Buffers and Isotonicity (12-13)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is a buffer?
A solution that resist changes in pH upon the additions of small quantities of strong acid or base
Why are many drug formulations buffered?
To maintain a constant pH
Why is a constant pH important in drug formulation?
pH affects the drugs solubility, therapeutic activity, absorption, and patients comfort.
What is the pH of human blood?
7.4
What buffers are found in the human blood?
Plasma proteins, hemoglobin, bicarbonates, and phosphates.
What is the pH of eye fluid? Does it require buffers?
7.4; yes
What do buffers most commonly consist of?
Weak acid and its conjugate base
Why are buffers not usually prepared from weak bases and their conjugate acids/salts?
Due to their instability.
What are some common buffer systems?
1. acetic acid and sodium acid
2. citric acid and sodium citrate
3. sodium phosphate monobasic and sodium phosphate dibasic
4. ephedrine and ephedrine HCl
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation?
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
What factors influence the pH of buffer solutions?
Addition of neutral salts, dilution, and temperature
What is buffer capacity?
The magnitude of resistance of a buffer to pH changes
How is buffer capacity expressed?
As the amount of strong acid or base, in gram equivalents, that must be added to 1 liter of the buffer solution to change its pH by 1 unit.
What is the equation for buffer capacity?
β= ΔB/ΔpH
What is ΔB?
The gram equivalent of strong acid or base needed to change the pH of 1 liter of buffer solution
What is ΔpH?
The pH change caused by the addition of the strong acid or base
What does the buffer capacity of 1 indicate?
1 gram equivalent of acid or base is added to 1 liter of buffer and the pH changes by 1 unit
What is the equation for buffer capacity of a weak acid and its salt?
β= 2.3C(Ka[H3O]/Ka + [H3O]^2)
What does C represent?
The total concentration of acid and salt
Buffers that have a higher concentration of acid and salt have a higher or lower buffering capacity?
Higher
What is the buffer capacity of human blood?
0.0385
When does maximum buffering capacity occur?
when pH=pKa
How does the equation for buffer capacity of a weak acid and its salt change when we consider that Ka is equal to pH (H3O concentration) at the maximum buffering region?
β= 2.3C([H3O][H3O]/[H3O] + [H3O]^2)= 0.575C
How does buffer capacity change if we move ±1 pH unit?
Falls to 33% of the maximum value
How does buffer capacity change if we move ±2 pH units?
Falls to 1% of the maximum value
What is the first step in preparation of pharmaceutical buffers?
Decide what pH the buffer is needed
What is the second step in preparation of pharmaceutical buffers?
Choose a conjugate acid-base pair so that pKa is as close as possible to the pH of the desired in step one
What is the third step in preparation of pharmaceutical buffers?
Apply the Henderson-Hasselbach equation to obtain the ratio of buffer salt to acid required to obtain the desired pH
What is the fourth step in preparation of pharmaceutical buffers?
Consider the individual concentrations of salt and acid needed to obtain a suitable buffer capacity. Concentration of 0.005 to 0.5M is sufficient, and buffer capacity of 0.01 to 0.1 is sufficient.
What is the fifth step in preparation of pharmaceutical buffers?
Consider other factors that will affect buffer such as stability of drug, buffer over time, toxicity, etc
What is the sixth step in preparation of pharmaceutical buffers?
Verify the pH of the resulting solution
What are three common buffer salts used in pharmaceutical solutions?
Acetates, Citrates, and Phosphate
What is the most commonly used buffer?
Citric acid
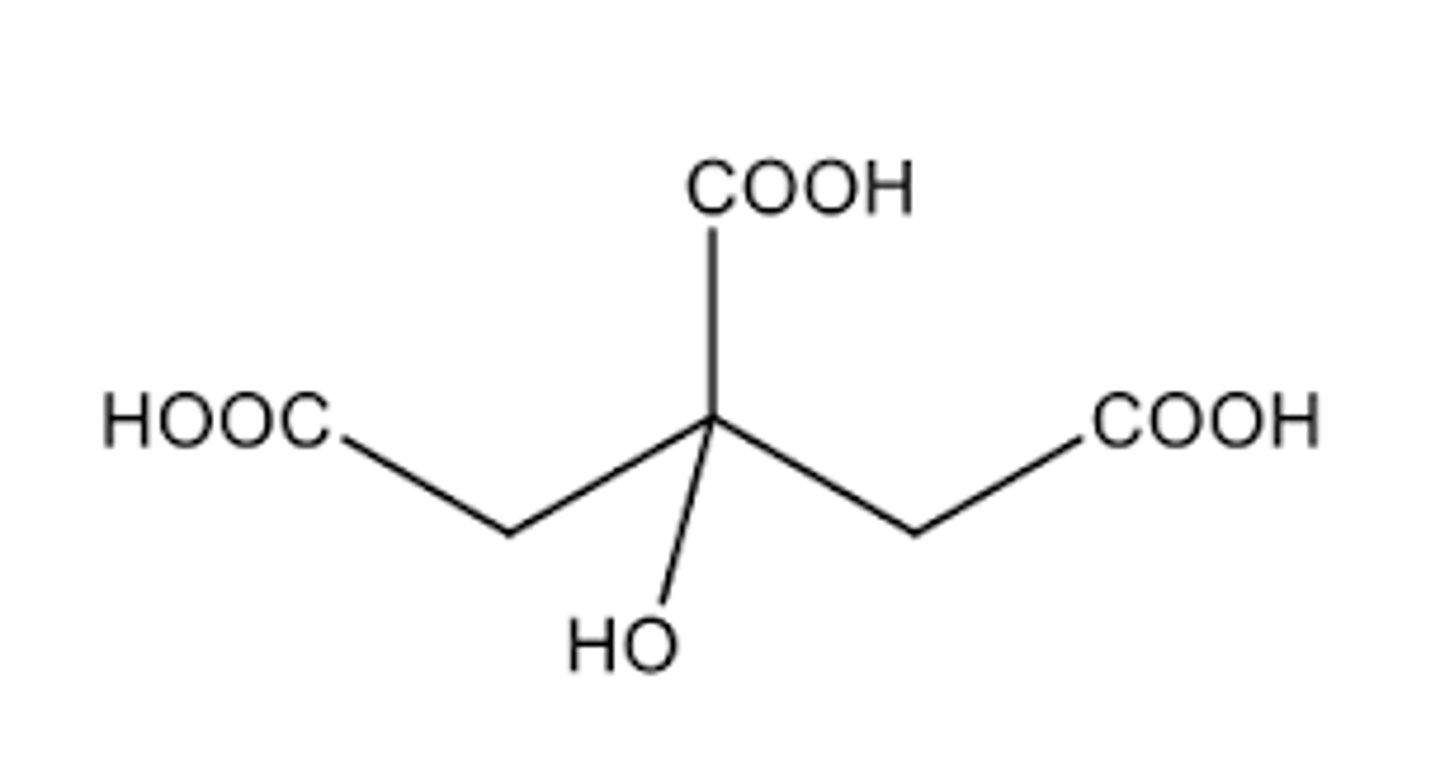
What is the differnce in citric acid and citrate?
Citric acid is the acidic form and citrate is the conjugate base
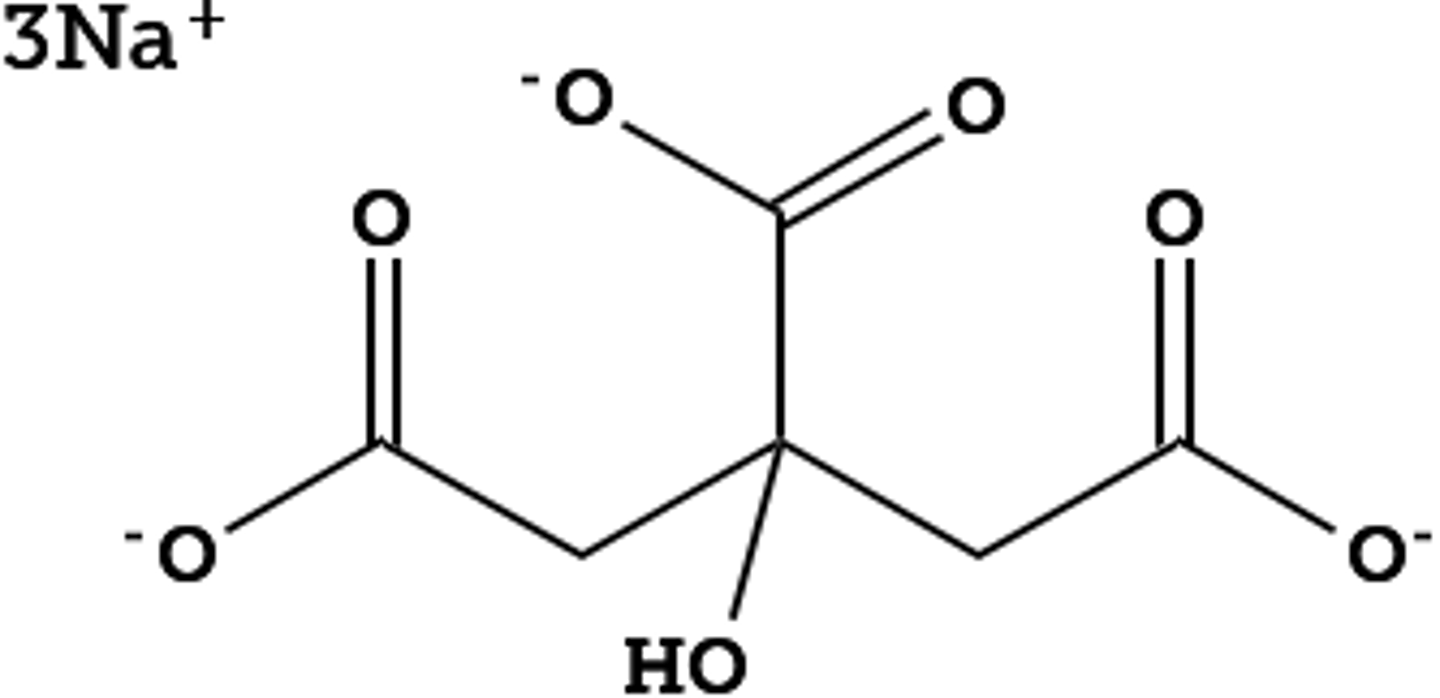
Describe the citric acid buffer
Trivalent buffer containing three carboxylic acids with pKa of 3.1, 4.8, and 6.4
What is osmosis?
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration
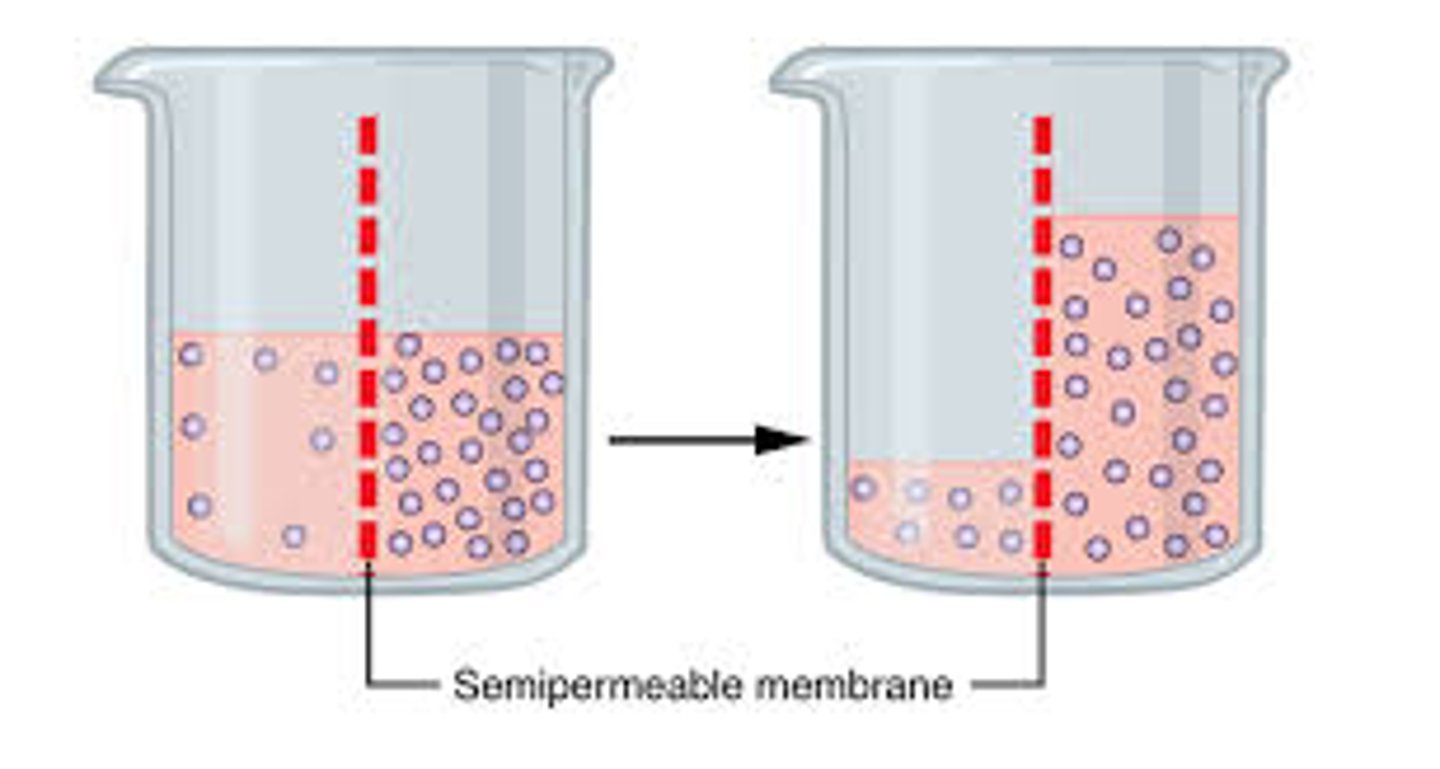
What is osmotic pressure?
The pressure created when solvent flows across the membrane to a region of higher solutes to equalize concentration. Measured at equilibrium.
What does osmotic pressure depend on?
The concentration of solutes
What does isosmotic mean?
when two or more solutions have the same osmotic pressure
How do electrolyte and non-electrolyte solutes differ regarding osmotic pressure?
A non-electrolyte only depends on concentration while an electrolyte depends on both concentration and degree of dissociation
What is the equation for osmotic pressure?
π = icRT
What does i represent?
van't Hoff factor
What does c represent? R? T?
molar concentration of solute, ideal gas constant, absolute temperature
Describe Van't Hoff Factor
The ratio between the actual concentration of particles produced when a substance is dissolved and the concentration of a substance as calculated from its mass
When does i=1
For non-electrolytes/substances with slight dissociation
When does i=1.8
substance that dissociate into 2 ions
When does i=2.6
substance that dissociate into 3 ions
When does i=3.4
substance that dissociate into 4 ions
When does i=4.2
substance that dissociate into 5 ions
What is an osmole?
The amount of substance that dissociates in solutions to form one mole of osmotically active particles
(moles of osmotically active particles)
What is osmolarity?
the number of osmoles of solute per liter of solution
(moles of osmotically active particles per liter of solution)
What is the equation to find osmolarity?
Molarity x i
What is osmolality?
the number of osmoles of solute per kg of solution
(moles of osmotically active particles per kg of solution)
What does osmolality NOT depend on?
The nature, shape, or size of a solute particle
All solutions containing the same number of osmotically active particles-regardless of their chemical properties- exhibit the same___?
Osmolality
What is an osmometer?
used to measure the osmotic strength of a solution, colloid, or compound
What are vapor pressure osomometers?
Determine the concentration of osmotically active particles that reduce the vapor pressure of a solution
What are membrane osmometers?
Measure the osmotic pressure of a solution separated from pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane
What are freezing point depression osmometers?
Determine the osmotic strength of a solution, as osmotically active compounds depress the freezing point of a solution
How can osmometers be useful clinically?
Can determine the total concentration of dissolved salts and sugars in blood and urine samples
What is tonicity?
Osmotic pressure exerted by the fluids containing non-penetrating solutes that can not cross the membrane
What is the osmotic pressure of body fluids such as blood and tears?
0.9% NaCl (290 mOsm/L)
Solutions with the same osmotic pressure as body fluids are termed?
Isotonic
Solutions with the a lower osmotic pressure as body fluids are termed?
hypotonic
Solutions with a higher osmotic pressure as body fluids are termed?
hypertonic
When extracellular fluid is hypertonic, what effect does this have on cells?
The fluid inside of cells will move towards the high concentration of solutes in the extracellular fluid, causing the cell to shrink.
When extracellular fluid is hypotonic, what effect does this have on cells?
The extracellular fluid will move towards the high concentration of solutes in the cell, causing the cell to swell.
When extracellular fluid is isotonic, what effect does this have on cells?
Volume remains unchanged
What is the most common method to adjust isotonicity of pharmaceuticals solutions?
Sodium chloride equivalent
What is the sodium chloride equivalent?
the amount of sodium chloride that produces the same osmolarity as 1 gram of the drug substance
What is the equation to find the relationship of two substances that are equivalent in tonicity?
Wt1/Wt2= (MW1 x i2)/(MW2 xi1)
What is the equation to find sodium chloride equivalent?
E= (58.4 x i)/ (MW x 1.8)
What is the theoretical effect of adding a hypertonic solution to the eye?
It would draw water out of the eye into the solution to establish concentration equilibrium
What is the theoretical effect of adding a hypotonic solution to the eye?
It would induce passage of water from the solution into the eye
How does the eye respond to hypertonic solutions compared to the theoretical assumption?
The eye is more tolerant to tonicity variations and can tolerate solutions equivalent to a range of 0.5-1.8% NaCl (remember, normal is around 0.9%). A hypertonic solution of 2-5% is more effective in drawing out water from the eye.