BIOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF CHANGING ALLELE FREQUENCIES
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is the gene pool in a population with high genetic diversity like
has a large number of alleles for each gene
What characteristics do populations with high genetic diversity tend to have
large in size
have gene flow with other populations' gene pools.
Why is genetic diversity important for populations
It allows populations to be resilient to environmental changes
Provides a higher chance that some individuals are adaptable and survive.
How does increased genetic diversity affect the chances of extinction
brings more variation into a population and reduces the chance of extinction
What are the potential biological consequences of increased genetic diversity
may lead to the addition of new alleles that can cause genetic disorders
Give an example of a genetic disorder introduced through increased genetic diversity
The cystic fibrosis allele introduced into Australian populations, a recessive genetic disorder affecting the mucus lining of the lungs
What does decreased genetic diversity lead to
limited variation in a population
making organisms more vulnerable to changes in selective pressures
thereby increasing the chance of extinction
What can greatly affect the genetic diversity of a population
Different events and various mechanisms that affect allele frequencies
What do large populations retain
high genetic diversity
What are the consequences of high genetic diversity in populations
higher adaptive capacity
potential for long-term survival
high resilience
What happens to genetic diversity in small, isolated populations
lose genetic diversity
What are the consequences of low genetic diversity in populations
lower adaptive capacity
weak potential for long-term survival
low resilience
What happens if a female cheetah mates with multiple males
Variability among the cubs is high\
the chance that all cubs will be susceptible to a new pathogen is low
What happens if a female cheetah mates with one male
Variability among the cubs is low
the chance that all cubs will be susceptible to a new pathogen is high
What usually happens to genetic diversity during natural selection and why
Decreased
During natural selection, a particular phenotype has a selective advantage, so particular alleles become more common, while others are removed
What usually happens to genetic diversity due to gene flow and why?
Increased
Usually, the movement of alleles results in new alleles coming into a population
What usually happens to genetic diversity due to genetic drift and why
Decreased
Random chance events may lead to a loss of alleles in a population
What usually happens to genetic diversity during a bottleneck event and why
Decreased
An event leading to the death of many members of a population may lead to a loss of alleles in a population.
What usually happens to genetic diversity due to the founder effect and why
Decreased
A population is descended from individuals with limited diversity in their genetic material
What usually happens to genetic diversity due to mutations and why
Increased
Mutations are the source of new alleles, increasing diversity in a population
What is the consequence of small populations with limited or no gene flow on genetic diversity
They generally have low genetic diversity
How does smaller population size affect inbreeding and genetic diversity
It increases the rate of inbreeding, which further reduces genetic diversity
What is the impact of low genetic diversity on a population's adaptability
It limits the population's ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions
Why are populations with low genetic diversity more vulnerable
They are more susceptible to disease and becoming extinct
Through which mechanisms can low genetic diversity occur in the wild
Through genetic drift mechanisms like the bottleneck effect and founder effect
How can low genetic diversity occur in domesticated settings
Due to selective breeding
What does the graph indicate about population size and genetic variation over time
The graph indicates that while population size can recover after a decline, genetic variation remains persistently low, highlighting a long-term loss in genetic diversity despite population growth.
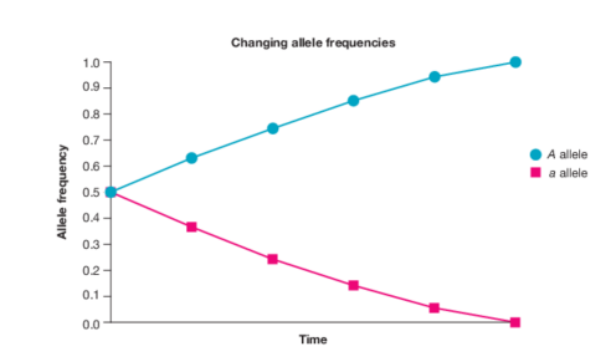
What does the graph suggest
Allele frequencies may be lost or fixed over time, resulting in decreased diversity.
While this shows a gradual change, the loss or fixation of an allele through genetic drift can be quite sudden
What event caused the Australian humpback dolphin to experience a bottleneck effect
An El Niño event between 1250 and 3750 years ago caused a warming of the dolphin's habitat, leading to a sudden decrease in its population size
What are the consequences of the bottleneck effect on the Australian humpback dolphin
The species is listed as vulnerable due to low genetic diversity and limited gene flow between its populations
When did cheetahs experience a bottleneck, and what was the consequence
Cheetahs experienced a bottleneck approximately 10,000 years ago, dramatically reducing their numbers and leading to inbreeding in the remaining small population
How does the genetic diversity of cheetahs compare to species with good genetic diversity
Species with good genetic diversity have around 20% variation in their alleles, while the cheetah population has only 1% variation
What are the consequences of limited genetic variation in cheetahs
caused a number of harmful mutations
reproductive challenges for male cheetahs
lethal genetic disorders
What is genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the amount of genetic variation in a population’s gene pool
Why is high genetic diversity beneficial for populations
Populations with high genetic diversity have a greater chance of successfully adapting to changing environments
Why are populations with low genetic diversity at risk
Populations with low genetic diversity are less likely to adapt to changing environments and are more likely to become vulnerable to extinction
What is antigenic drift?
Antigenic drift is when a point mutation alters a virus’ nucleic material, resulting in small changes so that it continues to be recognized and reacted to by the body’s immune system
What is antigenic shift?
Antigenic shift is when two or more strains of a virus combine to form a new strain with antigens from each of the original strains