AP Human Geo Unit 7
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
cottage industry
small-scale businesses, typically operated out of a person’s home (individuals use traditional techniques to produce by hand)
prevalent before Industrial Revolution
enclosure movement
In England, which took agricultural land that was publicly owned by the community and privatized it.
output of farms more efficient!
small farmers left rural areas and to urban areas
Industrial Revolution led to…
mechanization of farming
larger market with better transportation (like steam engine)
rise of middle class
Industrialization led to imperialism because
nations sought more raw materials(gold, iron, rubber, oil, diamond)
Berlin Conference
Primary sector
extraction of natural resources
secondary sector
use raw materials to manufacture to products
often near to primary sector to reduce transportation cost
located near transportation infrastructure
value-added product
products that have been processed in a way that increases their overall value
wheat into flour, strawberry to jam
tertiary sector
jobs and activities that provide a service for other individuals
often near consumers (but changed due to development of technology)
lawyers, doctors
Quaternary sector
part of tertiary sector; centered around information collection, processing, sharing
journalist, teachers
quinary sector
part of tertiary sector; centers around making decisions
senator, CEO, executives
industrialization & emerging economy affects sectors of economy by…
dominating sector of economy shifts to primary→secondary→tertiary
core countries
countries with the most advanced economies and highest standard of living
semi-periphery countries
countries that have emerging economies that are industrializing
located between core & periphery countries in terms of development
periphery countries
countries that still rely heavily on the exportation of raw resources to more economically developed countries
multinational corporation
company that has business operations in at least one country other than its home country
break of bulk point
a location where goods are transferred from one mode of transportation to another
ports; cargo ships→ trucks
Alfred Weber’s Least Cost Theory
location of production should be in a place where transportation cost and labor cost is minimized, and economic benefit of agglomeration is maximized
agglomeration
clustering of different economic activities and industries in a specific geographic area
leads to shared resources, labor pools, and infrastructure
bulk reducing good
product that becomes lighter and easier to transport as production occurs
have heavy and bulky raw resources
more transportation cost
bulk gaining goods
product that becomes heavier and more difficult to transport as production occurs
resources are more lighter
criticisms of Alfred Weber’s Least Cost Theory
oversimplifies factors that influence location of production
→ like: government policies, cultural preferences, environmental concerns
formal economy
economic activities recognized by law and are overseen by the government
doctors, teachers, servors
informal economy
economic activities that are not regulated by the government
street vendors, domestic work, small businesses
don’t have consistent income
no legal protection
hard to measure
GDP
total value of all goods/services produced within a country’s borders over a specific amount of time
consumption + investment + government spending + (exports-imports)
Gross National Product (GNP)
total economic output produced by a country’s residents and businesses, regardless of their location, during a specific time period
Toyota in the US would count as US GDP & Japan’s GNP
if GNP>GDP…
more number of citizens living abroad
lot of foreign investment & production with country’s borders
Gross National Income (GNI)
total amount of income generated by a country’s residents and businesses, both domestically and abroad, in a given year
different from GNP, which calculates value of all goods/services produced
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
composite index that measures gender-based inequalities in health, education, and economic participation
inequality in reproductive health, empowerment, labor market
between 0-1
higher=more inequalities
Human Development Index (HDI)
an index that is used to measure the social and economic development of a country
looks at: life expectancy, expected years of schooling, gross national income per capita
0-1
higher=more human development
global gender gap index uses…
economic participation and opportunity
educational attainment
health and survival
political empowerment
informal economy lack
health insurance
paid sick leave
guaranteed minimum wage
sexual harassment laws
women in informal economy
less economically developed countries have more gender gap
→ lower education, discrimination
→ women have larger participation in informal economy
bank accounts allow
store money
access credit
expand business
solutions to solve gender gap
microloans: small loans to who are typically excluded from traditional banking services
support small businesses
microfinancing: category of financial services who lack access to traditional banking services
access to savings account, insurance, money transfer services
supported by NGOs
Rostow’s stages of economic growth (development)
(from bottom to top)
traditional society
→ subsistence farming
preconditions of takeoff
→ more infrastructure, investment, education
→ more jobs in secondary sector
takeoff
→ more secondary sector activities
→ increased urbanization, advanced technology
→ foreign nations take advantage of other nations
drive to maturity
→ state specializes more, focus on global trade
→ more tertiary sector jobs
→ focused on producing consumer good
High Mass Consumption
→ majority of jobs to tertiary
→ state is independent
→ economy centered around consumption than manufacturing
dependency theory
theory that suggests that developing countries are dependent on developed countries for their economic growth
why don’t economically developing countries negotiate better terms of trade?
core countries.multinational corps would turn to other developing countries
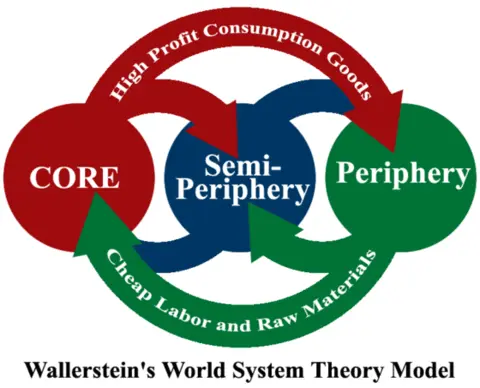
Wallerstein’s world system theory
views the global economy as a interconnected system of Core, Semi-periphery, and Periphery countries.
wealth flows from periphery to core countries
dependency and uneven power structure
affected by colonization
doesn’t account for NGO’s microfinancing & microloans
commodity dependence
when a country has more than 60% of its total exports made of just commodities
makes country’s economy vulnerable with price change (limits development)
Venezuela is commodity on dependent petroleum
→ 2014, when oil prices fell, collapse of economy
why trade
gain raw materials
get new technology, ideas
specialize to product service/good
strengthen political relationship
complementarity index score
measure used in economics and trade to assess the compatibility between the products and services that two countries produce and trade with each other
compares exports & imports
0-100
higher score=more likely to trade
comparative advantage
when countries have lower opportunity cost to produce compared to other countries
specialization leads to countries able to produce efficiently & export surplus & imports other products
tariff
tax imposed by government on imports
reduce trade and encourage domestic production
neoliberalism
economic and politic ideology that emphasizes individual freedom over government control, free markets, and free trade
free trade
WTO, IMF, Mercosur(South America), EU, OPEC
NAFTA
OPEC
union of oil producing countries
controls supply & price of oil
cons of neoliberalism
in favor of wealthier nations
deregulation from government can lead to unethical behavior
economy instability of developing countries as there is more competition
vulnerability of economy to global issues
more competition with global workforce
economic reconstructing
significant shift in production, employment, investment, trade patterns, or underlying economic systems and process
offshoring
process of relocating a business process or service to a foreign country
advantages of offshoring
lower labor costs
tax incentives
favorable economic conditions
outsourcing
when a business contacts out a service or job to an external provider in order to reduce their costs and increase their efficiency
economies of scale
as a company grows it is able to reduce the average cost to produce its product
international division of labor
concept that describes how countries utilize their comparative advantage to specialize in different economic activities, resources, and capabilities
special economic zone
regions within country that provide economic incentives to attract foreign investment and economic growth
tax breaks, less regulations, access to services
Free Trade Zones
regions where imported goods can be stored & processed without tariffs or trade barriers
is special economic zone, centered around ports
export processing zones
regions in a country that offer special economic regulations and incentives to promote the production of good/services for export
is special economic zone
e.g. Maquilladora in Mexico
multiplier effect
phenomenon where an original investment by an individual, business, government, or organization leads to a chain reaction of spending and icnreased economic activity
fordism
system of production that emphasizes mass production of standard goods
post-Fordism
system of production that emphasizes more flexible production methods where workers are trained in multiple tasks and produce custom goods
Just-in-time delivery
production and inventory control system where products and materials are delivered to the manufacturing plant precisely when they are needed in the production process
agglomeration
clustering of different economic activities and industries in a specific geographic area
growth poles
specific regions, cities, or economic sectors that are considered as centers of economic growth
Silicon Valley
Dubai, for business and tourism
deindustrialization
decline of industrial production in an economy
sustainabiltiy
use of Earth’s resources that ensures availability in the future
resource depletion & land degradation is led by
consumerism
more land usage (like irrigation, farmland…)
increased energy demand (fossil fuels)
ecotourism
promote conservation of environment
learning local culture
When sustainable development is encouraged(like SDGs)…
higher standard of living
more economic, social opportunities for individuals
protect environment