APES chapter 15/16/17 (chemical pollutants)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are natural air pollutants?
Volcanoes
forest fires
Plants (pollen)
animals
What are anthropogenic (from humans) air pollutants?
vehicles
power plants
industrial processes
waste disposal
What are the 6 Criteria air pollutants?
1) Sulfer Dioxide →SO2
2) Nitrogen Oxides→NOx
3) Carbon Monoxide →CO
4) Particulate matter →PM
5) Ozone →O3
6) Lead →Pb
Sulfur dioxide → SO2
Natural sources are volcanoes and fire
Anthropocentric sources are from the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gasoline)
primary polutant
Causes Acid Deposition and breathing problems

Nitrogen Oxides → NOx
Natural sources are soil bacteria and lightning
Anthropogenic sources are the burning of coal and oil
Primary polutant
It can irritate the eyes and throat as well as causing respatory issues.
Carbon Monoxide →CO
A highly toxic gas from the incomplete combustion of carbon-based materials.
primary polutant
It can cause death because it replaces the hemoglobin in your blood
Particulate matter →PM
Natural sources are volcanoes, fires, dust, pollen
Anthropogenic sources are fossil fuels and agriculture
A Primary polutant
Can absorb and scatter sunlight reducing photosynthesis causing cooling. Pariculate matter also leads to respiratory issues that lead to death.
What is smog?
“Normal smog” is a combination of oxidants and particulates.
Smog causes irritation to the eyes and respiratory systems, especially in : older people, children, and pregnant women

What is radon?
Radon is a colorless, orderless, radioactive gas that naturally occurs from the breakdown of uranium in rocks and soil. It leads to high risks of lung cancer.
Lead → Pb
Naturally occurs in rock
Primary polutant
Causes central nervous system and intelligence issues.
What are VOCS?
Volatile Organic Compounds
ex) Perfumes, Gasoline, Nail polish remover

Ozone →O3
secondary pollutant
A highly reactive gas that is a component of photochemical smog
This can affect respiratory illnesses and aggravate heart disease.
Mercury →Hg
Anthroprogenic sources are coal and oil
Primary polutant
This is toxic to the central nervous system

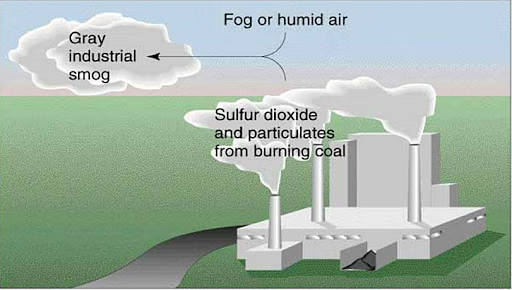
What is Industrial smog?
Burning fossil fuels mainly produces carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulfur, and mercury. Sulfur reacts with other chemicals in the air and creates compounds like sulfur dioxide.
gray smog

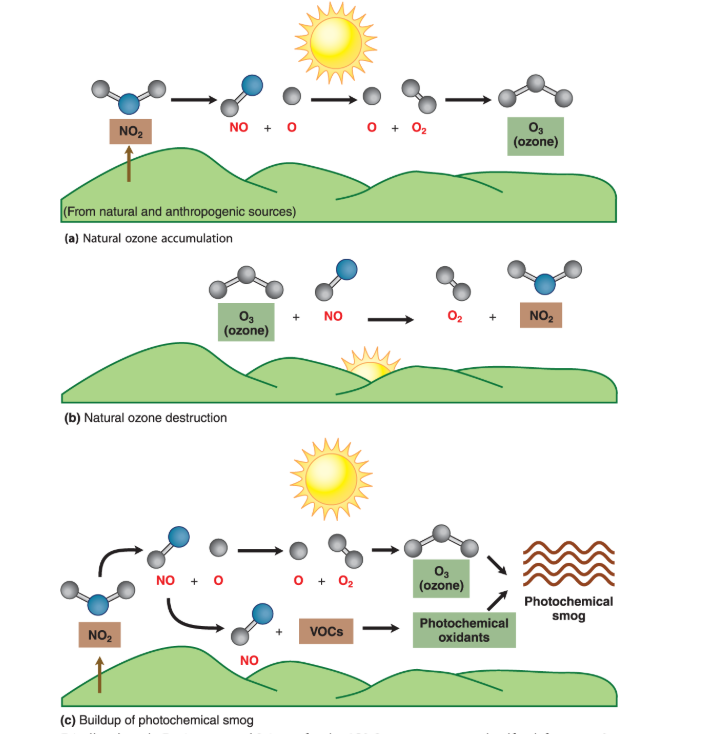
What is photochemical smog?
Forms when solar ultraviolet radiation interacts with an atmosphere polluted by hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides. Nitrogen oxides and VOC’s mix and this is where it becomes a problem.
Brown smog
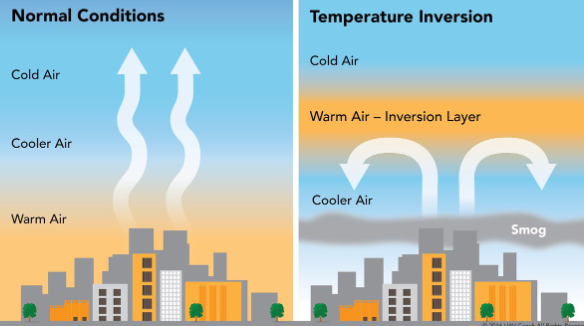
What is temperature inversion?
Instead of the usual temperature decreasing as you go up into the atmosphere, warm air gets taped trapping pollutants in the atmospheres. →leads to smog
How is photochemical smog related to combustion?
Both relate to the burning of fossil fulels
The more _____ soil, the better for plants
basic
What is a Catalytic converter?
A device added to automobiles to break down toxic car exhaust into water, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide.
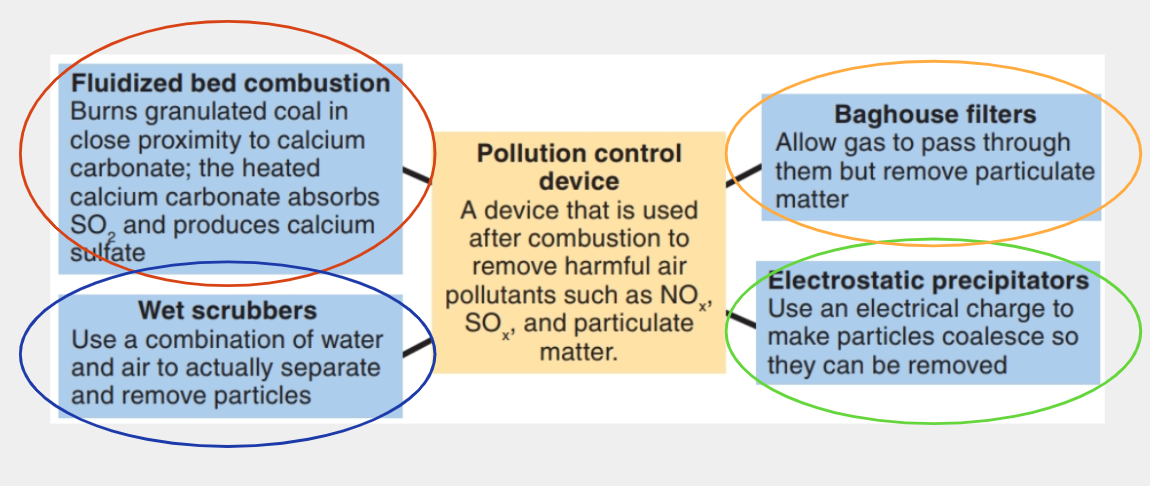
What are the 4 main kinds of pollution control devices?
1) fluidized bed combustion
2) Wet scrubbers
3) Baghouse filters
4) Electrostatic precipitators
What is fluidized bed combustion?
Limestone is burned with coal creating calcium sulfate. The byproduct is used to make plaster and drywall
→ burning things with LESS nitrogen emissions
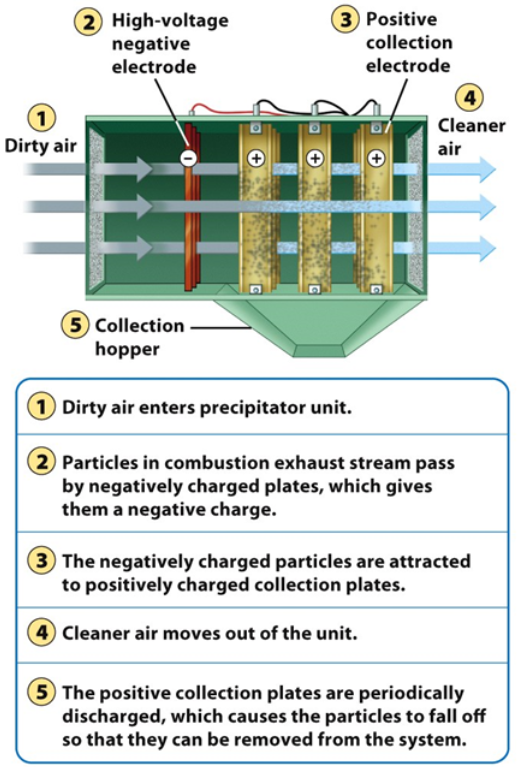
What is a Electrostatic Precipitator?
Uses electrical charges to force air particles to coalesce, removing them from air and reducing particulate matter
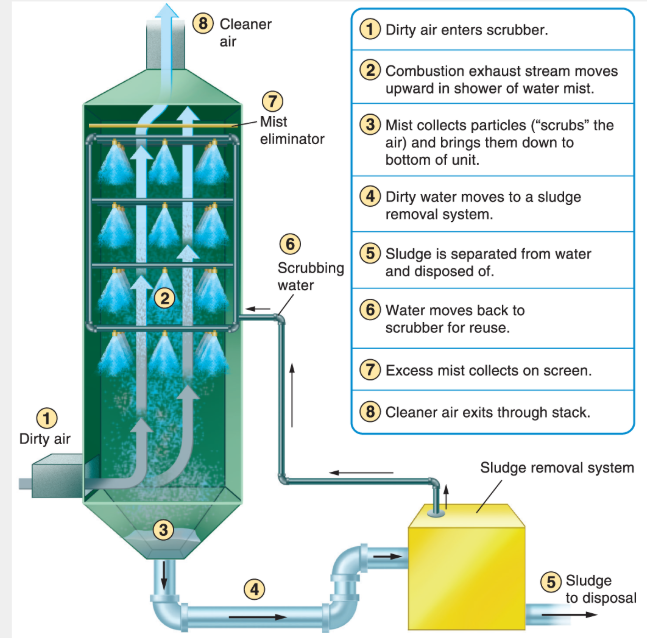
What is a scrubber?
Basicly a shower for the air
What was the clean air act of 1970?
It transformed federal air pollution regulations, allowing limits on emissions from industries and vehicles at both federal and state levels.
What is stratospheric ozone?
It is like sunscreen for the earth and protects us from UV rays. This is depleting.

What is the formation process of stratospheric ozone?
Ultraviolet light hits the O2 molecule and splits it in half resulting in 2 oxygen molecules that bond together to create ozone
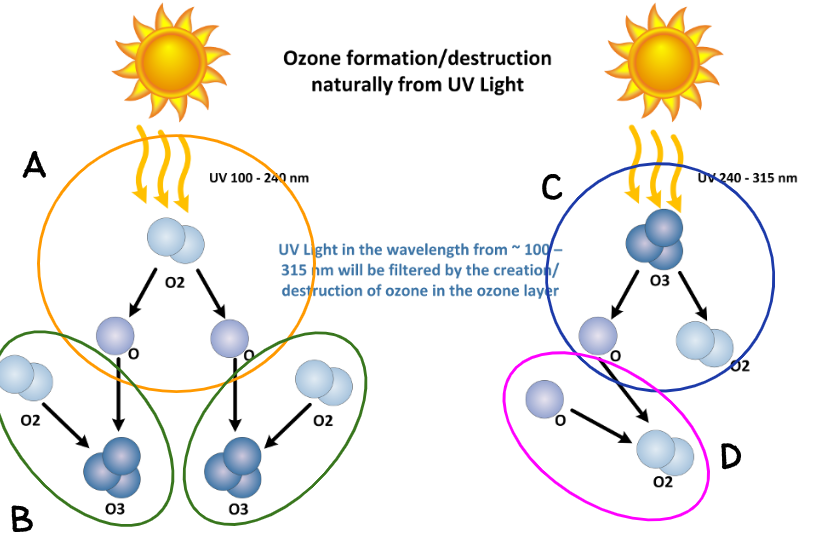
What are Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)?
A green house gas, used in aerosols and air conditioning for a while because they where cheap.
NOT GOOD
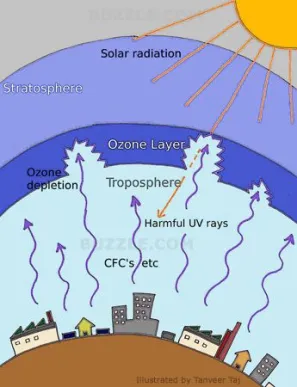
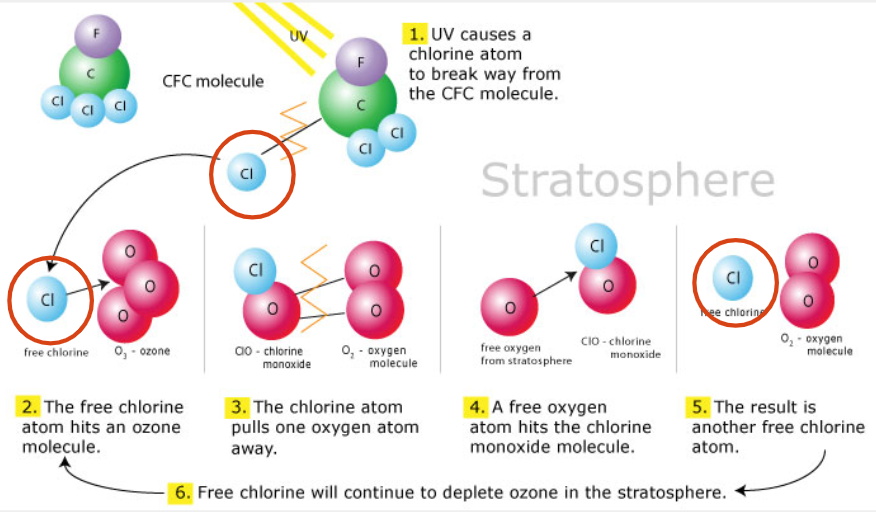
How are CFCs in the stratosphere bad?
Oxone doesn’t like the CFCs. The UV rays bounce off the CFCs, causing the CFCS to break off and to impact the oxygen molecules, resulting in oxygen depletion in the atmosphere
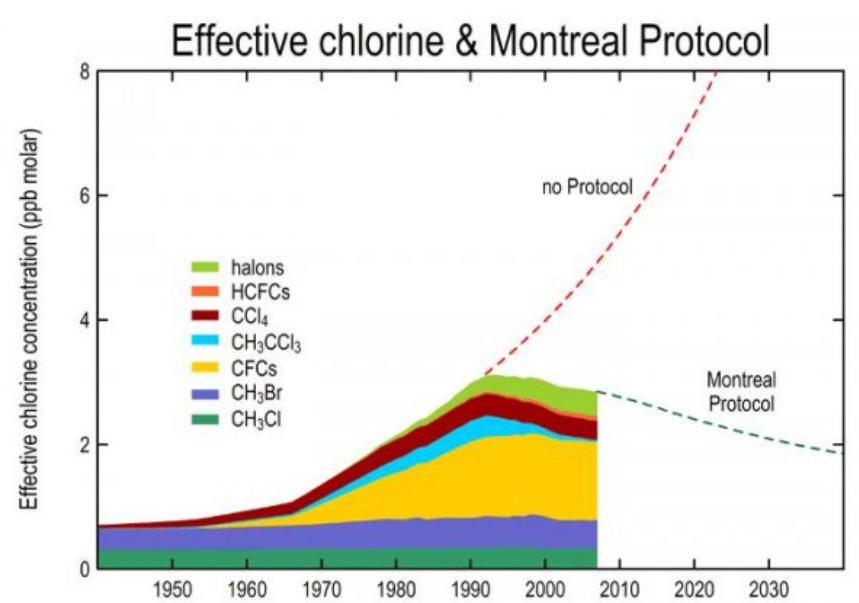
What is the Montreal protocol of 1987
The agreement to not use CFCs
What is the difference between stratospheric ozone and ground level ozone?
Ground-level ozone, often called "bad" ozone, forms when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in sunlight. Unlike "good" ozone found high in the atmosphere, which protects us from harmful UV rays, ground-level ozone is a harmful part of air pollution.
Indoor air pollution causes ____ deaths every year compared to outdoor air pollution.
more
What are the 3 main indoor air pollutants?
1) carbon monoxide
2) asbestos
3) radon
What is sick building syndrome?
Buildings with little ventilation which can cause accute health affects

What is planned obsolescence?
Things less quality so that you buy more

What is Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
Garbage
ex) Food scraps, paper, yard waste etc
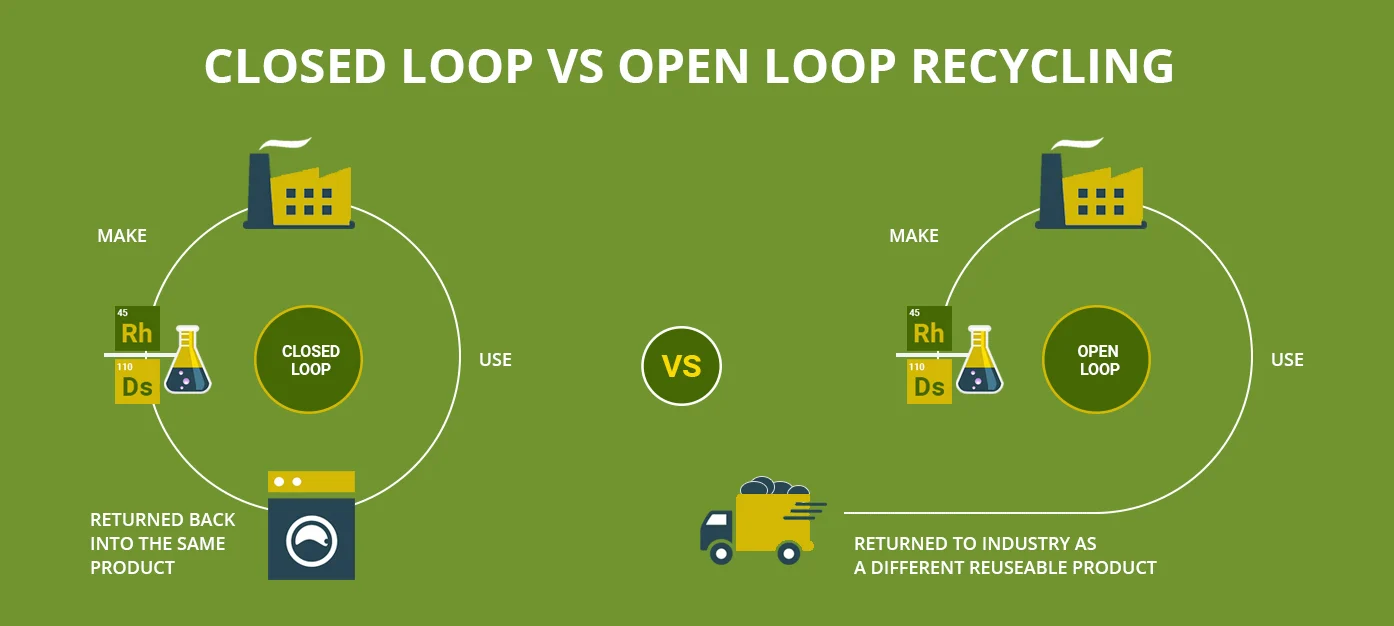
What is the difference between closed loop and open loop recycling?
Closed loop is when the item becomes the same thing while open look recycling becomes something completely new.

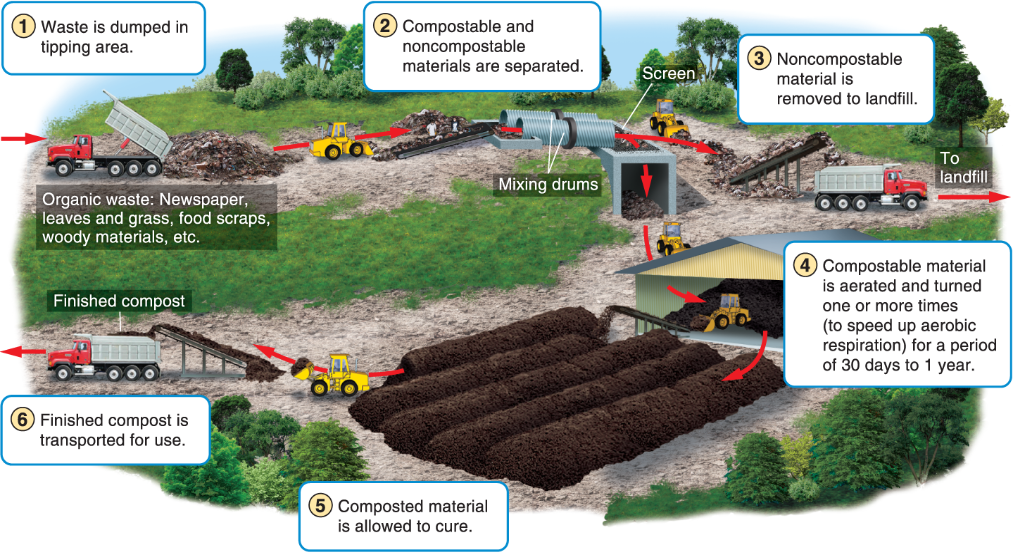
What is humus?
Organic matter that is a result from composting
What is a sanitary landfill?
little composition occurs in a landfill
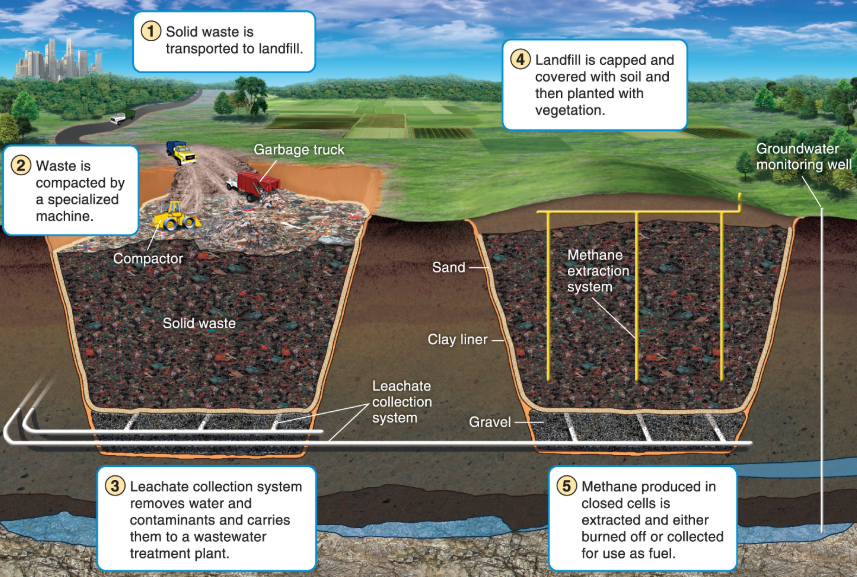
What is leachate?
liquid that contains elevated levels of pollutants from passing through MSW
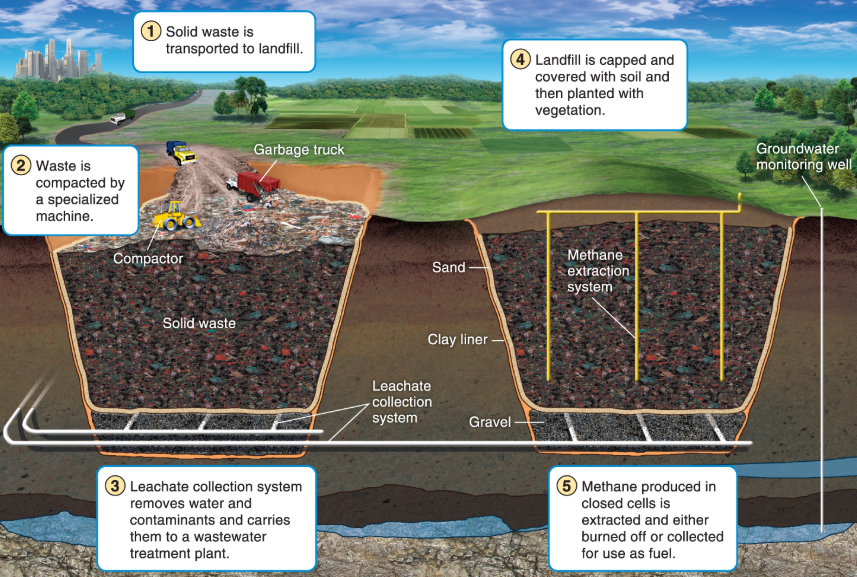
What type of soil would you want to build a landfill in?
Clay because it is full of pores
What is waste incineration
Burning waste reducing mass but releases toxic gas
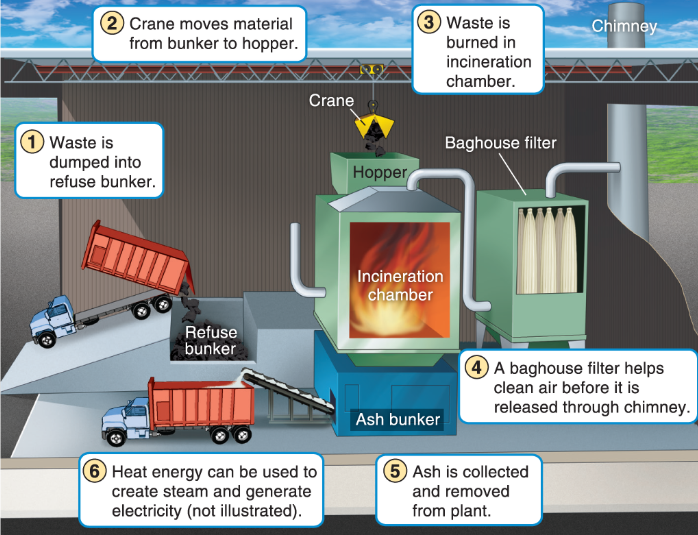
What is RCRA?
“cradle to grave”
not letting hazardous waste out of your sight in order to protect human health

What is the CERCLA or the superfund act?
The law imposes a tax on the chemical and petroleum industries for hazardous substance releases that could harm public health or the environment. It also establishes a trust fund for the cleanup of emergency and hazardous waste sites.
what is a brownfield?
A property on which the expansion, redevelopment, or reuse may be complicated by the presence or potential presence of a hazardous substance, pollutant, or contaminant.
Not as bad as a Superfund site

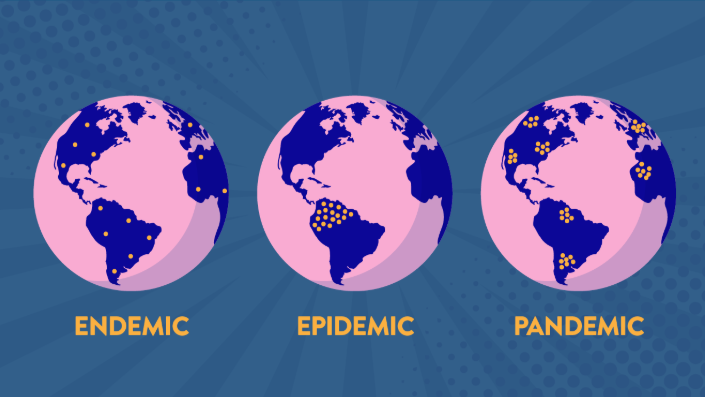
What is an endemic?
disease outbreak that is consistently present but limited to a particular region
ex) Malaria
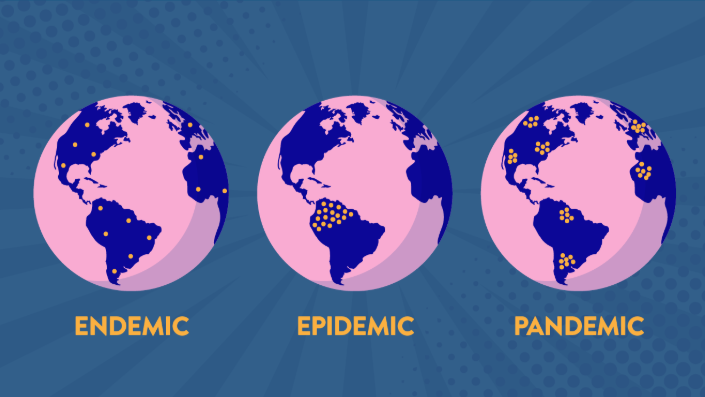
what is an epidemic?
Disease that affects a large number of people within a community (unlike an endemic it goes in waves)
ex) Obesity

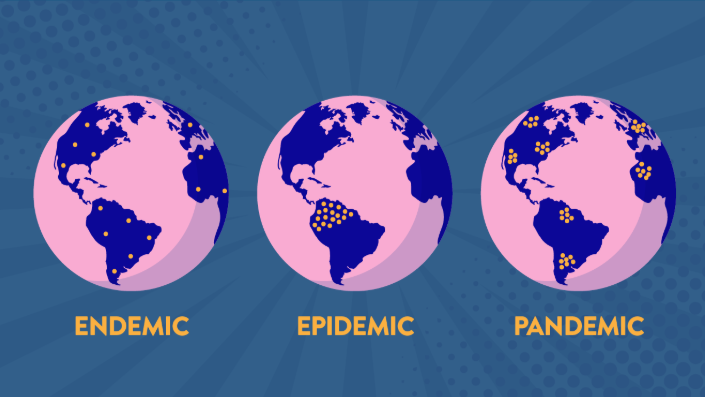
What is a pandemic?
An epidemic that has spread over multiple countries or continents.
ex) covid
what is an emergent infectious disease?
infections diseases that where previously not common for the past 20 years, often jump from animal host to human host
ex) ebola
What is a neurotoxin?
A chemical that causes impaired learning, nervous system disorders, damage to brain, kidneys, liver
ex) led
What is a carcinogen?
A chemical that causes cancer
ex) arsenic
What is a teratogen?
A chemical that reduces fetal growth, brain and nervous system damage
ex) fetal alcohol syndrome
What is an allergen?
Something that causes breathing difficulties, hives
ex) peanut allergies
What is a Endocrine Disruptor?
A chemical that impacts hormones
ex) DDT
What is LD50?
Lethal Dose that kills 50% of the test population
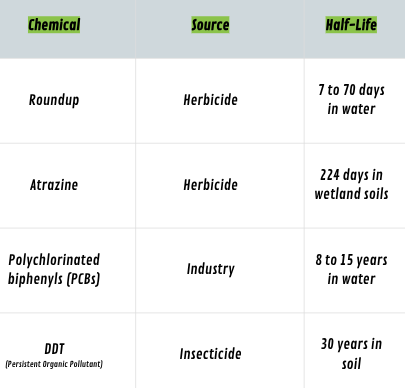
What is persistence?
how long a chemical stays in the environment