The nervous system
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the difference between graded and action potentials?
Graded=short distance in small regions of plasma membrane, magnitude of pot. diff. can vary, no threshold or refractory period
Action=long distance with large alterations in membrane potential, all or nothing law (fixed amplitude), threshold and refractory period
How can a graded potential be decremental?
Ions will leak out of membrane
Action potential mechanism
1) -70mV
Typical threshold stimuli requirements
15mV less negative than resting membrane potential
Structure of an axon
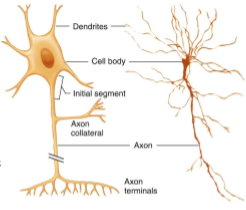
Glial cells
90% of CNS - provide physical and metabolic support to soma, axon and dendrite
What is a group of axons together in the CNS called?
Pathway/tract
Group of axons that links right and left of CNS
Commissure
Cell bodies of neurons with similar functions in PNS
Ganglia
Cell bodies with similar functions in the CNS
Nuclei
3 main regions of brain
Forebrain, Brainstem, Cerebellum
4 lobes to forebrain
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal
What are dendritic spines?
Protrusions that increase surface area and contain ribosomes
Name a difference between making of myelin in CNS and PNS
in CNS myelin made by oligodendrocytes whereas in PNS by Schwann cells
What is anterograde movement and which protein is responsible for this movement?
Kinesins aid movement from cell body to axon terminals e.g. nutrients, neurotransmitter, filled vesicles
What is retrograde movement and which protein is responsible?
Dyneins control movement from axon terminals to cell body e.g. recycles membrane vesicles, growth factors
What are the three functional classes of neurons?
1) Afferent neurons: from PNS (tissues) to CNS
2) Efferent neurons: from CNS to effector cells
3) Interneurons: within CNS (>99% of all neurons)
What is the composition of cell types in the CNS?
Neurons: 10% of cell types (but take 50% of space)
Glial cells: 90% (remainder)
Give 3 examples of glial cells
1) Astrocyte → regulates K+ and neurotransmitters in extracellular fluid/ form blood brain barrier by stimulating epithelial cells to form tight junctions
2) Microglial cells → specialised macrophage like cells
3) Ependymal cells → found in fluid filled cavities and regulate flow of cerebrospinal fluid
What are gyri and sulci
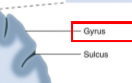
What is the outer cerebral cortex and inner cerebral cortex made of?
Outer = grey matter (interneurons, cell bodies, axons, glial)
Inner = white matter (myelinated fiber tracks)
What are the two components of the forebrain?
Cerebrum (two hemispheres) and diencephalon (central core)
What is the corpus callosum?
Massive bundle of nerve fibers connecting each cortex division

What are the two types of cells in the cerebral cortex?
Pyramidal → major output/ excitation
Non-pyramidal → major input/ receive signals
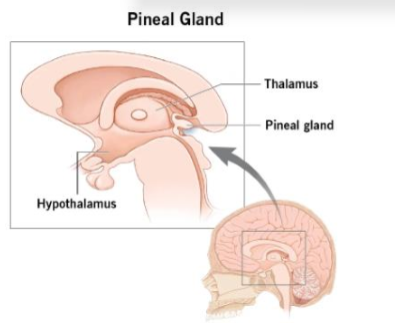
What are the 3 regions of the diencephalon?
1) Thalamus: movement, attention, arousal
2) Hypothalamus: homeostatic regulation of internal environment
3) Epithalamus: controls biological rhythms via pineal gland
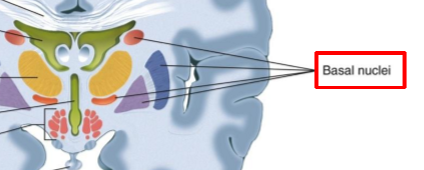
What is the role of the cerebellum?
Coordinates movement e.g. posture and balance through basal nuclei
What is the role of the brainstem?
Integrates input from all regions of CNS:
motor functions
cardiovascular, respiratory control, swallowing
regulates sleep, wakefulness, attention, eye movement
ESSENTIAL FOR LIFE
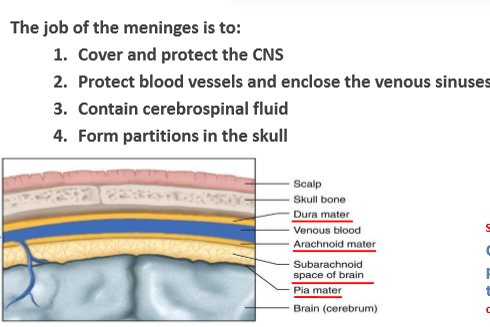
What are 3 types of meninges and what is their role?
Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, Pia mater are protective membranes around the CNS
What is the blood brain barrier?
A protective mechanism that helps to maintain a stable environment for the brain
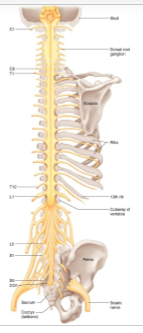
Where to afferent and efferent fibers enter and exit from?
Afferent → dorsal root
Efferent → ventral root
How many pairs of nerves do we have?
43 (12 cranial, 31 spinal) found in:
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
What are 3 components of brain stem?
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
What are the two divisions of the PNS?
Somatic (voluntary) and autonomic (sympathetic/ parasympathetic)