Anatomy of the Skeletal System: Bones, Functions, and Projections
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Skeletal system
Support and movement, protection of organs, production of red blood cells, calcium and phosphate storage
axial skeleton bones
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
axial skeleton function
protects brain, spinal cord, sense organs, and soft tissues of thoracic cavity; supports the body weight over lower limbs
appendicular skeleton function
Bones of each limb are organized into regions delineated and connected by different joints; joint types associated facilitate a large range of motion
appendicular skeleton bones
126 bones of upper limbs, lower limbs, bones of shoulder girdle and pelvic girdle
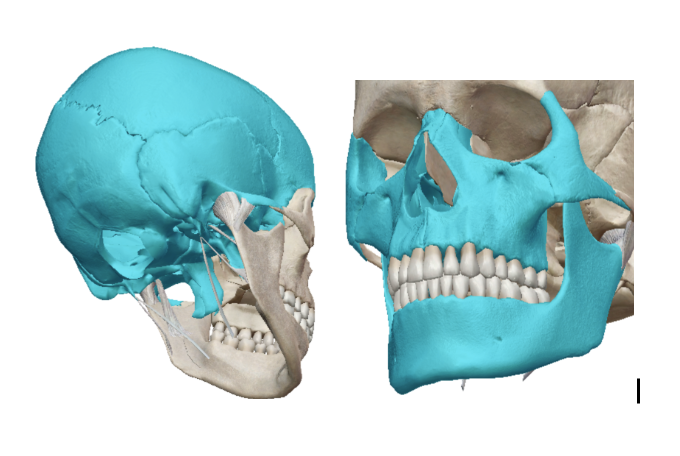
Skull
Consists of 22 bones from the cranial bones and facial skeleton
Vertebral column
Consist of twenty four Vertebrae, the Sacrum and coccyx
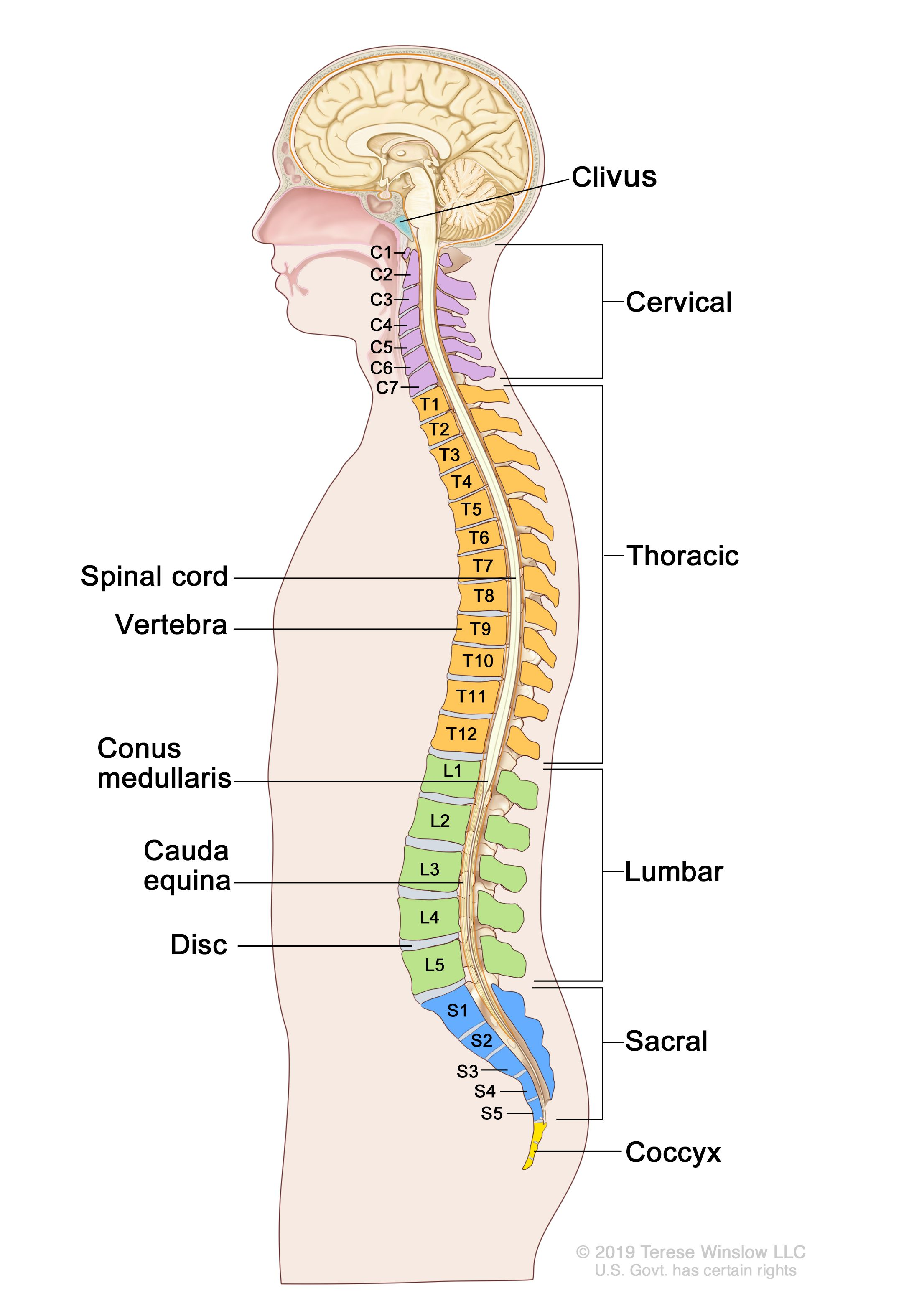
C7
T12
C1
S1
L5
Trocanter
A large projection on the side of the bone that allows connective tissues to connect to the bone.

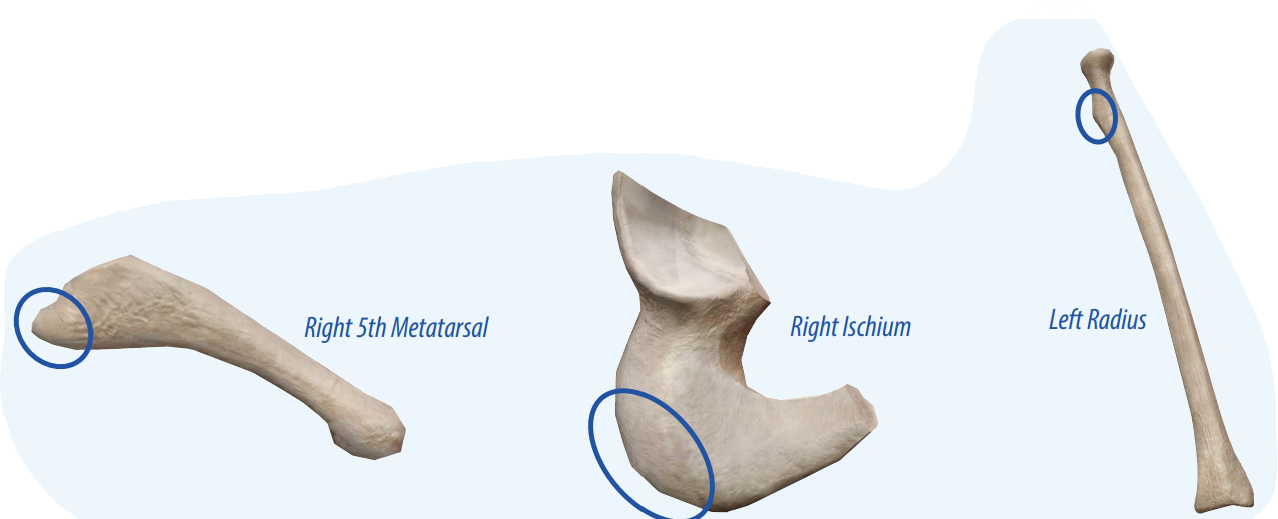
Tuberosity
A moderate projection that allows connective tissues to connect to the bone.
tubercle
A small round projection that allows connective tissues to connect to the bone.
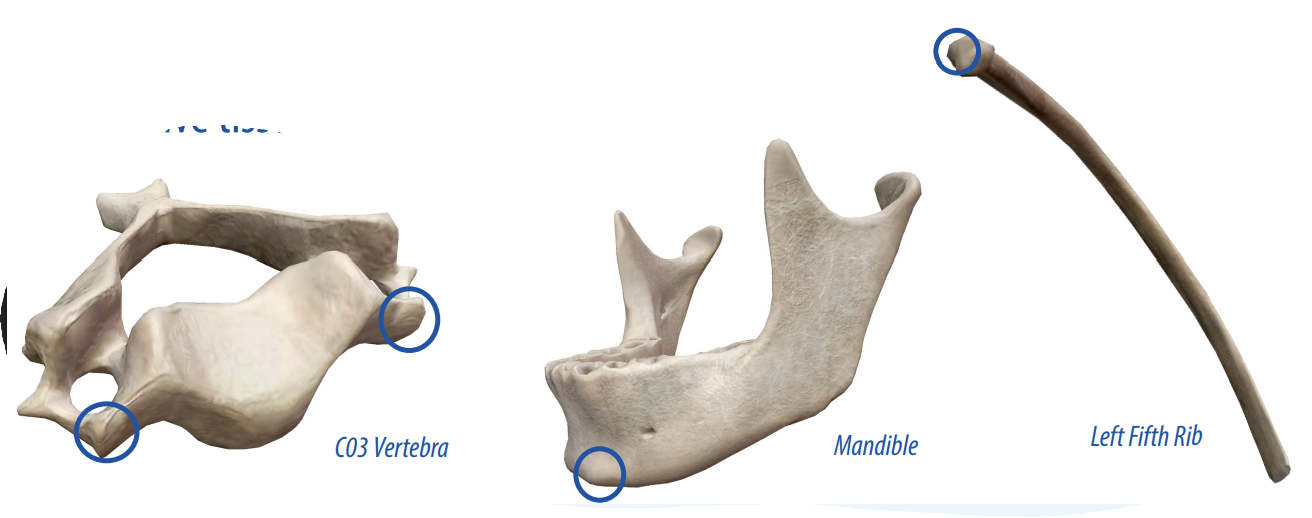
Projection
An area that projects above the surface of the bone.
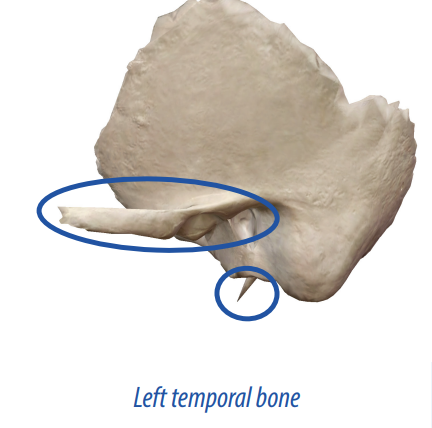
process
A outgrowth of bone from a larger body that allows articulation with other bones to form joints.
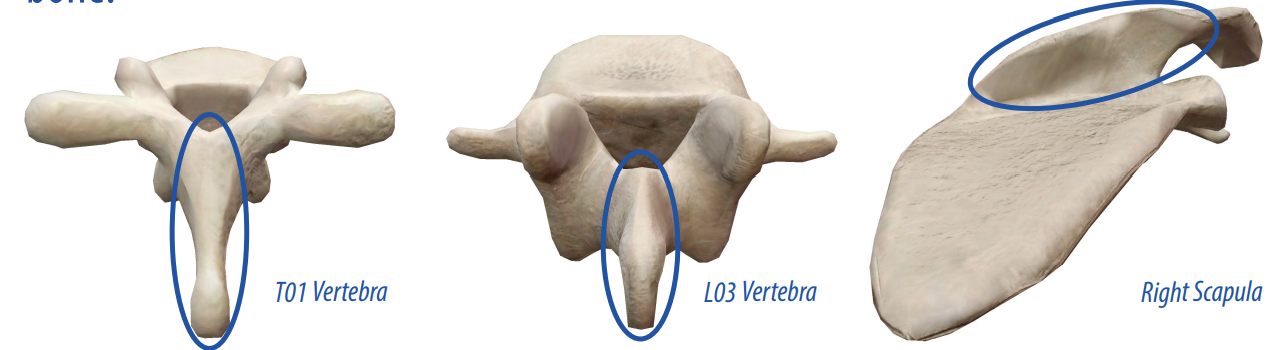
spine
A more pronounced raised, sharp elevation of bone that allows connective tissues and muscles to connect to the bone.
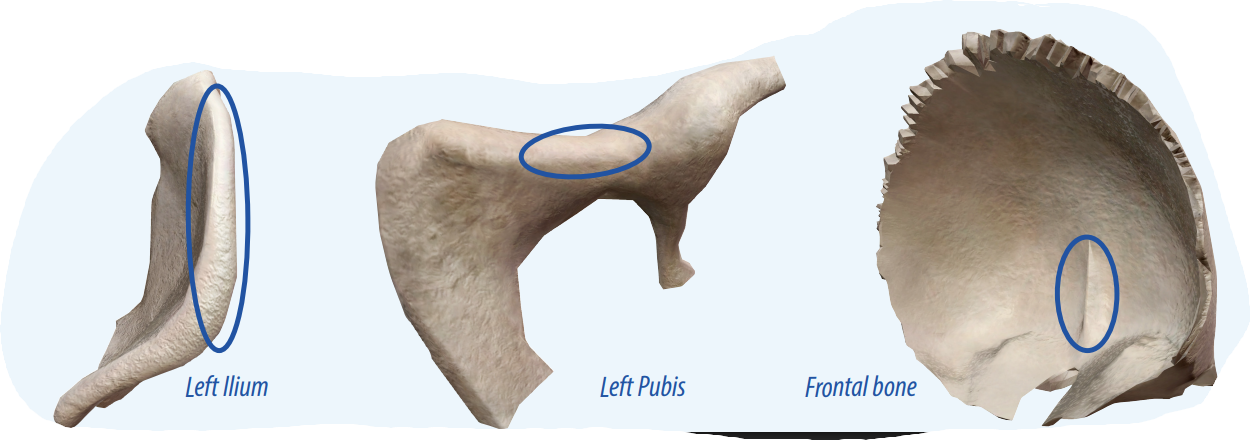
crest
A raised ridge projection that is part of the edge of a bone and allows connective tissues to connect to the bone.
Head
Round surface of a bone that helps form a joint.
Epicondyle
A rounded projection that sits on top of the condyle and allows connective tissues to connect to the bone.

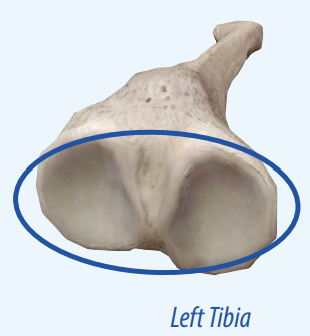
Condyle
Provides structural support and absorbs most of the force exerted by the joint.
Canal
a tunnel through a bone
Facet
A smooth and flat surface that helps form a gliding joint.
Fissure
A slit in the bone that usually houses nerves and blood vessels.
Foramen
A round hole where blood vessels, nerves, or ligaments pass through.
Fossa
A shallow depression in a bone’s surface that allows other bones to articulate with it.

Sulcus
A groove that accommodates a nerve, blood vessel, or tendon.
Flat Bone
Bones that protect internal organs such as the brain heart and lungs
What kind of bones are cranial bones?
Flat bones
What kind of bones are scapulae?
Flat bones
What kind of bones is the sternum
Flat bones
What kind of bones are the ribs?
Flat bones
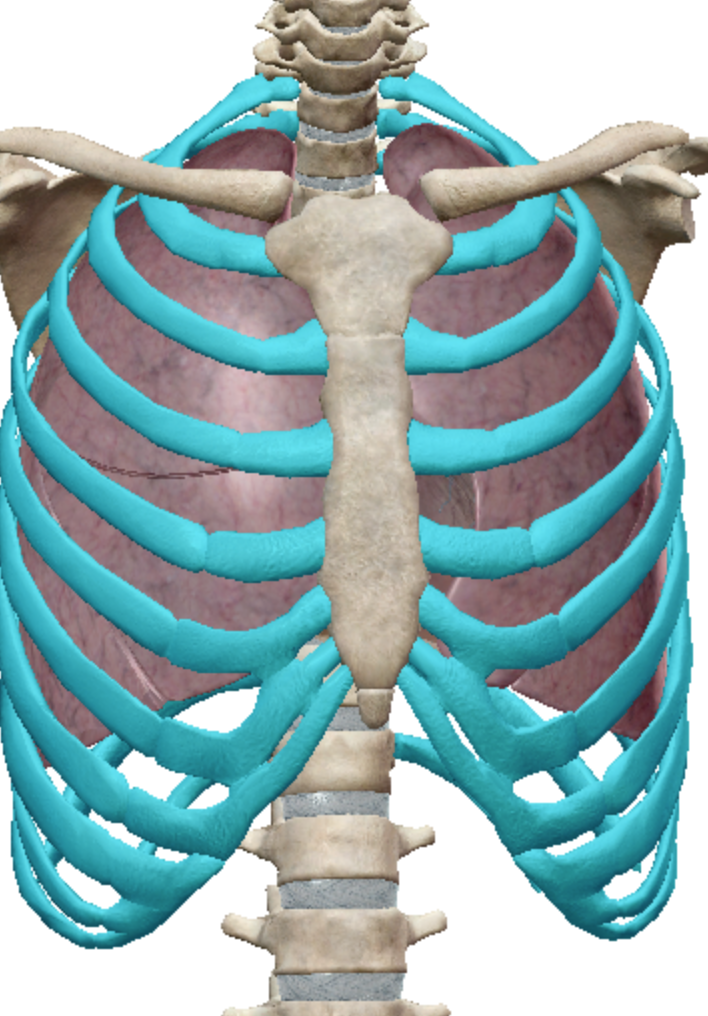
Long bones
Bones that support the weight of the body and facilitate movement
What kind of bones are the humerus?
Long bone
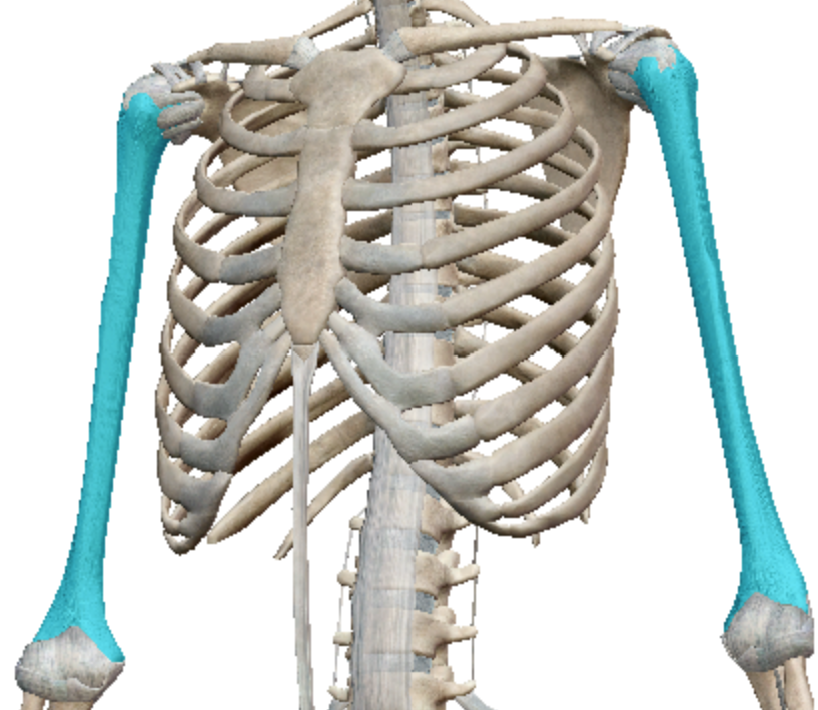
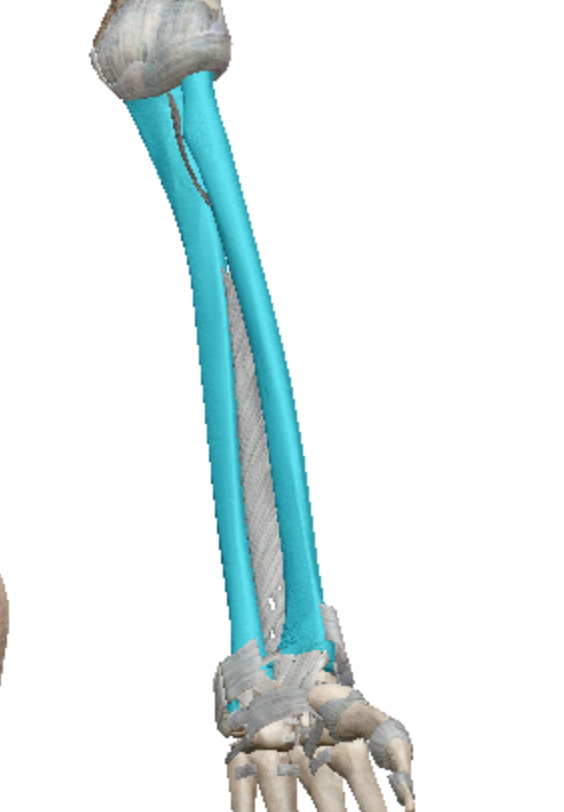
What kind of bones are the radius and ulna?
long bone
(radius inside, ulna outside)
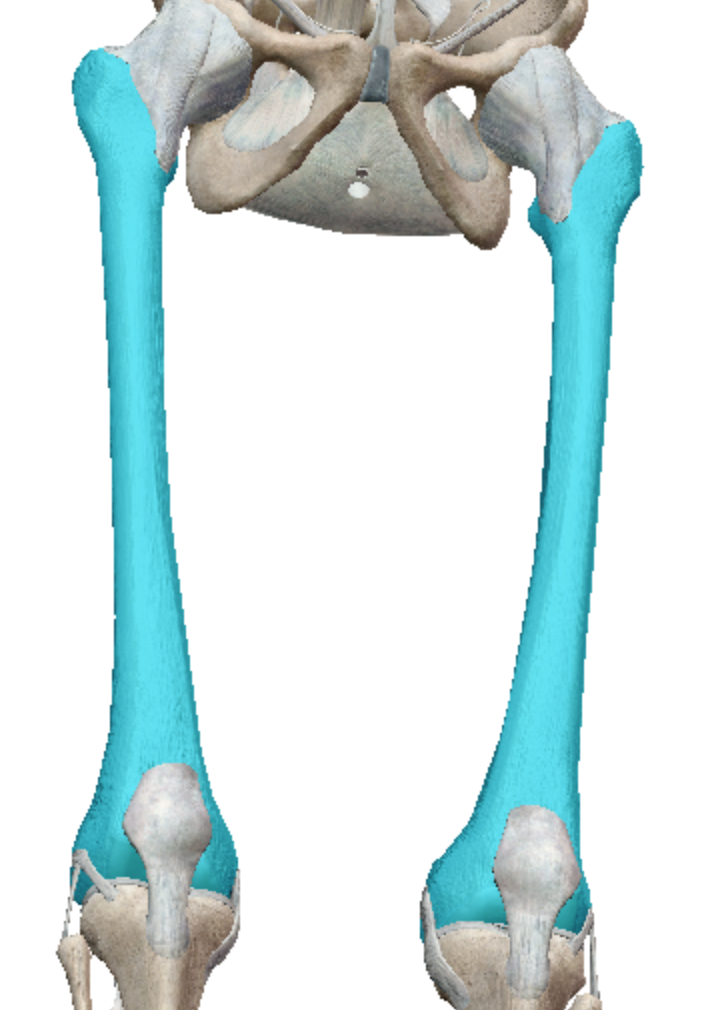
What kind of bones is the femur?
long bones
What kind of bones are the tibia and fibula?
Long bones
(tibia big, fibula small)
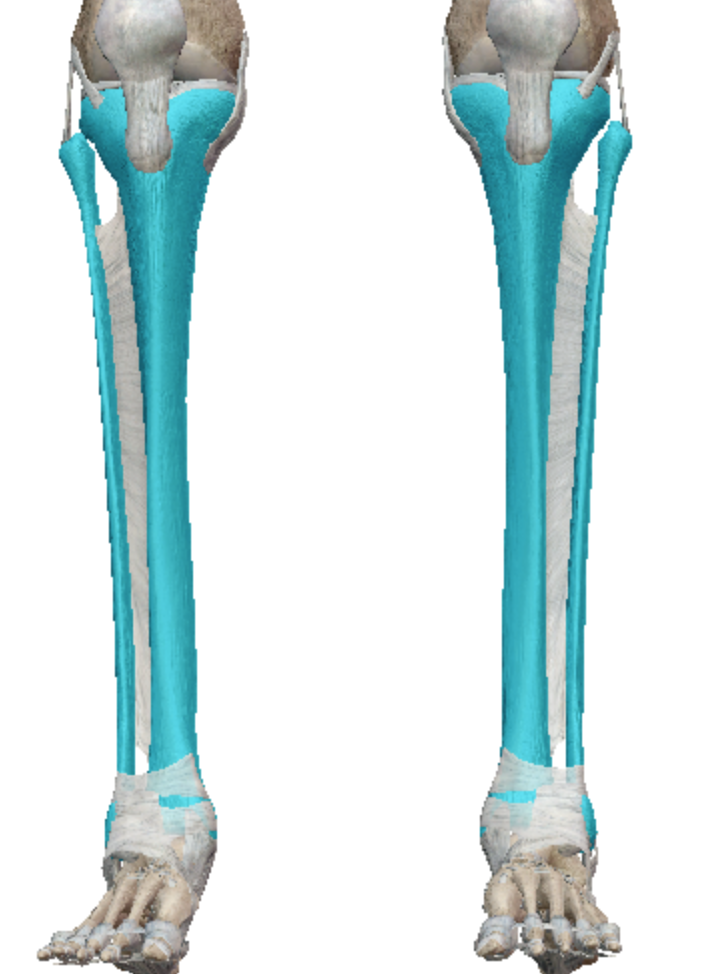
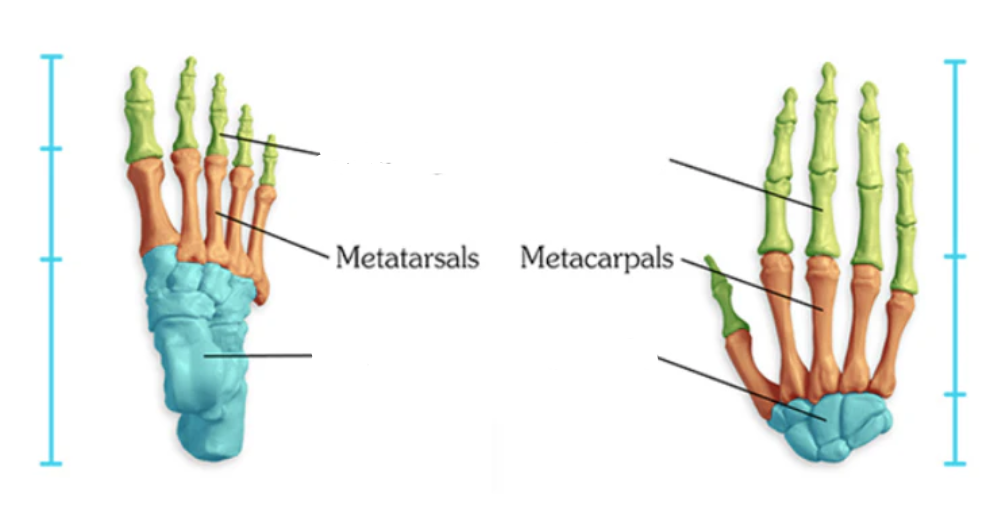
What kind of bones are the metacarpals and metatarsals?
long bone
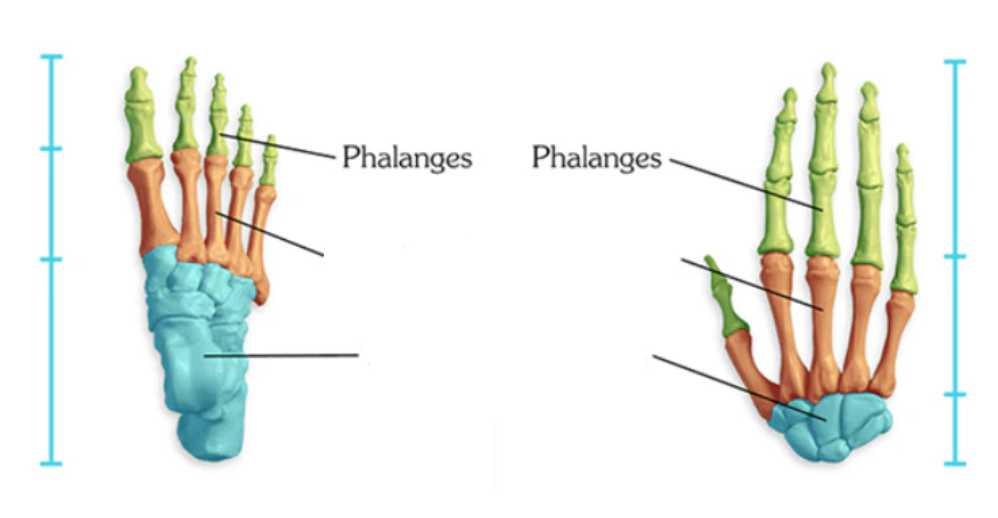
What kind of bones are the phalanges?
long bones
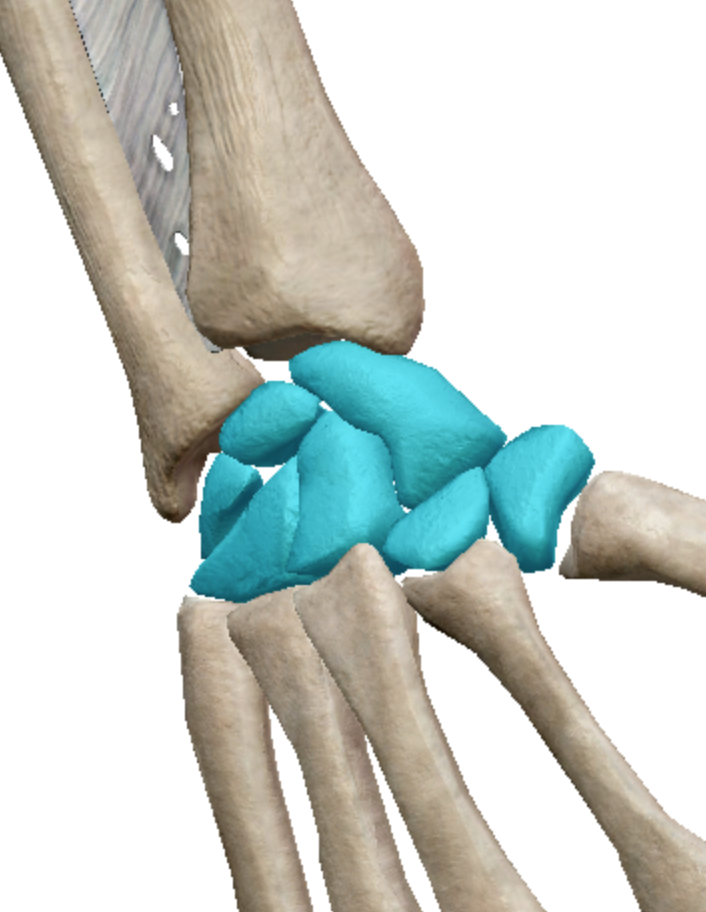
Short bone
Cube shaped components of the wrist and ankle joints
What kind of bones are carpals?
Short bones
What kind of bones are Tarsals?
Short bones
Irregular bones
Vary in shape and
What kind of bones are the vertebrae?
irregular bones
What kind of bones are the pelvic bones?
Irregular bones
Sesamoid bones
Reinforced tendons and protect them from stress and wear
What kind of bones are the Patella?
Sesamoid bones
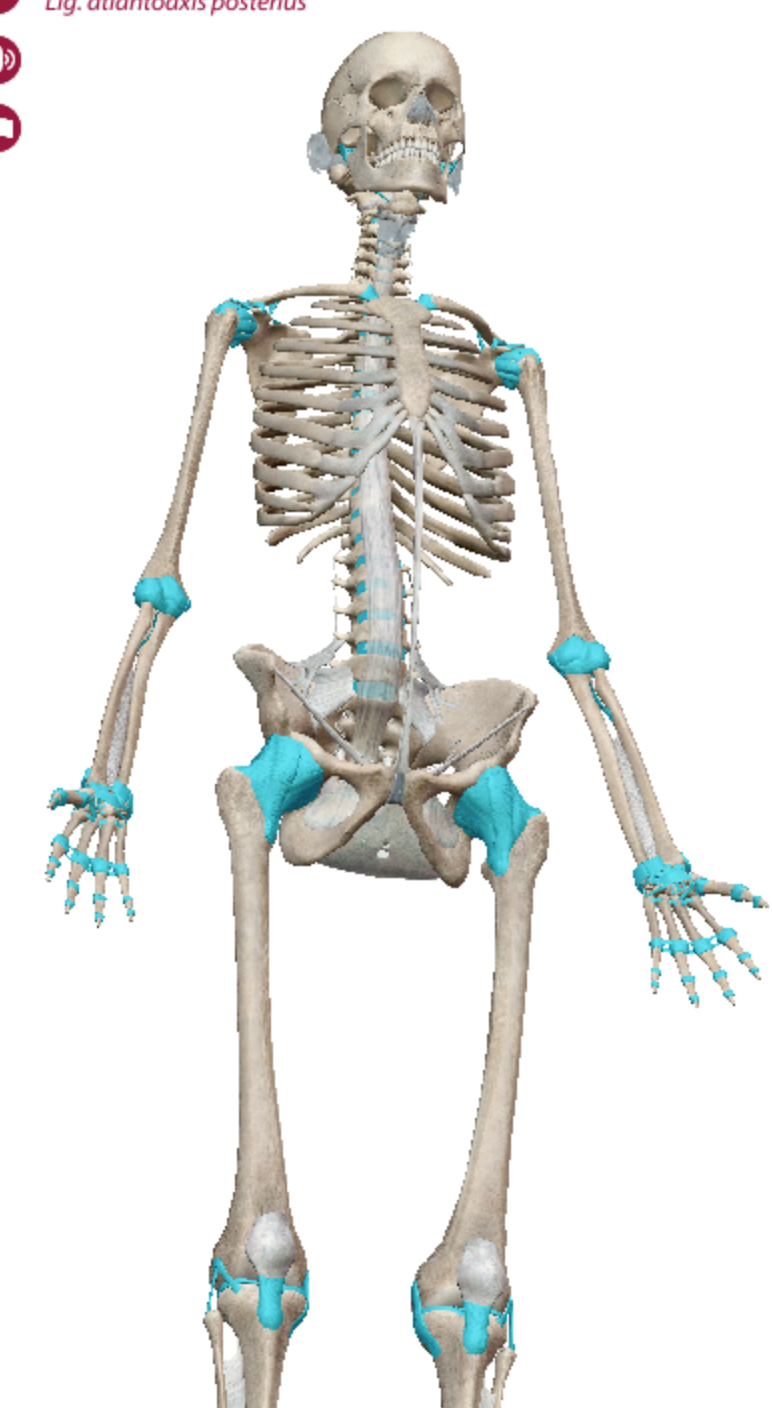
Synovial joints
Movable joints that occur throughout the body and six types of these joints allow for different ranges of motion
uniaxial joint
uniaxial joint is a type of synovial joint that allows movement along only one axis. Consists of Plane, hinge, and pivot
Gliding/plane joint
joints move against each other and include the intervertebral joints (thefacet joint between vertebrae and not the intervertebral disks), sacroiliac (SI) joint, carpaljoints, and tarsal joints.
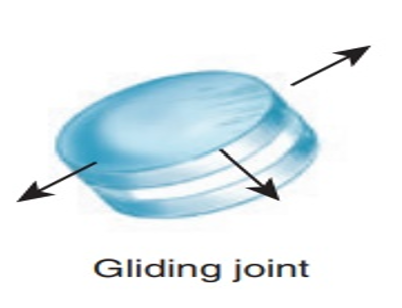
Gliding joints in the skeleton
consist of invertebral joints, carpral joints, tarsal joints
Hinge joints
move on one axis, allowing for flexion and extension, and include the elbow(articulation between the humerus and ulna) joint, knee and ankle joints and finger joints(interphalangeal)
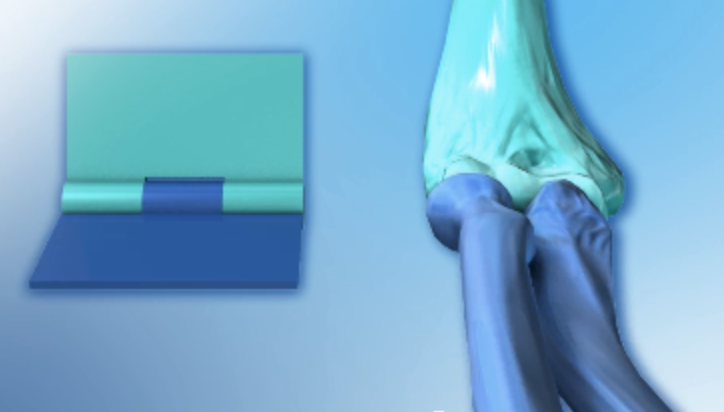
Hinge joints in skeleton
Elbow and finger joints
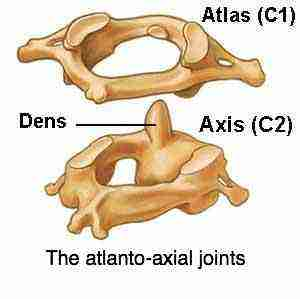
Pivot joints
At the top of the spine the axis and atlas form this joint that allows for the rotation of the head
Condyloid joints
allow for flexion and extension, abduction and adduction and limited circumduction and include the wrist (radiocarpal, metacarpophalangeal or knuckles,metatarsophalangeal) joint
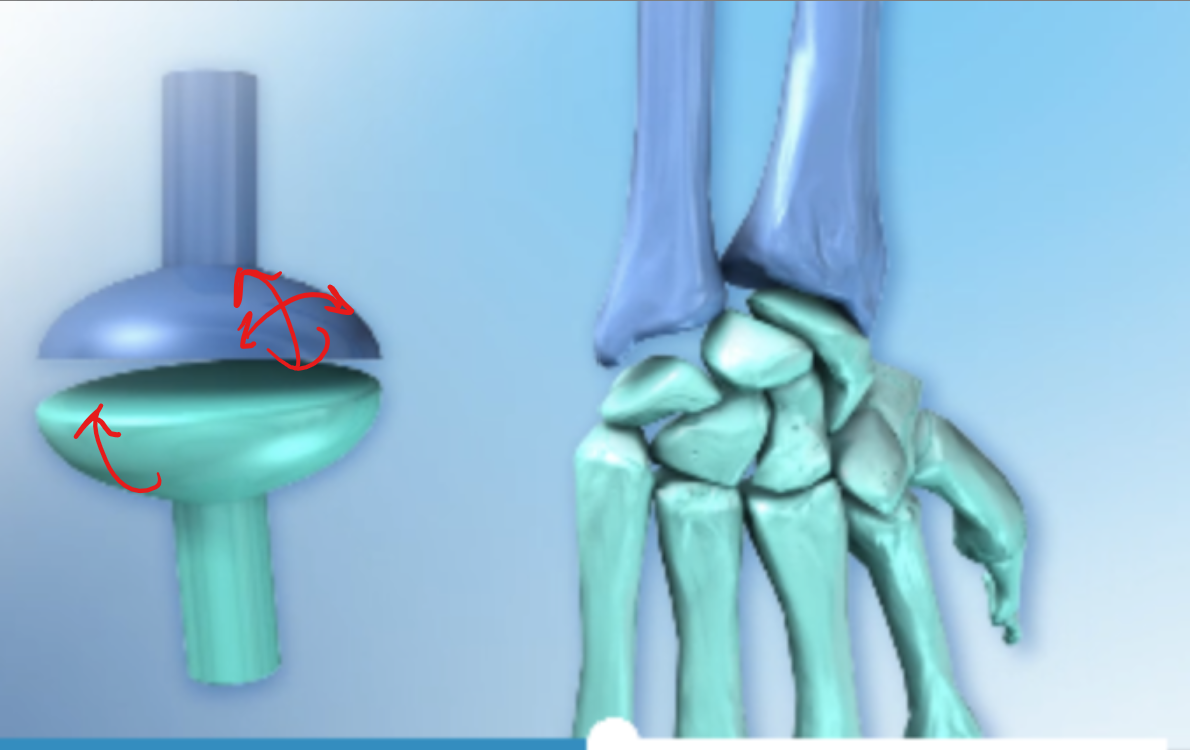
Condyloid joints in skeleton
Joint between radius and carpal bones, allows greater freedom of movement than a hinge joint, but less than a ball-and-socket joint
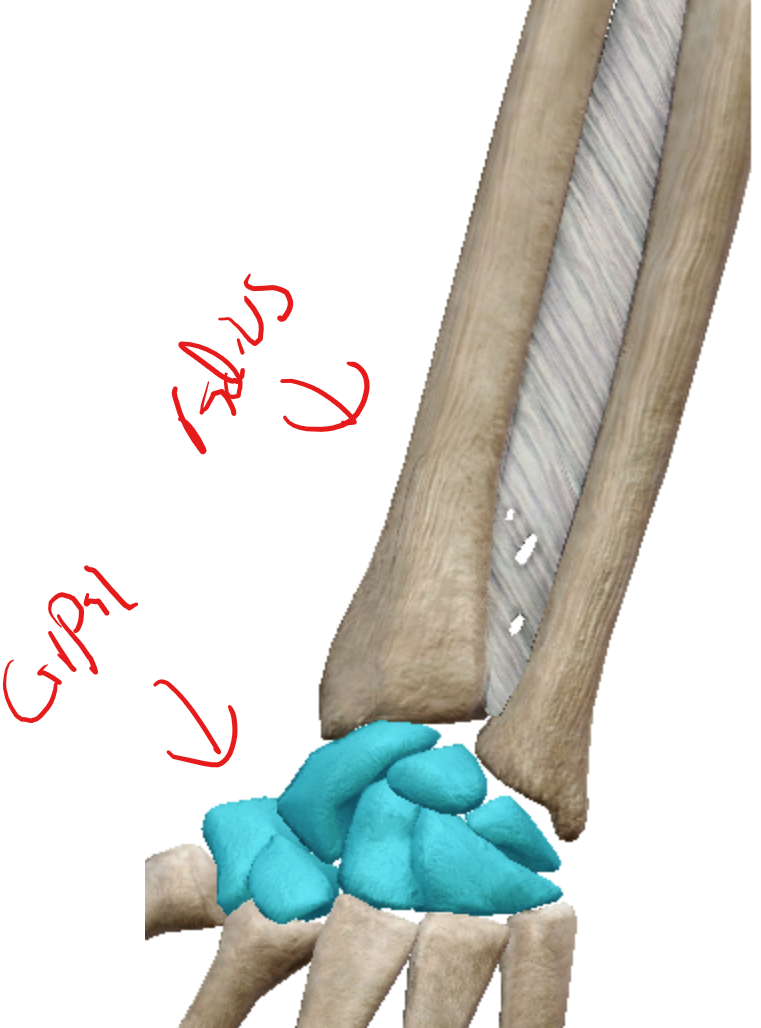

Saddle joints
In the hand this joint joint lets the thumb cross over the palm making it opposable
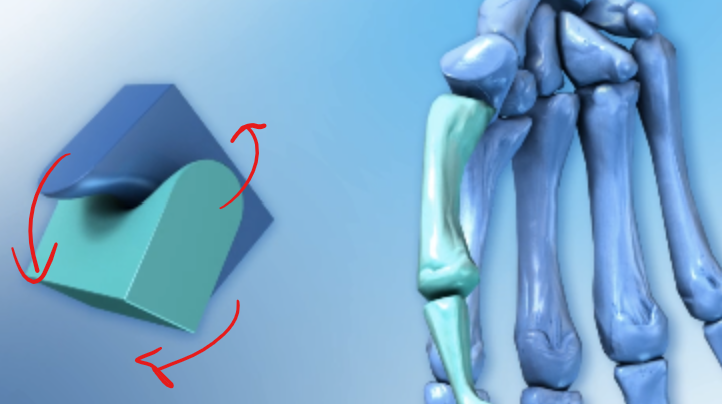
Saddle joint in skeleton
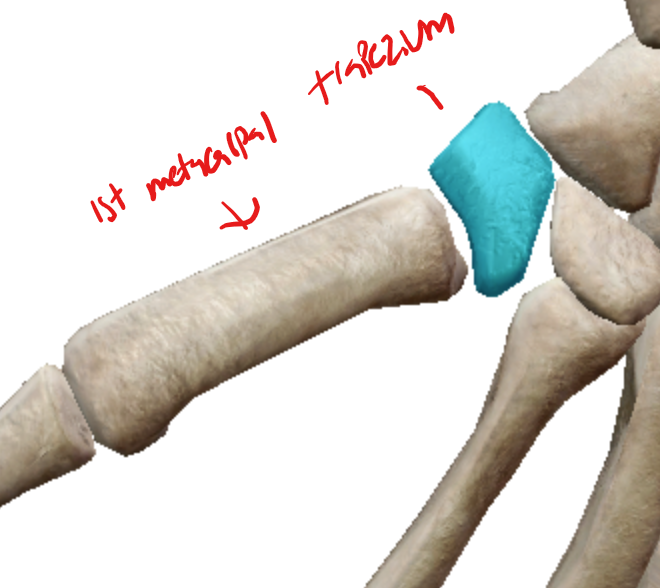
the joint between the first metacarpal and the trapezium
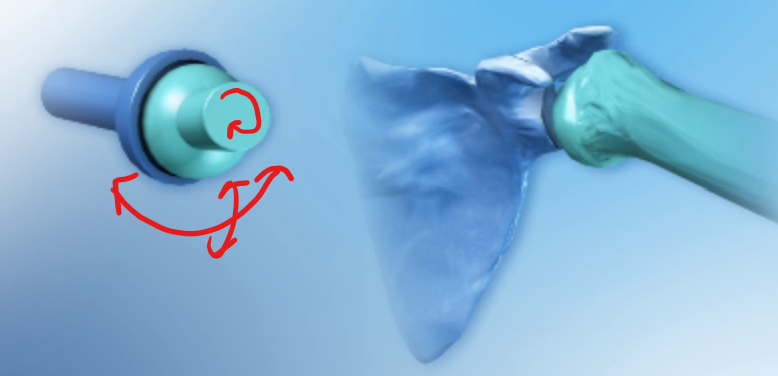
Ball and socket joints
This joint found in the shoulder is a freely moving joint that can rotate on any axis
Hip joint
An example of a ball and socket joint with head of the thigh bone fits into the socket of the ilium
Shoulder joint
Example of Ball and socket joints in the skeleton that connects the upper arm (humerus) to the shoulder blade (scapula)
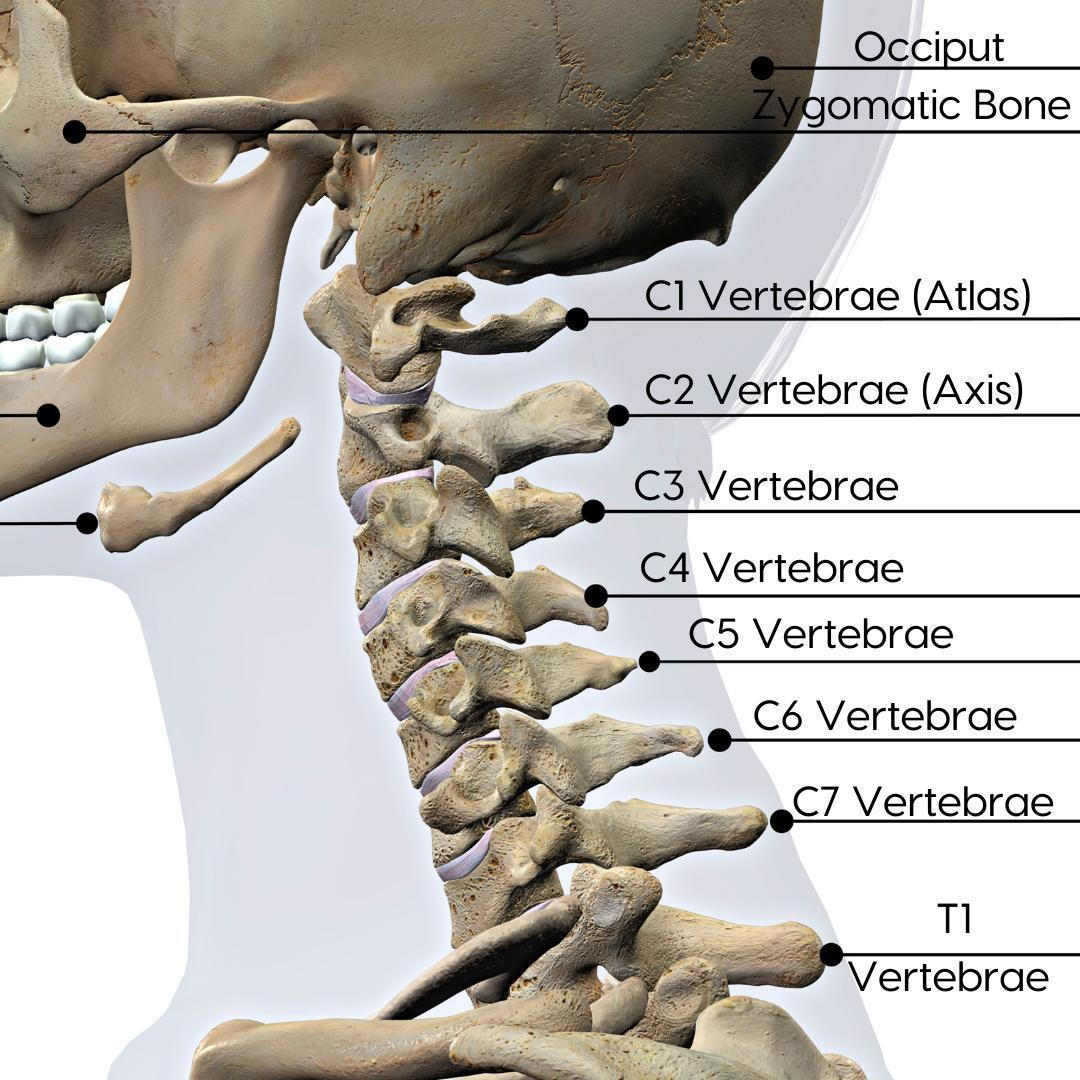
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
How many sacral vertebrae are there?
5
Coccyx
For coccygeal vertebrae fuse into one or two bones
Cervical spine
the upper portion of the spinal column, consisting of the first seven vertebrae (C1 to C7) located in the neck
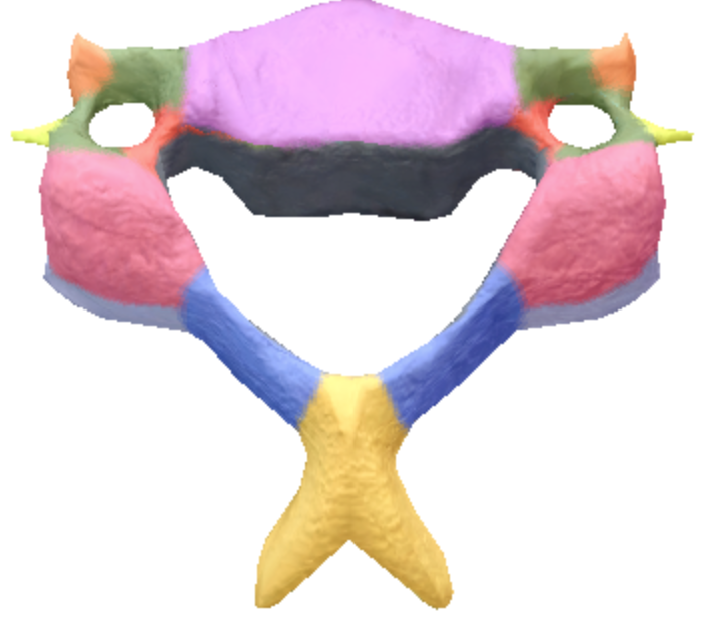
Where is the superior articular processes and facets on the cervical spine vertebrae?
Pink
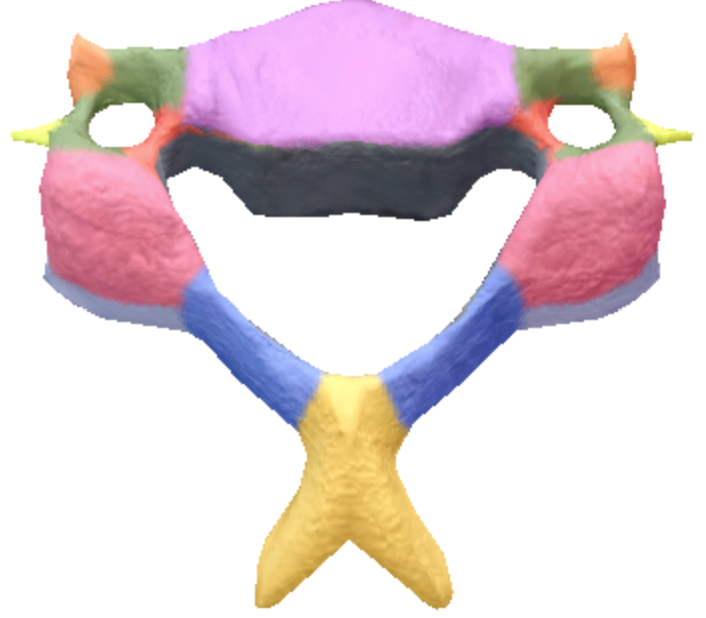
Where are the inferior articular processes located on the cervical spine vertebrae?
Gray
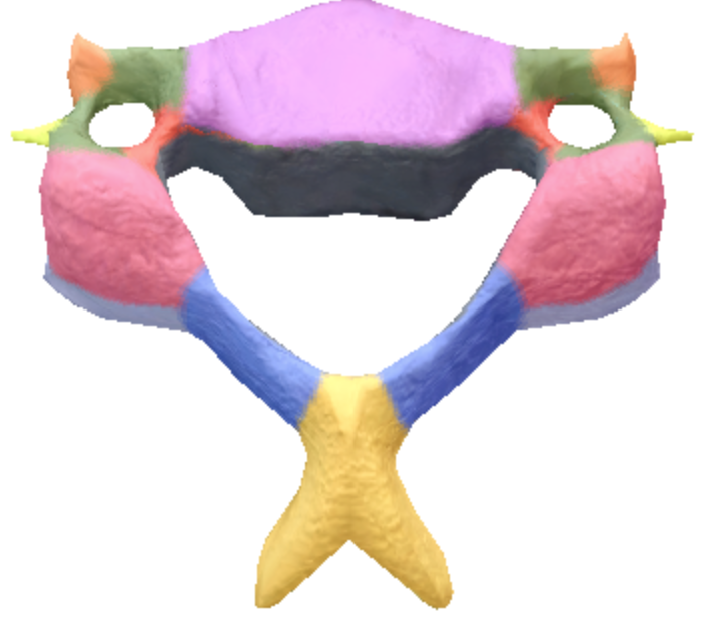
Where is the Bifid Spinous process in the cervical spine vertebrae?
Yellow
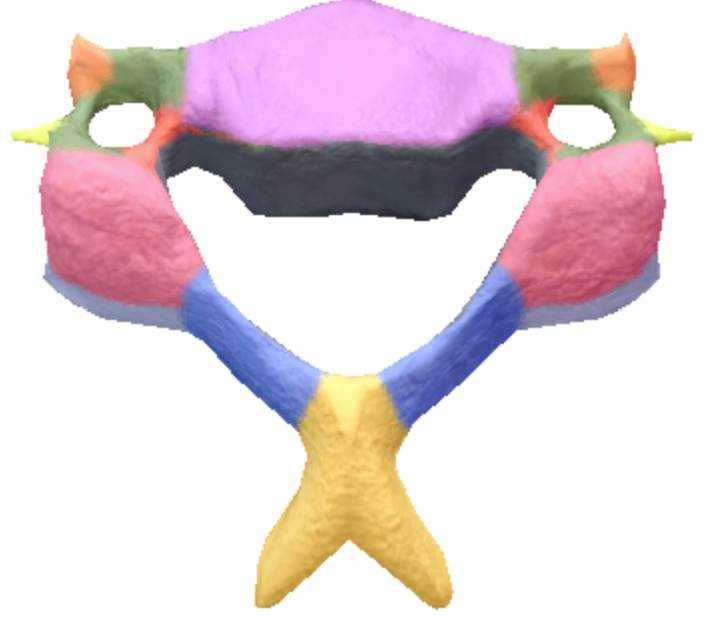
Where is the transverse processes and Foramina in the cervical spine vertebrae?
Green
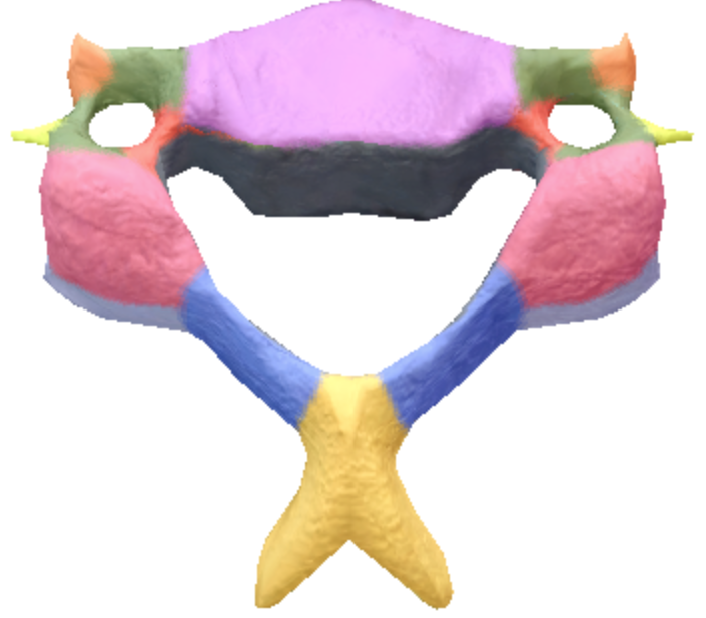
Where is the vertebral foramen in the cervical spine vertebrae?
Black
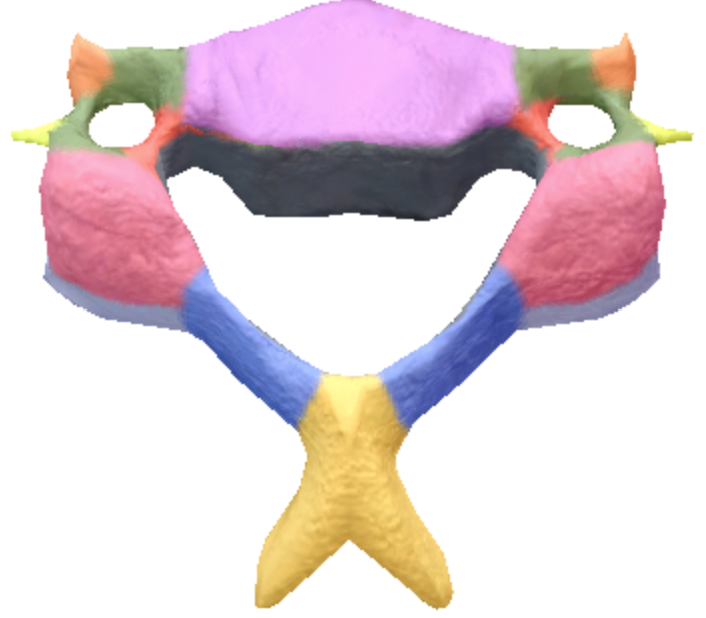
Where is the laminae located in the cervical spine vertebrae?
Blue
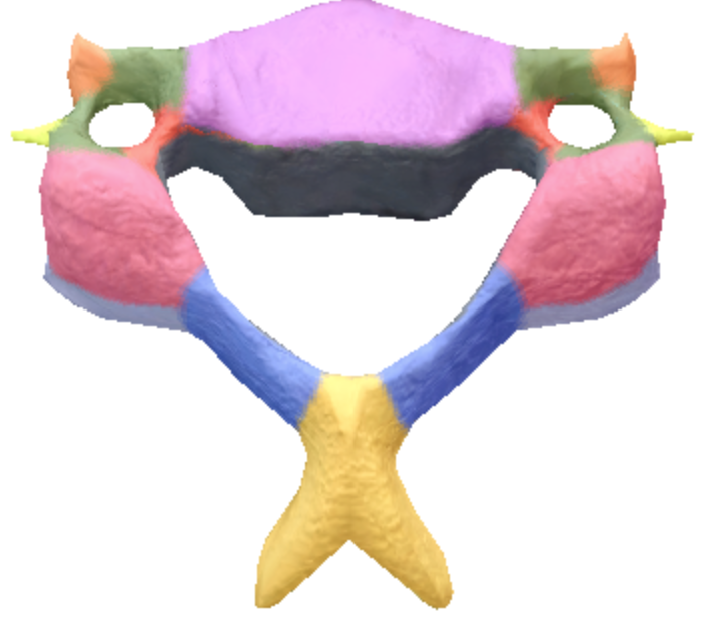
where are the pedicles located on the cervical spine vertebrae?
Red
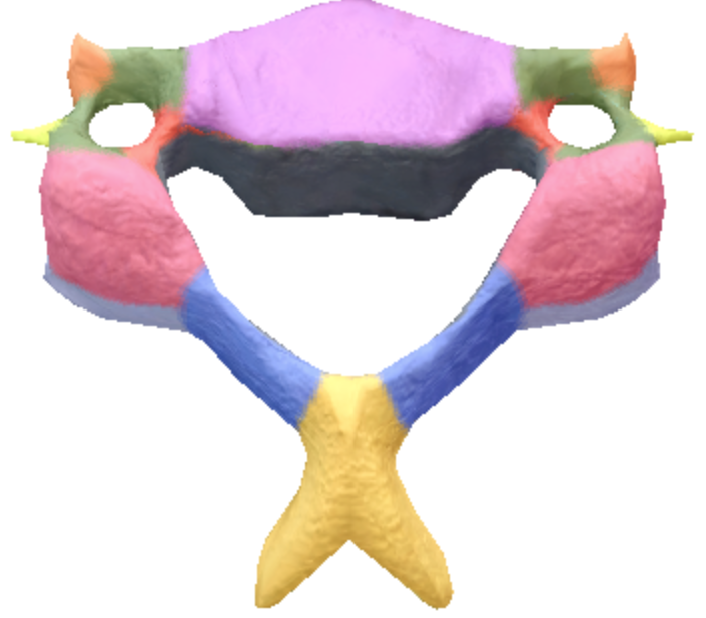
Where is the anterior tubercules of transverse processes located on the cervical spine vertebrae?
Orange
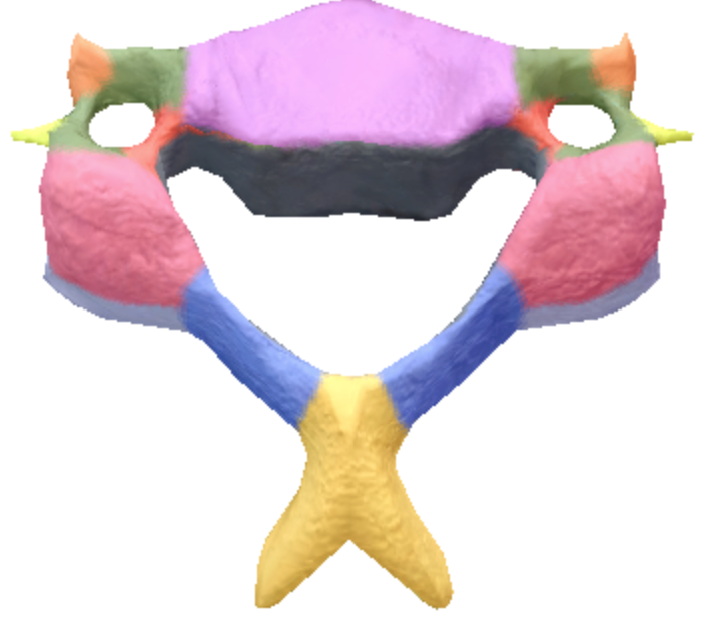
Where is the posterior tubercles of transverse processes located on the cervical spine vertebrae?
Light Yellow
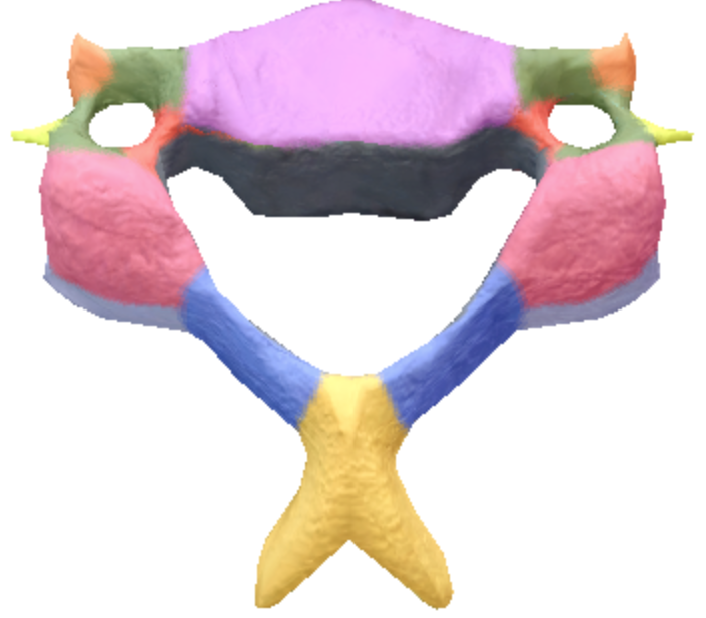
Where is the body of the cervical spine vertebrae located?
Purple
Thoracic spine
the middle section of the human spine, consisting of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12) connecting the neck (cervical) to the lower back (lumbar).
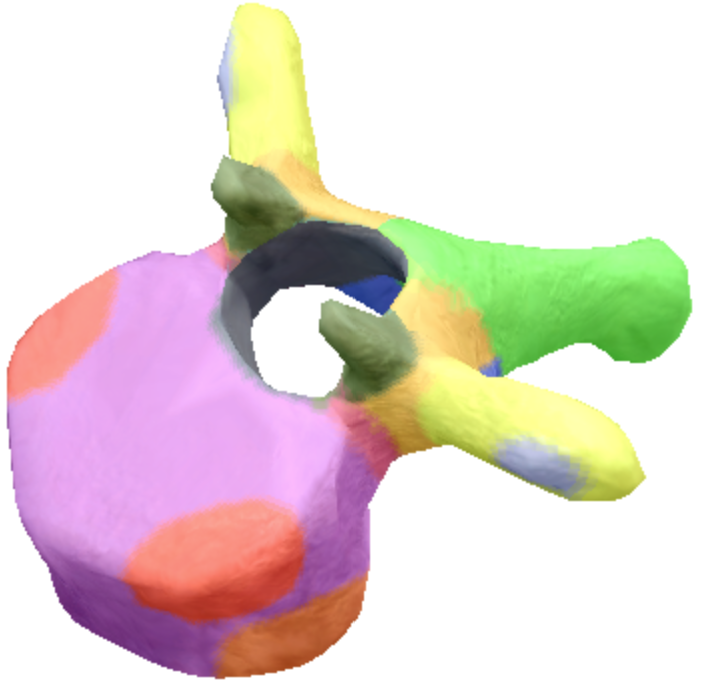
Where is the Spinous process of the thoracic spine vertebrae located?
Green
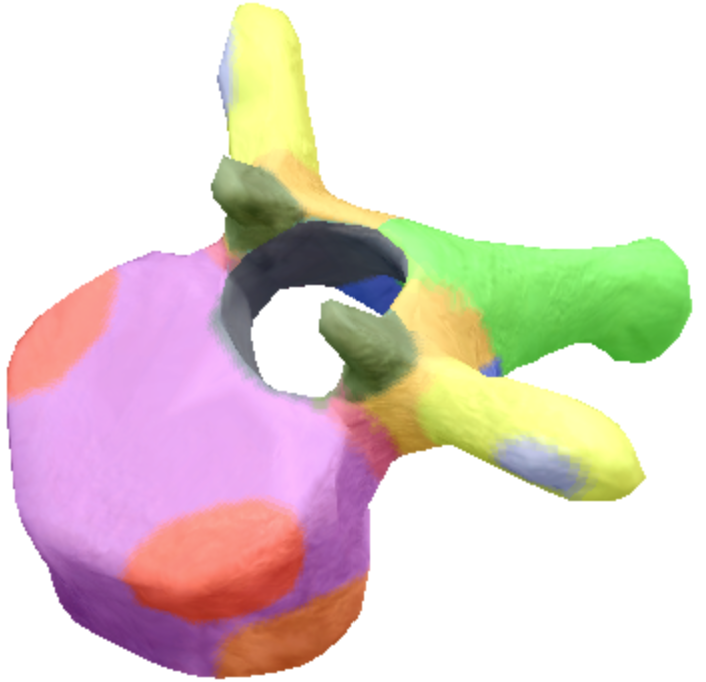
Where are the transverse processes located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
yellow
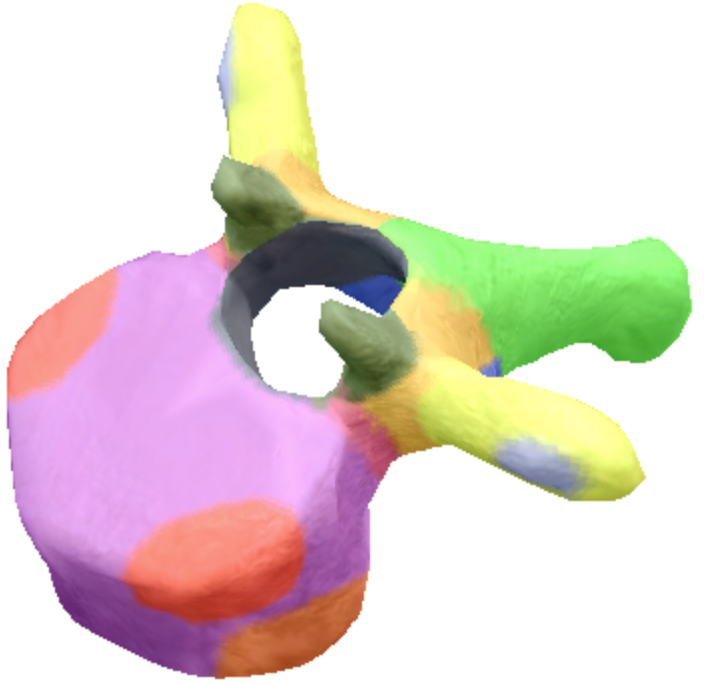
Where is the transverse coastal facet located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
Gray
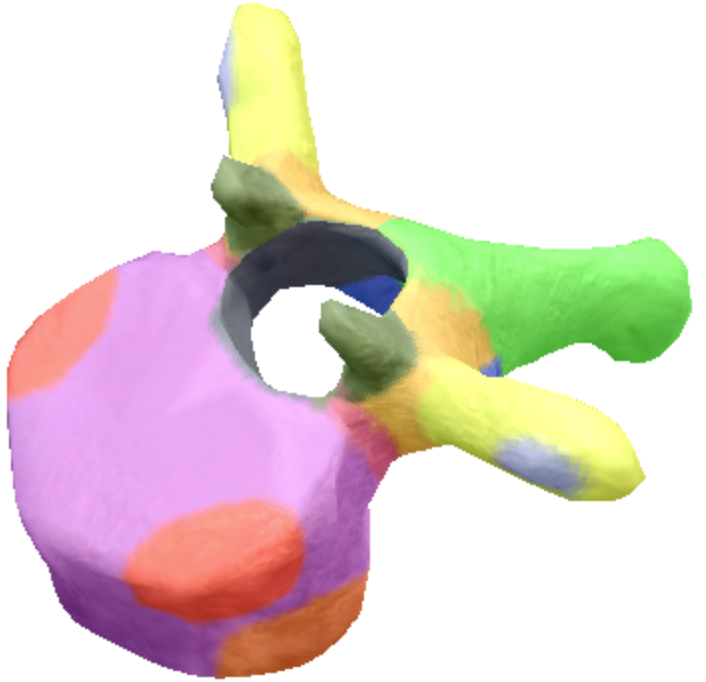
Where are the superior coastal facets located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
Red
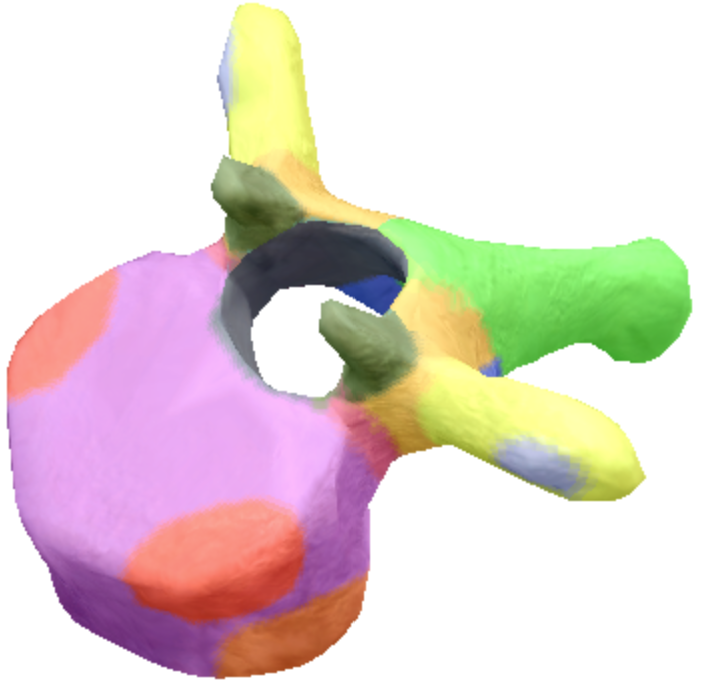
Where is the body located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
Purple
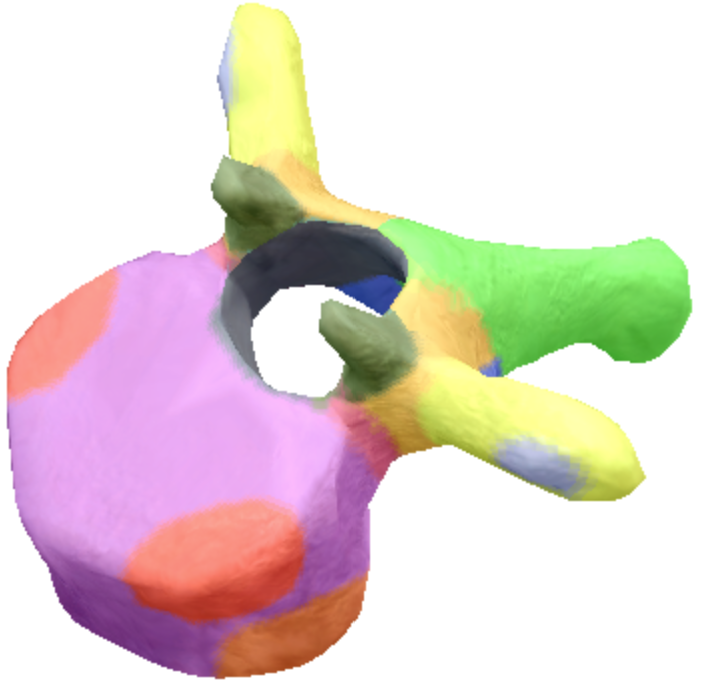
Where is the inferior notch on a thoracic spine vertebra located?
Brown
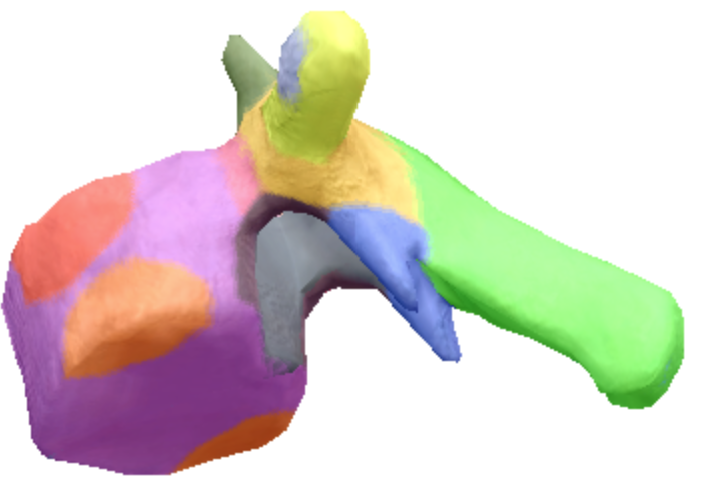
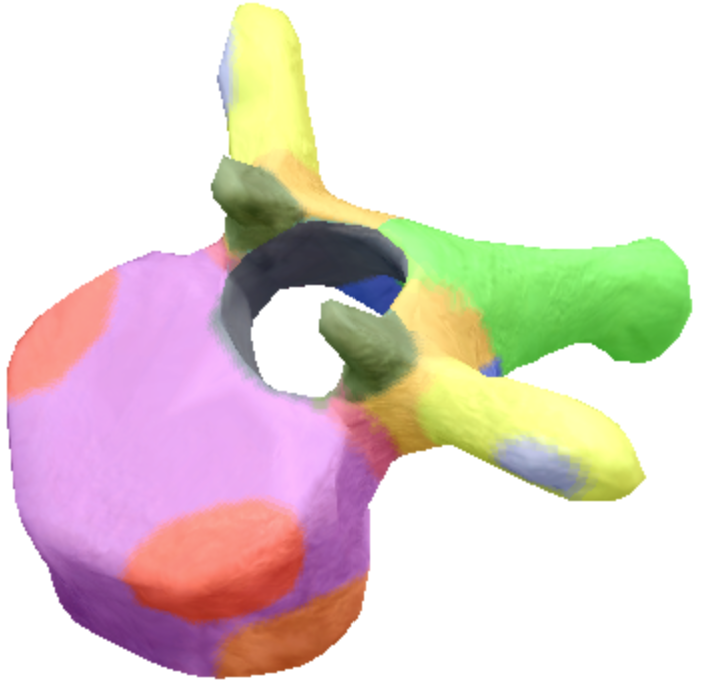
where are the inferior coastal facets located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
Dark orange
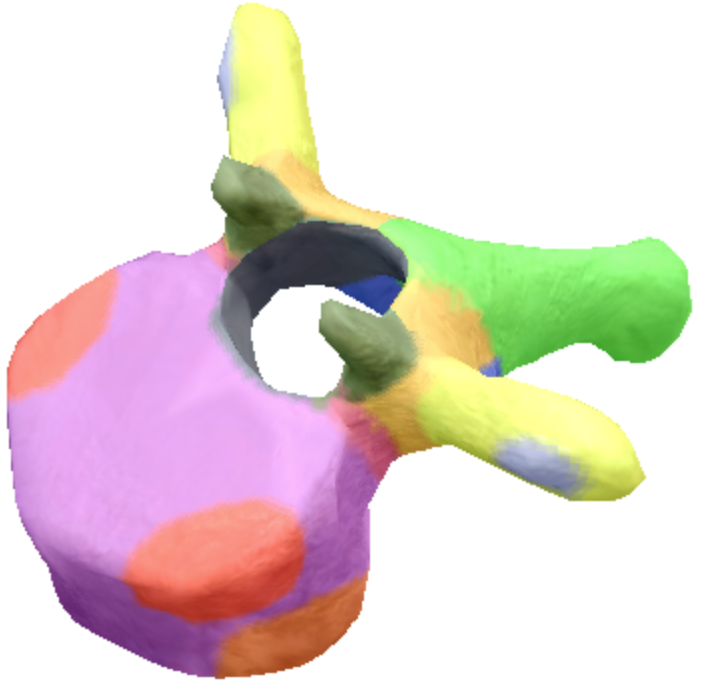
where is the vertebral foreman located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
Black
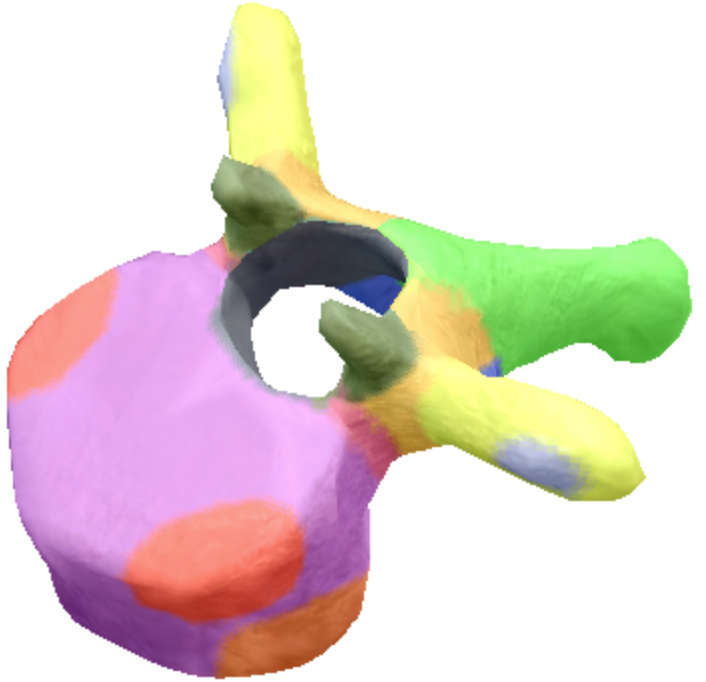
Where are these superior articular processes and facets located on these thoracic spine vertebra?
Dark green
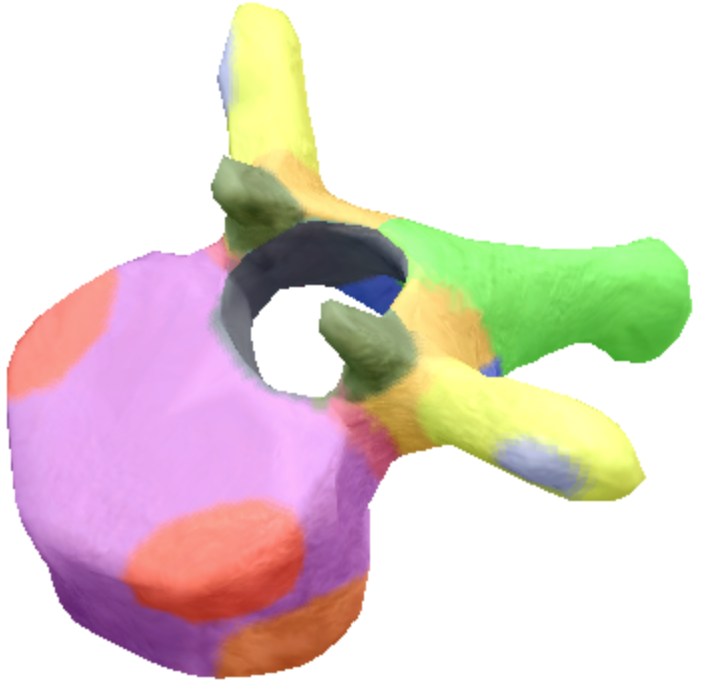
Where is the pedicle located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
pink
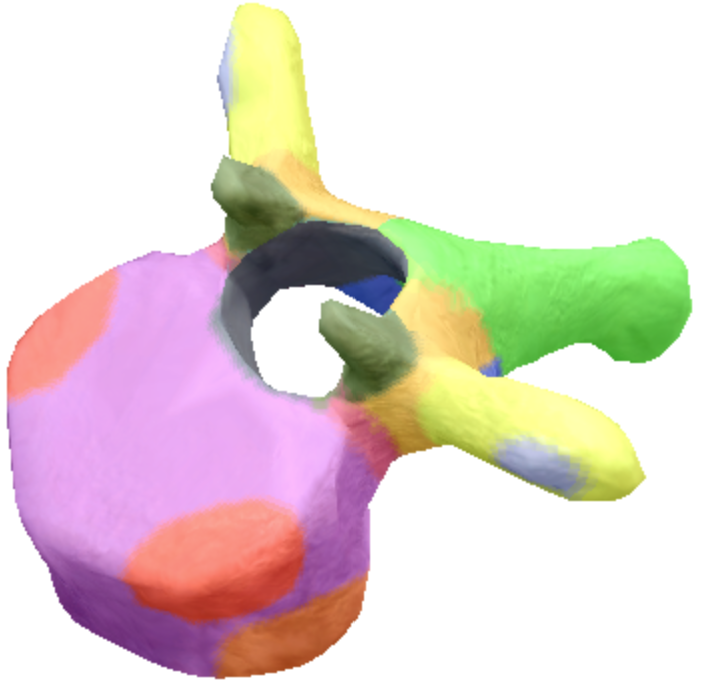
Where is the Laminae located on the thoracic spine vertebra?
Orange
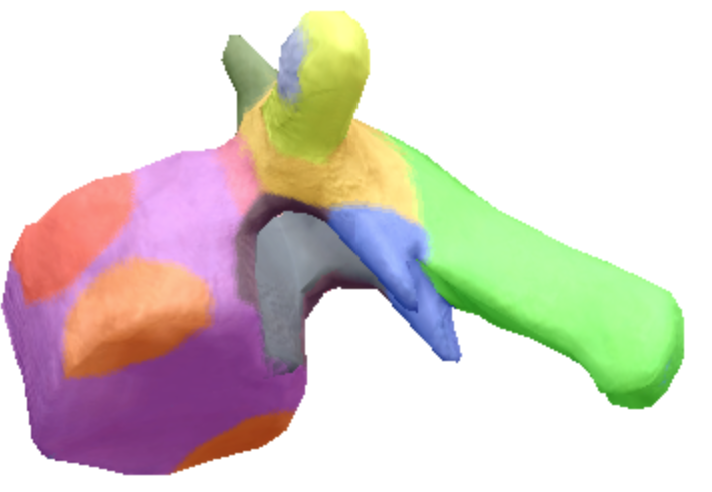
Where is the inferior articular processes facets located in the thoracic spine vertebra?
Blue
Lumbar spine
the lower portion of the spinal column, located between the thoracic spine and the sacrum. It consists of five vertebrae (L1-L5) that support the weight of the upper body and allow for movement in the lower back.
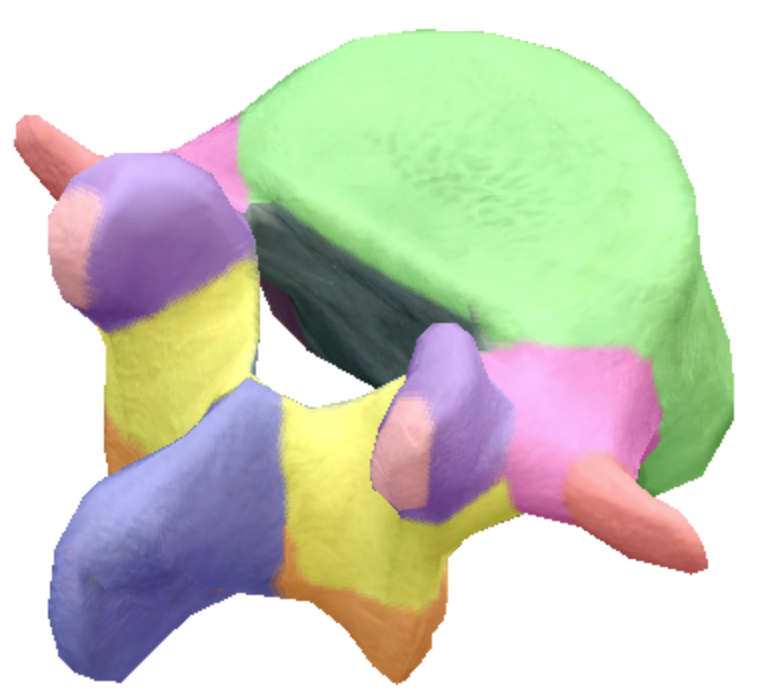
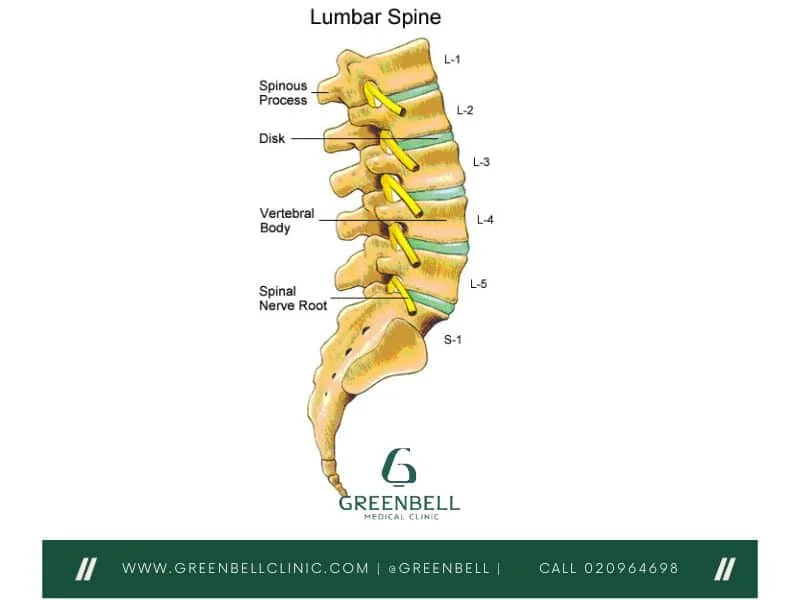

Where is the vertebral foreman on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Gray
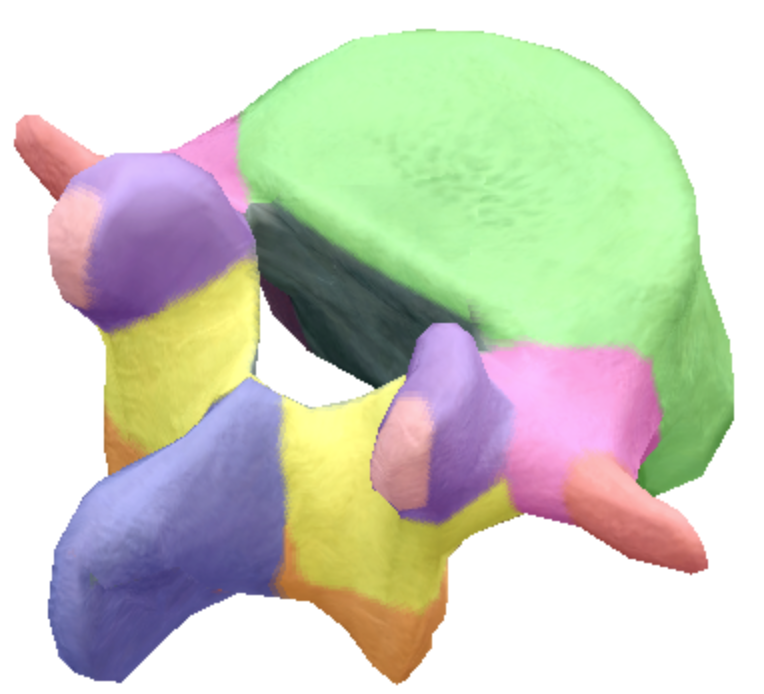

where is the spinous process located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Dark purple
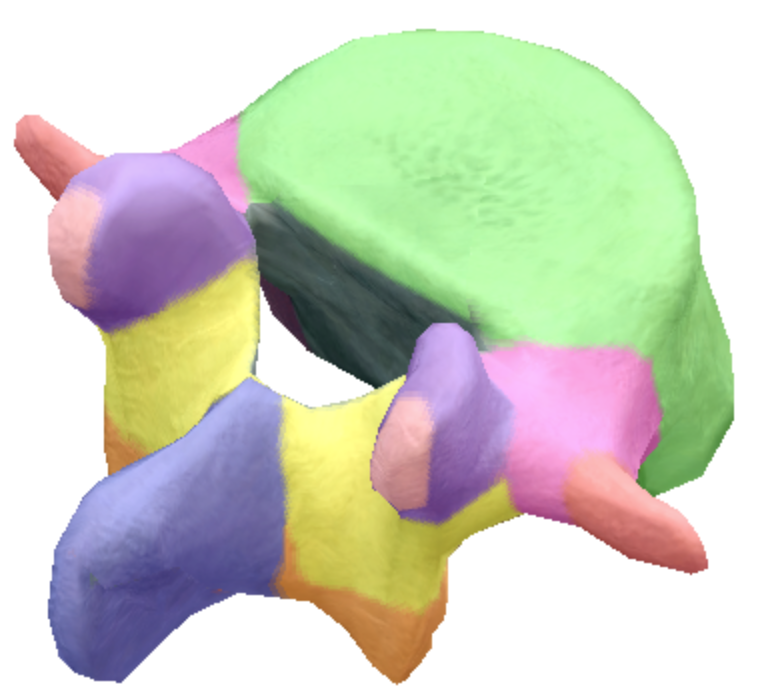

Where are the transverse processes located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Red
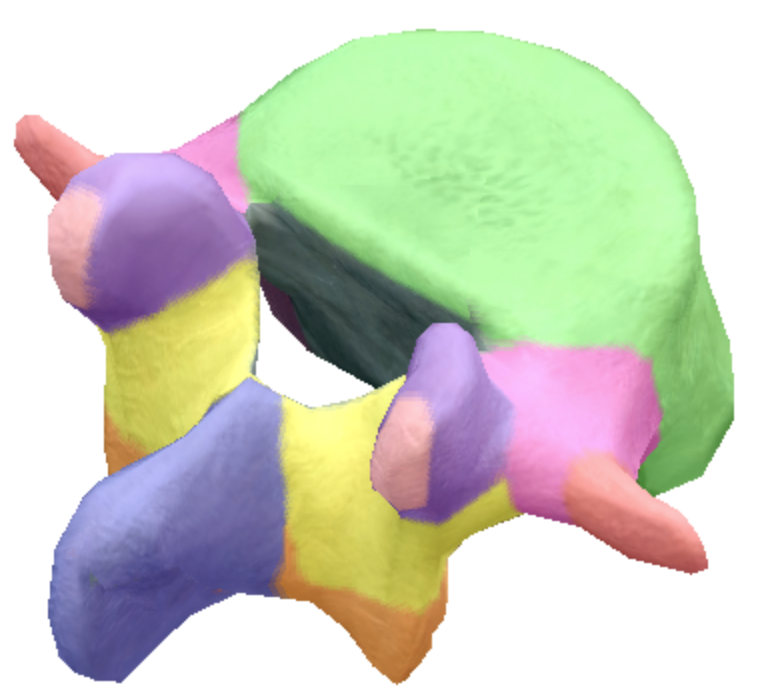

Where is the body located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Green
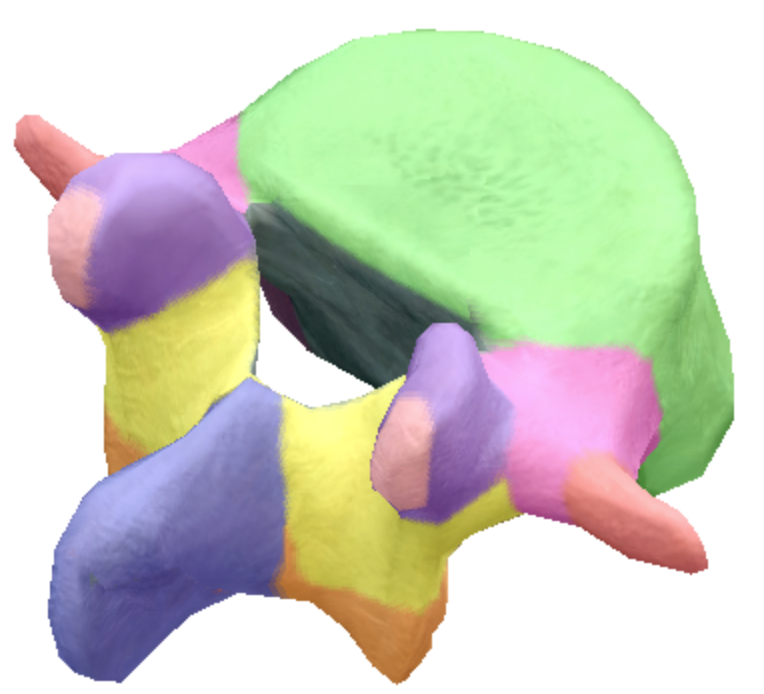

Where is the superior articular processes and facets located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Light purple
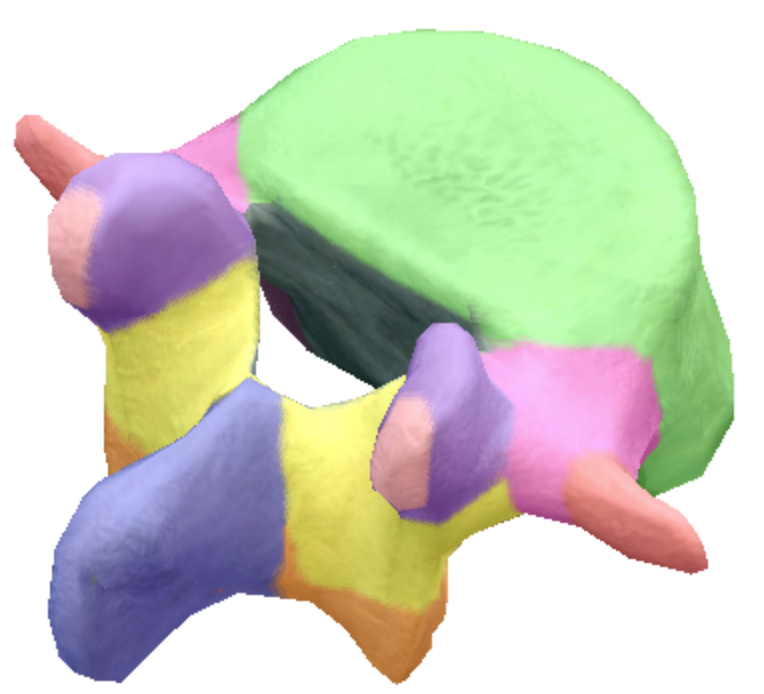

Where are the inferior articular processes and facets located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
orange
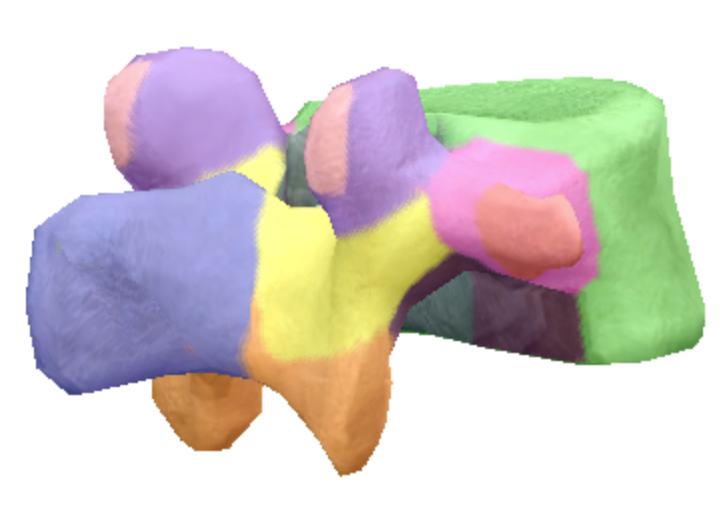

Where is the inferior notch located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Brown arch
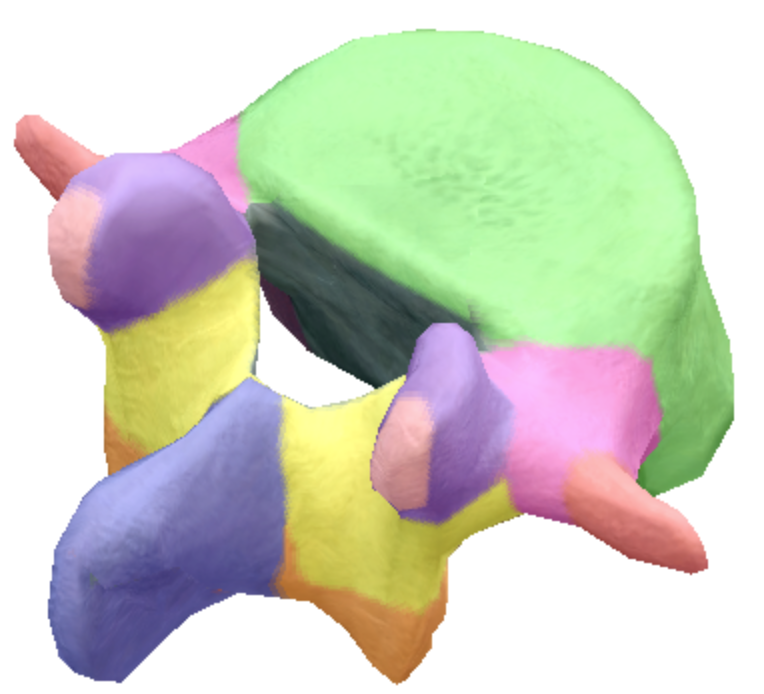

What are the pedicles located on the lumbar spine vertebra?
Pink