Muscalar System
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
The 3 Types of Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated Involuntary muscle
Found in 2 forms
Visceral (stomach/intestines)
Large sheets of cells in walls of hollow organs
Multiunit (iris)
Small discrete groups of cells
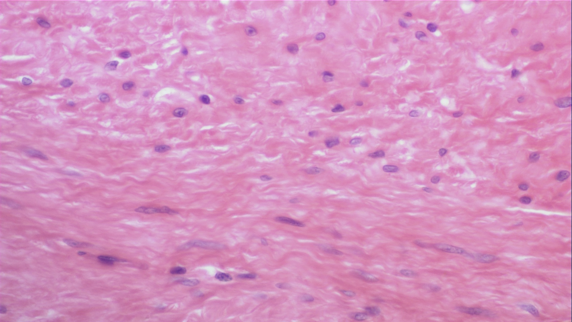
Visceral Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle that forms large sheets of cells in walls of hollow organs
Stomach, Intestine, Uterus, Urinary bladder, Blood Vessels, Respiration
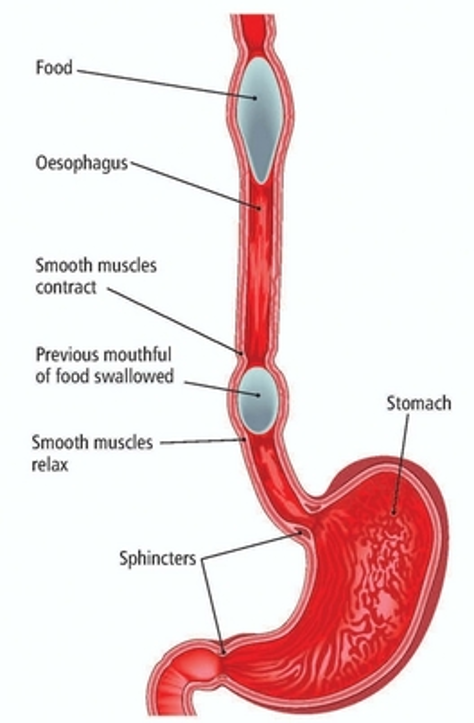
Does not carry out fine movements, but reacts in rhythmic waves
Peristalsis in the gastrointestinal tract
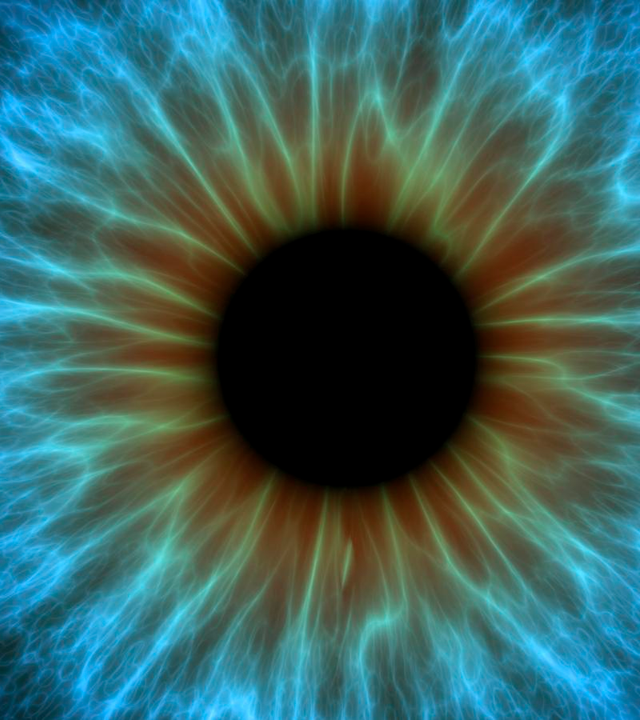
Multiunit Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle that forms small discrete groups of cells for delicate movement
Iris and Ciliary body of eye, Small blood vessels and air passageways
Require specific impulses from nervous system to contract
Changes in light, oxygen demand
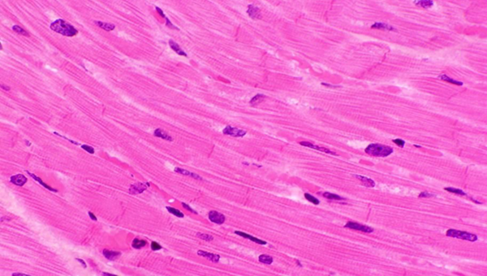
Cardiac Muscle
Striated Involuntary muscle
Forms most of the volume of the heart and makes up most of the walls of the cardiac chambers.
Contracts rhythmically, without external stimulation
Groups of cardiac muscle cells adopt the contraction rate of the most rapid cell in the group.
Skeletal Muscle
Striated Voluntary muscle
In charge of movement
“Cruise Control”
Breathing, swallowing, posture
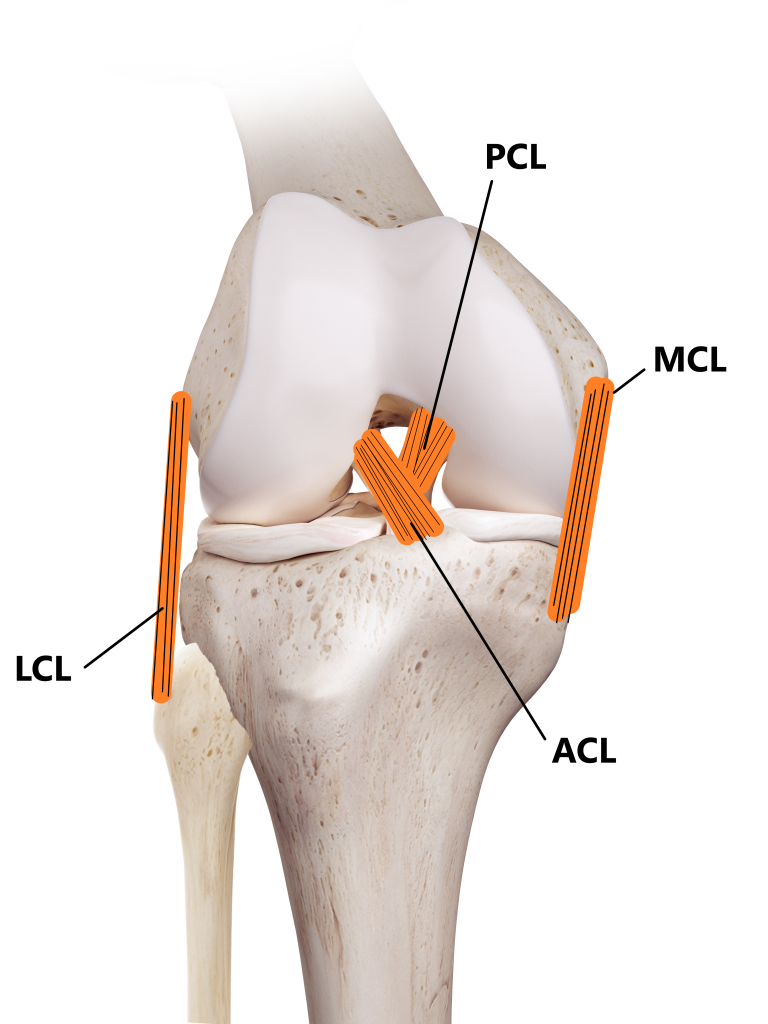
Ligaments
Attach bone to bone
Ex. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
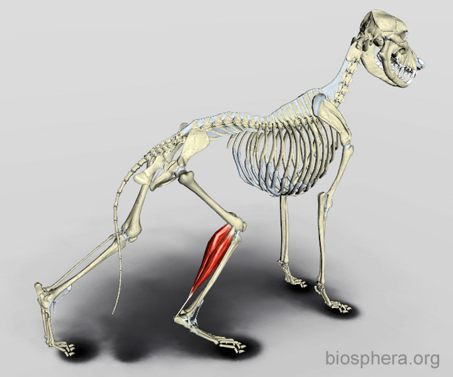
Tendons
Muscle to bone
Ex. Gastrocnemius tendon, Patellar tendon
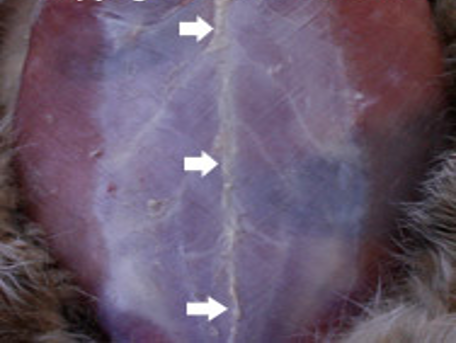
Aponeuroses
Muscle to bone or to another muscle
Ex. Linea alba
Muscle Actions
Have one job… move the skeleton
Stimulated by a nerve impulse > Contracts by pulling on its attachment sites on bone > Movement of bones and other structures
Work in groups, seldomly do they work alone
Prime mover (agonist)
Muscle group that directly produces a desired movement
Antagonist
Muscles that directly opposes the action
Synergist
Muscles that contracts at the same time as a prime mover and assists in the action.
Fixator
Muscles that stabilize joints to allow other movements to take place.
Extrinsic Muscles
Muscle that attach the limb to the body
Muscles originate on the neck and thorax and extend to the shoulder or forelimb
All domestic mammals have 8 extrinsic muscles including:
Superficial Pectoral
Deep Pectoral
Trapezius
Latissimus dorsi
Serratus ventralis
Intrinsic Muscles
Muscles that attach only to the bones within the limb
Includes:
Infraspinatus
Supraspinatus
Subscapularis
Triceps brachii
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Extensor carpi radialis
Common digital extensor
Superficial digital flexor
Deep digital Flexor
Muscles of Neck and Head
Muscles that are:
Vital for neck and head movement
Necessary for chewing
Important injection site for food producing animals
Muscles of the Pelvic Limb
Muscles that:
Help propel the animal forward when walking or jumping.
Have large musculature and are a common place for intramuscular injections.
Location in relation to the sciatic nerve is important.
Muscles of the Abdominal Wall
Muscles that work to flex the ventral column and assist in:
Urination/defecation, Parturition, Vomiting
The lateral and ventral abdominal wall is made up of four pairs of muscles:
External abdominal oblique
Internal abdominal oblique
Transversus abdominis
Rectus abdominis