AP Biology Review
1/122
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Cohesion
Water sticks to itself through H-bonds
Adhesion
Sticking to other types of molecules through polarity
Capillary action
uses cohestion AND adhesion, goes against gravity, water goes up xylem
How does carbon allow for molecular diversity?
variations in carbon skeletons, can form macromolecules, and crucial for 4 types of macromolecules/polymers: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins
What does Nitrogen and carbon make up?
proteins and nucleic acids
What does phosphorous and carbon make up?
nucleic acids and some lipids
functional groups
Hydroxyl group, carbonyl group, carnoxyl group, amino group, sulfhydryl group, methyl group, phosphate group
Hydroxyl group
Polar
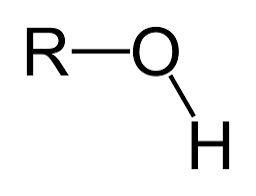
carbonyl group
polar
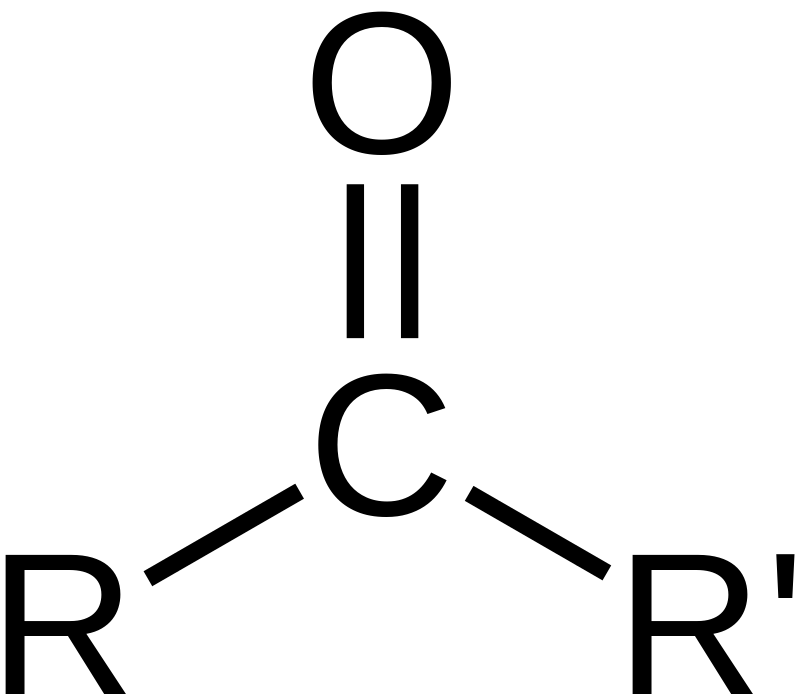
carboxyl group
polar
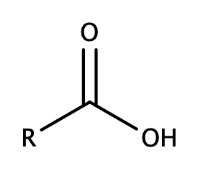
amino group
polar
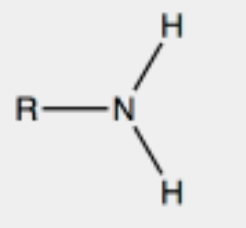
sulfhydryl group
polar
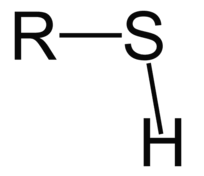
methyl group
nonpolar
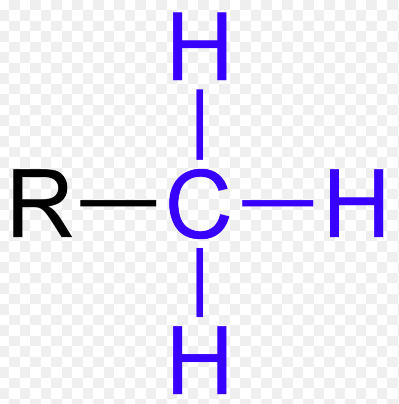
phosphate group
polar (H’s may be absent & replaced by -)
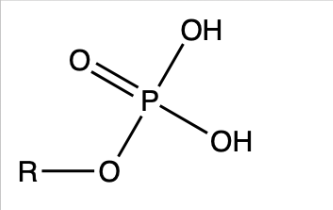
dehydration synthesis
bonds 2 monomers with the loss of H2O
Hydrolysis
breaks the bonds in a polymer by adding H2O
Storage polysaccharides
glucose monomers: starch for plants, glycogen for animals
Structural polysaccharides
Cellulose: tough substance that forms plant cell walls
Chitin: forms exoskeleton of arthropods
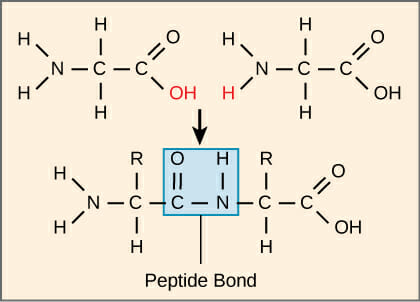
Forming peptide bonds
dehydration synthesis, CARBOXYL group (C-terminus) of one AA must be positioned next to the free AMINO group (N- terminus) of the other AA
molecules in proteins
CHONS
types of secondary protein folding structure
Beta pleated sheet- hydrogen bonds between peptide chains lying side by side(messy)
Alpha helix- hydrogen bonding between every 4th AA(organized)
triglyceride molecular structure
glycerol and 3 fatty acids via ESTER LINKAGE
What makes up fats?
glycerol (w hydroxyl group) and fatty acids (w carboxyl group)
ester linkage
bonds fats
saturated vs unsaturated fatty acid
saturated- full of H, no double bonds or kinks
unsaturated- some double bonds because not full of H, not straight, has kinks
phospholipid structure
Head: glycerol and phosphate group
tails: one saturated fatty acid and one unsaturated
what are steroids?
lipids with 4 fused rings w/ groups attached that determines steroid type
ex: testosterone & cholesterol
purines v pyrimidines
purines = 2 rings (pur As Gold)
pyrimidines = 1 ring, (CUT the py)
deoxyribose vs ribose
both 5 carbon sugars (pentose)
ribose less stable, extra OH, RNA
Nucleoside
nucleotide half without the phosphate group/backbone (aka sugar and nucleic acid)
What bond links nucleotides?
phoshodiester linkage
elements that make up nearly all living matter
CHON (95%) (PS both also important)
smooth ER function
Synthesizes lipids
Metabolizes carbs(does chemical reactions with carbs)
Detoxifies the cell
golgi complex structure
Contains flattened membranous sacs called CISTERNAE
Each cisternae is not connected
directionality:
CIS face: faces Rough ER
Function: receives vesicles from Rough ER
TRANS face: faecs membrane
Function: sends vesicles back out into the cytosol to other locations or to the plasma membrane to be secreted
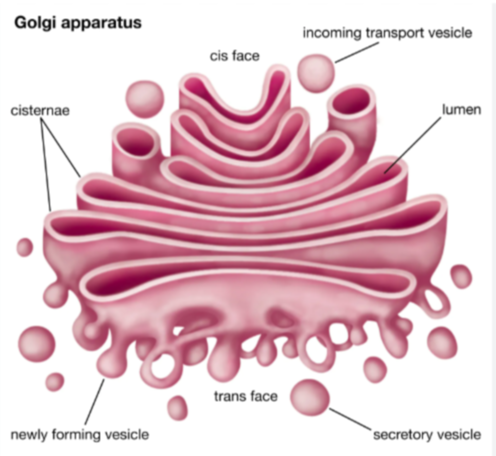
golgi complex function
Receives transport vehicles with materials from Rough ER
Modifies the materials(makes sure that new proteins are folded/modified correctly)
Sorts the materials
Adds molecular tags
Packages materials into new transport vesicles that EXIT the membrane via EXOCYTOSIS
Lysosome function
contains hydrolytic enzymes (breaks things down w hydrolysis)
digests things inside cell
involved in endocytosis
peroxisome function
some oxidative reactions and catalyzing
protects cell from H2O2
produces some energy?
metabolizes lipids maybe?
Food vacuole
Forms via PHAGOCYTOSIS(cell eating) and then digested by lysosomes
contractile vacuole
not in humans
controls amount of water in cell
central vacuole
found in plants
important for turgor pressure
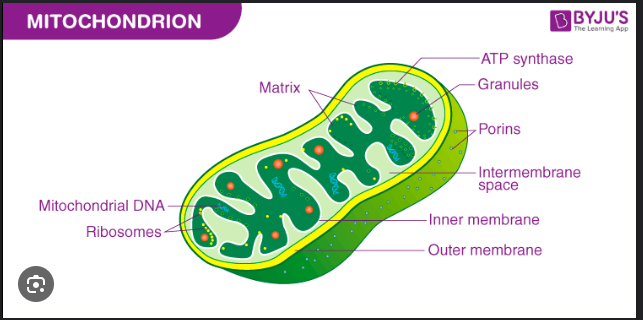
mitochondrial structure
outer membrane
intermembrane space
inner membrane (has folds called cristae that increase surface area)
enclosed in inner membrane is mitochondrial matrix, site of KREBS CYCLE
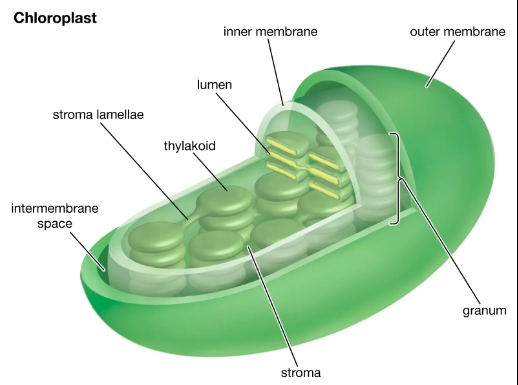
chloroplast structure
Thylakoids
Membranous sacs that can organize into stacks called GRANA
Light dependent reactions happen here
Contains the green pigment chlorophyll
inside thylakoid is lumen
Stroma
Fluid around the thylakoids
Location for the Calvin cycle/light Independent reactions
Contains:
Ribosomes
Chloroplast DNA
Enzymes
SA:V ratio
higher is more efficient for diffusion
fluidity of double membrane and temperature
Temperature affects fluidity
Unsaturated hydrocarbon tails help maintain fluidity at low temperatures
Kinked tails prevent tight packing which allows more things through
Cholesterol: helps maintain fluidity at high and low temperatures
High temp: reduces movement
Low temp: reduces tight packing of phospholipids
integral vs peripheral proteins
integral aka transmembrane proteins embedded
peripheral loosely bonded to membrane surface
amphipathic
part hydrophilic part hydrophobic
membrane carbohydrates
Important for cell to cell recognition
Glycolipids
Carbs bonded to lipids
Glycoproteins
Carbs bonded
Most abundant
transport proteins
channel and carrier proteins that are specific for substances that it facilitates movement for
channel proteins
Channel for ions and molecules to move through
Hydrophilic
Many are gated channels which means that they only allow molecules to pass when there is a stimulus
aquaporin
channel protein specific to water
carrier proteins
Undergo conformational changes for substances to pass through
Membrane potential
unequal concentration of ions across the membrane results in an electrical charge(electrochemical gradient)
Sodium-potassium pump
electrogenic pump
uses ATP and conformational changes
Animal cells will regulate their relative concentrations of Na+ and K+
3 Na+ goes OUT of the cell
2K+ goes INTO the cell
Results in a net +1 charge to the extracellular fluid
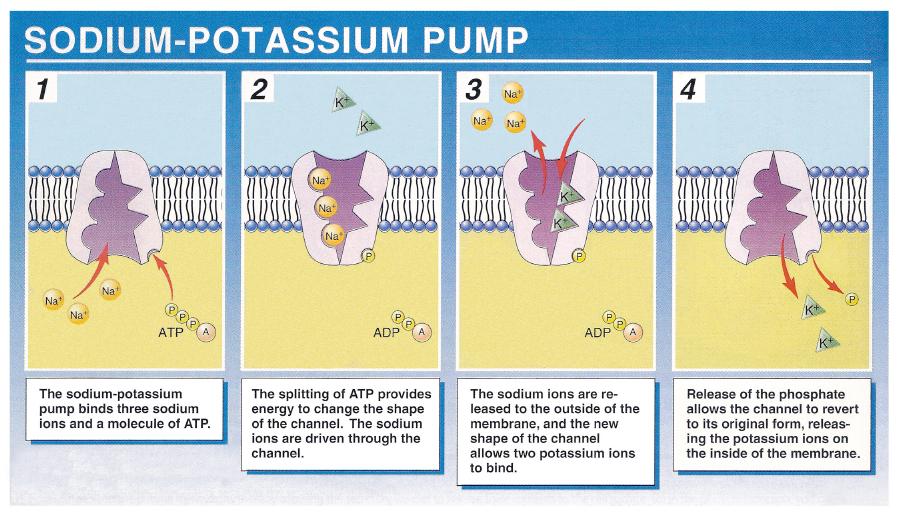
electrogenic pump
Proteins that generate voltage across membranes, which can be used later as an energy source for cellular processes
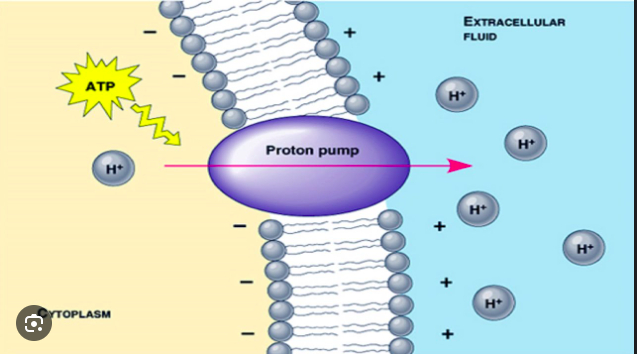
proton pump
Integral membrane protein that builds up a proton gradient across the cell
Used by plants, fungi and bacteria
Pumps H+ out of the cell
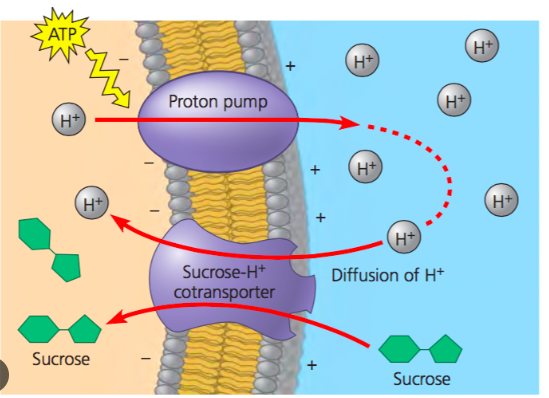
cotransport
The coupling of a favorable movement of one substance with an unfavorable movement of another substance
Uses the energy stored in electrochemical gradients(generated by the pumps) to move substances against their concentration gradient
Favorable movement: downhill diffusion
Unfavorable movement: uphill diffusion
Plants use cotransport for sugar and amino acids
Sucrose-H+ cotransporter
Sucrose goes into the the plant cell AGAINST its concentration gradient only if it is coupled with an H+ ion that is diffusing down its electrochemical gradient
exocytosis
the secretion of molecules via vesicles that fuse to the plasma membrane
endocytosis
the uptake of molecules from vesicles fused from the plasma membrane
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated
phagocytosis
endocytosis, larger food particles
when a cell engulfs particles to be later digested by lysosomes
Cell surrounds particles with pseudopodia
Packages particles into a food vacuole
Food vacuole fuses with a lysosome to be digested
pinocytosis
endocytosis, larger liquid molecules
nonspecific uptake of extracellular fluid containing dissolved molecules
Cell take in dissolved molecules in a protein coated vesicle
Protein coat helps to mediate the transport of molecules
receptor-mediated endocytosis
specific uptake of molecules via solute binding to receptors on the plasma membrane
Allows the cell to take up large quantities of a specific instance
When solutes bind to the receptors they cluster in a coated vesicle to be taken into the cell
isotonic solution
no net movement of water
The concentration of nonpenetrating solutes inside the cell=to that outside the cell
plasmolysis
plants
vacuole shrinks and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall
hypertonic solution
if solution is hypertonic to the cell
then: solution has a higher solute concentration, lower free water concentration
so: water leaves cell to balance concentrations, leaves cell shriveled/plasmolyzed
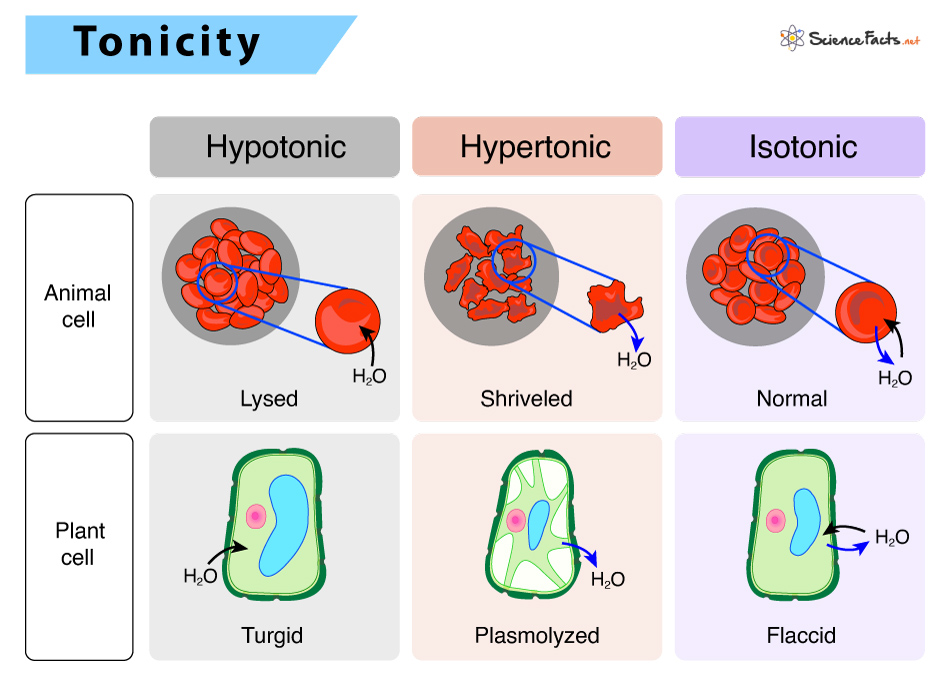
hypotonic solution
if solution is hypotonic to the cell
then: solution has a lower solute concentration, higher free water concentration
so: water enters cell to balance concentrations, cell swells/bursts aka lyses
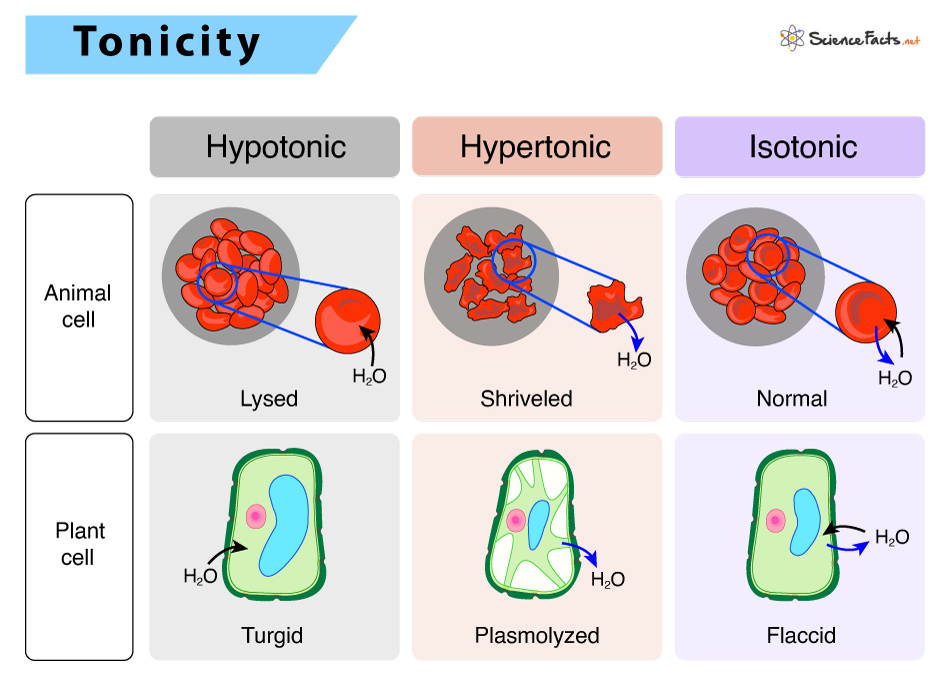
turgor pressure/turgidity
plants
the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall
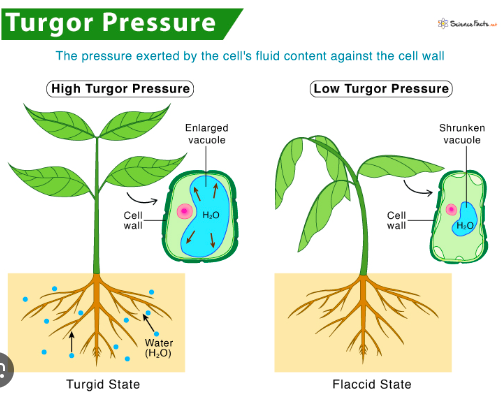
water potential relationships (formula on ref sheet)
Water will flow from:
HIGH water potential->LOW water potential
LOW solute concentration->HIGH solute concentration
HIGH pressure-> LOW pressure
catabolic pathways
break down, release energy
anabolic pathways
building, using up energy
exergonic
releases energy
endergonic
absorbs energy
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy CANNOT be created or destroyed
Energy CAN ONLY be transformed or transferred
2nd law of thermodynamics
Energy transformation increase the ENTROPY (disorder) of the universe
During energy transfers/transformations, some energy is unusable and often lost as heat
phosphorylation
ATP sends its terminal phosphate group to bind to something to give it energy for something like a conformational change, becomes ADP
cofactors
inorganic, help enzymes
coenzymes
organic, helps enzymes
allosteric site
not active site
photosynthesis redox reaction
Electrons are transferred with H+ (from split H2O) to CO2 reducing it to sugar (glucose)
stomata
pores in the leaves that allows CO2 in and O2 out
photosynthetic pigments
Chlorophyll a
Primary Pigment
Involved in light reactions
Blue/green pigment
Chlorophyll b
Accessory pigment
Carotenoids
Broaden the spectrum of colors that drive photosynthesis
Photoprotection: carotenoids absorb and dissipate excess light energy that could damage chlorophyll or interact with oxygen
Photosystems
Thylakoid membrane has 2 photosystems, system 2 comes first
reaction center and light capturing complexes (group of proteins stuck together to form a task)
Reaction center: a complex of proteins associated with chlorophyll a and an electron acceptor
Light capturing complexes: pigments associated with proteins
electron transport chain path/photosynthesis light dependent rxn
NADP+/NADPH electron carriers
PS2 gets energy from sun, excites an electron. Photolysis: H2O donates H+, O2 released as byproduct.
Electrons move through ETC and cytochrome, pumping H+ into lumen to create a gradient
PS1 takes energy from sun again, excites electron, and also uses past electrons, which reduces NADP+ to NADPH which goes onto calvin cycle
ATP Synthase makes ATP when protons passively diffuse through it. ADP + Pi → (powered by proton gradient/proton motive force) ATP
diffusion direction: lumen (High H+) → stroma (low H+)
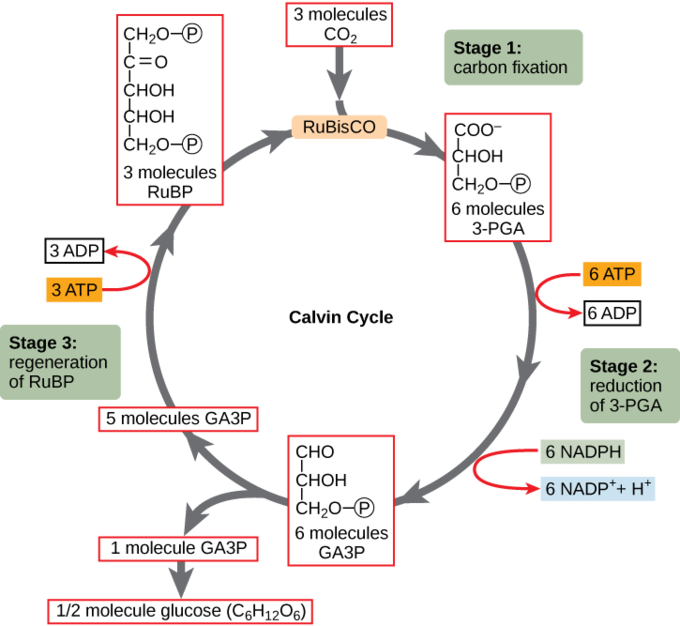
calvin cycle general
light independent
powers turning CO2 (inorganic) into usable organic C3 molecule glucose
3 stages: carbon fixation, reduction, RuBP regeneration
uses ATP and NADPH, REDUCES CO2
to net synthesize 1 G3P molecule, must take place 3 times bc need 3 CO2 per G3P but CO2 really goes in only one at a time
what is photolysis
using photon sun energy to break apart H2O
why is rubisco important
its an enzyme responsible for carbon fixation in calvin cycle
most abundant enzyme on the planet
what products of the light reactions are used in the calvin cycle
ATP & NADPH
final electron acceptor in photosynthesis
NADP+
what products of the calvin cycle are used in the light reactions
ADP, NADP+
what substrate uses rubisco enzyme to fix carbon dioxide?
RuBP
photosynthesis electron donor
water/H20
final electron acceptor
O2
carbon fixation (phase 1 calvin cycle)
CO2 combines w RuBP
rubisco enzyme catalyzes rxn
reduction (phase 2 calvin cycle)
energy inputs from ATP & NADPH lead to G3P formation
regeneration of RuBP (phase 3 calvin cycle)
3C compounds reorganize and combine to produce RuBP, uses some ATP
regenerates RuBP which helps to restart cycle
how does the concentrations of CO2, O2, and RuBP change as photosynthesis goes on and on and on
CO2 decreases, O2 increases, RuBP fluctuates
guard cells
near stomata
osmotic pressure changes shape causing them to swell. can create an opening for gas exchange or close to prevent water loss
photorespiration
when rubisco mistakenly binds to O2 instead of CO2, no sugar is produced and wastes energy
bad and can happen more when plants close stomata on hot days to prevent water loss because [O2] increases and [CO2] decreases
C3 plants
nothing special, 85% of plants
fixes CO2 directly from air
less efficient in hot and dry regions
photorespiration reduces photosynthesis by 25%
C4 Plants
minimizes photorespiration
separates calvin cycle and CO2 fixation into different cell types
bandle sheath cells
plants like sugarcane and corn
CAM Plants
minimizes photorespiration
fixates carbon at night and does the rest of carbon cycle during the day
can keep stomata closed during the day, preventing water loss due to heat, while opening them at night to decrease oxygen concentration
plants like pineapples and succulents