PRAXIS 5621 (STUDENTS AS LEARNERS)
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
What may happen when a school cant provide FAPE?
The district is legally required under IDEA to refer the parent to a program and face all financial obligations associated with the placement.
The school must also provide transportation to and from the program at no cost to the family
the cost would not have been faced if the rural school had offered the program.
FAPE and the district
it is the responsibility of the school district to provide FAPE to students with qualifying disabilities
FAPE provides instructional services designed to address the educational needs of disabled students to max extent as comparable to non-disabled children
FAPE standardizes and establishes due process procedure. Evaluation, reevaluation, and placement procedures were put in place to ensure appropriate placement and classification of a student with a disability.
extra support ELLS may need when demonstrating their learning
teachers can provide scaffolds such as sentence stems to help students with their writing or speaking
may need additional time for assignments since cognitive load is increased when processing content and new language
aquire a significant amount of language through peer interaction so make time for group work, socialization, and discussion
should be given multiple opportunities to demonstrate knowledge in various ways
make sure they are set up for success to demonstrate their academic skills. They should be given the language support they need to succeed.
ELLs should NOT receive different content, they should use ___________.
linguistically supported content
The teacher needs to ensure ____ access so all students can fulfill the assignment requirements successfully
equitable
Children in high socioeconomic families
may have parents that are motivated by grades/performance and push their children to work harder until they have achieved their standard of success
may also experience lack of parental involvement if the parents work a lot or focus on their jobs
may need guidance in social areas
ways to recognize disadvantages in socioeconomic conditions
get to know your students lives outside the classroom
expecting your parents to participate in homework isnt realiztic if a students parent work multiple jobs
students lacking food at home may be unable to put their main focus on school until they eat food at lunch
disadvantages in home life that may affect classroom learning
lack of food
lack of parental involvement
neglect/psychological trauma
poor physical living situations
An effective teacher _____ their classroom and plans instruction with an awareness of ______ and ________ factors that may affect students classroom expectations
manages; social and cultural
Views on teachers and schools
There are cultural variations in the degree to which teaching is viewed as a high-status, highly respected profession
Body language
some children are taught to look down when being reprimanded to show respect; amounts of personal space given when talking to someone also varies from culture to culture
individualism and collectivism
the needs of the group are valued above the needs of the individual
students are accustomed to working in groups and may never have been required to complete an assignment individually
you may observe some students having difficulty distinguishing between group and independent activities in the classroom
asking questions
some cultures believe it is disrespectful to ask a person in authority questions. as a result, some students may not realize that asking questions is encourages and appropriate in the classroom
punctuality
there is less emphasis on arriving at a set time
there is a general understanding that arrival times are reliable and flexible
students may need to receive help understanding the importance of adhering to the schedule
eye contact
some cultures believe its impolite to make _______ with a person of authority. therefore some students will avoid ____ with a teacher when speaking to them.
stereotype threat
children that are not part of the dominant or privileged group are susceptible to this
can cause them to experience anxiety in situation that can potentially reinforce negative stereotypes about their social groups
EX: if stereotypes indicate that a particular minority isn’t strong in math, then members of that minority group can develop anxiety about math tests because they fear they will confirm to the negative stereotypes about their social group
modifications change _____ is taught. accommodations change ______ it is taught.
what; how
when planning learning experiences/assessments for students with disabilities, teachers should….
make sure students with disabilities are included and dont feel isolated or overwhelmed
group projects should be adopted to math their academic abilities
accommodations can sometimes benefit the whole class and be used without drawing attention/isolating that student
first step when adapting curriculum for students with disabilities
read through the IEP and identify their requirements
TIP: meeting with the sped teacher can help to ensure you are meeting the students needs
considerations that should be made when developing curriculum for gifted and talented students
should be given tasks and assignments and extension activities that require a higher level of blooms taxonomy
can be given an independent long-term project to work on that relates to the material being taught in class
should still participate in whole class lessons and group activities
working with their peers provides opportunities for developing important social skills
during whole group and small group lessons, the teacher should plan higher level thinking questions, but can benefit and be answered by all students
gifted and talented students may display these traits
show an ability to understand abstract experiences more easily than their peers
have strong problem solving skills
have diverse abilities and interests
question ideas and often show skepticism about what theyre told
have strong critical thinking skills
have a keen or more mature sense of humor
be highly creative and intuitive
seem to have emotional intensity particularly surrounding moral issues and right vs. wrong
have high energy levels and enthusiasm
become frustrates when they are unsuccessful with a task
talk frequently and ask lots of questions
display behavior problems if they are bored or appropriately challenged
struggle to connect or make friends with children their age
wont show all these traits. may have excellent behavior where some may struggle behaviorally
comprehensible input
information that can be understood despite language barriers. legally required to be provided to all ELL students under statutes set by Lau vs. Nichols
EX: if a teacher uses ______ for her ELL students, they can understand the essence of what is being said even if they do not know every word or structure used in the message
Gifted and talented learners
learners or students who perform or show potential to perform at a significantly higher level than their peers
most of these students are identified through a combination of standardized tests and screening tools, gifted/talented testing, and teacher recommendations
higher than average grades ≠ giftedness; may not always perform better than their peers
Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
ensure that students with disabilities are give the opportunity to be in class with other grade level peers to the greatest extent possible based on ability level
Reading/Writing learning
students learn through engaging with texts and writing
ex: note taking, journaling, text annotating
Individualized Education Programs (IEP)
specifies strengths and challenges the students has in each content area
specifies accommodations and modifications required to be implemented for the student
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
nationwide law that ensures services for students with disabilities
sometimes known as exceptional student education (ese)
governs how state and local school districts provide early interventions, special education, and related services for students with disabilities aged 3-21
has 6 main elements: FAPE, IEP, LRE, appropriate evaluations, parent and teacher participation, and procedural safeguards
ways to support ELLS during classroom instruction through scaffolding and comprehensible input:
provide visuals = word walls, vocab lists, pictures, gestures, props
vocab support = pre-teach key terms, reference materials, word banks, dictionaries, glossaries
adjustments to delivery = no idioms, straight-forward language, gestures, non-verbal cues, slowdown when speaking, and pause after complete thoughts
English Language Learners (ELLs)
students who are learning the English language or for whom English is not a first language
Local Education Agency (LEA)
The education agency responsible for the school
Modifications
change what from the curriculum is being taught to the child example having an intellectually disabled
child learn only five body systems rather than all 13 in a science curriculum
Exceptional Student Education (ESE)
The services offered at schools to children with disabilities
Helps each child with a disability progress in school and prepare for life after
includes specially, designed instruction to meet the unique needs of the child
Review of Existing Data (REED)
A mandated review of all existing evaluation data, including the initial evaluation and any reevaluation, classroom observations, and standardized testing to determine if dismissal of services is necessary
The Americans with Disabilities Act
is a civil rights law that is designed to protect the rights of all Americans with disabilities
Not written with only education focuses
IDEA or 504 laws may offer more specific protections necessary for student success
Assures public education for disabled people and ensure physical access for physically
The law that best protects a students needs can be applied in any given situation
Multimodal Teaching
should be implemented to meet the needs of every student in the classroom
This method of teaching employees, multiple instruction methods strategies, and modes of communication to support diverse learning styles
emphasizes flexibility and student choice
Word Wall
an ongoing bulletin board with terms used frequently in the classroom
Words are often added as they are introduced
Culturally responsive teaching strategies
learn about students, backgrounds, and interests to cultivate authentic relationship relationships in which students feel respected and valued
Activate students prior knowledge and understand it will differ from child to child
Teach concepts in context
Draw connections to real world
Include literature into the curriculum about various cultures and ways of life written by diverse authors
Presenting concepts to students using their vocab and incorporating their interests
Culturally responsive teaching
an approach that recognizes the importance of including students cultures in all aspects of learning to promote learning for all students
seeks to make education, meaningful, and valuable to all cultural groups and combat stereotype threats
inclusion
ensuring students with disabilities are included in classroom activities as much as possible
visual learning
students learned through seeing and observing
Example: charts and graphs, graphic organizers, visual aids, like slideshows and videos
free appropriate public education (FAPE)
legal guarantee that students with disabilities will receive services that are individualized
Will help the student reach their highest potential
Are provided at no cost of the family
Was developed out of concern that schools were just babysitting students with severe disabilities instead of teaching them
kinesthetic learning/tactile learning
students learned through hands-on experiences and movement
Manipulative like magnetic letters, Play-Doh or shaving cream, role-play and movement games hands-on experiments
section 504 of the rehabilitation act of 1973
students who do not have a disability that is severe enough for an IEP can fall under 504. The students can perform on grade level with supportive accommodations.
504 plan
Designed to designate accommodations for students in a general education classroom when the student has an impairment that significantly impacts their life
Not the same as an IEP and is available to student students with disabilities not in sped
May provide require requirements for teachers to adjust instruction of classroom environment to better meet the needs of the student
Example access to audio versions of print materials, test, questions or instructions read aloud opportunity to dictate answers instead of writing them extra time on test/assignment assignments, Frequent breaks seat near the teacher.
gender/sexuality
term used to describe how a person identifies himself/herself
The outward ways in which a student chooses to express his/her gender via dress behavior or other factors
ex: queer
sex
the physical state of being male or female
cultural/individual stereotypes
General assumptions made about individuals or groups
Sometimes based on information that is not correct or incomplete
Example: boys are better than girls at math
accommodations
change how content is taught
Assist in a learning process
Determine the district and state assessments that the student will participate in
auditory learning
students learned through listening and speaking
Example: read aloud, verbal instructions, discussions, rhymes, and songs
response to intervention
Scientific research based instructional intervention delivered in general education classroom
is a process to monitor and measure student progress in the general education curriculum
Systematic process for students who are experiencing learning/behavior difficulties and may not meet grade level achievement standards
Referral to sped services would begin if no progress is made in intervention
Referral can come through parents, teachers, or other social officials
Parents must consent to evaluation, regardless of who requests it
punishment
discouraging a behavior
reinforcement
encouraging a behavior to happen again
teacher wait time
The silence that often comes after a question has been asked, but before students have finished considering their answer and/or find the courage to speak
non-verbal response
A way to communicate without speaking
Example, the teacher taught the students the ______ of setting their pencils down when they were ready for the next question
feedback
Information provided to individuals about their performance or behavior
Often highlights strengths, areas of improvement and suggestions for further development with the aim of promoting learning, growth, and improvement
student engagement
The level of attention and interest students demonstrate while learning
rubric
assessment tool that outline specific criteria or performance levels for evaluating student work, providing clear guidelines and standards for both instructors and student students to ensure consistent and objective grading
instrinsically motivated
students draw all their motivation from the learning process itself
extrinsic/external motivators
The motive for the activity comes from outside the individual
behaviorism
Learning theory, rooted in the notion that all behaviors are learned through interaction with the environment
scaffolding
providing support to students to achieve a task
Example: I do, we do, you do to gradually release text analysis
maslows needs in order
1) physiological needs: food, water
2) Safety: security, freedom from fear
3) Love/belonging: relationship, relationships, family
4) esteem: confidence, feelings of achievement
5) Self actualization: meeting potential, creative abilities
abraham maslow
American psychologist who focused on humanistic psychology
His work was influenced by many including Native Americans, Blackfoot people
Theorize that people have a hierarchy of needs
In order for people to meet their full potential, they must meet a series of needs
If some needs at more basic levels are not met. It is difficult to begin. Meeting needs at a higher levels.
extra behavior support strategies
student/ teacher conferences:
identify the root of the issue
make a plan towards finding a solution
behavior contracts:
agreement between the student and teacher
covers the behavioral goal and steps towards reaching it
these are not effective when the behavior is dangerous
punishment/reinforcement chart

negative punishment
we removing a stimulus in reaction to a behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behavior
Example: a student is caught playing non-instructional games on the schools computer so the teacher removes the privilege of working on the school computer for the duration of the class period (the teacher is removing the stimulus a.k.a. the computer to decrease the likelihood of the student playing such games in the future)
positive punishment
presenting a stimulus and reaction to a behavior to decrease the likelihood of that behavior
example: A student passes a note during class, and the teacher writes him a detention (the teacher is presenting a stimulus a.k.a. the detention to decrease the likelihood of the student passing notes in the future
negative reinforcement
removing a stimulus and reaction to a behavior to increase the likelihood of a behavior
Example: the teacher allow students to talk to each other. If they all make A’s on a quiz, the teacher is removing a stimulus a.k.a. class wide silence in response to a behavior to increase the likelihood of the behavior.
Typically used to remove a positive punishment already in place
Teacher should not begin class with a negative stimulus
positive reinforcement
presenting a stimulus in response to behavior to increase the likelihood of that behavior
Example: a student answers a question and the teacher gives him a compliment. The teacher gives the compliment to increase the likelihood that the student will participate in class again.
proactive approaches to behavior management
establish clear expectations from the very beginning
Seek student input about class behavior, expectations to develop their sense of ownership and responsibility
Establish incentive and consequences and implement them consistently
Erik Erikson
stages of development = people must pass through eight life stages in order to fulfill their own potential
Failure to complete any phase will hinder their ability to continue growth with success
Skinner
developed operant conditioning: (uses a positive and negative stimulus to gain a particular outcome)
Pavlov
classical conditioning: positive stimulus is paired with a neutral stimulus and repeated. then, the positive stimulus is removed and the neutral stimulus has the same effect
maslow (again)
hierarchy of needs: in order for people to meet their full potential, they must meet a series of needs
watson
behaviorism: focuses on the behaviors of individuals rather than internal value (thinking or feeling)
sought to only analyze psychology based on what could be observed
thorndike
connectionism: students learn by repeating a series of stimulus and response
interactionists
assumes that actions can be explained by analyzing the factors around the child
They think the child growth occurs during interactions between the child and society and by studying all the factors it is possible to understand and conceivably alter behavior by altering the various factors
teacher and student work together to monitor behavior
Teacher removes negative factors from the environment and encourages the student to increase positive participation
Teacher may provide tally marks on a sticky note to give a visual of great choices and reminders to be on task
interventionists
assume people need external stimulation to guide behavior basically the opposite of non-interventionists
teacher tries to create incentives to manage student behavior through a highly structured classroom
Teacher monitors how the incentives are changing behavior and alters the incentives accordingly
Teacher takes responsibility for all behaviors
non-interventionists
assume that people naturally strive to be good and want to improve
Teacher does not need to intervene regarding behavior issues because the child is trying to improve
Believe that adults need to allow children as much room as they need to grow and improve naturally
discipline students much less because they don’t want to punish or impede a students natural desire to improve
Students managed their own behaviors with subtle guidance from the teacher teacher, such such as eye contact, or gentle pat on the shoulder when misbehaving
3 main theories of behavior management
non-interventionist
Interventionist
Interactionist
warm-up assignments
an activity students can complete independently as part of their starting class routine
Should be done while the teacher sets up for a lesson or completes administrative tasks like attendance
routines/procedures
should be explicitly taught and practice at the beginning of the school year until they become easily established
encourages independence to help maximize instructional time
timely feedback
students must have time to apply the feedback they receive
The sooner our teacher can correct a misconception the better
specific feedback
students need to specifically understand what is right and wrong or strong or weak about their work or performance
Need to be clear in their understanding of what to do about it
teacher should be specific about the next steps for improvement
balanced feedback
students need to know both what they did well and what needs to be improved
Positive feedback may be encouraging and should help students from feeling defeated. It serves a greater purpose too.
student needs to know what they did right so they know to do it again
differentiating instruction
it is critical for the teacher to recognize when those diversities are putting limits on student learning and work to provide the best support and adjustments in teaching strategies for the student to help them learn and perform.
how to use diversity to inform how students develop the environment and activities in a classroom
teachers should strive to promote understanding of diversity by acknowledging and celebrating the differences that exist within the classroom
students should have the opportunity to share and get to know each other throughout the year
students should be led away from forming ignorant/derogatory opinions that could lead to inappropriate or discriminatory behavior
take opportunities during readings or lessons to pull texts or activities that relate to student cultures or interests
use student diversities as strengths to guide group work and lesson planning
teachers will meet multiple types of diversities that may affect students performance in the classroom including…
interests
skills
ethnicity
culture
language background
gender
sexuality
socioeconomic status
Exceptionalities related to:
behavior
speech
communication
cognitive ability
physical ability
intellect
giftedness
Ego integrity vs. despair
Erikson
65+ years of age
Focus is finding a sense of fulfillment in their lives
Hope to see their lives as meaningful
If they fail to see meaning, they will experience a sense of despair
generativity vs. stagnation
Erikson
40-65 years of age
Find meaning in work
Feel they should be able to contribute something meaningful to society and leave a legacy
If they fail to achieve this, they will feel as though they have been an unproductive member of society
intimacy vs, isolation
Erikson
18-40 years of age
Seeking intimacy in partners, friends, and family relationships
In this stage, people are particularly vulnerable to loneliness
The reaction to failed relationships can be to isolate oneself for protection
identity vs. role-confusion
Erikson
12-18 years of age
Developing sexual identity and self discovery
Identity crisis might occur during this transition into adulthood
Young people might be confused about the age-appropriateness of some activities
Young people can also experience crisis because of expectations from peers and parental figures
industry vs. inferiority
Erikson
5-12 years of age
Children continue to mature and develop more self-awareness
they are able to understand scientific facts, logic, and more complex processes
they also become more competitive and compare themselves with peers
if a child is unable to do things they see their peers doing, they will feel inferior
elementary ages students begin to compare themselves to others, a tendency that will continue for many years to come
initiative vs. guilt
erikson
3-5 years of age
children learn to explore and do things independently
new concepts are learned in school and practiced in real life
if a child cannot complete learned tasks independently, they may feel a sense of guilt
autonomy vs. shame/doubt
Erikson
1 ½ - 3 years of age
young children learn how to take care of themselves in basic ways
toddlers develop self-concept
failure to successfully learn to dress and feed themselves will lead children to doubt their abilities and struggle moving forward
trust vs. mistrust
erikson
0-1 ½ years of age
infant need stability and consistent care
if care in consistent and predictable, the infant will carry this trust into future relationships (secure attachment made)
if care is inconsistent or neglectful, the infant will ignore the caregiver and develop an anxious and or avoidant personality (insecure attachment made)
ERIKSONS 8 STAGES
Trust v. Mistrust
Autonomy v. Shame/Doubt
Initiative v. Guilt
Industry v. Inferiority
Identity v. Role confusion
Intimacy v. Isolation
Generativity v. Stagnation
Ego Integrity v. Despair
titties. are. incredibly. infectious. if. i. get. erect.
Erik ERIKSON (again)
german american psychiatrist famous for his theories on how humans develop
personality and identity form phases of psychosocial development each of which is accompanied by what he called psychosocial crisis
to move onto the next level of development, the individual must overcome this crisis by establishing healthy relationships with others
8 stages of psychosocial development
general outline for process of phase identification, assessment, admission, and dismissal for RTL
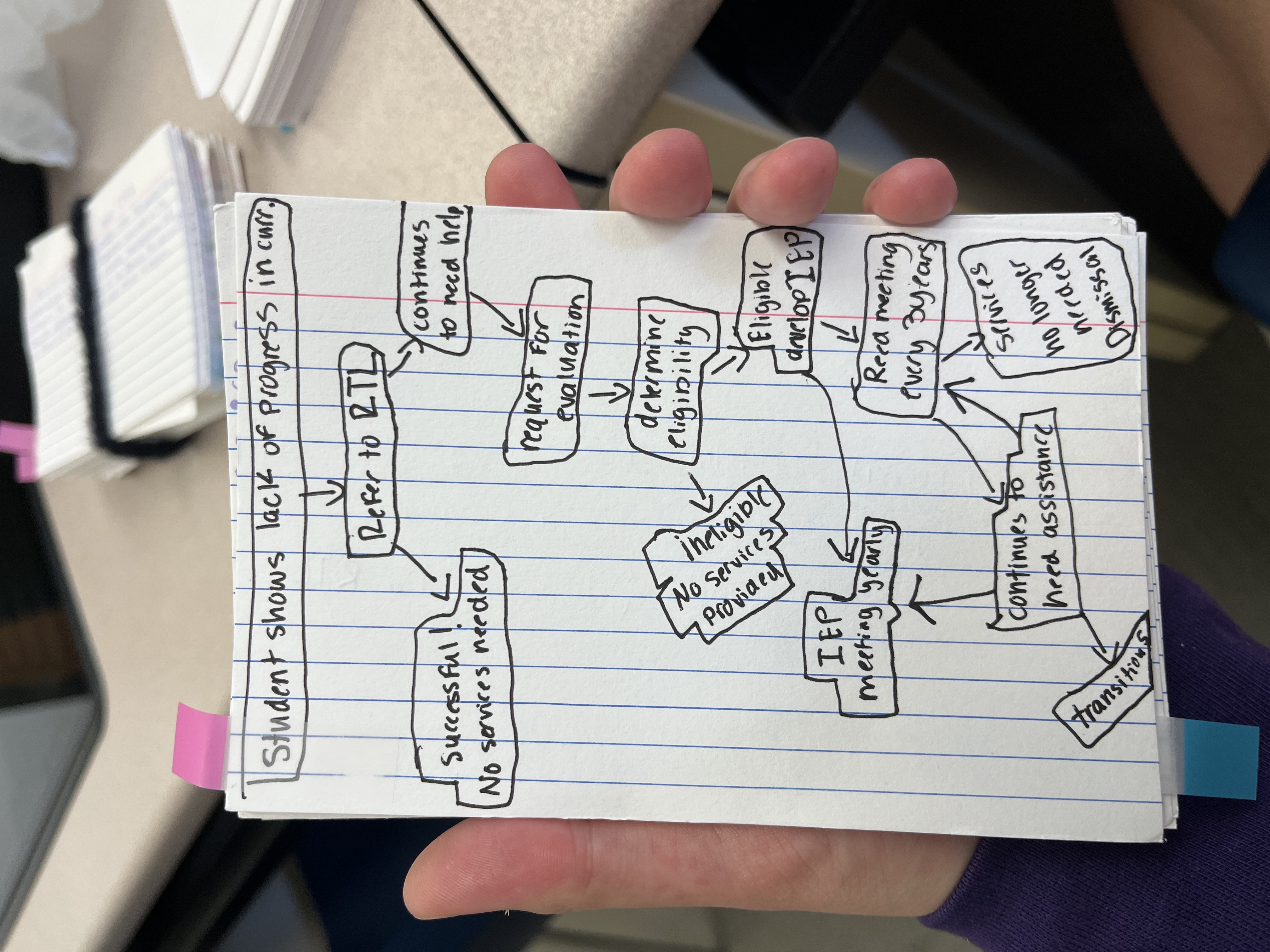
automatic interventions
self-monitoring, structured reminders, reinforcing the absence of behavior (differential reinforcement)