PRD 132: Crown Prep on Anterior Tooth (lithium Disilicate
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Ceramic
Zirconium oxide is a
Silicate (glass)
Lithium disilicate and zirconia reinforced silicate ceramics
Glass ceramic
Lithium disilicate is a type of
Layered/monolithic; pressed/milled
Lithium disiliciate can be ___ or __
Aesthetics
We mostly use lithium disilicate for
Aluminum oxide
Minimized chemical solubility
Potassium oxide
Lowers the viscosisty
Phosphorus pentoxide
nucleating agent and helps bulk crystallizing process
Zirconium oxide
Nucleating agent and helps promoting surface crystallization
Zinc oxide
Improves chemical stability, optical translucency
Magnesium oxide
Increases the viscosity of glass matrix
Pigments/color fluorescence
For aesthetics
Veneers
We use lithium disilicate for ___ (thin 0.4 mm and conventional)
Partial crowns
We use lithium disilicate for ___ (inlays, onlays, overlays)
Single crowns
We use lithium disilicate for ___ IN ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR AREAS
Three unit bridges
We use lithium disilicate for __ IN THE ANTERIOR AND PREMOLAR AREAS
DEEP SUBGINGIVAL PREPARATION
A major contraindication for lithium disilicate is (prep)
Four unit bridges
A major contraindication for lithium disilicate is (too much to support)
Missing teeth
A major contraindication for lithium disilicate is PATIENTS WITH SEVERELY REDUCED RESIDUAL DENTITION
Bruxium
A major contraindication for lithium disilicate is (teeth grinding)
Conventional/digital
An advantage of lithium disilicate is that you can take __ impressions
Aesthetics
An advantage of lithium disilicate is that it has high ___ to natural tooth
Same day
An advantage of lithium disilicate is that you can do Chair-side CAD/CAM production process
indications
An advantage of lithium disilicate is that it has Wide range of __ from thin veneers to three-unit
bridges
Biocompatibility
An advantage of lithium disilicate is that it has __, less plaque accumulation
Intraorally
An advantage of lithium disilicate is that it can be __ repaired in case of chipping
bonding
A disadvantage of lithium disilicate is that it has to be cemented by __ (technique sensitive) advantage of lithium disilicate is that
Thermal processing
A disadvantage of lithium disilicate is that __ can influence the strength of LD
restorations.
Brittle
A disadvantage of lithium disilicate is that it has Intrinsic __ behavior.
literature
A disadvantage of lithium disilicate is that there is a distinct lack of __ discussing long-term survival
and outcomes for the material.
Monolithic Zirconia or FVC
Lithium disilicate is Less bright than
__ (metal alloy)
Ingots, blocks
What are two types of lithium disilicate
Pressed
___ LD is Produced according to a unique bulk casting
production process to create the ingots
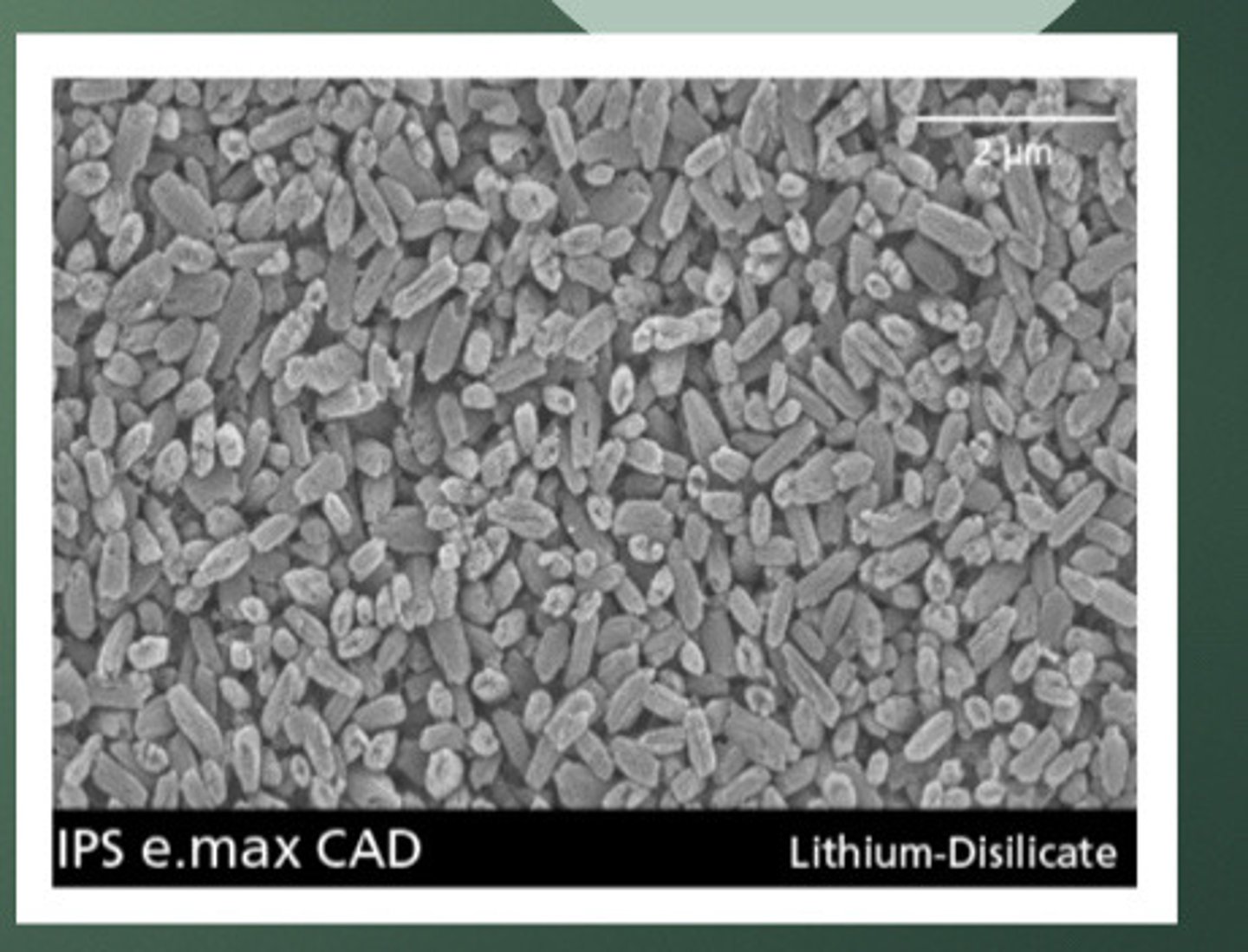
E max press
Ivoclar vivident ingots
E max CAD
Ivoclar vivadent blocks

Pressed ingots
The ___ LD is more fracture resistant
70%
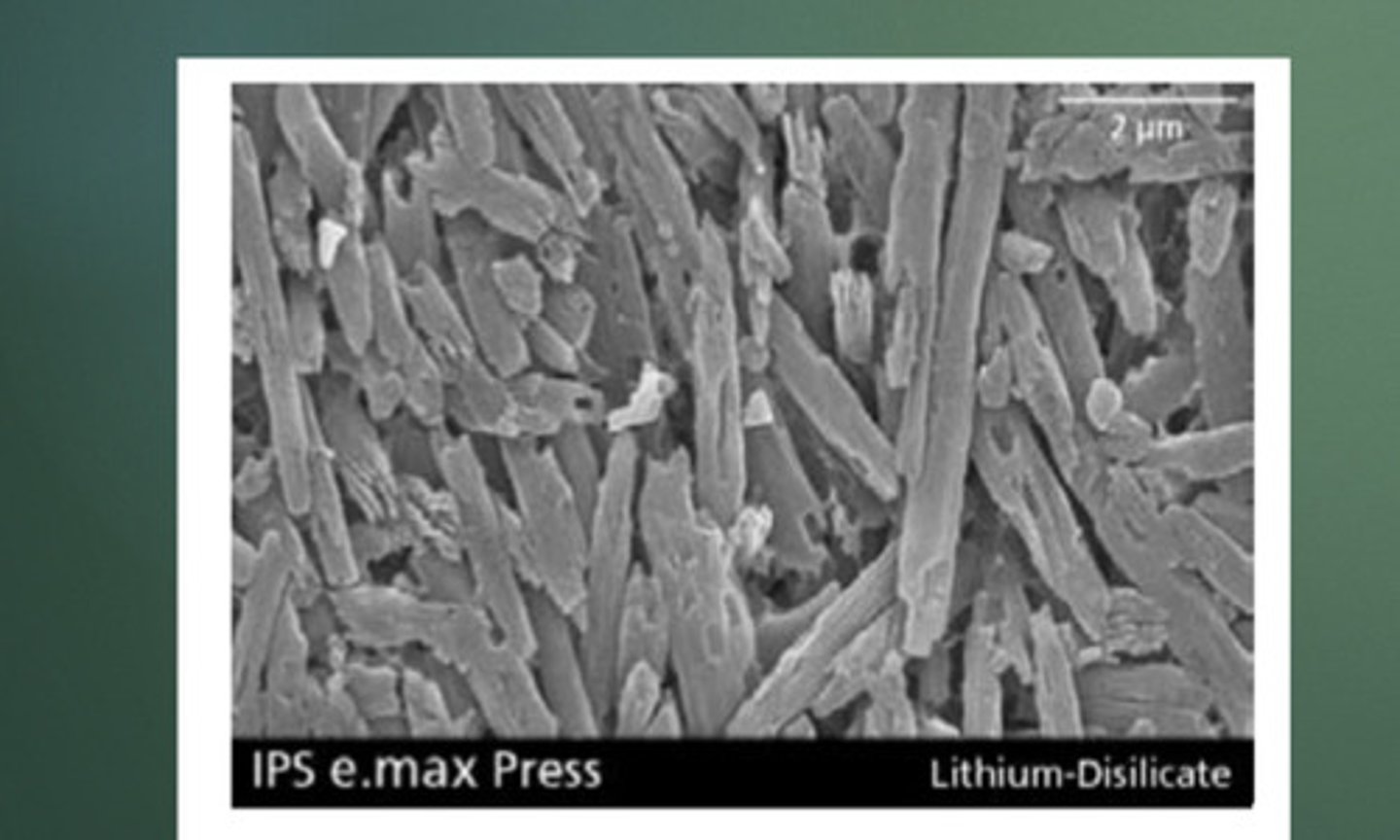
The pressed ingot LD Microstructure consists of approximately __ needle production process to create the ingots like lithium disilicate crystals embedded in a glass matrix, approx 3-6 microns in length
3-6 microns
The pressed ingot LD Microstructure consists of approximately 70% needle production process to create the ingots like lithium disilicate crystals embedded in a glass matrix, approx __ in length
lost-wax hot-pressing
Pressed ingots Utilizes in __ technique in which lithium metasilicate in ingots are converted to lithium disilicate.
70%
Pressed ingots is pressed into the mold at approximately 850 degree Celsius for 20-25 minutes to form __ volume of crystalline lithium disilicate
lab
Heat-pressed technique must be done in the ___ and, requires higher manufacturing time and technical skills
Milled LD
Require intermediate (partial) crystallization to ensure blocks can be milled efficiently in an intermediate blue phase
lithium metasilicate
In milled LD, the intermediate process leads to formation of __ crystals.
40%
The lithium metasilicate crystals are __ platelet shaped lithium metasilicate crystals embedded in glass, range from 0.2-1 micron. Flexural strength is ~ 130Mpa
70%
Post crystallization (after firing) milled LD microstructure consists of __ fine grained lithium disilicate crystals embedded in a glass matrix
CAD-CAM technology
In milled technique, The __ charge-coupled camera device is used for making
3D impression of the tooth and crown is designed.
milled
Based on this digital information, block is __ to form a restoration
40%
Non-fired blue blocks consist of about __ vol % crystals embedded in a glass matrix (mostly lithium metasilicate, small amount of lithium orthophosphate, and lithium disilicate)
technically efficient
Machine milled more __ and can be done in a single appointment.
Milled/pressed
Like LD, Bilithic Zirconia (Porcelain fused to Zirconia) could
Be
milled; pressed
For Bilithic Zirconia, the zirconia substrate will be __
first, then the Porcelain or LD part will be __ over it.
2
Second the putty into __ halves not 1/3s
1mm
Cervical reduction
1-1.2mm
Fossa reduction
1-1.5mm
Facial reduction
1.5-2mm
Incisal reduction
Football bur
Use on lingual surface
Two planes
The facial reduction you must follow the
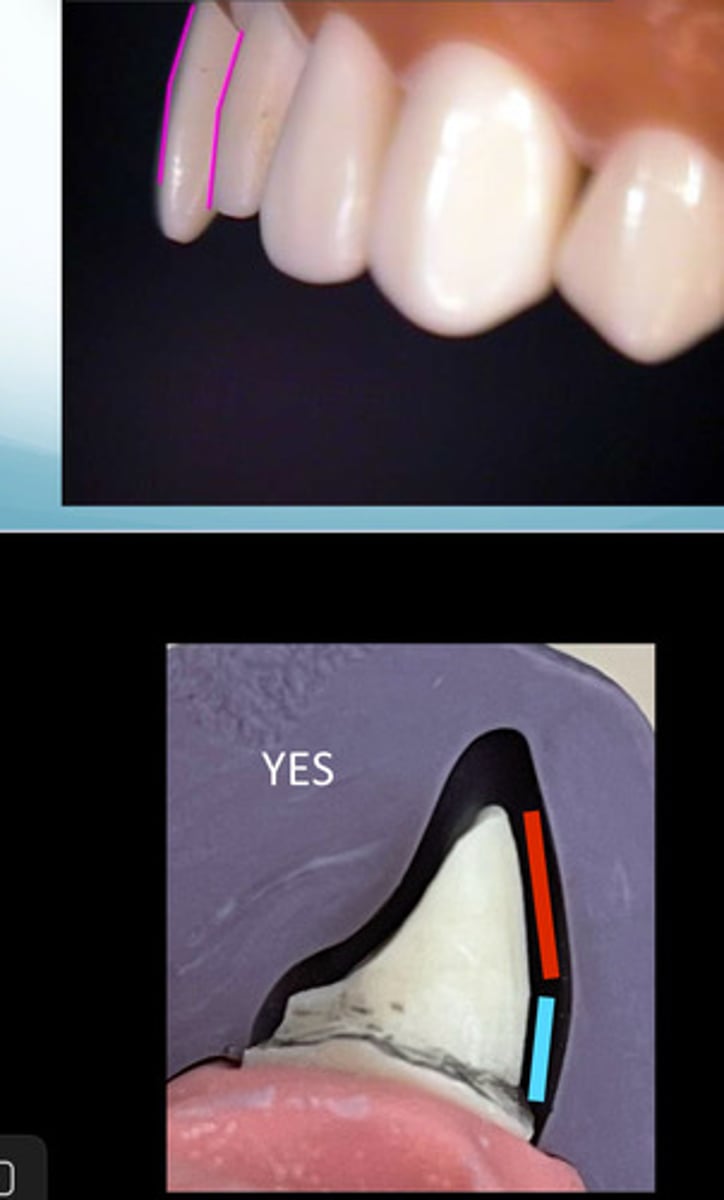
Path of insertion
the direction in which the RPD is inserted & removed from the abutment teeth (cervical follows)
3-5 degree
There should be a ___ taper
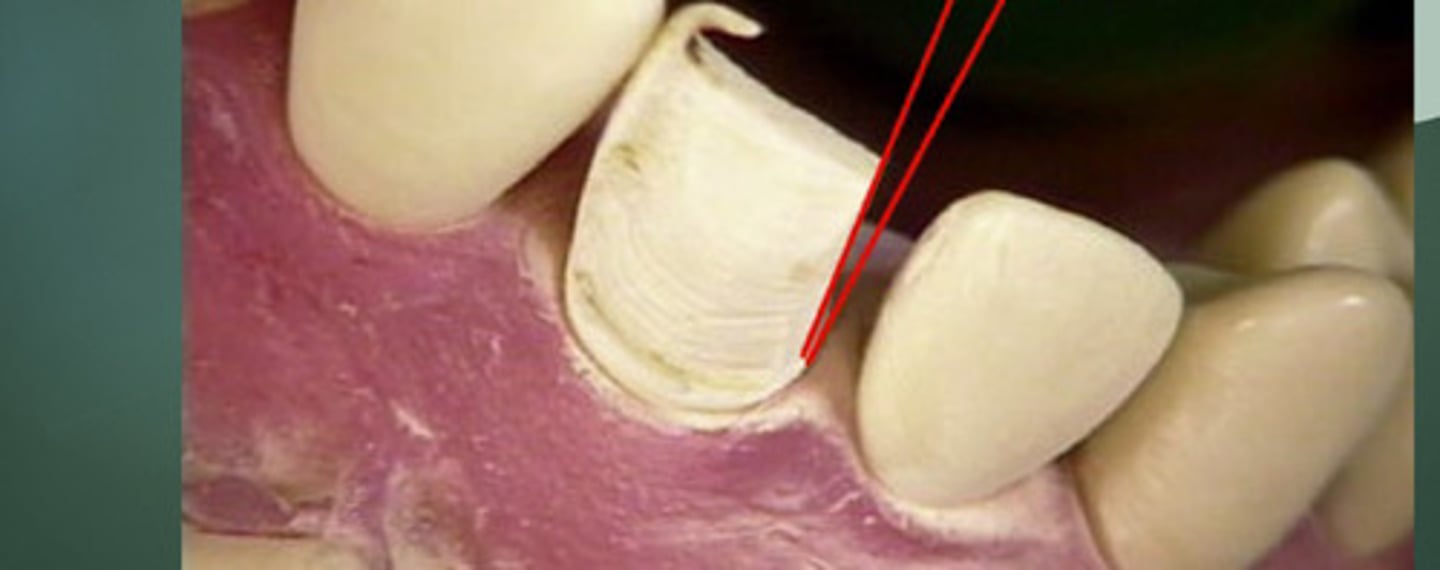
Dental ferrule
A band (of tooth structure) that encircles the external dimension of tooth structure
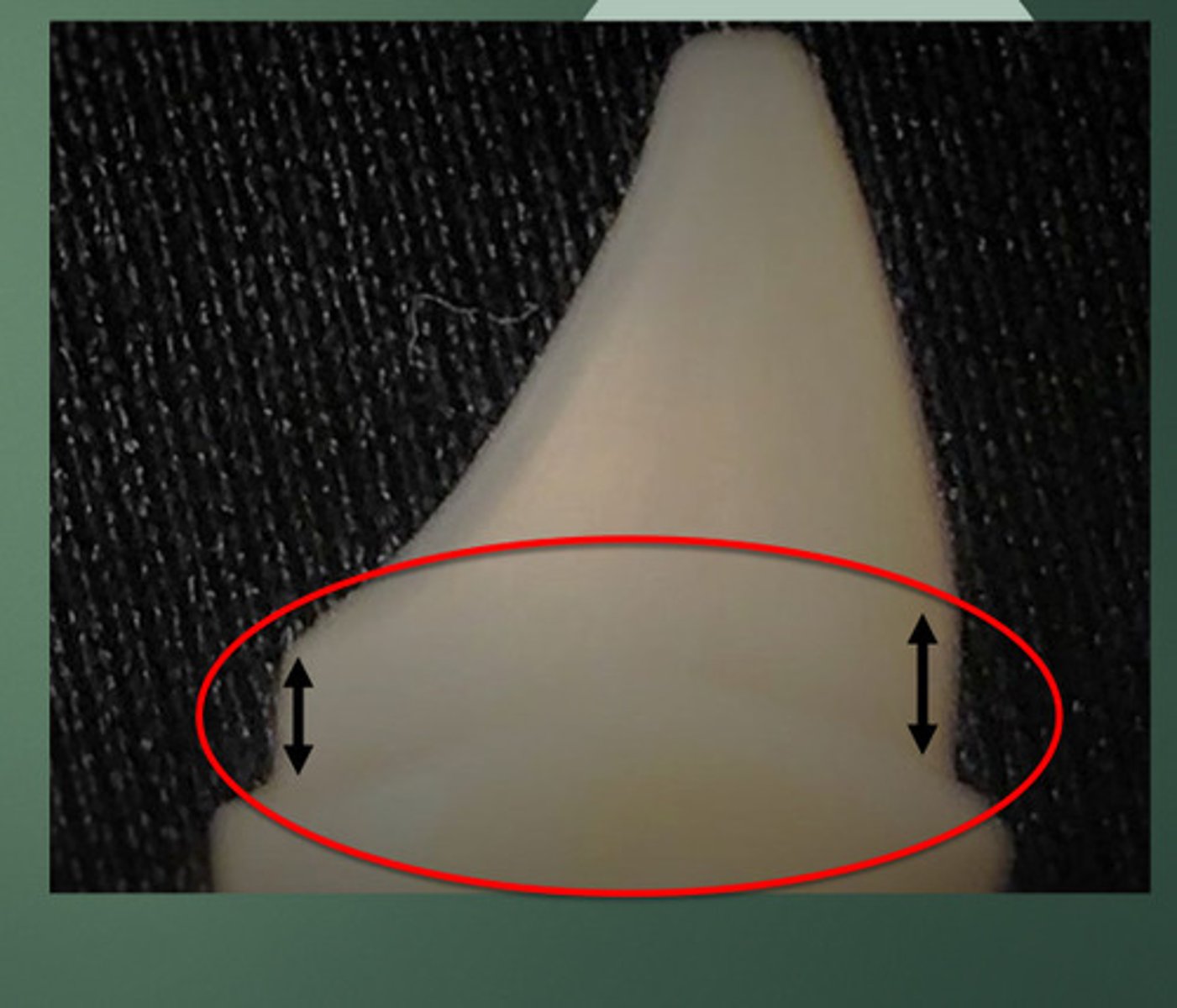
fracture
Ferrule Provides __ resistance
(more about that with endo)
retention
Ferrule Provides adequate __ and
resistance for the indirect
restoration
external
Ferrule Distributes __ forces evenly
2-3mm
Ideally, Maintain a height of_____ on the lingual wall (1.5-2 mm is ok)
Sharp edges
A common error are
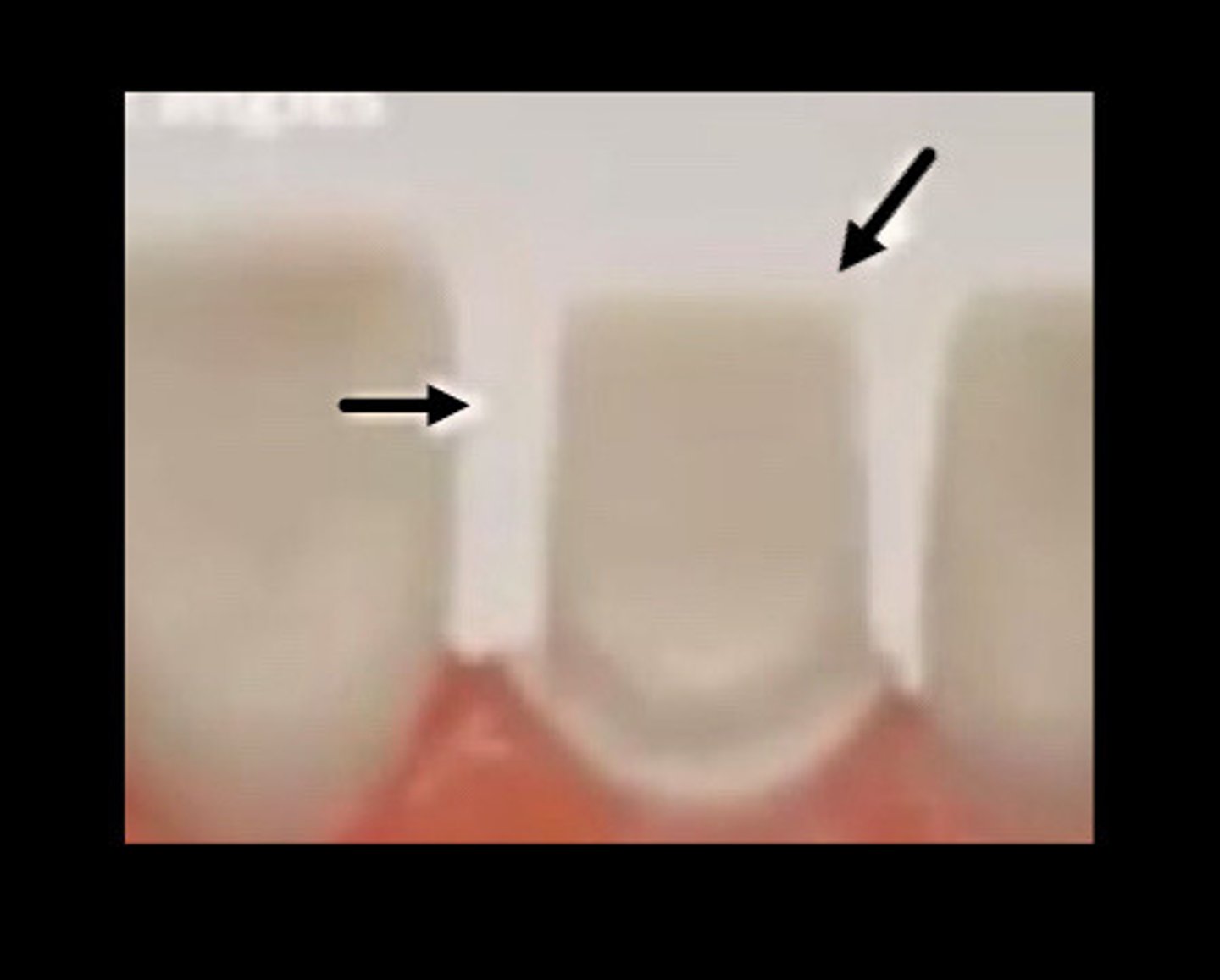
Undercut
A common error is
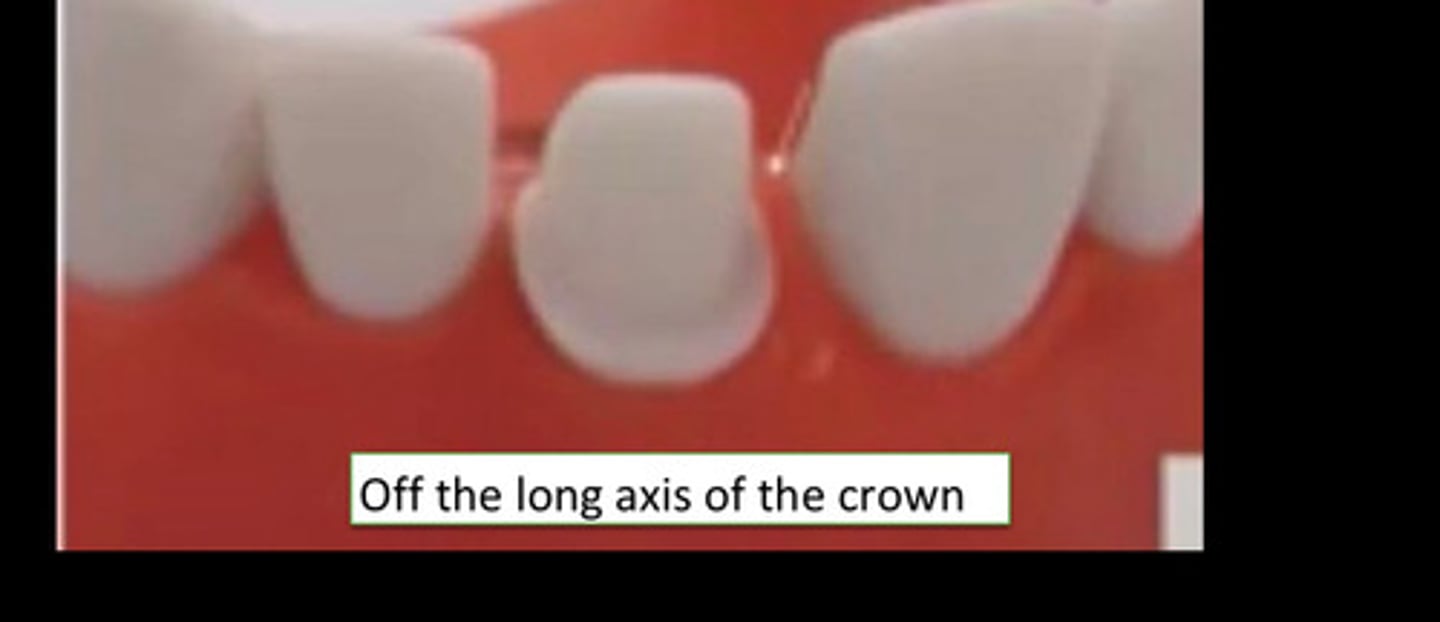
Overtaper
A common error is
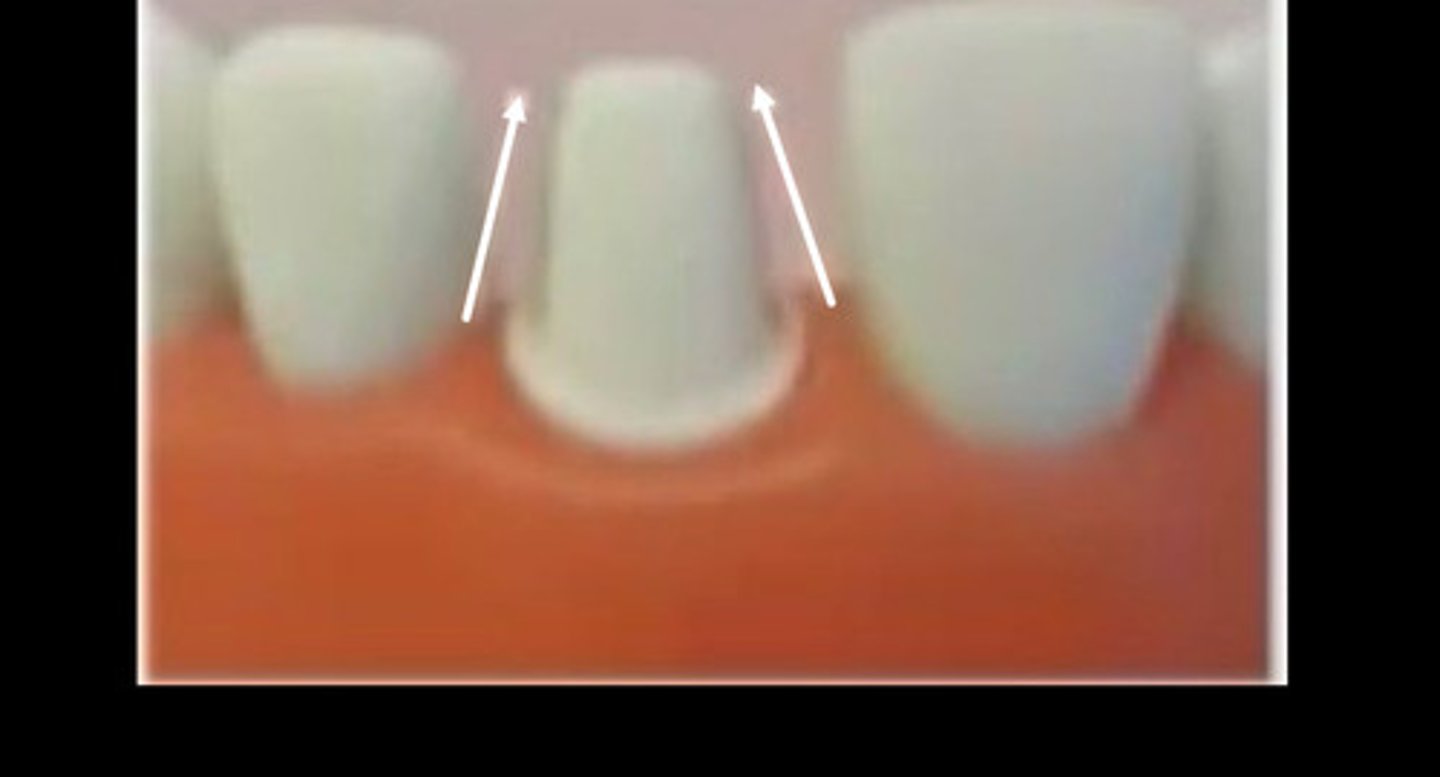
Under reduced
A common error is
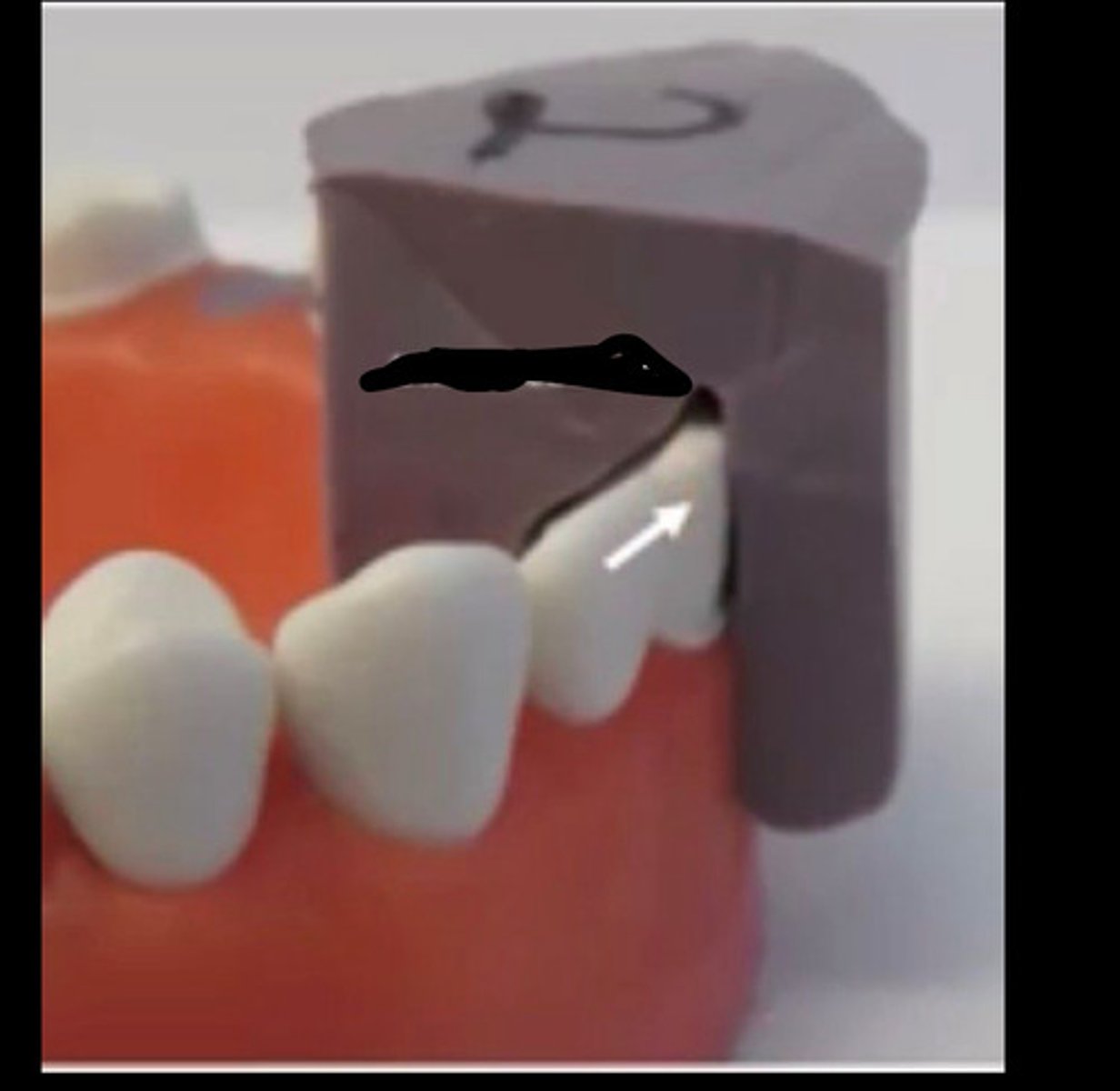
Over and under reduced
Black
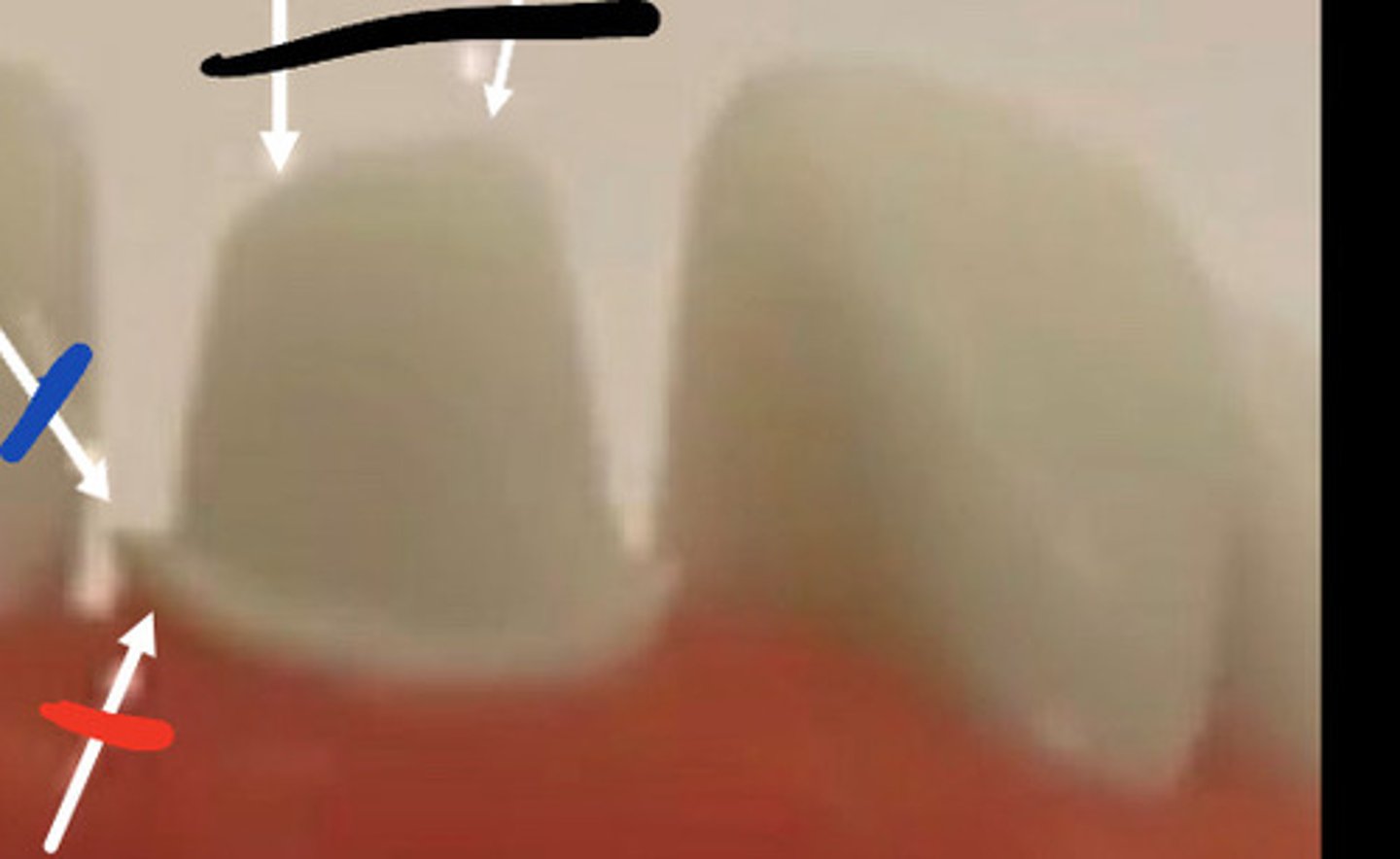
J lip
Blue
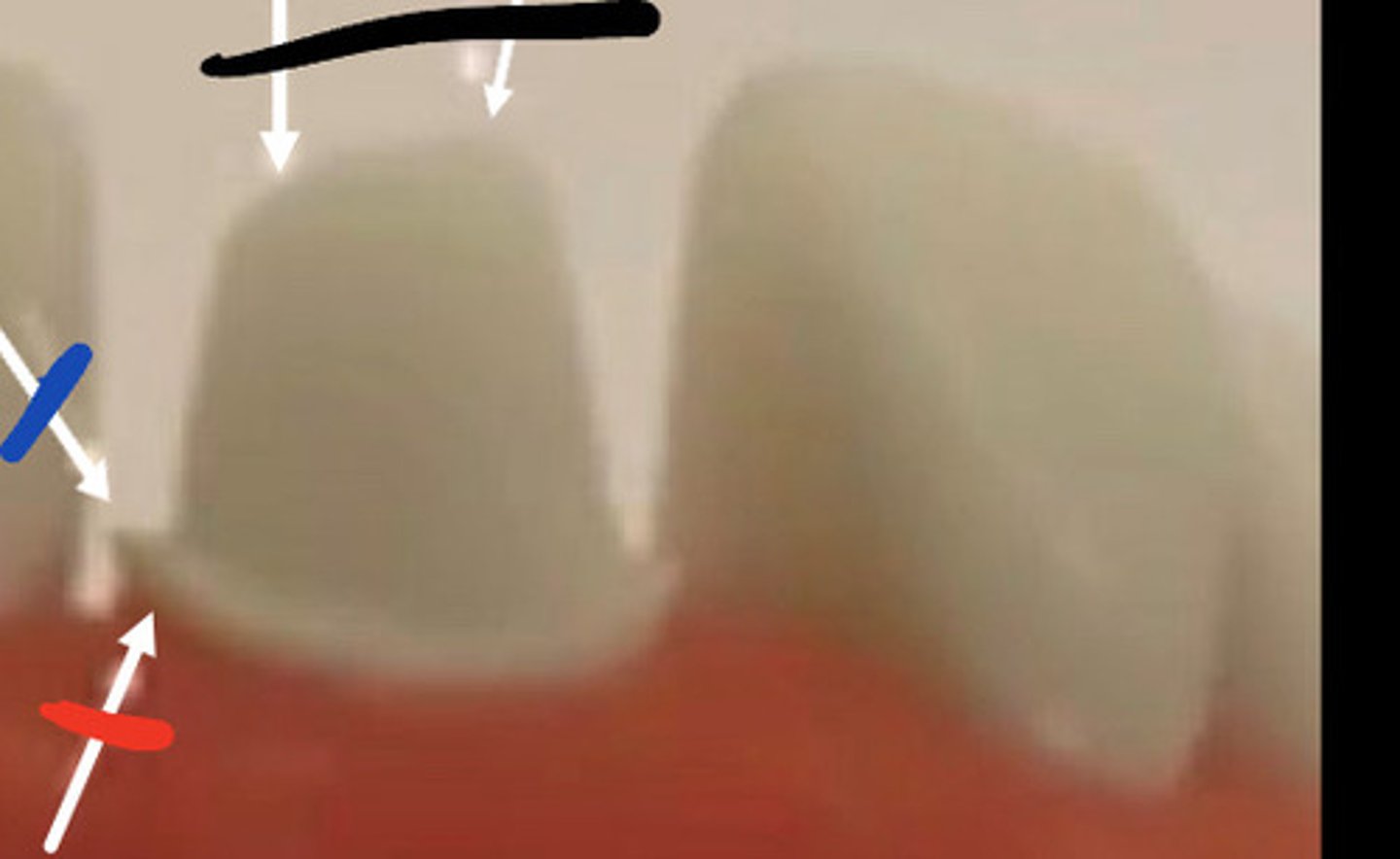
Margins more than 0.5mm above gum
Red
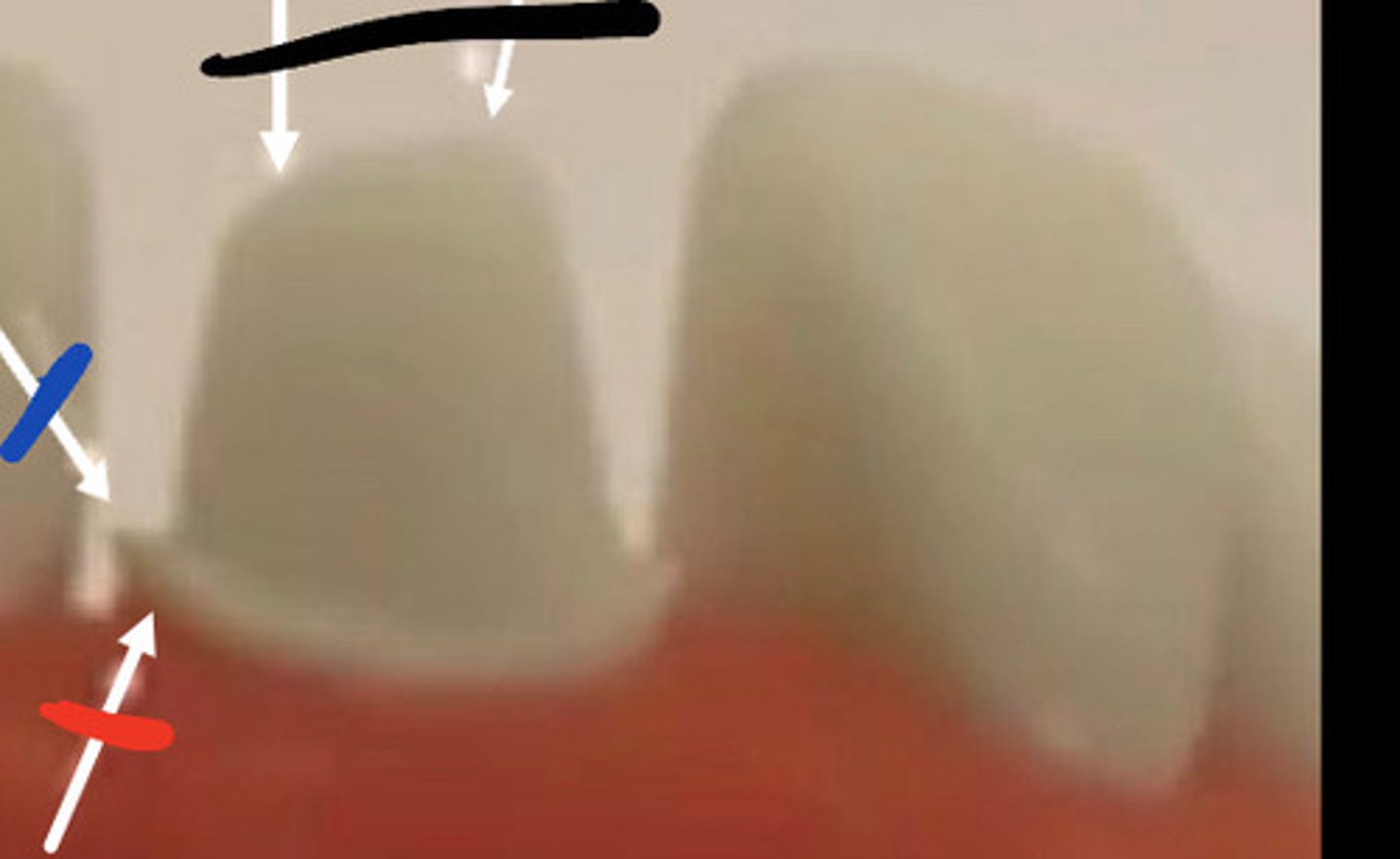
End cutting bur
Fix j lip with