Fungi (Topic 4)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
Unicellular, flagellated ancestor
Opisthokonta Derived Trait
2
New cards
470 mya
Fungi colonized \~___ ___ (before plants!)
3
New cards
Characteristics of Fungi
* mostly haploid lifecycle
* no photosynthesis
* heterotrophs - digest externally through hydrolases
* cell wall contains chitin
* no photosynthesis
* heterotrophs - digest externally through hydrolases
* cell wall contains chitin
4
New cards
Body structure of fungi
can either be…
* single celled
* yeasts only
* multicellular
* ==mycelium== (pl. mycelia) = fungal body that grows in & around food source
* ==hyphae== = long branched filaments
* single celled
* yeasts only
* multicellular
* ==mycelium== (pl. mycelia) = fungal body that grows in & around food source
* ==hyphae== = long branched filaments
5
New cards
Mycelium
Fungal body that grows in & around food source
6
New cards
Hyphae
Long branched filaments
7
New cards
Hyphae functions
* Structure
* Feeding
* Predatory
* Mutualistic
* like ==haustoria== found in ==mycorrhizae==
* Reproductive
* ==Aerial hyphae==: aids in spore dispersal
* ==Fruiting bodies==: multicellular, complex
* ie: mushrooms
* Feeding
* Predatory
* Mutualistic
* like ==haustoria== found in ==mycorrhizae==
* Reproductive
* ==Aerial hyphae==: aids in spore dispersal
* ==Fruiting bodies==: multicellular, complex
* ie: mushrooms
8
New cards
Haustoria
Penetrate plant tissue - parasitic or mutualistic
9
New cards
Mycorrhizae
Mutualism between fungi and plant root
10
New cards
Spore
* A single cell
* Starts a new individual with haploid
* In sexual OR asexual reproduction of fungi
* dispersed by
* wind
* H2O
* animals
* Starts a new individual with haploid
* In sexual OR asexual reproduction of fungi
* dispersed by
* wind
* H2O
* animals
11
New cards
Sexual
This life cycle is ______
1. 2 haploid (n) fungi
1. hyphae releases pheromones & test compatibility
2. ==Plasmogamy== (fuse cell membranes)
1. n+n cell
2. two nuclei in the same cell
3. results in: ==heterokaryon== (cells contain multiple haploid nuclei (n+n))
3. Time passes
4. Environmental change triggers ==karyogamy==: nuclei fuse
1. 2n cell = zygote
5. Meiosis → 4 (n) cells
1. 2 haploid (n) fungi
1. hyphae releases pheromones & test compatibility
2. ==Plasmogamy== (fuse cell membranes)
1. n+n cell
2. two nuclei in the same cell
3. results in: ==heterokaryon== (cells contain multiple haploid nuclei (n+n))
3. Time passes
4. Environmental change triggers ==karyogamy==: nuclei fuse
1. 2n cell = zygote
5. Meiosis → 4 (n) cells
12
New cards
Alleles
In a sexual life cycle of a fungus, # of mating types depends on # of _______
13
New cards
Plasmogamy
Fusion of cell membranes → n+n cell
14
New cards
Heterokaryon
Cell that contains multiple haploid nuclei (n+n)
15
New cards
Karyogamy
Nuclear fission → 2n cell = zygote
16
New cards
Asexual
This life cycle is _______
1. spores
2. germination (mitosis)
3. mycelium
1. spore-producing structures
1. spores
2. germination (mitosis)
3. mycelium
1. spore-producing structures
17
New cards
Filamentous fungi (spores via mitosis), single-celled yeast (cell division/budding)
Two main types of asexual fungi
18
New cards
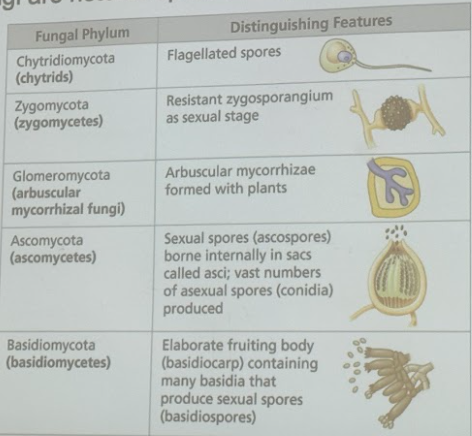
Chytrids, Zygomycetes, Glomeromycetes, Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes
5 Phyla of Fungi
19
New cards
Chytrids
* basal fungal group
* derived characteristics: flagellated spores (it’s ancestral to other fungal groups, which lack flagella)
* zoospores unique to ________
* terrestrial, freshwater, marine
* derived characteristics: flagellated spores (it’s ancestral to other fungal groups, which lack flagella)
* zoospores unique to ________
* terrestrial, freshwater, marine
20
New cards
Zoospores
Flagellated spores unique to chytrids
21
New cards
Zygomycetes
* derived characteristics: zygospores in zygosporangia
* most are soil decomposers
* ex: black bread mold (*rhizopus stolonifer*)
* most are soil decomposers
* ex: black bread mold (*rhizopus stolonifer*)
22
New cards
Glomeromycetes
* derived characteristics: ==mycorrhizae== = symbiotic relationship w/ most plants
* mutualism present in >80% of plants
* help uptake water & ions
* mutualism present in >80% of plants
* help uptake water & ions
23
New cards
Ascomycetes
* derived traits:
* spores contained in sacs (ascopores?)
* can be single-celled or filaments
* largest number of known species (\~65k)
* examples (so many!)
* penicillium
* morels and truffles
* baker’s/brewer’s yeast
* component of lichens (will discuss later)
* spores contained in sacs (ascopores?)
* can be single-celled or filaments
* largest number of known species (\~65k)
* examples (so many!)
* penicillium
* morels and truffles
* baker’s/brewer’s yeast
* component of lichens (will discuss later)
24
New cards
Basidiomycetes
* spores in basidiocarp (gills) (basidiospores?)
* “mushrooms”
* no asexual stage in life cycle
* examples
* bracket fungi
* puff balls
* wheat rust, corn smut
* edible mushrooms
* “mushrooms”
* no asexual stage in life cycle
* examples
* bracket fungi
* puff balls
* wheat rust, corn smut
* edible mushrooms
25
New cards
* Decomposers
* Mutualists
* Parasites/Mycosis
* Practical Uses
* Mutualists
* Parasites/Mycosis
* Practical Uses
Ecological Importance of Fungi
26
New cards
Decomposers
* break down organic material (including cellulose & lignin)
* essential - recycle inorganic nutrients
* no decomposers, no life
* essential - recycle inorganic nutrients
* no decomposers, no life
27
New cards
Mutualists
* Absorb nutrients from host, provide some benefit to them
* Leaf clutter ants and fungi
* Fungus plant examples:
* mycorrhizae
* Mutualism between fungi and plant root
* Endophytes
* inside leave or stems, make toxins
* deter herbivores
* Lichen
* symbiotic association
* fungus and photosynthetic microorganism
* fungal part = ascomycetes
* provides habitat for microbe growth
* protection, retains water & nutrients
* Leaf clutter ants and fungi
* Fungus plant examples:
* mycorrhizae
* Mutualism between fungi and plant root
* Endophytes
* inside leave or stems, make toxins
* deter herbivores
* Lichen
* symbiotic association
* fungus and photosynthetic microorganism
* fungal part = ascomycetes
* provides habitat for microbe growth
* protection, retains water & nutrients
28
New cards
Parasites
* fungal infection
* ==mycosis== = fungal infection in an animal
* examples
* thrush: fungal infection in baby’s mouth & mom’s nipples
* ringworm: contagious fungal infection on flush (antifungal treatment), related to athlete’s foot
* Ergots on rye: on plants (common in Europe during wet summers)
* ==mycosis== = fungal infection in an animal
* examples
* thrush: fungal infection in baby’s mouth & mom’s nipples
* ringworm: contagious fungal infection on flush (antifungal treatment), related to athlete’s foot
* Ergots on rye: on plants (common in Europe during wet summers)
29
New cards
Practical Uses
* medicine
* antibiotic production
* research
* eukaryotic genetics
* consumption/food
* blue cheese, wine & beer
* yeast
* ferments sugars into CO2 & alcohol
* antibiotic production
* research
* eukaryotic genetics
* consumption/food
* blue cheese, wine & beer
* yeast
* ferments sugars into CO2 & alcohol
30
New cards
Summary
31
New cards
I & III
Identify which of the following is/are characteristic of fungi
I. reproduce with spores
II. photosynthetic
III. absorptive heterotrophy
IV. cellulose cell wall
I. reproduce with spores
II. photosynthetic
III. absorptive heterotrophy
IV. cellulose cell wall