AQA Physics Particle Model of Matter
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Solid
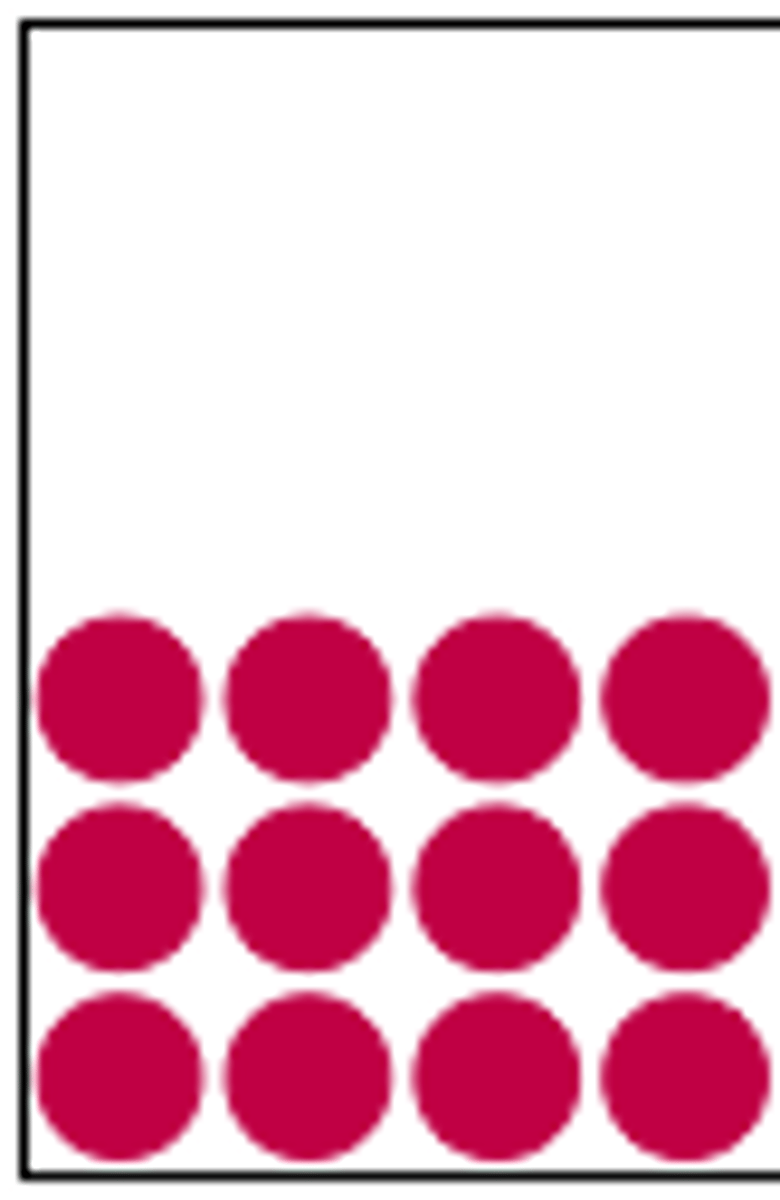
The state of matter where the particles are linked by strong forces. They are packed closely together and move very little. The particles usually form a regular and specific pattern.
Liquid
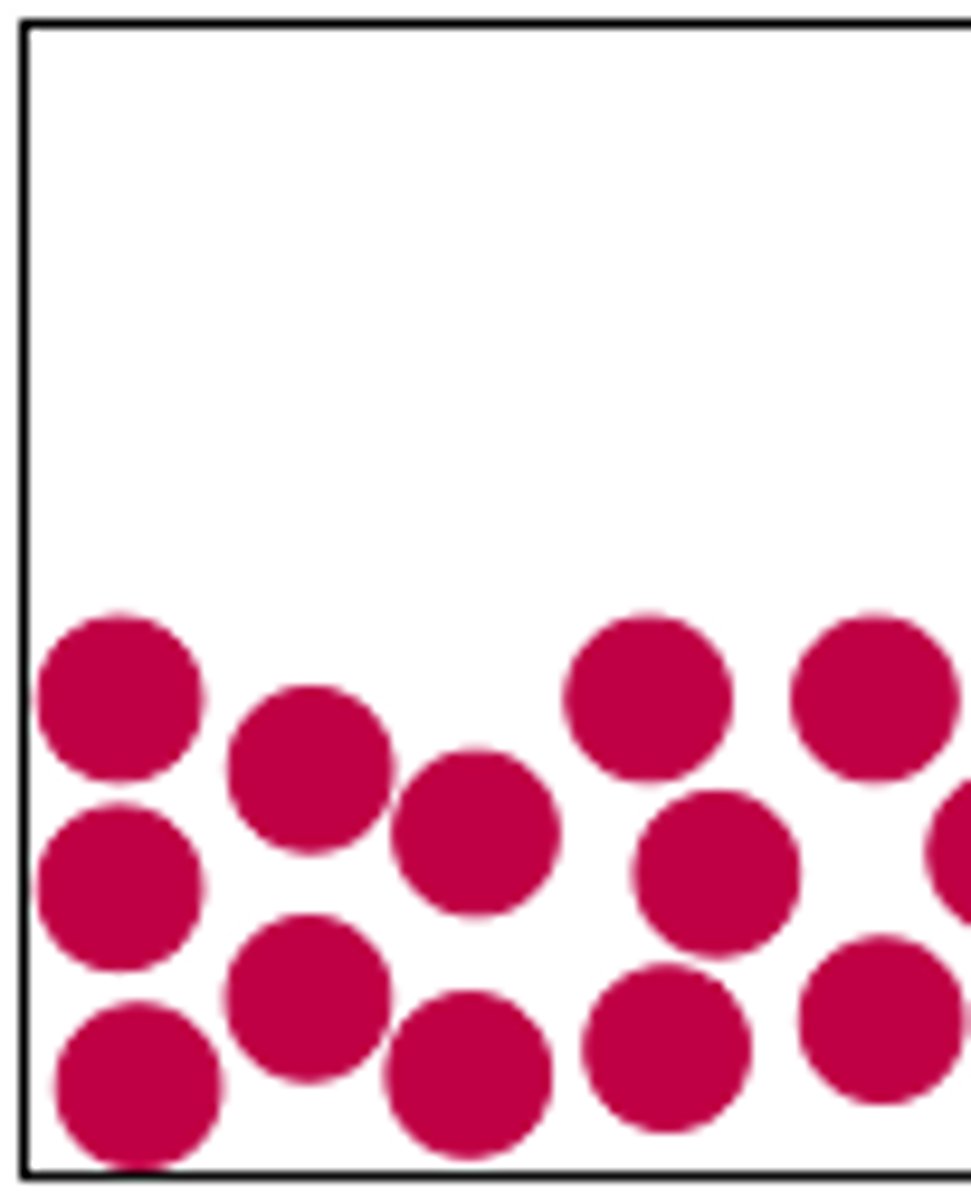
The state of matter where the particles have weaker bonds. They are still tightly packed but may move around each other.
Gas
The state of matter where particles are far apart and are in constant random motion. There is no interactive between the particles.
Melting Point
The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid .
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
Melting
When a solid changes to a liquid.
Boiling
When a liquid changes a gas at the boiling point
Evaporating
When a liquid changes to a gas below the boiling point
Condensing
When a gas changes to a liquid.
Physical Change
A change that does not produce a new substance. If the change is reversed the substance recovers its original properties.
Internal Energy
The total energy in the kinetic and potential stores of all the particles (atoms and molecules) that make up a system.
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of a substance by one degree Celsius. Often represented by the symbol 'c'. Its unit it J/kg°C.
Specific Latent Heat
The amount of energy required to change the state of one kilogram of the substance with no change in temperature. Often represented by 'L'. Its unit is J/kg..
Gas pressure
When molecules collide with the wall of their container they exert a force on the wall. The total force exerted by all of the molecules inside the container on a unit of area of the wall is the gas pressure.
Kinetic Theory
The theory that explains the different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) by the arrangement and energies of their particles.
Solid (particle diagram)

Liquid (particle diagram)

Gas (particle diagram)
Volume
The amount of space that a substance or object occupies, or that is enclosed within a container. Often represented by 'V'.
Metres cubed (m³)
The unit of volume.
Density
The mass per unit volume of a material. It can be thought of as representing how tightly packed the particles are within the material. Often represented by 'ρ'. The unit of density is kg/m³.
kg/m³
The standard unit of density.
Kinetic Theory Of Matter
Particle model of solids, liquids and gases which describes their properties.
States Of Matter
A form that substances take (e.g. solid, liquid and gas).
Change Of State
When a substance changes from one state of matter to another (e.g. a solid changing into a liquid).
Solidifying
When a liquid changes into a solid.
Freezing
Another word for when a liquid changes into a solid.
Evaporation
When a liquid changes into a gas.
Condensation
When a gas changes into a liquid.
Sublimation
When a solid changes into a gas when it is heated without becoming a liquid first.
Reversible Change
A change to a substance, which when reversed, allows the substance to recover its original properties.
Conservation Of Mass
The law that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction or change of state. In a closed system there is no net change to the amount of mass in the system if a chemical reaction or a change of state occurs.
Degrees Celsius (°C)
The unit of temperature and temperature change.
Latent Heat
The energy needed for a substance to change state.
Specific Latent Heat Of Fusion
The amount of energy required to change one kilogram of a solid into a liquid with no change of temperature.
Specific Latent Heat Of Vaporisation
The amount of energy required to change one kilogram of a liquid into a gas (vapour) with no change of temperature.
Heating Curve
A graph which shows how the temperature of a substance changes as it is heated.
Cooling Curve
A graph which shows how the temperature of a substance changes as it is cooled.
Random Motion
The unpredictable path that an individual gas particle follows.
Pressure
The total force exerted by all the molecules inside a container on a unit area of the walls of the container. Often represented by 'p'.
Pascals (Pa)
The unit of pressure.