BIO 101 Chapter 2B
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Organic molecule
compound containing carbon and hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
compound made up of just carbon and hydrogen
How does the structure of carbon contribute to the diversity of organic molecules?
Carbon is made up of 6 electrons. It has 4 valence electrons in the outer ring. It seeks 4 more electrons to make it stable. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms. This allows carbon to form varying chains and structures with other atoms.
Structural isomer
same molecular formula, arranged differently
What are the four classes of large (biologically important) organic molecules?
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids
Monomer
single unit of polymer
Polymer
collection of monomers (similar subunits)
Dehydration synthesis
enzyme removes hydroxyl group from one molecule and hydrogen atom from another, forming H2O and a new covalent bond between the molecules. Loss of water
Hydrolysis
splitting covalent bonds between monomers by adding water. One molecule receives hydroxyl group, and another receives a hydrogen atom.
Carbohydrates
compound containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (1:2:1)
Two main carbohydrate groups
Simple carbohydrates (monosaccharides and disaccharides) and complex carbohydrates (oligosaccharides, glycoprotein, polysaccharides)
Monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
Glycosidic bonds
covalent bonds that link monosaccharides
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis
Oligosaccharides
3-100 monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
100+ monosaccharides
Energy storage polysaccharides in plants
Starch
Energy storage polysaccharides in animals
Glycogen
Structural polysaccharide in plants
Cellulose
Structural polysaccharide in animals
Chitin
Monomer of proteins
amino acids
How many types of amino acids are there?
20
Peptide bond
Covalent bond between adjacent amino acids, from dehydration synthesis.
Peptides
2-99/<100 amino acids.
Polypeptides
100+ amino acids.
Proteins
Polypeptide(s) folded into functional 3-D shape.
What is one of the most important roles of proteins in cells?
catalyst/enzyme; to increase the rate of speed in reactions.
Protein denaturation
Modification of protein shape, so that its function is destroyed.
Conditions for denaturation
Extremes of temperature and pH.
Types of proteins
Structural (collagen), contractile (muscles), transport (membrane channel proteins), storage (egg protein), enzyme (digestive), antibodies.
Primary structure
Linear, amino acid sequence of polypeptide.
Secondary structure
Folded into coils, sheets, loops.
Tertiary structure
Overall shape of polypeptide.
Quaternary structure
Overall protein shape, multiple polypeptides.
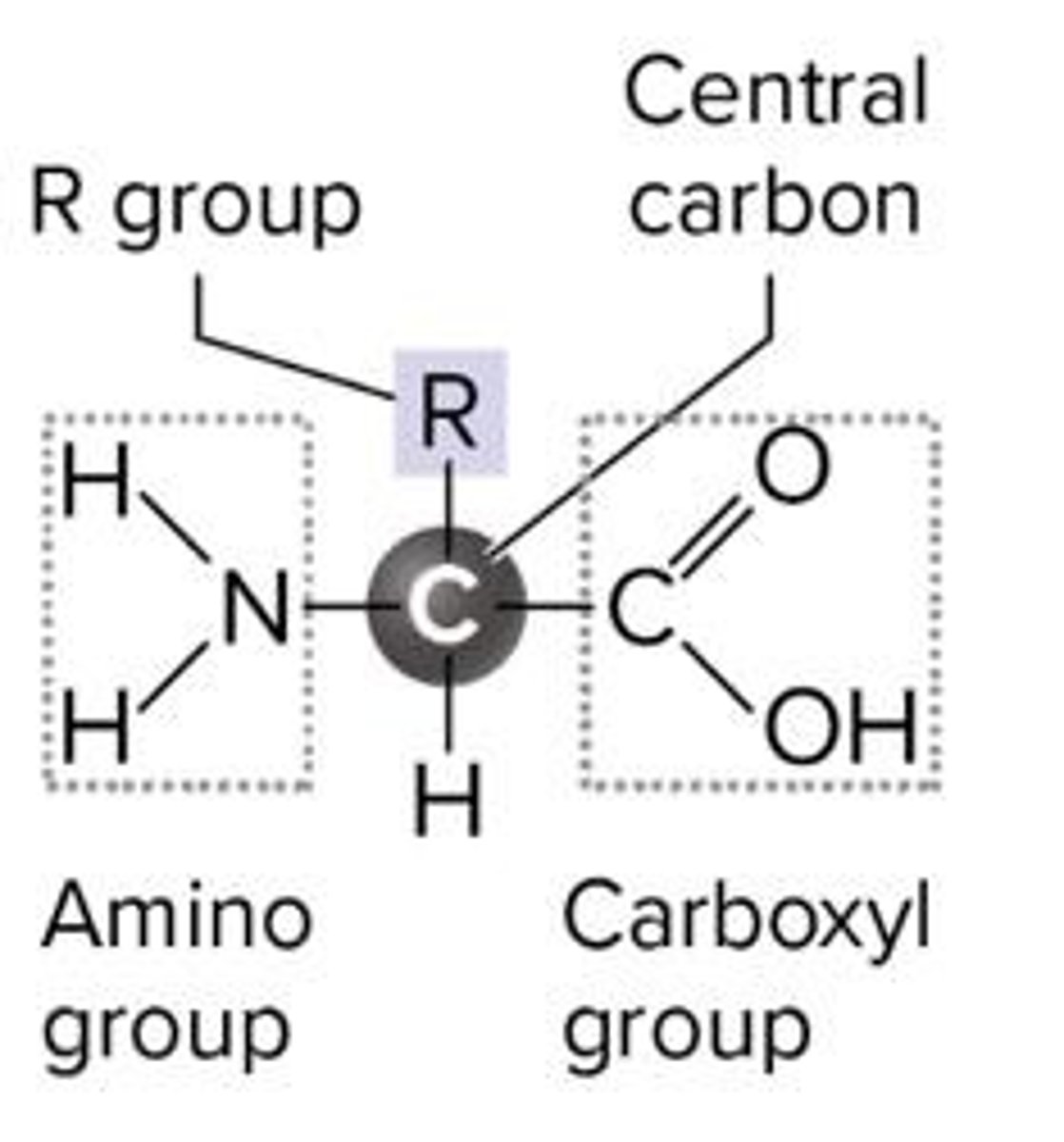
Five components of amino acids
R group, central carbon, hydrogen atom, amino group, carboxyl group.