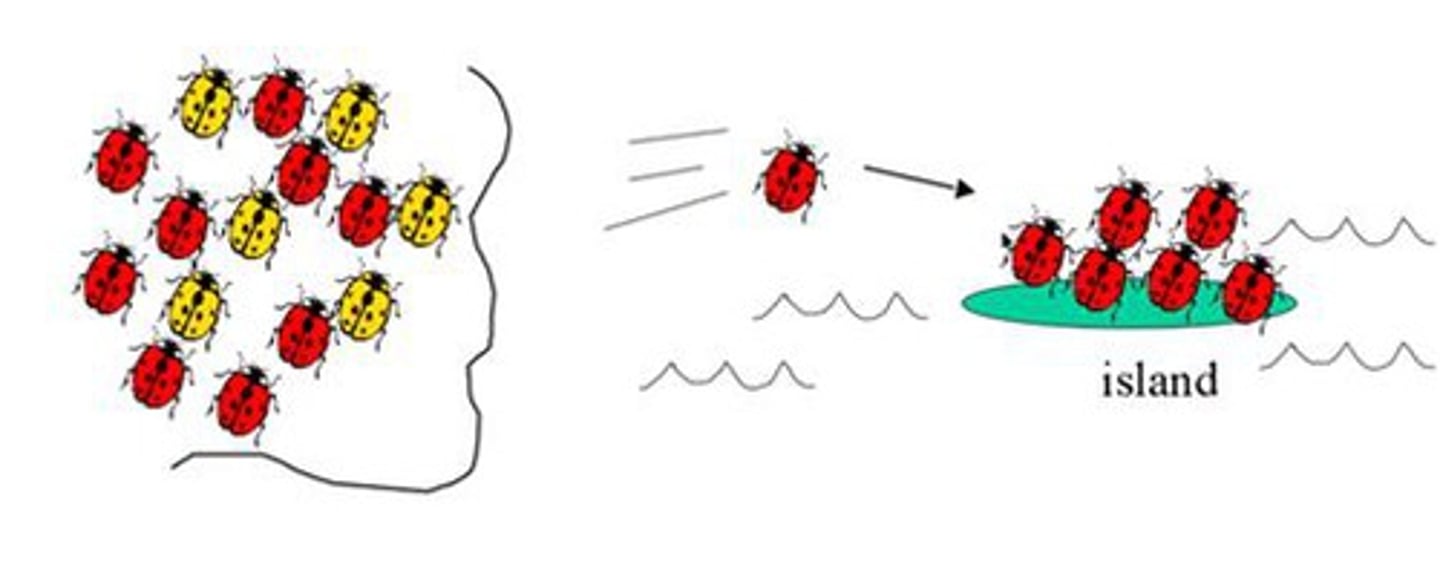
founder effect (genetic drift)
occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population
p
frequency of dominant allele
q
frequency of recessive allele
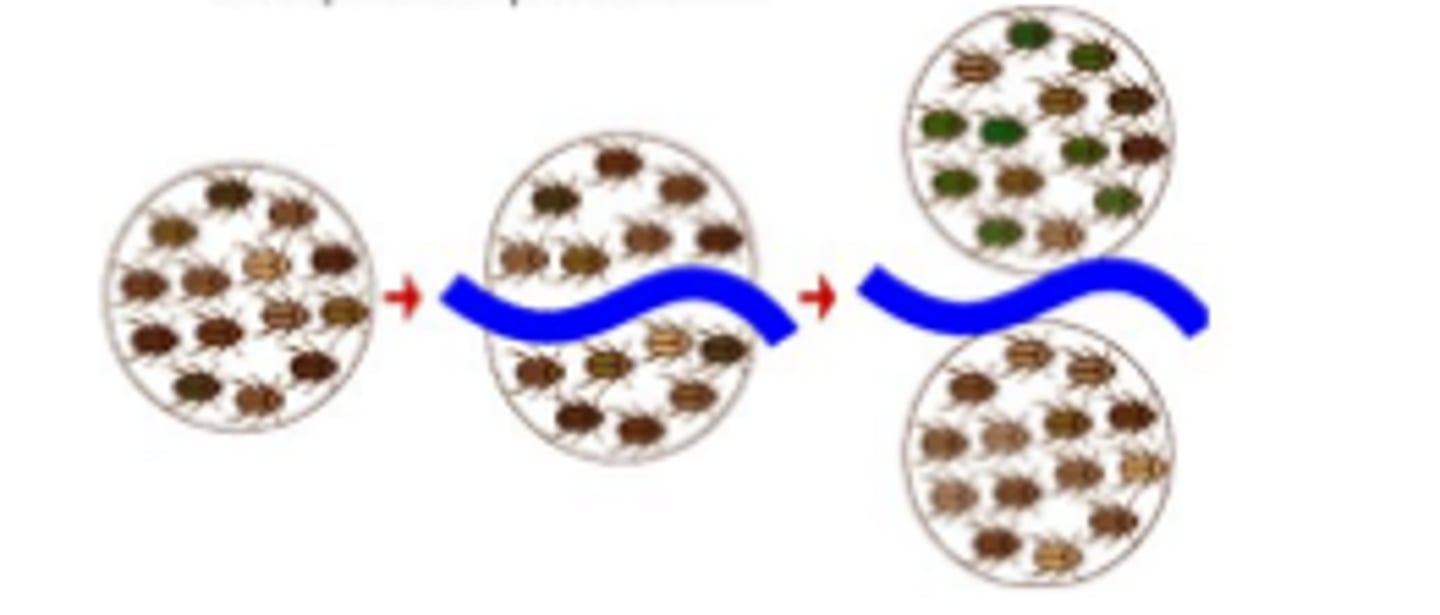
allopatric speciation
the process of speciation that occurs with geographic isolation
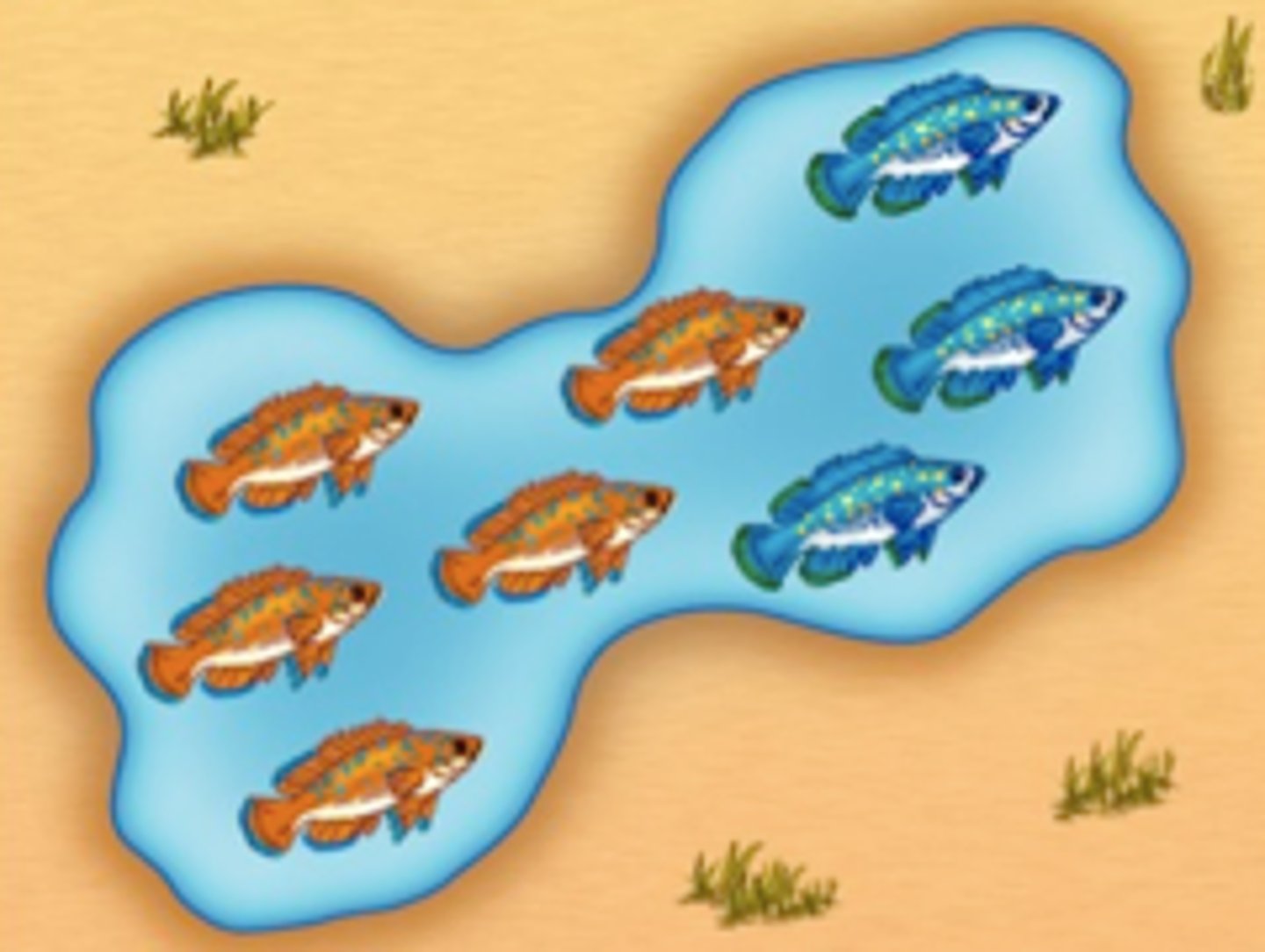
sympatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
The condition describing a non-evolving population (one that is in genetic equilibrium).