Medchem Exam 2
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
salts can be used to _______ lipid and water solubility
increase
an acid reacting with a base results in a?
salt (chemical reaction)
what makes a salt different from an ionized acid/base?
salts contain a counter-ion (Cl-)
what are the two types of salts?
1. inorganic
2. organic
what are inorganic salts?
counter-ion is not carbon based
what are organic salts?
counter-ion is carbon based
what are cationic salts?
counter-ion is a cation
cationic salts are commonly produced using?
NaOH, KOH, CaOH
if the counter ion is positive, the drug must be __________
negative (acidic)
what are anionic salts?
counter-ion is an anion
how are anionic salts commonly produced?
HCl, HBr, H2SO4, H3PO4
if the counter ion is negative, the drug must be ____________
positive (basic)
what is the main advantage of inorganic salt formation?
- increased water solubility
- enhances solvation + dissolution of solid drug in water
increased water solubility of inorganic salt formation requires an _____________?
equilibrium between ionized + unionized species
--> takes time
---> not 100%
can inorganic salts enhance lipid solubility?
No
what are the uses of organic salts?
enhance water solubility OR lipid solubility
how are water soluble organic salts commonly produced?
using sugars, sugar analogs, + biosynthetic intermediates (lactate, malate, citrate, etc.)
water soluble salts contain numerous _________ groups capable of H-bonding with water
polar
Why use organic water soluble salts if inorganic salts are available?
• sometimes organic salt formulations are better suited to a particular route of administration
• basic solutions can cause stinging + burning
what routes of administration are inorganic salts not optimal for?
IV and opthalmic
what routes of administration are inorganic salts more optimal for?
oral
what are lipid soluble organic salts used to form?
lipid soluble suspensions (administered via IM depot injections)
lipid soluble organic salts contain substantial _______ _________ that act to enhance lipid solubility
nonpolar hydrocarbons
what drug is a lipid soluble salt that is formulated for IM injection?
Pen G Benzathine
acidic drugs mixed with basic drugs results in __________
drug-drug interactions
--> will form a salt
--> precipitation in an IV can cause serious harm to the patient
Heparin (administered via IV as acidic sodium salt) can never be administered in the same IV line as basic drugs such as _________ and __________
Diazepam and Haloperidol
what type of drug is Atropine Sulfate?
basic
what type of drug is Leucovorin Calcium?
acidic
basic drugs are cations in salt form and thus have ________ counter-ions
anionic
acidic drugs are anions in salt form and thus have ________ counter-ions
cation
what type of drug is Ketorolac tromethamine?
acidic
what type of drug is Erythromycin Stearate?
basic
what are the ways to determine a drug's solubility in either water or lipid?
1. physically measured in a lab experiment (better)
2. estimate how the drug will behave
describe what is needed to physically determine a compound's stability:
1. a separatory funnel + 2 beakers
2. two solvents: water (polar phase) + n-octanol (non-polar phase)
3. the test compound
4. a way of measuring the amount if compound in solution
what does n-octanal closely mimic?
biological membranes (ie phospholipids)
describe the experimental procedure for physically determining a compound's stability:
• add a test compound to a mixture of n-octanol + water
• equilibrate (shake + allow phases to separate)
• drain each phase into a beaker
• determine the concentration of test compound in each phase
What is the partition coefficient (P)?
the ratio of a drugs concentration found in the n-octanol layer to the concentration found in the water layer
what is the formula for the partition coefficient (P)?
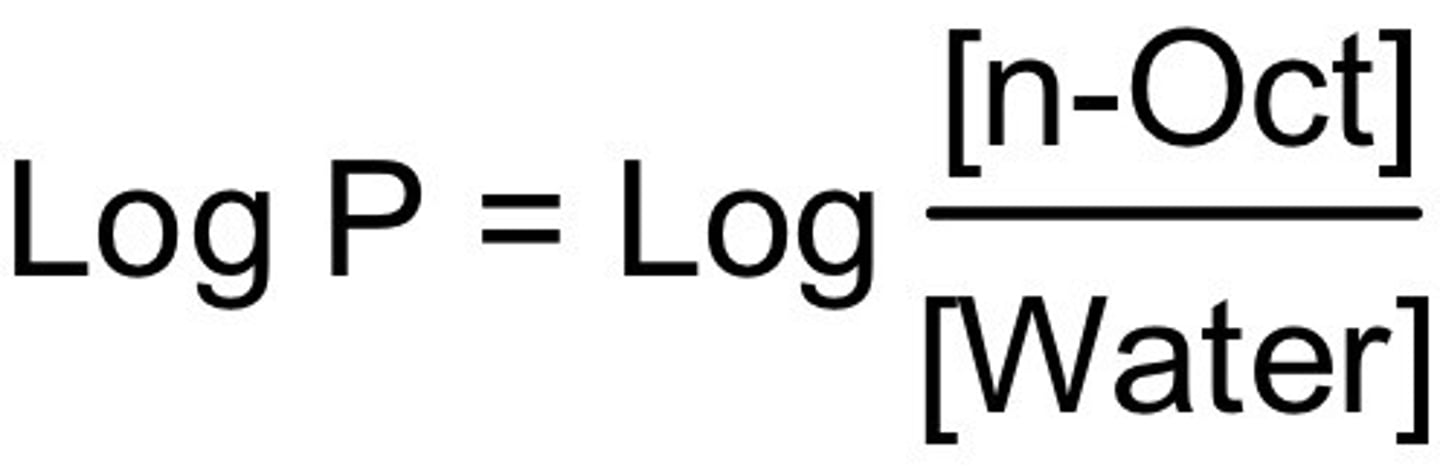
charged functional groups (acids + bases) will have the strongest interaction with _________
water
functional groups that are polar but will not H-bond will have properties in between ________ and _________
aqueous and lipid loving
functional groups that are non-polar (such as alkyl groups) will interact well with a _________ environment
lipid/fatty
for an alcohol group, if there are 3 or less carbons per alcohol group, the molecule will be ____________
water-soluble
butyl alcohol, which has 4 carbons is __________
marginally water soluble
pentanol is _______________ due to the 5 carbons it possesses
not water soluble
do you count the carbonyl carbon for the functional groups that have one?
no
# carbons solubilized < actual # carbons
not water soluble
# carbons solubilized > actual # carbons
water soluble
# carbons solubilized = actual # carbons
boderline
what are isomers?
- same formula, different arrangements
- produce different constitutions
what are stereoisomers?
- same atoms, same arrangement
- different placement in 3D space (bold+wedge)
what are the two types of stereoisomers?
geometric isomers and optical isomers
what are geometric stereoisomers?
- different shapes
- different compounds
- different chemical + biological properties
what are cis isomers?
isomers have at least one of the same functional group on the same side
what are trans isomers?
isomers have at least one of the same functional group on opposite sides
maleic acid is the _______ isomer
cis
fumaric acid is the ____ isomer
trans
why is trans-diethylstilbesterol the more active isomer?
because it mimics the natural compound better... not because of sterics
What is a Z isomer?
- an isomer where the functional groups are on the same side
- different R groups
- ZAME
what are E isomers?
- Molecules where the highest priority groups are on opposite sides
- different R groups
what are enantiomers?
- exact opposite
- mirror images
chiral is _____
unsymmetrical
--> cannot contain a mirror plane
achiral is ______
symmetrical
enantiomers have _______ chemical + physical properties
identical
what are the two things enantiomers differ in?
1. the direction they rotate polarized light
2. how they interact with other chiral compounds
each enantiomer will rotate polarized light equally but in _________
opposite directions
What is a racemic mixture?
50/50 mixture of two enantiomers
Do racemic mixtures rotate plane-polarized light?
No
once a racemic mixture has formed, can it be separated by normal means? why?
no bc enantiomers have identical physical + chemical properties
how to calculate the number of isomers?
2^n
n = # of stereocenters
RR --> SS
enantiomers
RS --> SS
diastereomers
any molecule that has a non-identical mirror image is _______
chiral
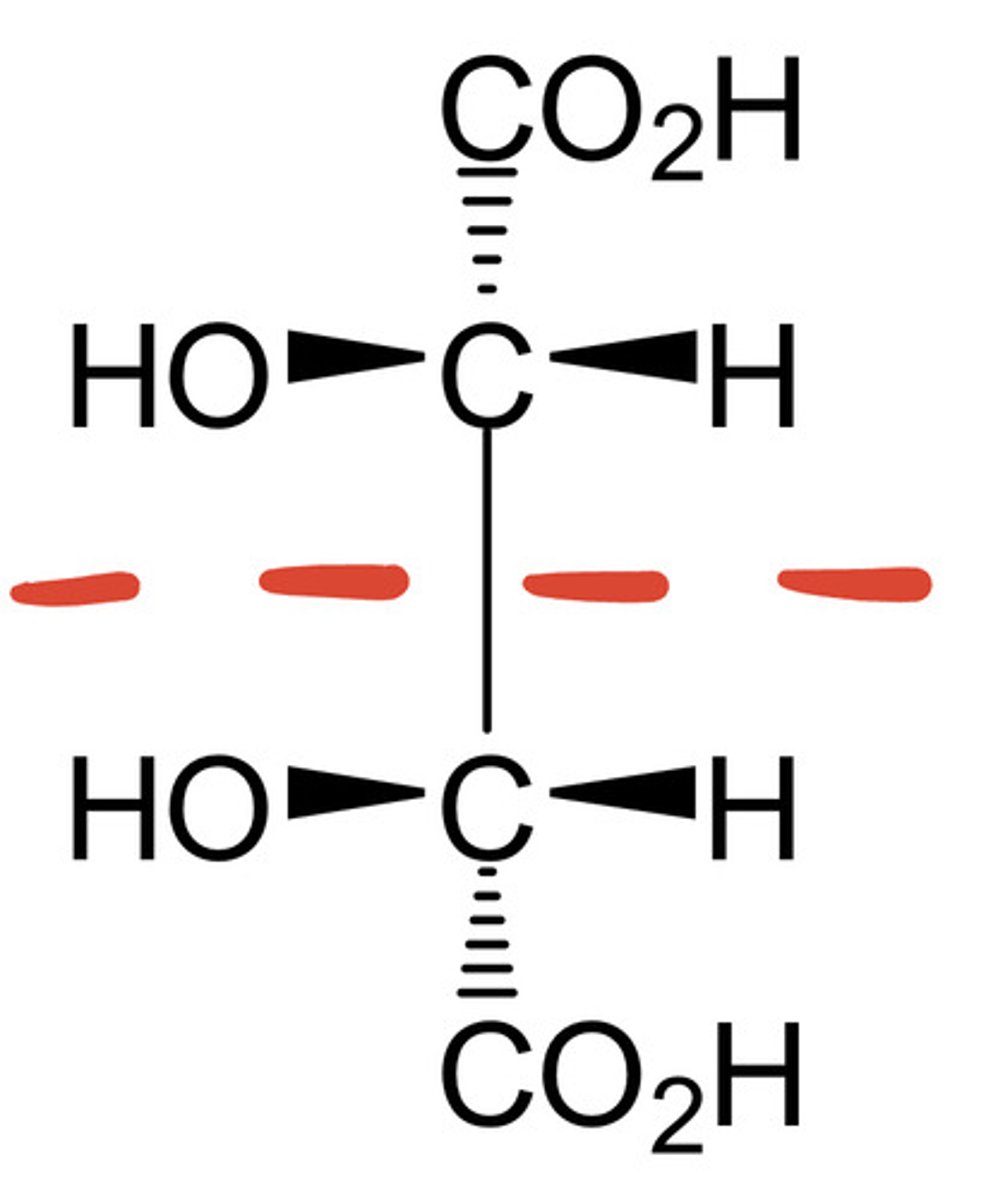
why is this molecule achiral even though it has two stereocenters?
it contains a mirror plane
R stereocenter
clockwise
S stereocenter
counterclockwise
in an achiral environment enantiomers...
have identical chemical + physical properties
are receptors and enzymes chiral or achiral?
chiral
How is ephedrine related to psuedoephrine?
they are diastereomers
what is a eutomer?
better fitting enantiomer, higher potency/affinity
what is a distomer?
the lower affinity (lower potency) enantiomer
why is there a push for producing single enantiomer drugs?
decrease side effects
what is a disadvantage for producing single enantiomer drugs?
a lot more expensive to make
What is the eudismic ratio (ER)?
represents how much better the eutomer is compared to the distomer
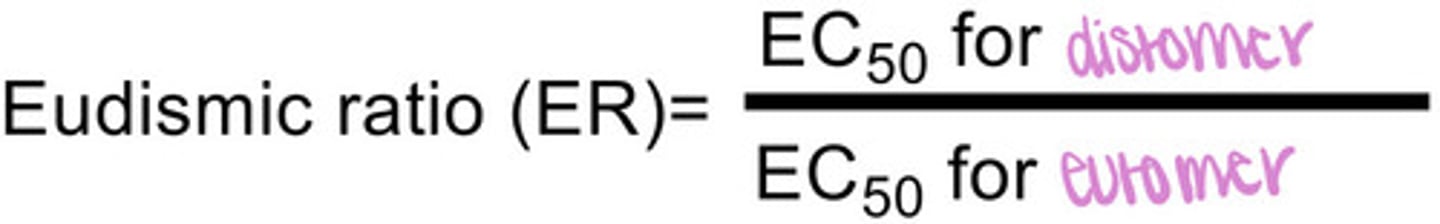
what does ER = 1 mean?
both eutomer and distomer contribute equally to the side effect
when the drug is based on the structure of an amino acid, the "___" enantiomer will be the more potent form
S
Amino acids are the "___" enantiomers in mammals
S
what does "es-" in front a drug's generic name mean?
it is the "S" enantiomer
what enables the drug to bind to the receptor with potency and specificity?
intermolecular forces
what is the ∆G value for covalent bonds?
very strong interaction: ∆G = -40 to -100 kcal/mole
covalent bonds are
irreversible (unless broken or reversed)
what is a bad example of covalent bond?
mercurials
--> reverse this reaction by breaking the covalent bond by giving the Hg+ a thiol SH to bond to
what are examples of good covalent bonds?
1. enzyme inactivators
2. alkylating agents
what are ionic interactions (aka salt bridges)?
opposite charges attract each other
What is Coulomb's Law?
q = charge on group
r = distance
D = dielectric constant
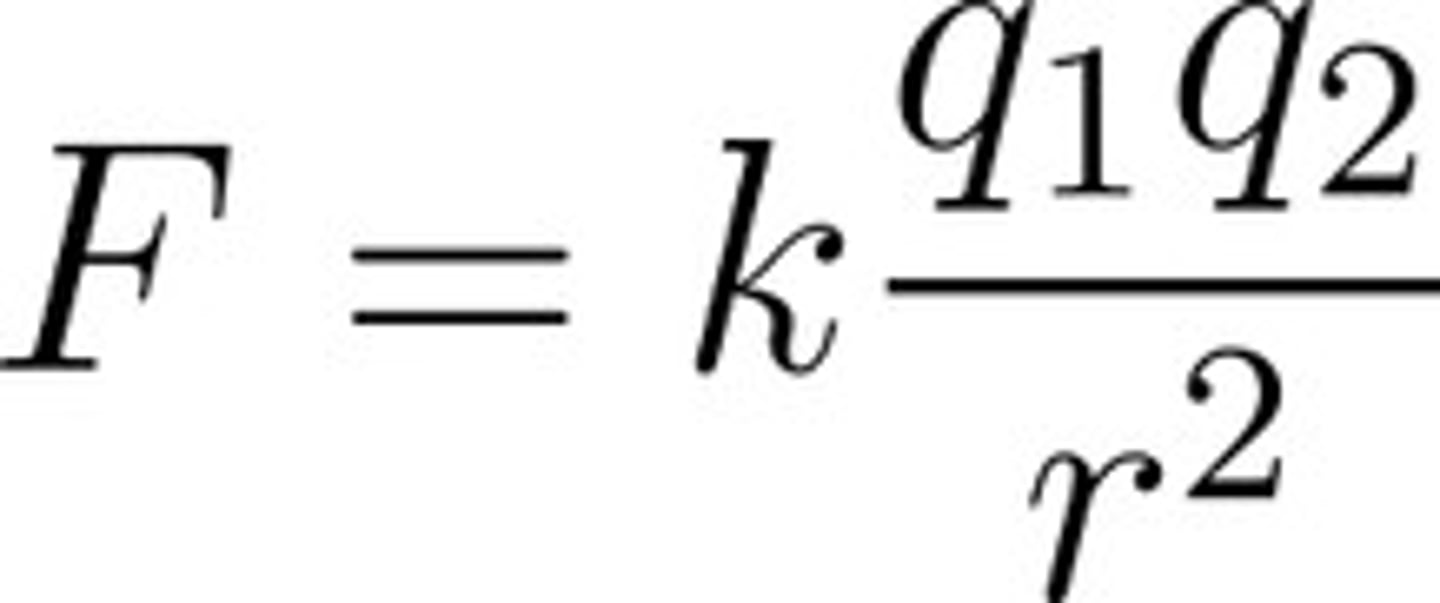
what is the ∆G for ionic interactions?
-5 to -10 kcal/mol
where do we find these charges on our drugs? (ionic interactions)
ionized acidic and basic functional groups + quartenary amines
where do we find these charges on targets? (ionic interactions)
acidic and basic amino acids in proteins + phosphate backbone in nucleic acids
what are the acidic targets? (ionic interactions)
- Asp
- Glu
- Tyr
- Cys
what are the basic targets? (ionic interactions)
- Lys
- Arg
- His
what charge will acidic targets have?
negative = anionic