ch 13. Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Obligatory intracellular parasites
require living host cells to multiply
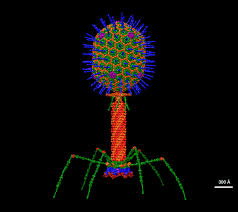
Bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria
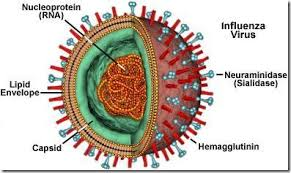
Animal virus
receptor sites are typically on the plasma membrane
virion
complete, fully developed viral particle
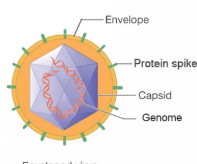
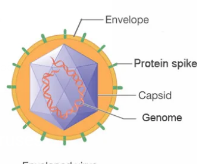
capsid
protein coat made of capsomeres (subunits)
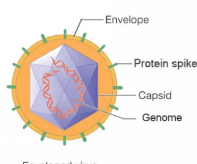
Envelope
lipid, protein, and carbohydrate coating on some viruses
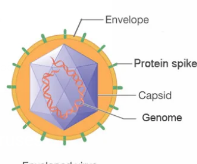
spikes
projections from outer surface
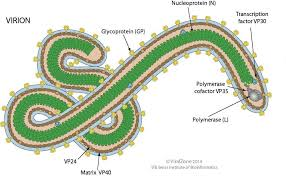
Helical viruses
hollow, cylindrical capsid that is helical (rabes; Ebola)
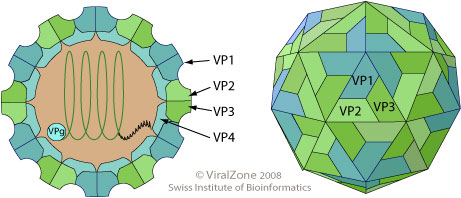
polyhedral viruses
many sided; Most are an icosahedron (20 triangular facets and 12
corners); adenoviruses and poliovirus
enveloped viruses
roughly spherical
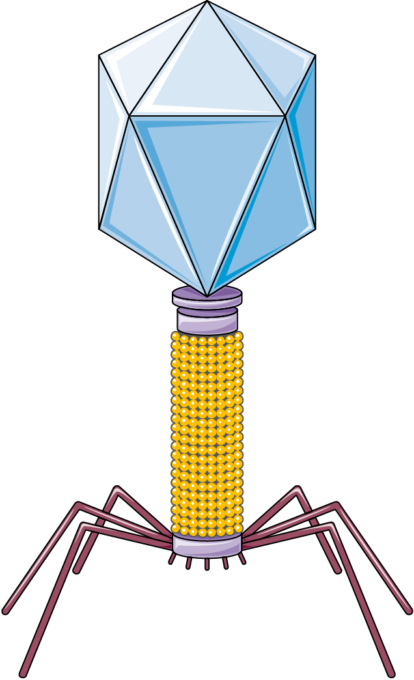
complex viruses
complicated structures (bacteriophage)
Viral species
a group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and ecological niche (host)
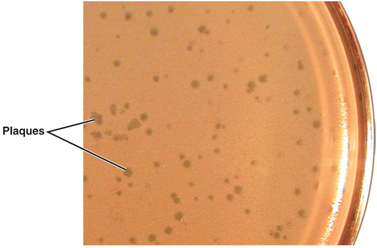
plaques (bacteriophages)
clearing on a lawn of bacteria on the surface of agar
plaque forming units (PFU)
Each plaque corresponds to a single virus; can be expressed
ELISA
virus is detected and identified by its reaction
with antibodies
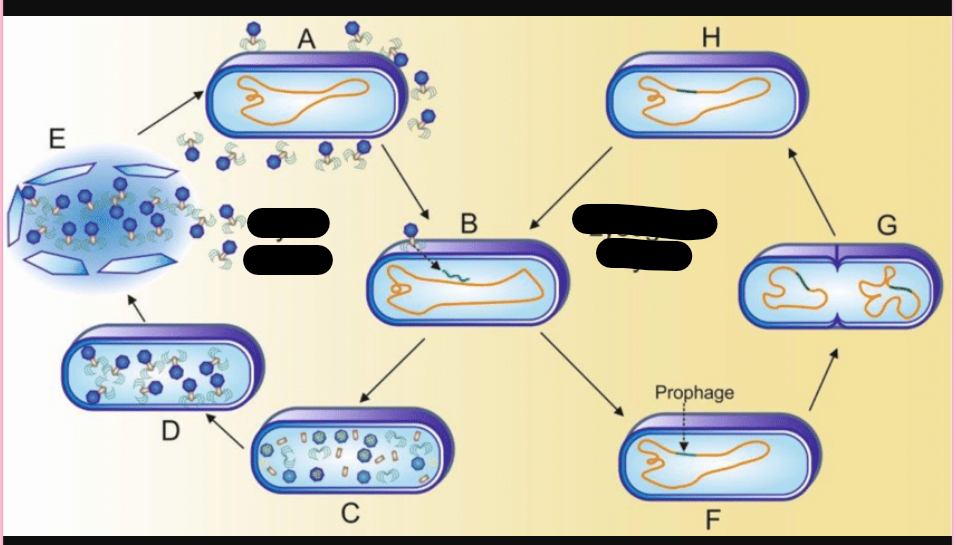
lytic cycle
phage causes lysis and death of the host cell (Tequatrovirus)
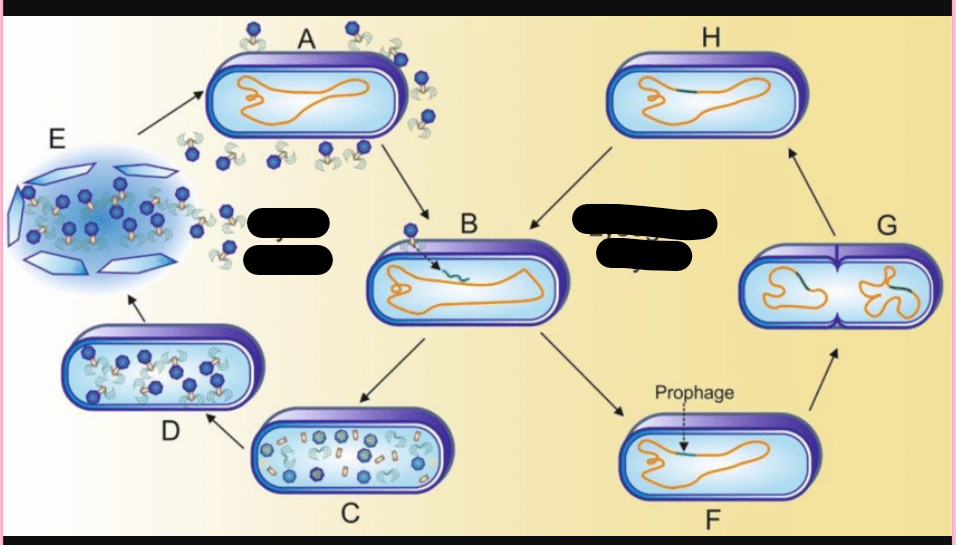
Lysogenic cycle
phage DNA is incorporated in the host DNA, phage conversion, specialized transduction
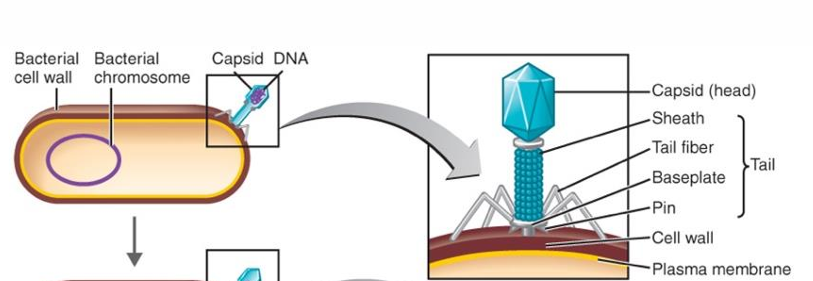
Attachment
phage attaches by the tail fibers to the host cell
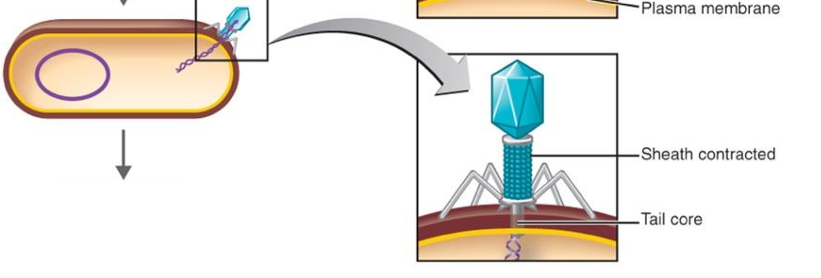
Penetration
phage lysozyme opens the cell wall; tail sheath contracts to force the tail core and DNA into the cell (similar to a hypodermic syringe)
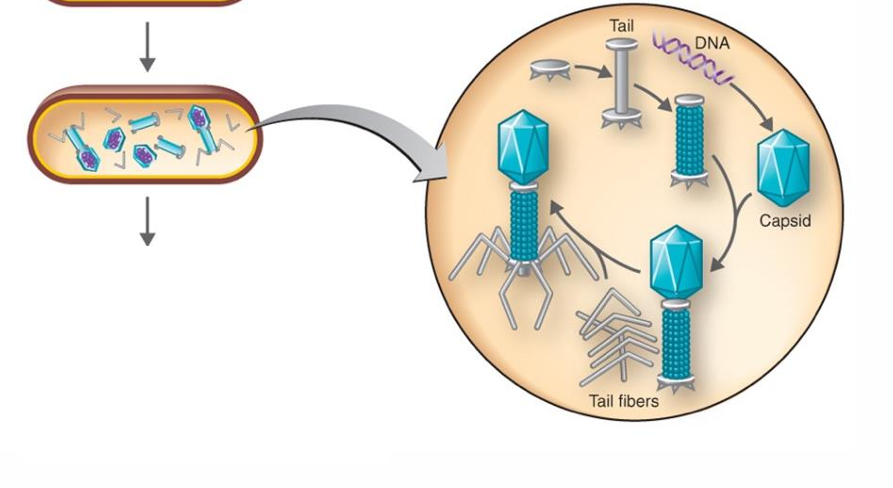
Biosynthesis
production of phage DNA and proteins; Host cell protein synthesis is halted
Maturation
assembly of phage particles
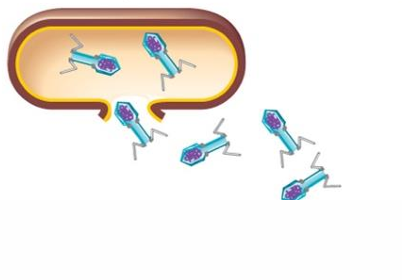
Release
Phage lysozyme breaks the cell wall
prophage
inserted DNA phage
Phage conversion
the host cell exhibits new properties, encoded by the prophage DNA ( production of diphtheria toxin by Corynebacterium diphtheriae)
Specialized transduction
Specific bacterial genes transferred to another bacterium via a phage (Changes genetic properties of the recipient bacteria)
Entry (animal virus)
receptor-mediated endocytosis or fusion
uncoating
(separating the viral nucleic acid from its capsid) by viral or host enzymes; or envelope if present
Biosynthesis: production of nucleic acid and proteins
production of nucleic acid and proteins
Maturation:
nucleic acid and capsid proteins assemble
ssRNA; + (sense) strand
Viral RNA serves as mRNA for protein synthesis
ssRNA -(antisense) strand
Viral RNA is transcribed to a + strand to serve as mR NA for protein synthesis
dsRNA
double stranded RNA
Sarcoma
cancer of connective tissue
Adenocarcinomas
cancers of glandular epithelial tissue
Proto-oncogenes:
genes that encode proteins involved in stimulating normal cell growth; Mutated proto-oncogenes become oncogenes
Oncogenes
transform normal cells into cancerous cells
Transformation:
cells acquire distinct properties leading to cancer
Oncogenic viruses
become integrated into the host cell’s DNA and induce tumors
A transformed cell harbors
a tumor-specific transplantation antigen (TSTA) on the surface and are often irregularly shaped
Oncolytic viruses:
infect and kill tumor cells or cause an immune response against tumor cells
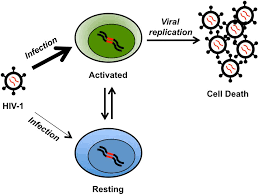
Latent virus
remains in asymptomatic host cell for long periods; all herpesvirus, may reactivate due to changes in immunity
Varicellovirus
Shingles
persistent viral infections
occurs gradually over a long period; is generally fatal (measles virus)
Plant viruses:
enter through wounds or via insects; plants cells are protected from diseases by their cell walls; wounds cause diseases
Viroids
short pieces of naked RNA
virusoids
viroids enclosed in a protein coat; only cause disease when plant cell is coinfected with a virus; need another virus
prions
Proteinaceous infectious particles
PrP^c:
normal cellular prion protein, on the cell surface
PrP^sc:
scapie protein; accumulates in brain cells, forming plaques
Disease is caused by the conversion of a normal host glycoprotein
PrP^c
an infectious misfolded form
PrP^sc