Physics and Hemodynamics
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What are hemodynamics?
Study of blood and how or why it moves
What is systemic circulation?
Part of circulatory system that carries oxygenated blood from LV to rest of body (arteries, veins, venules, etc.)
What is pulmonary circulation?
Part of circulatory system that carries deoxygenated blood from RV and returns oxygenated blood to LA
Where is oxygen saturation the HIGHEST in the body?
Pulmonary veins
Where is oxygen saturation the LOWEST in the body?
SVC and IVC
What is the role of the cardiac pump during SYSTOLE?
High LV pressures exceed aortic pressures to push blood into arteries via contraction
What is the role of the cardiac pump during DIASTOLE?
Low LV pressures causes LV to fill with blood
What are the primary mechanisms that control arterial flow volume changes or BP during the cardiac cycle?
CO
Peripheral resistance
What is a normal heart rate?
60-100 BPM
Bradycardia < 60 BPM
Tachycardia > 100 BPM
What is kinetic energy?
Energy of motion or ability of blood to do work (velocity)
What is the primary form of energy driving blood flow?
Potential energy
What is potential energy?
Stored or resting energy that is influenced by hydrostatic pressure of distending vessels
What is hydrostatic or gravitational energy?
Effect of gravity on circulatory system
What is total fluid energy or total composition of blood?
Sum of potential, kinetic, and hydrostatic energy
What is a pressure gradient?
Difference in pressure between two points of a vessel that creates flow
What are the factors that affect blood flow?
Decreased cardiac function that causes decreased flow velocities
Increased cardiac function that causes increased flow velocities
Peripheral resistance
Vessel compliance
Tone of vascular musculature
Pattern of branches or collaterals
Vasoconstriction due to coldness, anxiety, smoking
Vasodilation due to exercise, heat, HTN medication, proximal stenosis, adrenaline
Viscosity
How does vessel compliance affect the amount of blood flow?
Stiffer or calcific vessels cause higher resistant flow
How does the tone of vascular musculature affect the amount of blood flow?
Muscular patients cause less compliant vessels and higher resistant flow
What is viscosity?
Measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow, thickness of blood, or amount of hematocrit
How does viscosity affect the amount of blood flow?
Thick blood causes higher resistant flow
How does exercise affect the amount of blood flow?
Induces vasodilation in distal vascular beds of skeletal muscles
What is autoregulation?
Ability of vascular beds to alter resistance to flow to maintain flow levels required for normal function
What is resistance?
Opposition of flow
What is the resistance equation?
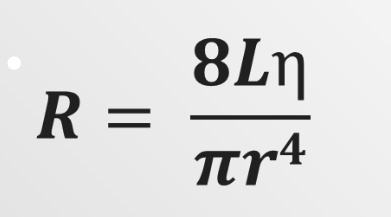
What is resistance dependent on?
Length
Viscosity
Lumen or radius
Which property has the greatest affect on flow resistance?
Changes in vessel radius such as stenosis and vasoconstriction
An increase in resistance requires an… to maintain constant flow.
Increase in pressure
What is the sonographic appearance of a vessel with high resistance?
Sharp upstroke
Rapid deceleration
Minimal diastolic flow
Diastolic flow reversal
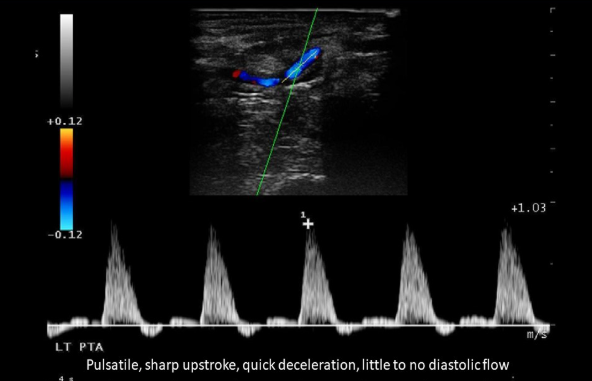
Where in the body does blood flow have high resistance or triphasic waveforms?
Muscles
Extremities
Where is the highest pressure located in the circulatory system?
LV at 120 mmHg
When does flow occur in vessels with HIGH resistance?
ONLY during SYSTOLE
What is the sonographic appearance of a vessel with low resistance?
Slow upstroke
Slow deceleration
No diastolic flow reversal
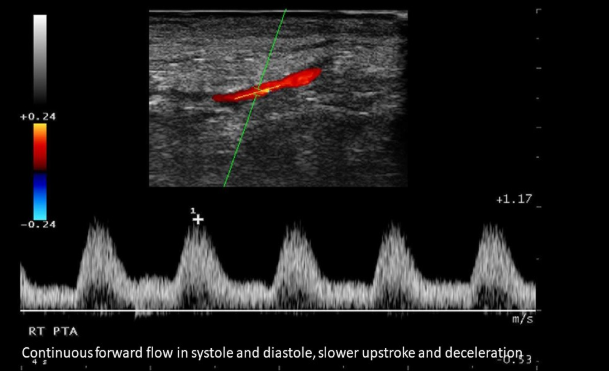
Where in the body does blood flow have low resistance or monophasic waveforms?
Brain
Kidneys
Spleen
Liver
When does flow occur in vessels with LOW resistance?
Throughout cardiac cycle or systole AND diastole
What is Poiseuille’s Law?
Demonstrates relationship between pressure, volumetric flow rate, and resistance
What is the equation for Poiseuille’s Law?
OR Q = P/R
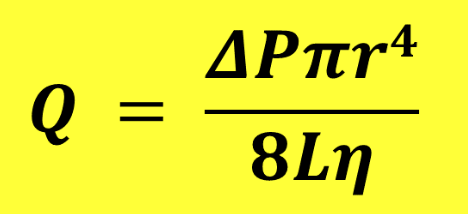
When can we apply Poiseuille’s Law?
Straight, rigid tube with laminar flow (NOT STENOSIS)
What is Ohm’s Law?
Poiseuille’s Law in electronics
What is the equation for Ohm’s Law?
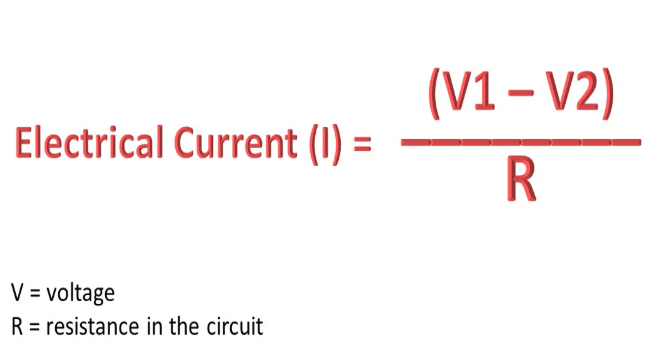
What is Bernoulli’s Law?
Where there is a decrease in pressure in regions of high flow speed (velocity)
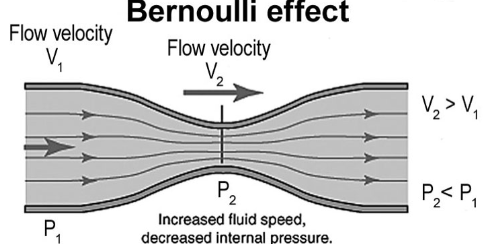
What is the equation for Bernoulli’s Law?
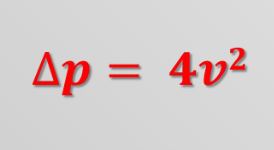
What is the average pressure in veins?
2 mmHg
What is the average pressure in arteries?
100 mmHg
Flow volume is always proportional to…
BP
What is laminar flow?
Flow that travels in concentric rings or layers with various velocities
Center of flow = FASTEST
Periphery of flow = SLOWEST due to friction from vessel walls
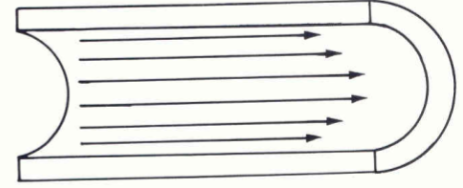
What is parabolic flow?
Similar to laminar flow, but has a smaller velocity range and is only found in medium sized vessels
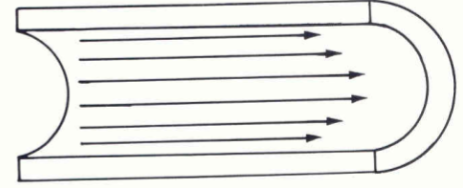
What is plug or blunt flow?
Flow that travels at one speed and is found during systole in larger vessels, arterial branch origins, and proximal to stenosis
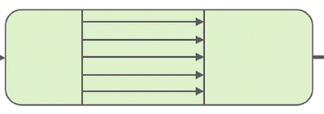
What is arterial pulsatility?
Primary factor that determines resistance characteristics and is related to number of changes in flow direction during one cardiac cycle
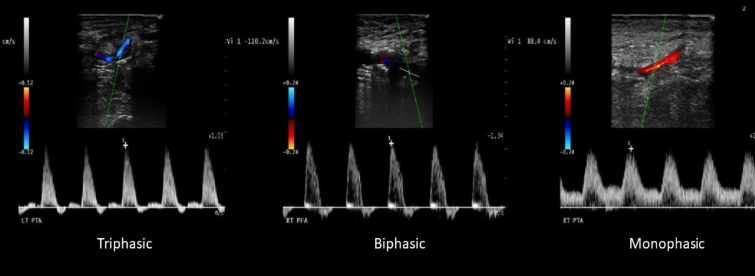
What is a monophasic waveform?
When antegrade flow continues through cardiac cycle
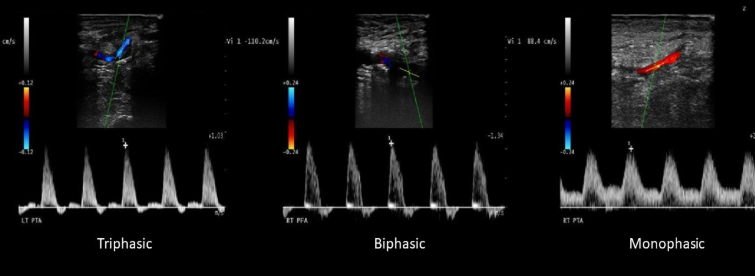
What is a biphasic waveform?
When flow during systole is antegrade and some flow is reversed during diastole
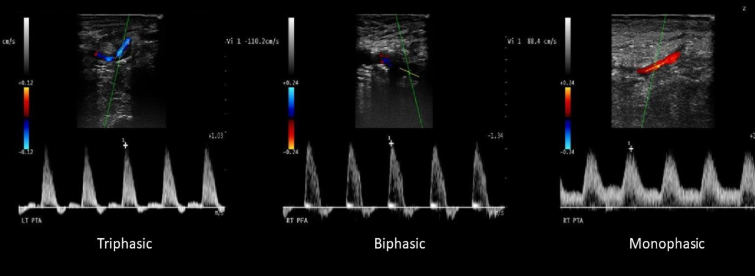
What is a triphasic waveform?
When flow during systole is antegrade, some reversal initially in diastole, and a small amount of forward flow in end diastole
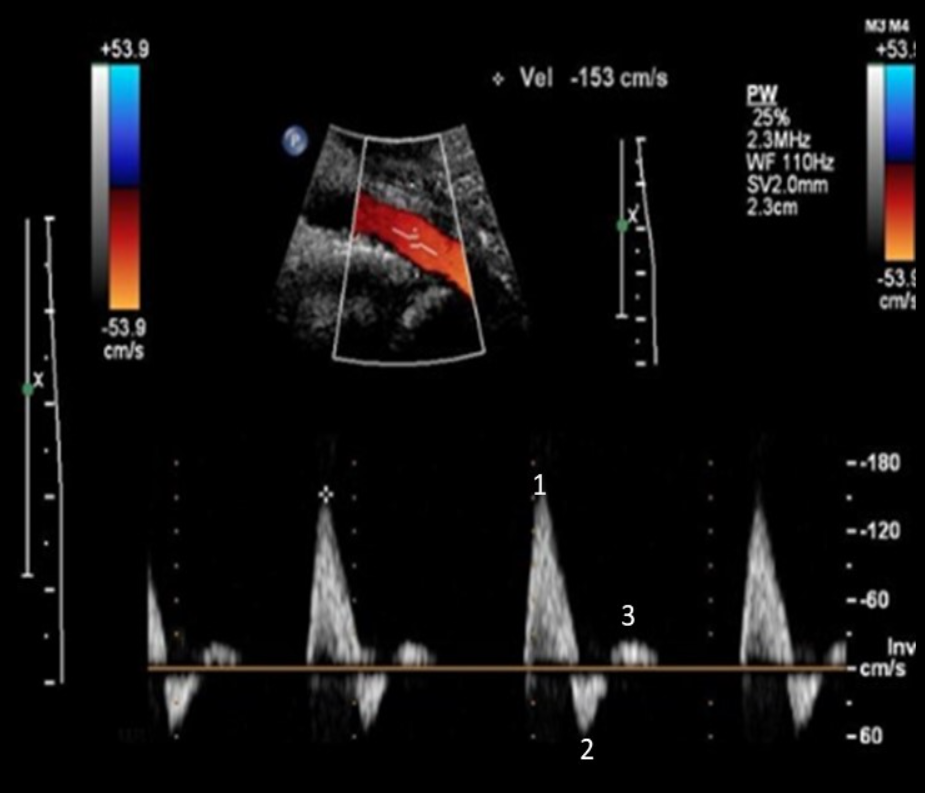
Identify this image.
Antegrade flow or systolic peak
Retrograde flow or diastolic peak
Antegrade flow at end diastole due to vessel wall compliance
What is turbulence?
Chaotic flow distal to stenosis
What are the anatomic causes of turbulence?
Bifurcation
Tortuosity
Kinking
Coiling
Eccentric change in course
What are the acquired causes of turbulence?
Atherosclerosis
Stents
Bypass grafts
Myointimal hyperplasia
Aneurysms
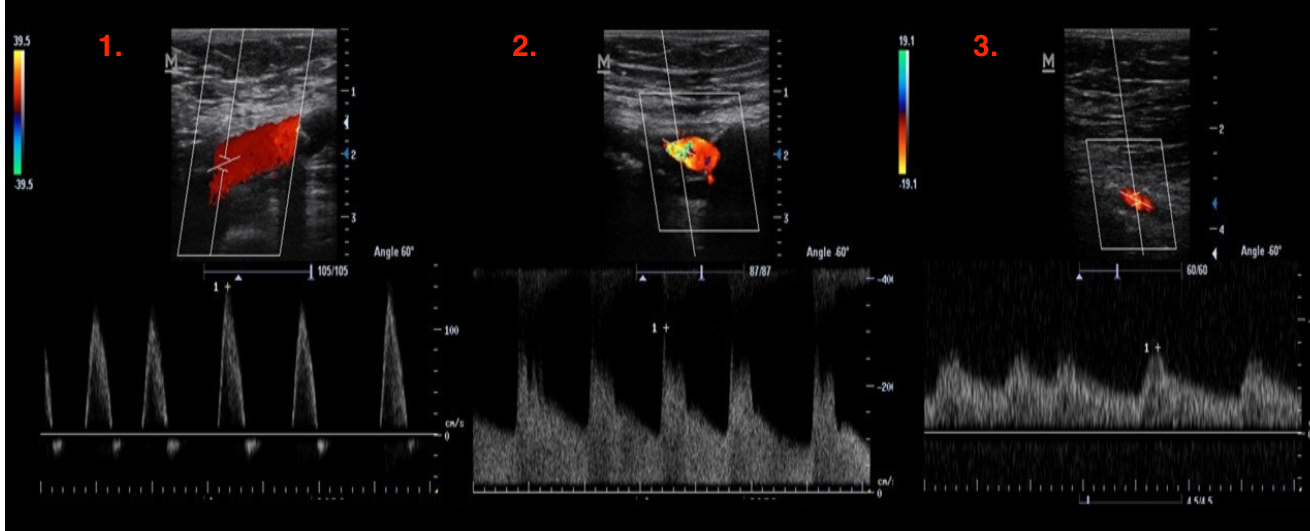
Identify this image.
Normal flow proximal to stenosis
Elevated velocities and spectral broadening at stenosis
Monophasic and low resistance waveform with distal to stenosis
What is a stenosis?
Narrowing of a vessel lumen
What are the factors that determine the hemodynamic significance of a stenosis?
Shape and degree of stenosis
Diameter of stenosis
Length of stenosis
Contour of stenosis
Distal peripheral resistance
Pressure gradient
Presence of collaterals
What are stenoses in a series?
Multiple areas of stenosis in same vessel that cause a higher effect on resistance to flow than parallel stenoses
What are stenoses in parallel?
Stenosis in different vessels coursing in same direction that cause a lower effect on resistance to flow than series stenoses
What is considered a hemodynamically significant stenosis?
50% diameter
75% area

Identify this image.
Distal obstruction due to newly high resistance waveform
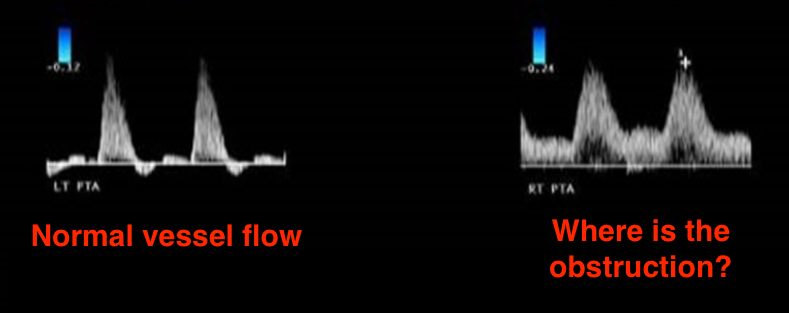
Identify this image.
Proximal obstruction due to newly low resistance waveform
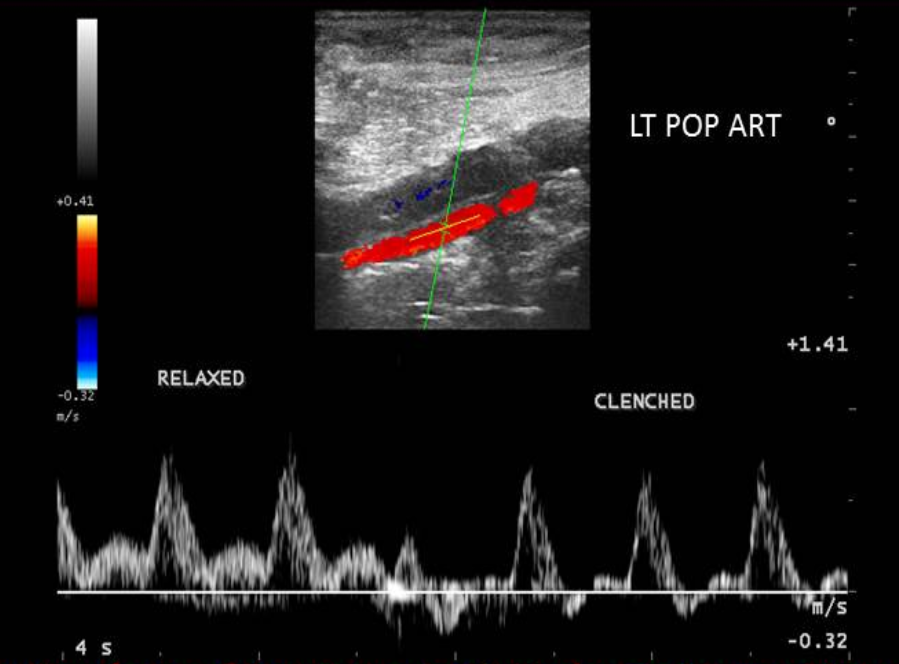
Identify this image.
Low resistance flow in distal arm and calf arteries due to vasodilation in distal vascular beds
Relaxation shows newly low resistance waveform
Clenching hands or toes increases resistance and returns flow pattern to normal
What is the most common reason for underestimation of an arterial stenosis?
Improper sample volume location
What are eddy currents or vortices?
Turbulent and swirling blood found distal to stenosis
What is a murmur?
Abnormal blood flow sound in heart most commonly from valvular regurgitation or stenosis
What is a bruit?
Abnormal blood flow sensation in a blood vessel due to a stenosis, branching, or tortuosity
What is a thrill?
Abnormal blood flow sensation or vibration in a blood vessel due to a stenosis, pseudoaneurysm, and NORMAL hemodialysis grafts
What factors cause a reduced systolic velocity in arteries?
CHF
CAD
Diastolic dysfunction
AS
MS
Dilated CM
Pericarditis
Increased blood viscosity
Coldness
Reduced HR
Hypocalcemia
What factors cause an elevated systolic velocity in arteries?
Arrhythmias
Volume overload due to liver and renal disease, pregnancy, or obesity
Systemic HTN
AR
Hypertrophic CM
Reduced blood viscosity
Warmness
Increased HR
Hypercalcemia
What is spectral broadening?
Widening of spectral waveform or filling of spectral window
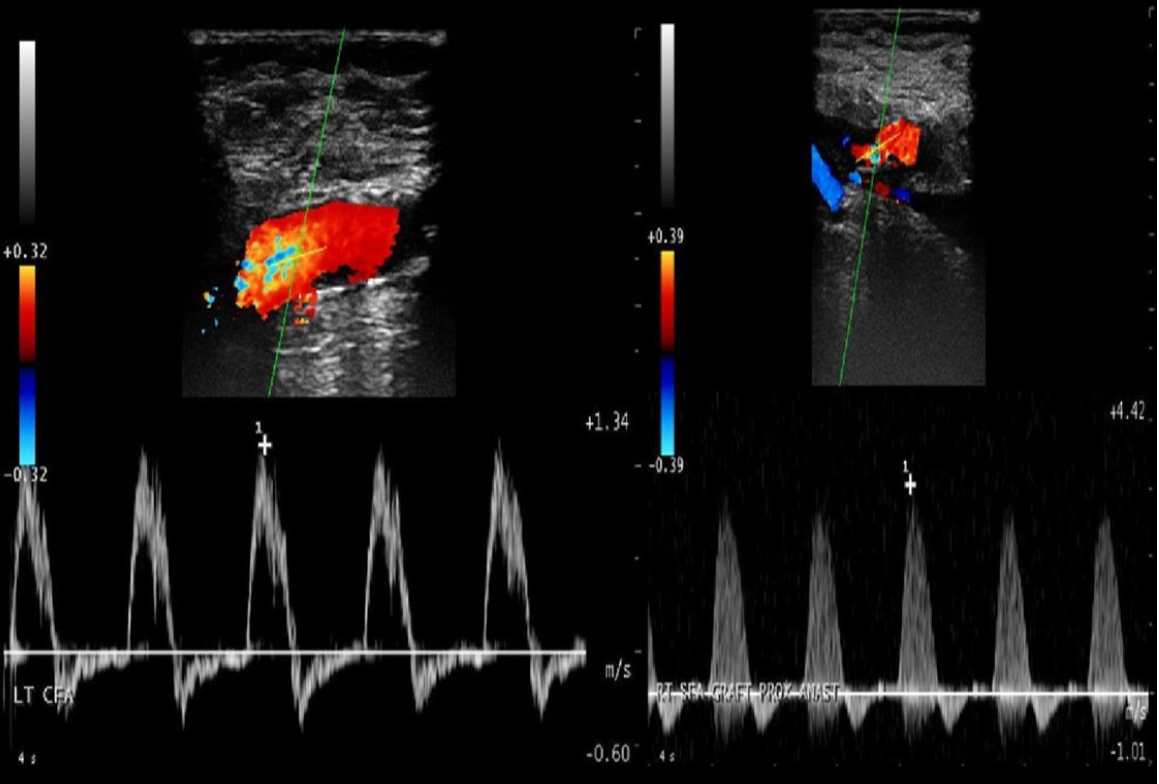
What is bandwidth?
Difference between highest and lowest frequencies or velocities
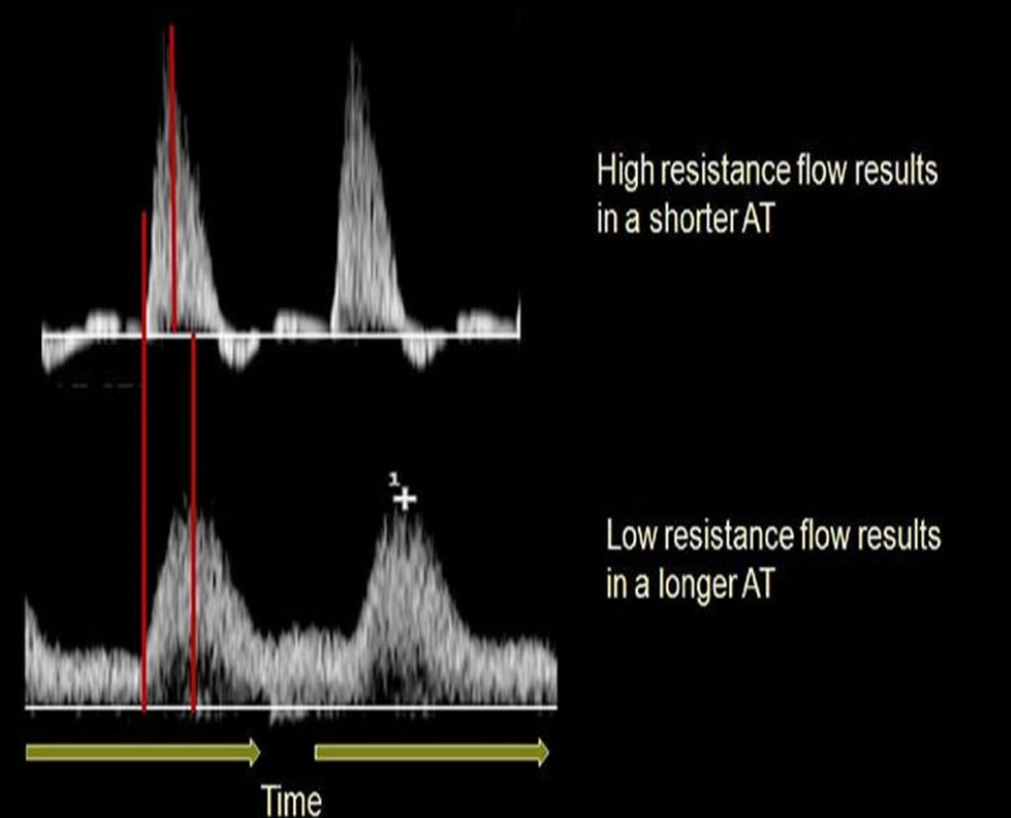
What is acceleration time (AT)?
Time from onset of systole to point of maximum systolic peak and is used to differentiate inflow from outflow disease
What is resistive index (RI)?
Comparison between systolic and diastolic velocities to maximum velocity of vessel segment and is used to evaluate tissue resistance to blood flow
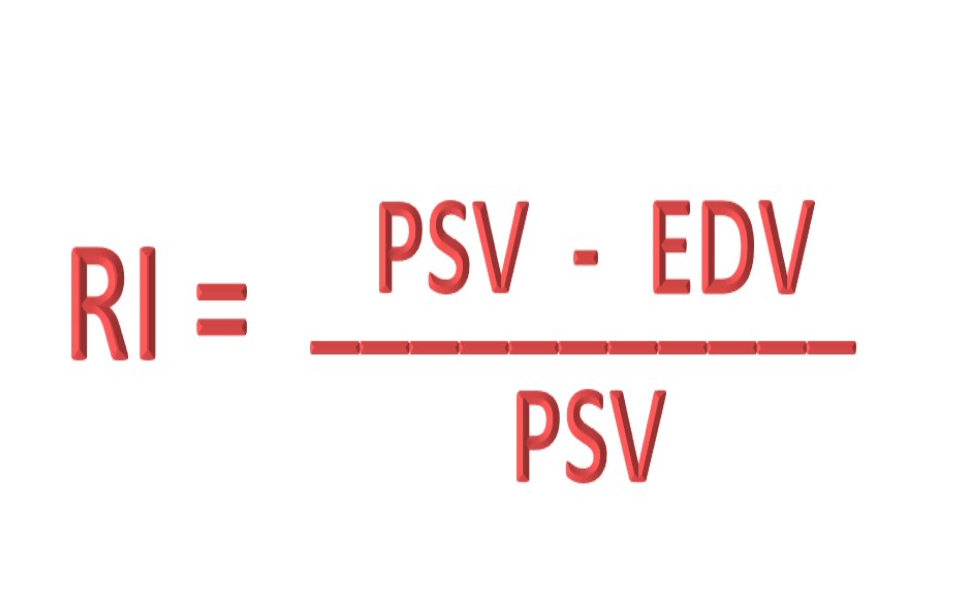
What is the equation for resistive index (RI)?
RI = PSV - EDV / PSV
What is pulsatility index (PI)?
Degree of resistance in a vessel measured by determining velocities during cardiac cycles and is used to distinguish proximal from distal disease
What is the equation for pulsatility index (PI)?
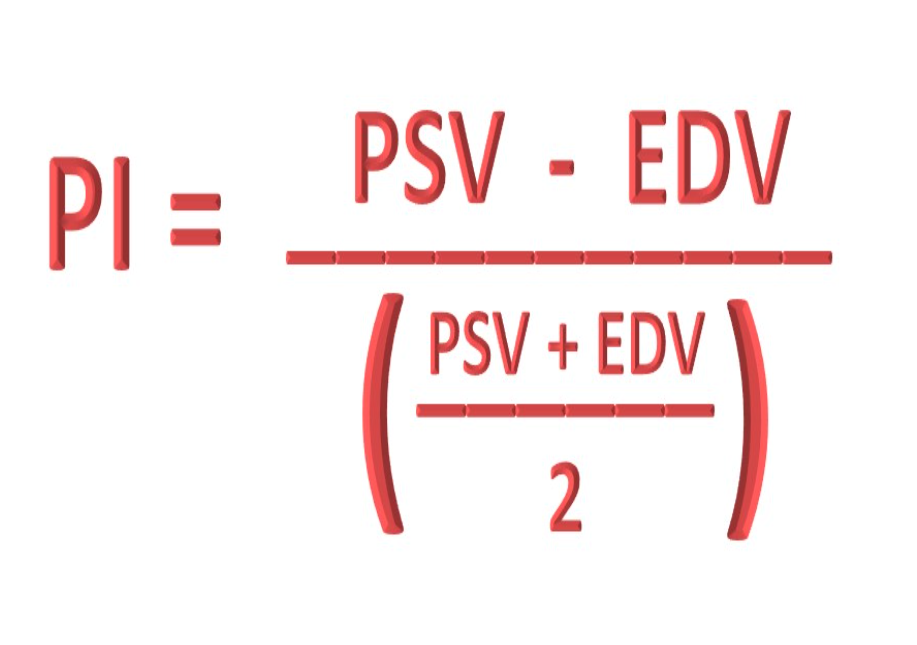
(T/F) PI decreased the further the blood travels from the aorta.
False; PI increases the further blood travels from the aorta
What is the effect of exercise on NORMAL arterial flow?
Increases flow
Increases pressure gradient
Decreases resistance
What are collaterals?
Numerous, smaller vessels that provide an alternative pathway for CHRONICALLY diseased vessels
What are the flow characteristics of collaterals?
Higher resistance than native arteries due to decreased vessel diameter and increased vessel length
What is hydrostatic pressure?
Weight of column of blood inside vessels
What is the equation for hydrostatic pressure?
Fluid density X Gravity X Height of column
When standing, what is the hydrostatic pressure above the heart?
Negative or lower than true circulatory pressure
*Average = - 30 mmHG at head
When standing, what is the hydrostatic pressure below the heart?
Positive or higher than true circulatory pressure
*Average = 100 mmHg at ankle
When supine, what is the hydrostatic pressure both above and below the heart?
0 mmHg due to arteries and veins being at same level as heart
What is ambulatory venous pressure?
Lowest pressure level in limbs during exercise
What is transmural pressure?
Pressure of blood against vessel walls that determines shape of vessel
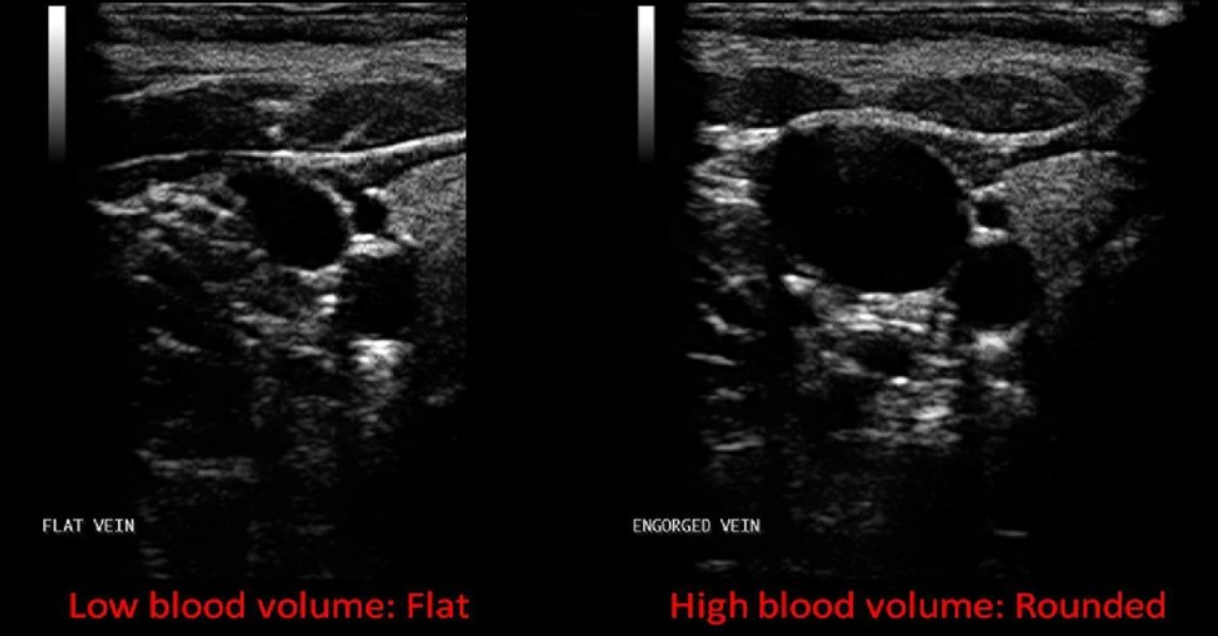
When will a vessel assume a dumbbell or elliptical shape?
When transmural pressure is low or there is a low blood volume
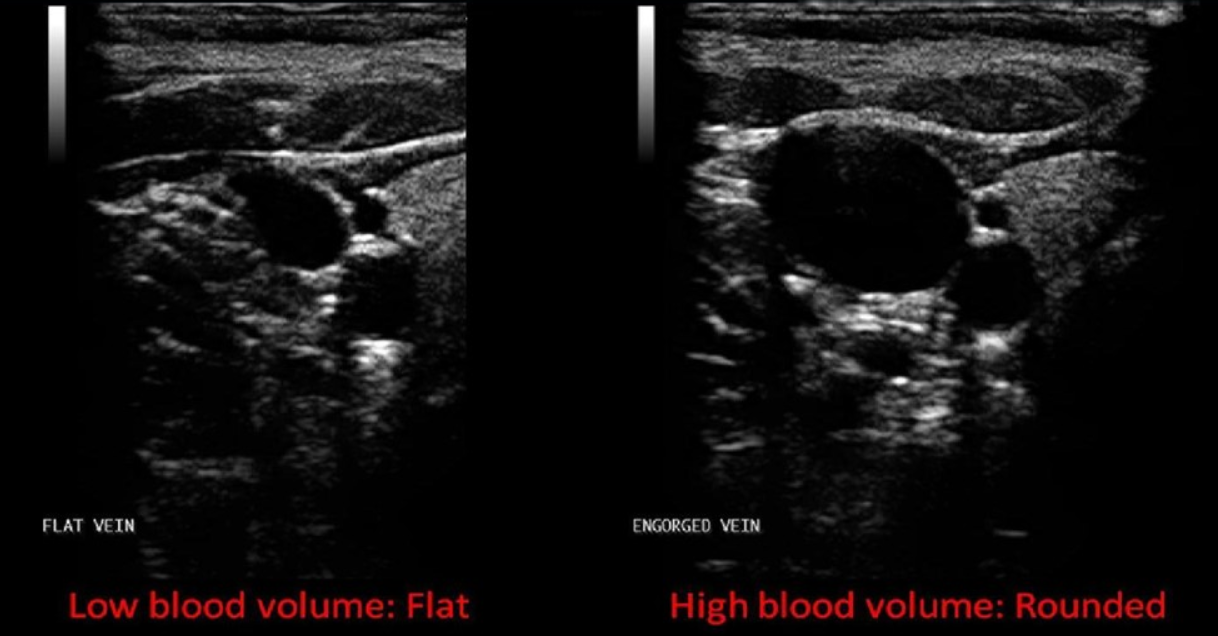
When will a vessel assume a circular shape?
When transmural pressure is high or there is a high blood volume
How does venous flow occur?
Calf muscle pump
What is the function of the calf muscle pump during contraction?
Contraction in calf muscles force venous blood movement
Deep venous valves open to allow blood flow up towards heart
Perforator valves close to prevent caudal flow
What is the function of the calf muscle pump during relaxation?
Relaxation in calf muscles
Deep venous valves close
Perforator valves open to allow blood to flow from superficial to deep system
What are causes of calf muscle pump failure?
Muscle wasting
Obstruction
Incompetent valves
What is spontaneous flow?
When flow is detected in veins without augmentation
What is respiratory phasicity?
When flow moves from areas of high pressure to low pressure during breathing
What happens to pressure in the body upon inspiration?
Diaphragm descends
Increase in intra-abdominal pressure
Decrease in intrathoracic pressure
Decreased flow in lower extremities through IVC
Increased flow in upper extremities toward heart
What happens to pressure in the body upon exhalation?
Diaphragm raises
Decrease in intra-abdominal pressure
Increase in intrathoracic pressure
Increase in flow from lower extremities through IVC
Decreased flow in upper extremities toward heart
What is cardiac pulsatility?
Ripples of motion caused by adjacent cardiac contraction that creates pulsatile flow in proximal vena cava, upper arms, and hepatic veins