Lecture (wk1 - wk2) SAQs
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Explain a scenario when you would expect to get an endowment effect and a scenario when you would not expect to get an endowment effect.
The endowment effect refers to the value that we have for the things that we own being more than the things we do not.
Scenario with Endowment Effect:
White elephant gift exchange and getting an ugly sweatshirt. Even though you would never buy the ugly sweatshirt voluntarily you give it more value now that you own it versus a scenario where you did not.
Scenario without Endowment Effect:
The endowment effect is avoided when evaluating an object at its proper price. For example, in lecture we discussed a study where a group of people were given token that they could trade with the experimenters for a certain amount of money. The group of people who could trade their tokens for only $1 with the experimenter were very much willing to give up their token for a dollar amount greater than $1. There is no endowment effect in this scenario considering how easily they were willing to give up an item they owned.
what about prospect theory allows it to explain the endowment effect?
The endowment effect refers to people’s inclination to over value object they own more than they would have if they did not own said object. The interesting thing about prospect theory is how it explains people feeling the pain of a loss much more strongly than the pleasure of an equivalent gain. The reason this explain the endowment effect is because if people feel the pain of losses much greater than gains they would be less willing to give up something they own because it require one experiencing loss.
what is likely to affect the elasticity of supply and demand?
For demand:
Willingness to buy product
how essential it is for someone’s life (ex. healthcare) makes it a necessity to buy regardless of the price resulting in inelasticity
Proportion of one’s budget
(ex. rent / mortgage) take up a large proportion of one’s budget so if the price reaches a certain point, people will get priced out and forced to move leading to an increased elasticity
For supply:
Availability of supply
very limited supply (ex. original picasso paintings) leads to increased inelasticity
why can expectations about future prices be self-fulfilling prophecy?
if enough people believe a price will rise, they may act on that belief by buying now, which can actually drive the price up, thus validating their initial expectation and creating a cycle where more people then buy, further increasing the price
why is the demand curve downward sloping and the supply curve upward sloping?
Explanation of Demand Curve
The demand curve represents the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded for said good. When the price is high there is less of that item that is demanded by the people. When the price is low, more of that item is demanded by the people. When plotted on a graph, the relationship is shown to be downward sloping.
Explanation of Supply Curve Upward
The supply curve represents the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied by the producer. When the price of the good is low, the producer is less willing to supply that item leading to a lower quantity. When the price of the good is high, the producer is more willing to supply higher quantities of that item. When plotted on a graph, the relationship is shown to be upward sloping.
what happened in the building bionicles study? what does it tell us about keeping workers motivated and productive?
Background:
Participants of the study were paid to build Bionicles. The amount paid per Bionicle decreased, the more Bionicles the participant assembled.
Two Groups:
Meaningful Condition: Completed Bionicles collected in box
Sisyphean Condition: Completed Bionicles disassembled in front of participants
Results:
Meaningful Condition: Average Amt Completed = 10.6
Sisyphean Condition: Average Amt Completed = 7.2
Explanation:
The reason less Bionicles were constructed in the Sisyphean condition was because people were less willing to continue given the fact that there work was being disassembled in front of them. This can lead one to conclude that workers’ motivation and productivity is directly tied to their ability to see the meaningfulness in their work. The study showed that even when presented with financial compensation people who loved Legos were not willing to continue if they felt like the work was meaningful.
How can PPC lead to the conclusion that specialization is good?
The PPC shows the possible productivity output of an individual’s ability to produce two different goods. It is usually used to highlight the opportunity cost for an individual to invest in the production of a specific product versus another one. The lower the opportunity cost shows an increase in losses meaning lower opportunity costs are better. Given this information, it has led people to the conclusion that people should specialize in the production of specific goods that they have the lowest opportunity cost for. In theory, this would generate the most productivity in the shortest amount of time.
Describe what happens in competitive market when there is excess supply or excess demand? Why is a situation with excess supply or demand not an equilibrium?
Excess Demand
In a competitive market experiencing excess demand, there exists a higher quantity demanded for a products, but not enough of that product to go around. The example shown in class was of price ceiling policies such as rent control. It was discussed that this would theoretically cause a decrease in the availability of supply since rent is more affordable and there aren’t enough housing available to fulfill the demand.
Excess Supply
In a competitive market experiencing excess demand, there exists a higher quantity of an item supplied than the demand calls for. The example used in class was of price floor policies such as minimum wage. In theory, this would lead suppliers (workers) to be experiencing unemployment.
Not in Equilibrium
Policies that set prices floors and price ceilings cause there to be a disruption. This makes it so that the competitive market is unable to reach an equilibrium between supply and demand due to policy factors that obstruct said equilibria. For example, rent control makes housing more affordable, however the quantity supplied is unable to keep up with the increased demand for the forced lowered pricing. This leads to a perpetual state of excess demand.
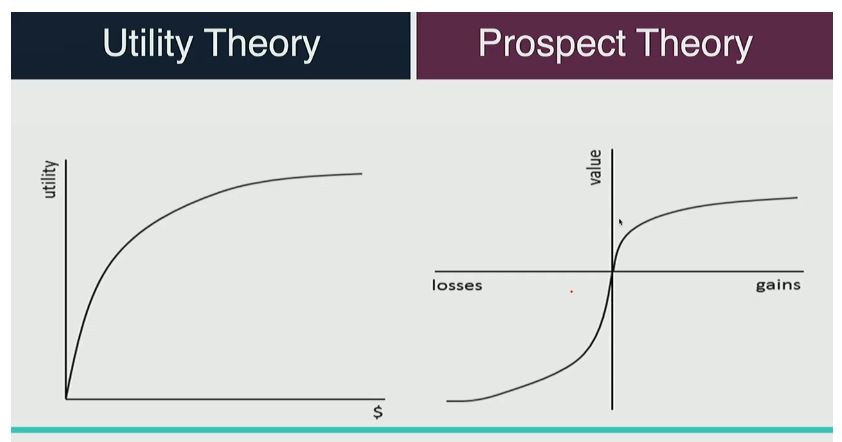
Compare and contrast utility theory and prospect theory.
Utility Theory
the marginal utility gained from consuming a product decreases the more you consume it. For example, marginal utility of consuming pizza slices decreases after every slice.
Prospect Theory
basically, utility theory plus a loss factor to consider
the marginal utility decreases from the loss of a product/thing/object. The decrease is greater than the increase, but the amount lost decreases over time.