M-mode, Basic Measurements, Doppler Basics and TDI
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is located on the x-axis and y-axis in m-mode?
X = Time
Y = Distance
Identify this image.
PLAX image showing LA and AV
RV
Aortic root
AV leaflets opening
LA
Identify this image.
PLAX image showing LA and AV
Identify this image.
PLAX or PSAX image showing MV
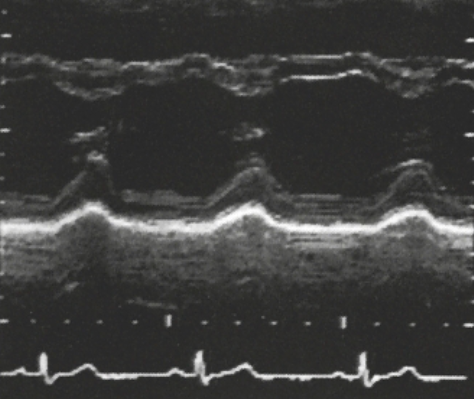
IVS
RV
LVOT
Anterior MV leaflet
Posterior MV leaflet
Posterior wall
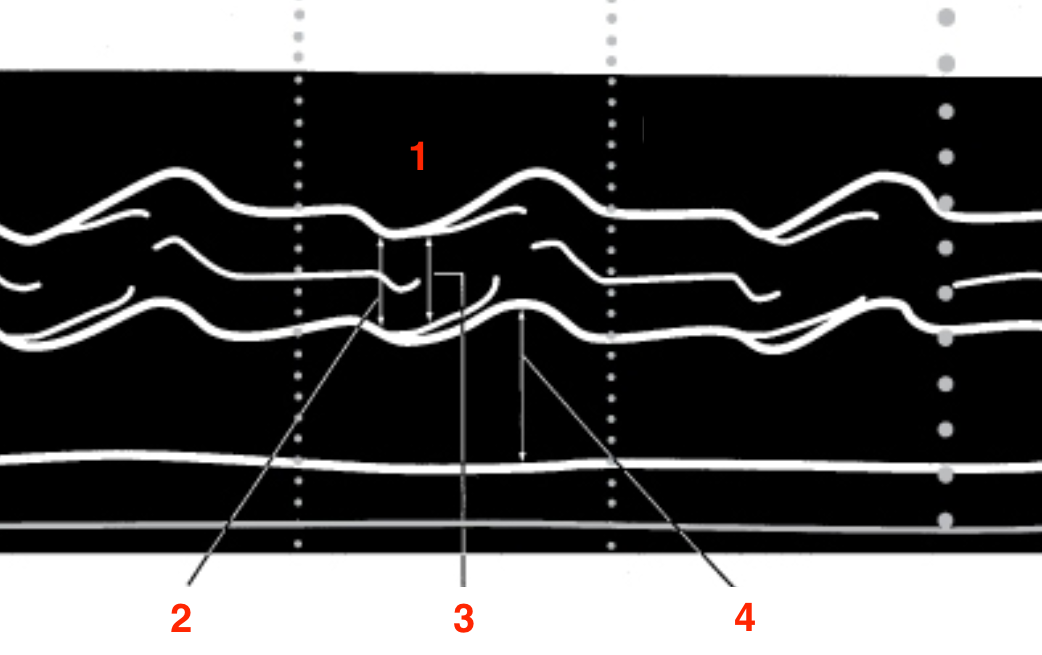
Identify this image.
PLAX or PSAX image showing MV
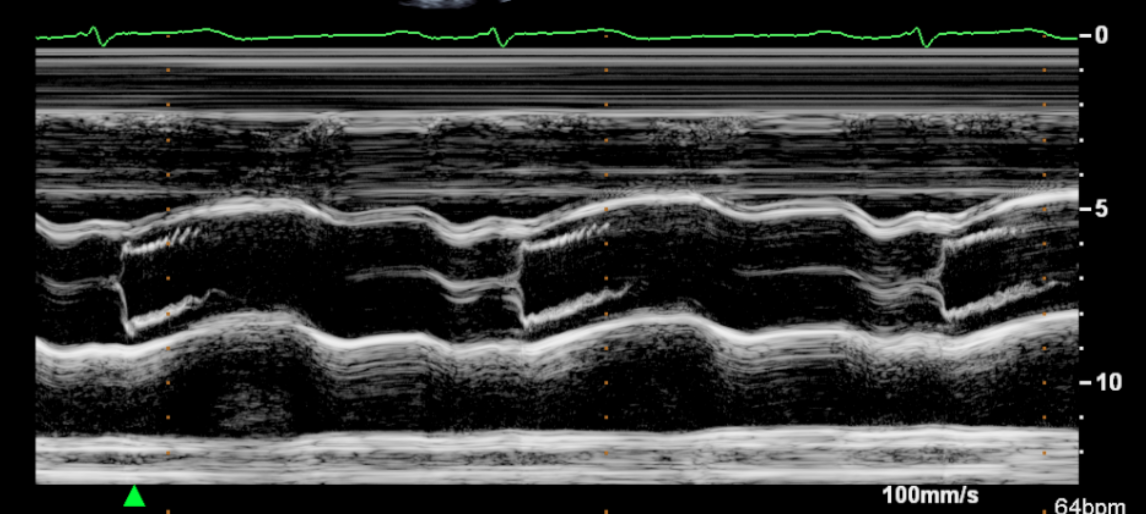
Identify this image.
PLAX or PSAX image showing LV
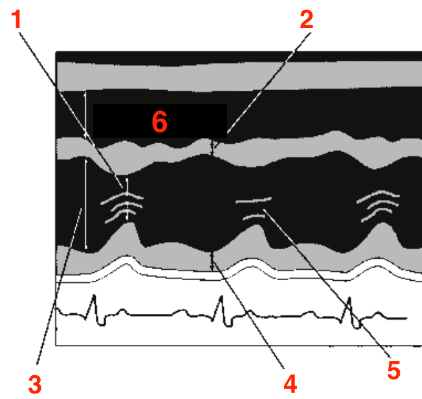
LV end systolic dimension
IVS
LV end diastolic dimension
LV posterior wall
Chordae
RV
Identify this image.
PLAX or PSAX image showing LV
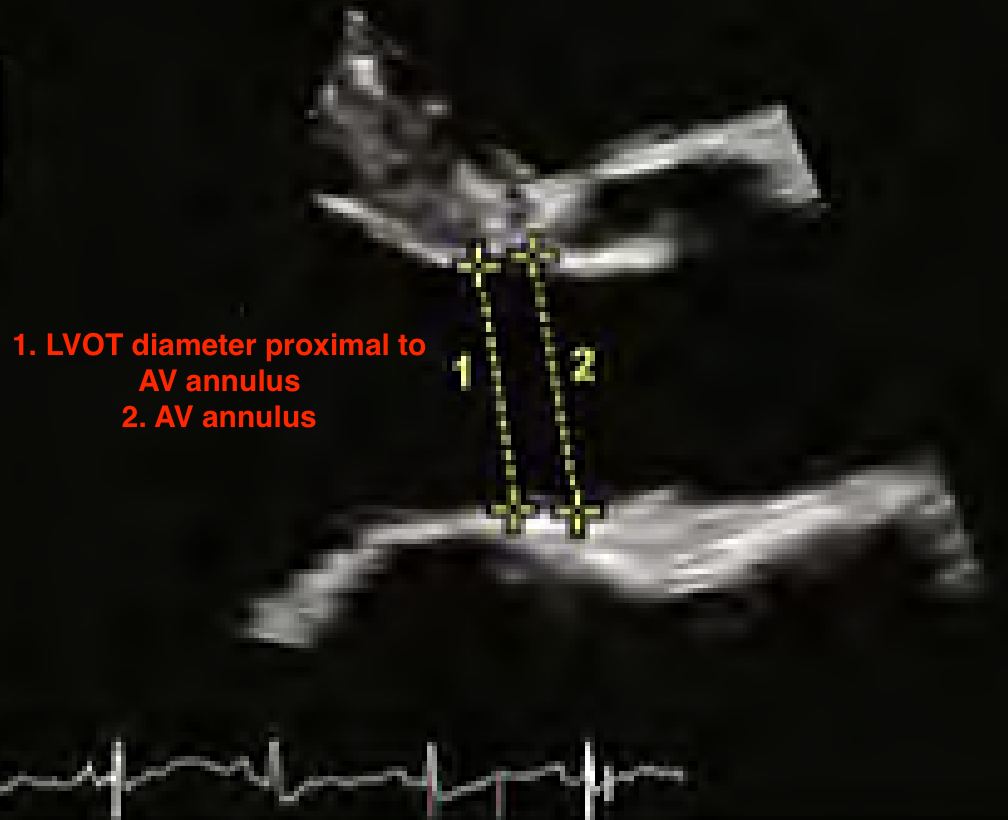
How do you measure the LVOT?
PLAX
Mid systole
Inner to inner
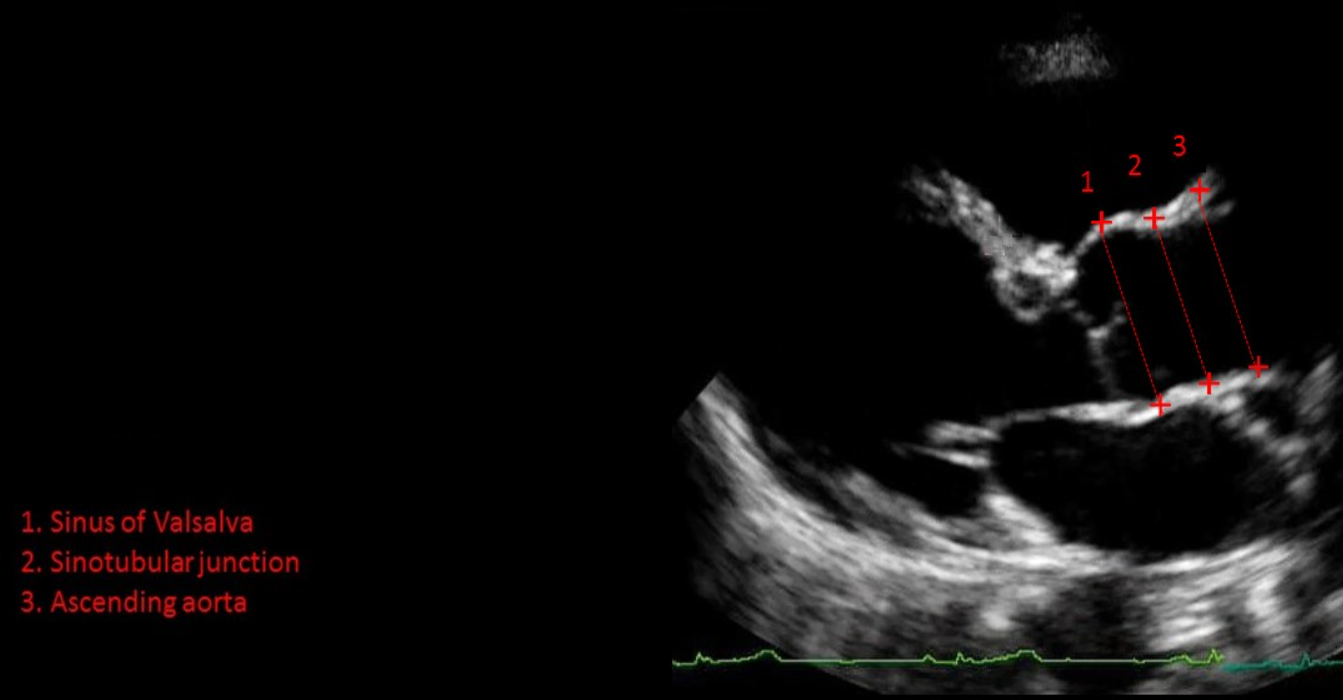
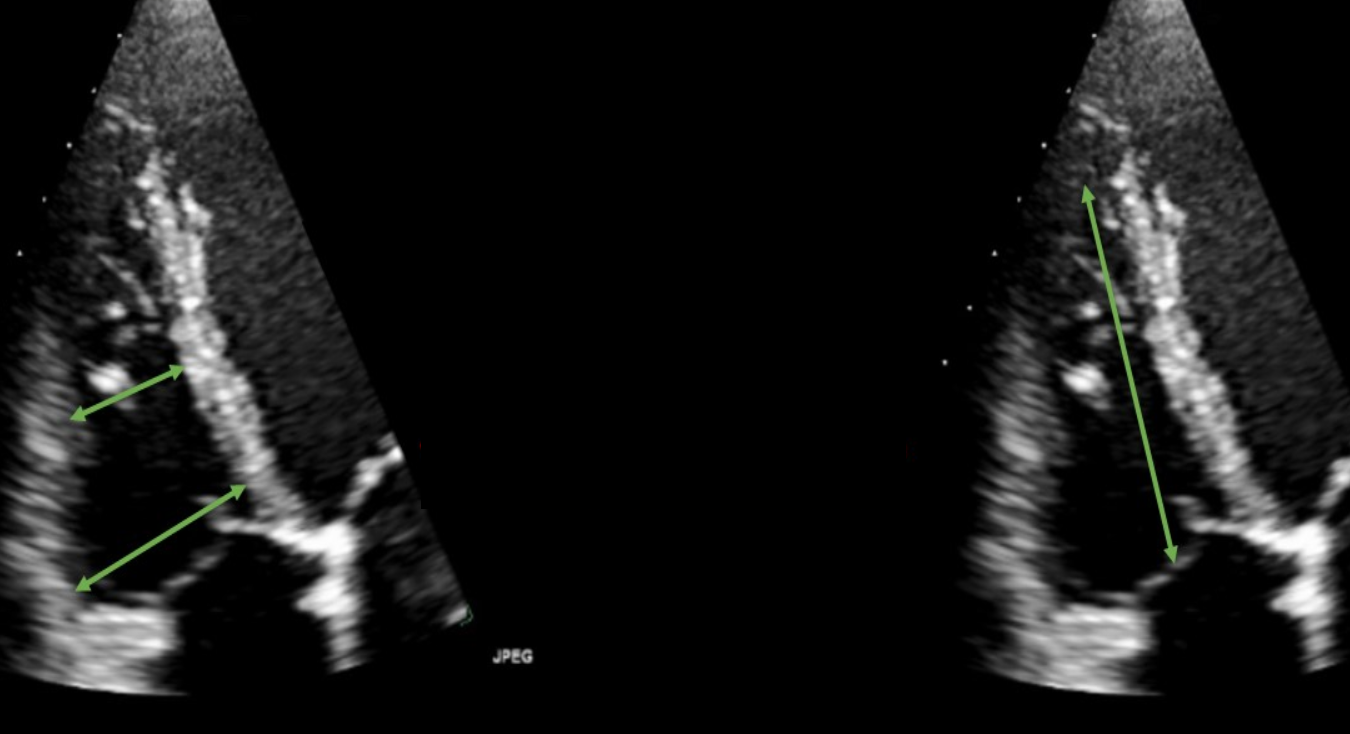
How do you measure the aortic root, STJ, and ascending aorta?
PLAX
End-diastole (before AV opens)
Leading edge to leading edge
How do you measure the LV size or Linear Meas in end-diastole?
PLAX
End-diastole
LARGEST LV diameter
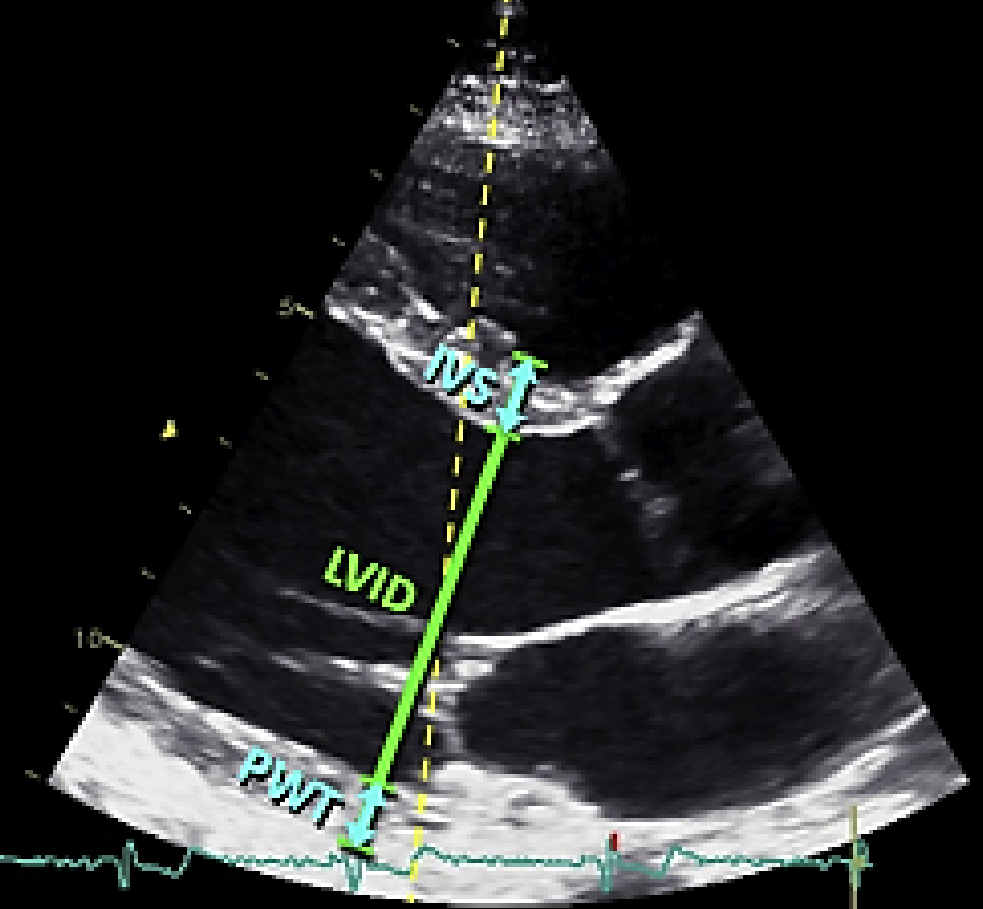
How do you measure the LV size or Linear Meas in systole?
PLAX
End-systole
SMALLEST LV diameter
How do you measure LA diameter?
PLAX
End-systole
Inner to inner with caliper line perpendicular to LA posterior wall
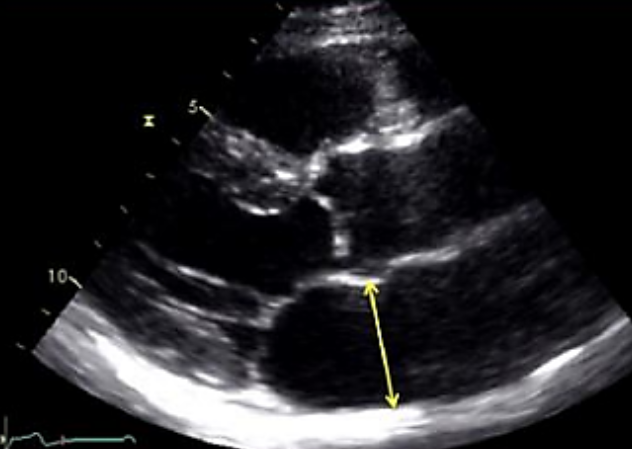
What is the normal value for LA diameter?
Men: < 4 cm
Women: < 3.8 cm
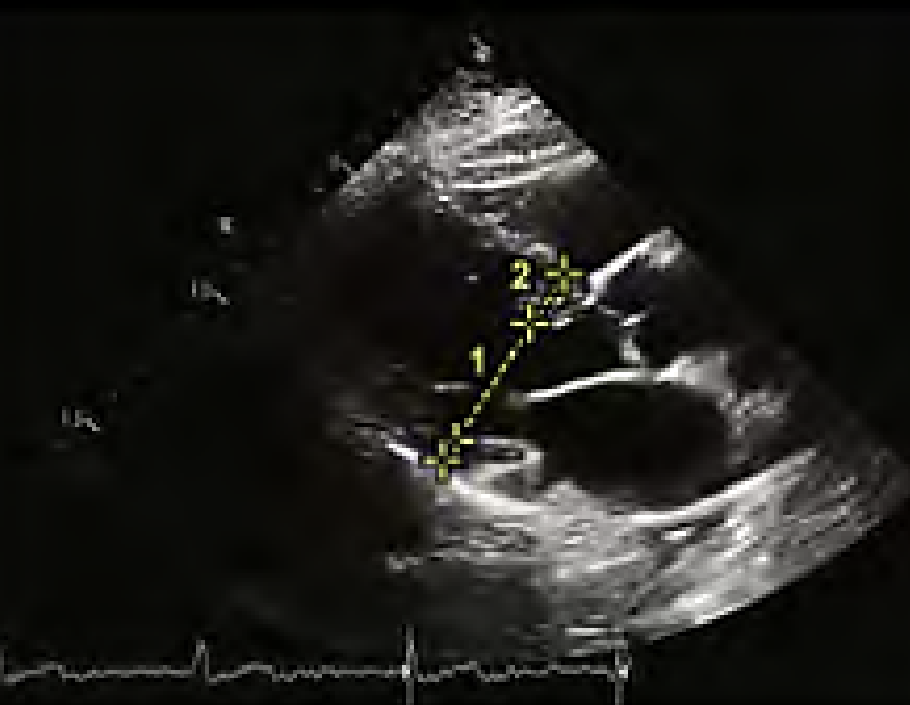
How do you measure LA volume?
A4C and A2C
End-systole
Calipers placed inner to inner on each MV annulus border
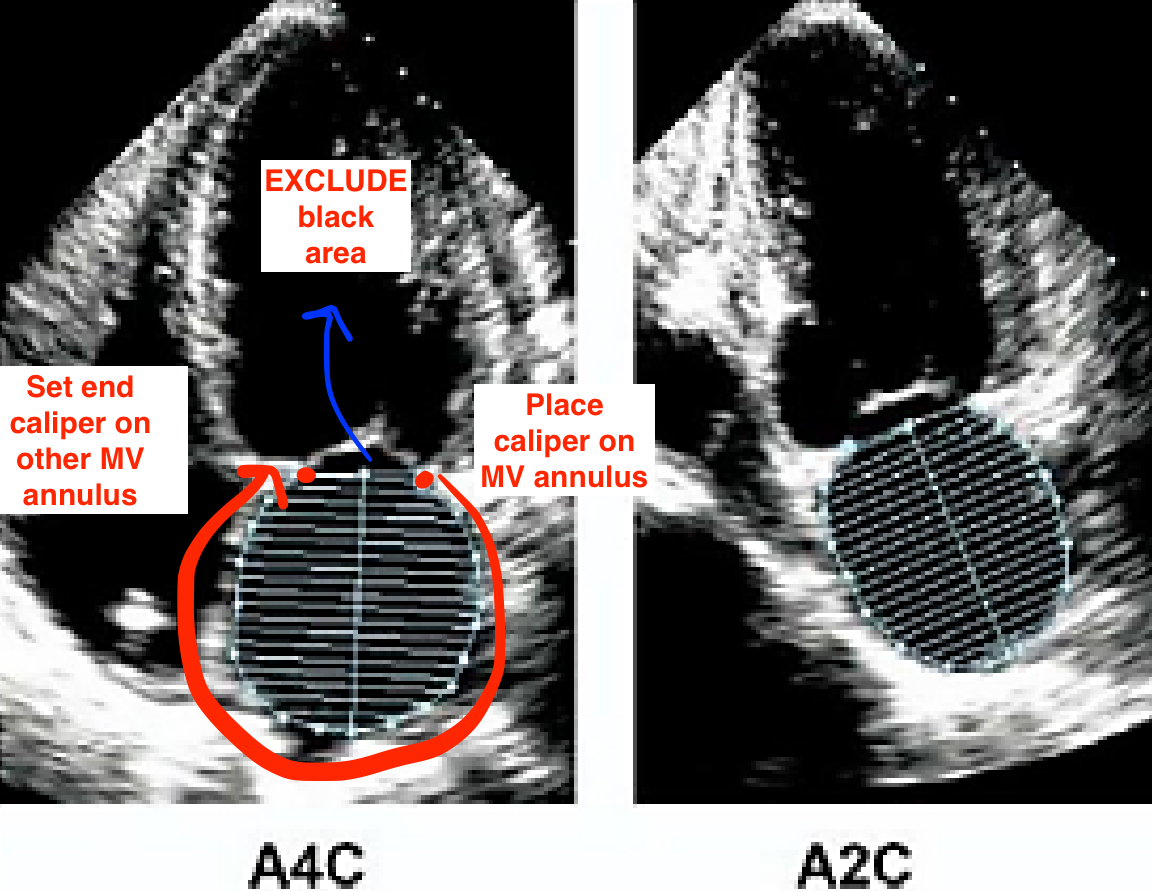
What structures should be excluded from a LA volume measurement?
MV annulus
PVs
LAA
What is the normal value for LA volume index?
< 34 ml/m²
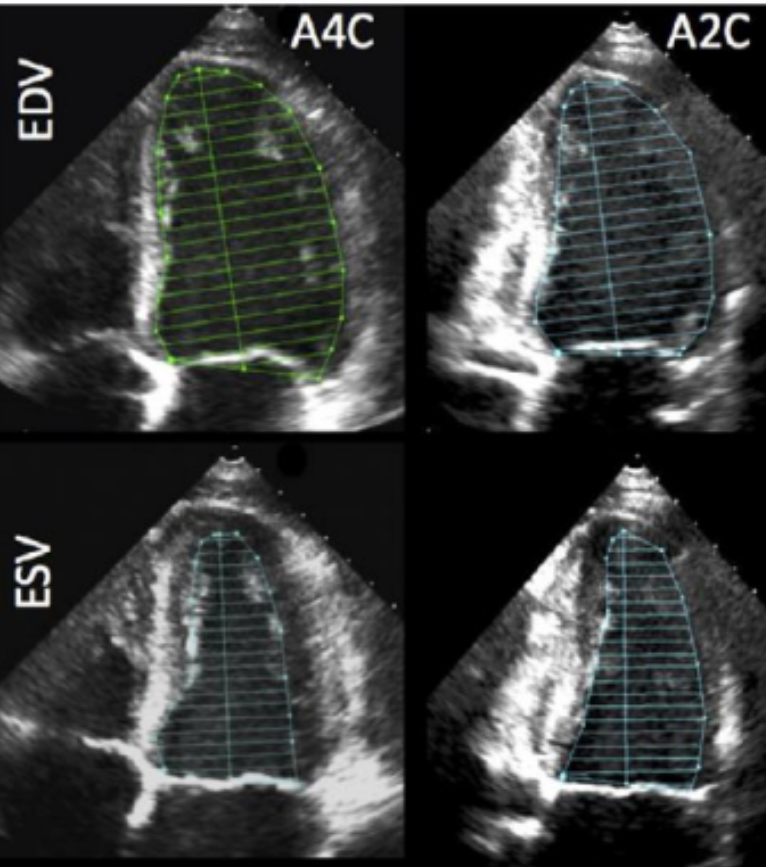
How do you measure LV volume and LVEF?
A4C and A2C using modified Simpson’s
What is the formula for LVEF?
LVEF = LVEDV - LVESV / LVEDV
What is the normal range for LVEF?
Men: 52 - 72%
Women: 54-74%
What is the formula for fractional shortening (FS)?
FS = (LVd - LVs / LVd) x 100
What is the normal value for fractional shortening (FS)?
FS > 25%
How do you measure RV size?
A4C
End-diastole
Width at basal and mid level
Length from annulus to apex
What is TAPSE?
Measurement performed to determine RV systolic function
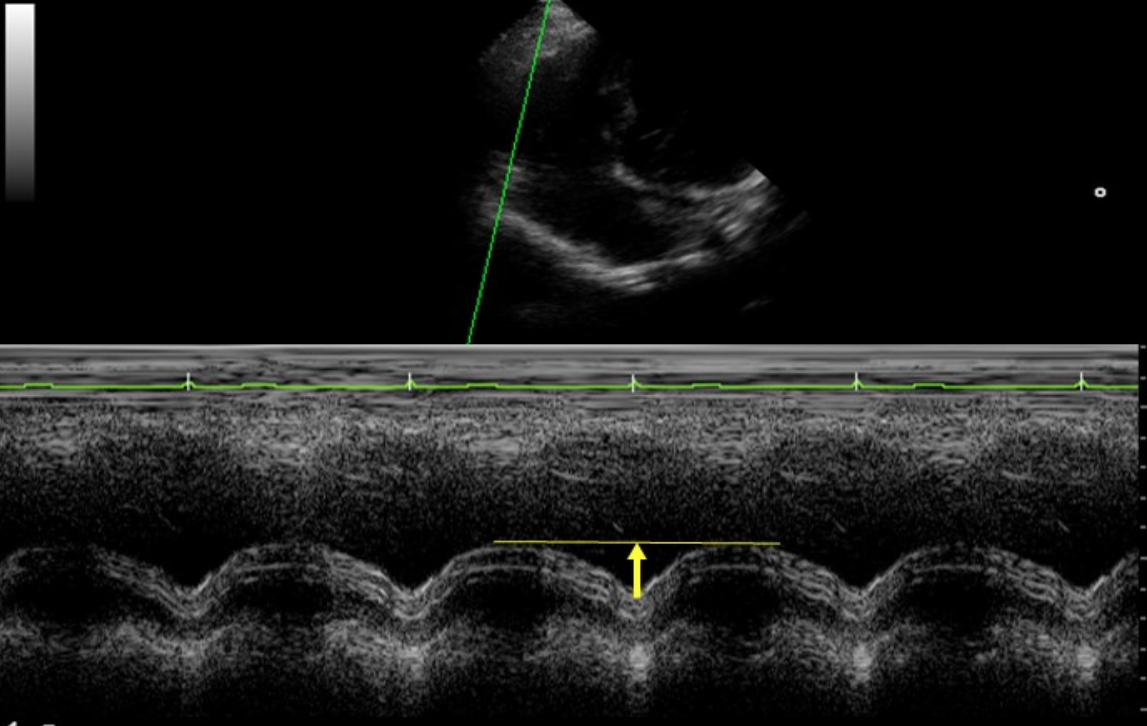
What is the normal value for TAPSE?
> 17 mm
What is RV TDI?
Measurement that determines how fast basal RV free wall moves during systole
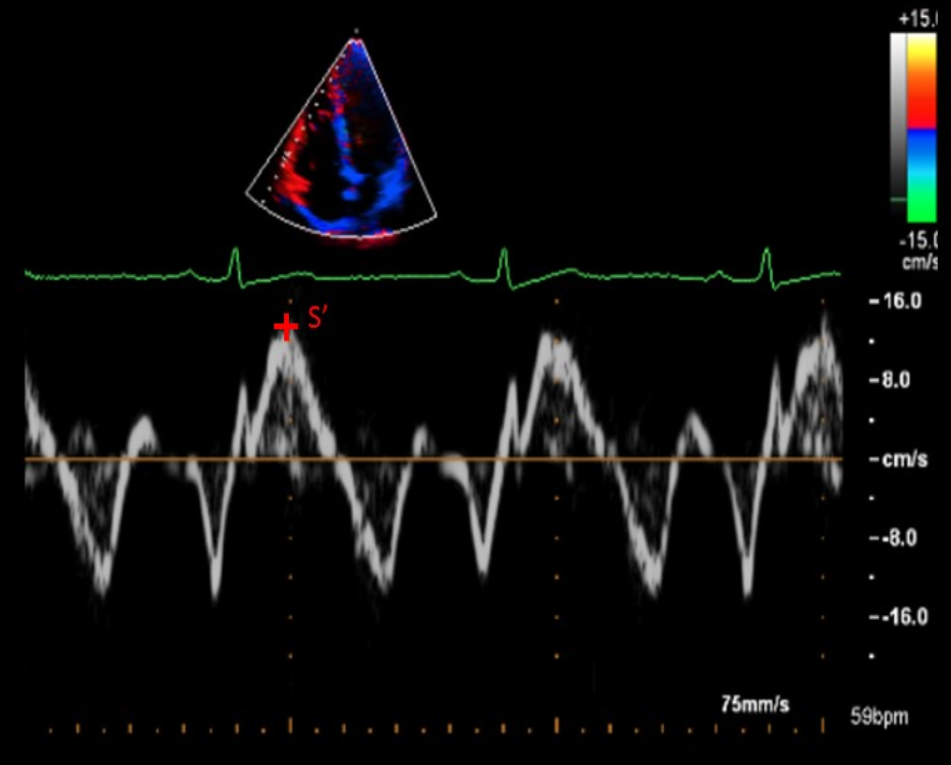
What is the normal value for RV TDI?
S’ > 9.5 cm/sec
What is RIMP?
Measurement of global RV performance
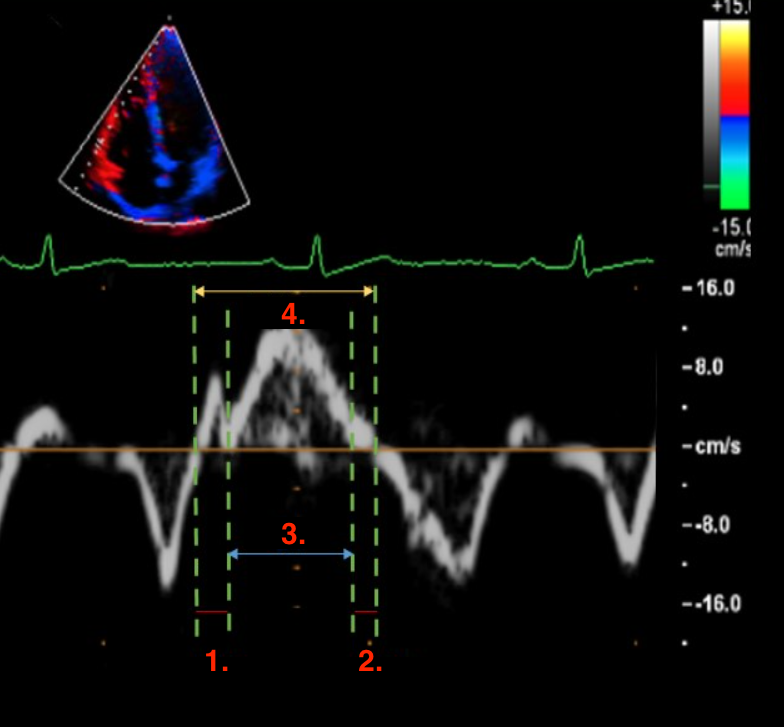
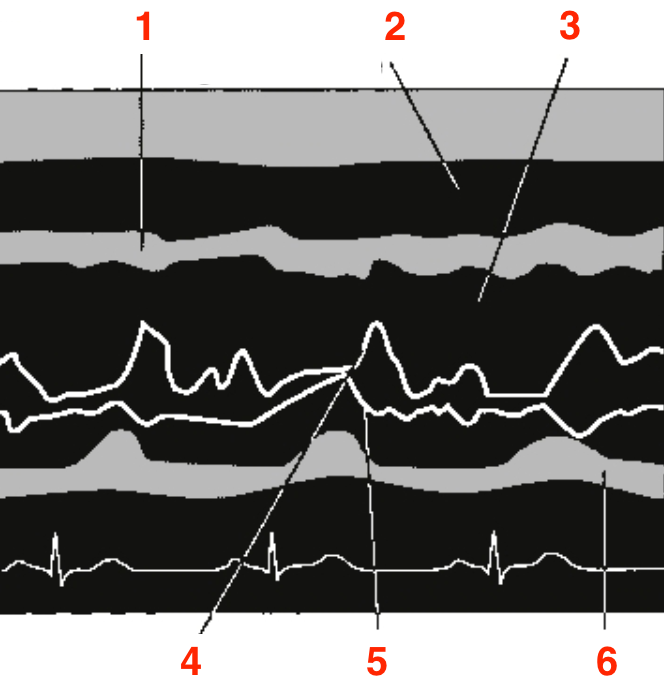
Identify this image.
RIMP
IVCT
IVRT
ET or ejection time
TCO or TV closure opening time
How do you measure RA volume?
A4C
End-systole
Calipers placed inner to inner on each TV annulus border
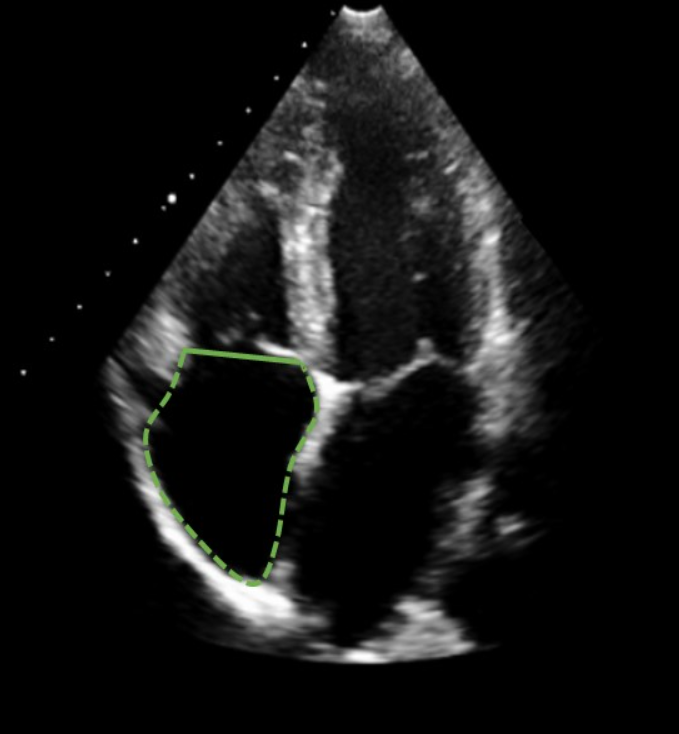
What is the normal value for RA volume?
Men: < 32 L/m²
Women: < 27 mL/m²
How do you measure the IVC?
Subcostal long
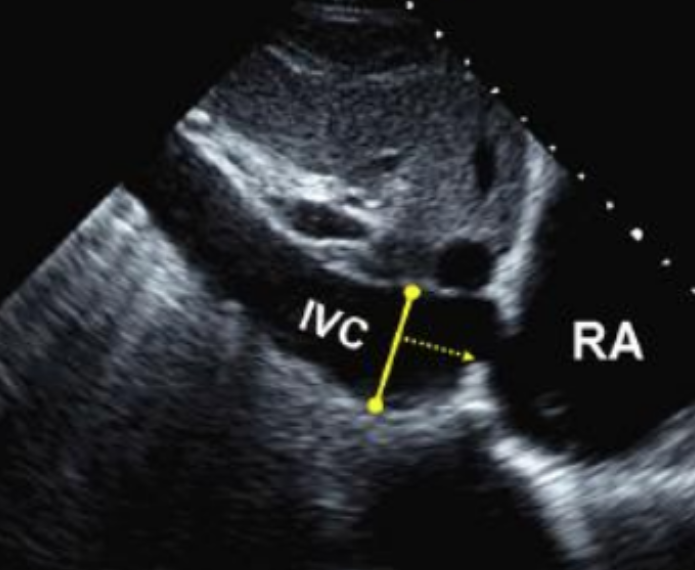
Which measurement is used to calculate RA pressure?
Measuring IVC
What are the normal ranges for RA pressure?
3 mmHg (normal) = IVC diameter < 2.1 that collapses > 50% w/ sniff
15 mmHg (high) = IVC diameter > 2.1 that collapses < 50% w/ sniff
8 mmHg = IVC diameter and collapse do not fit other options
What is RVSP?
Measurement of pulmonary artery systolic pressure
What is the formula for RVSP?
RVSP = 4v² + RAP
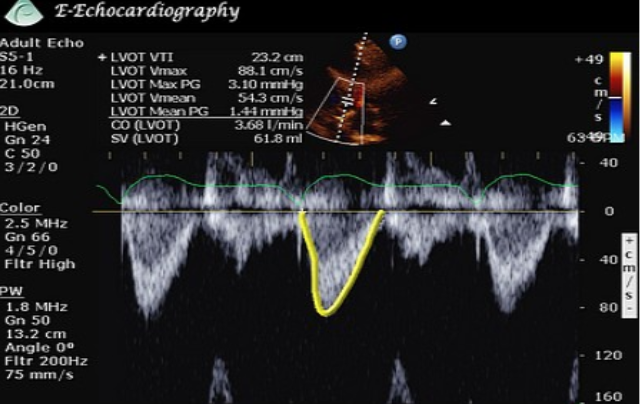
How do you calculate velocity time integral (VTI)?
Trace flow profile
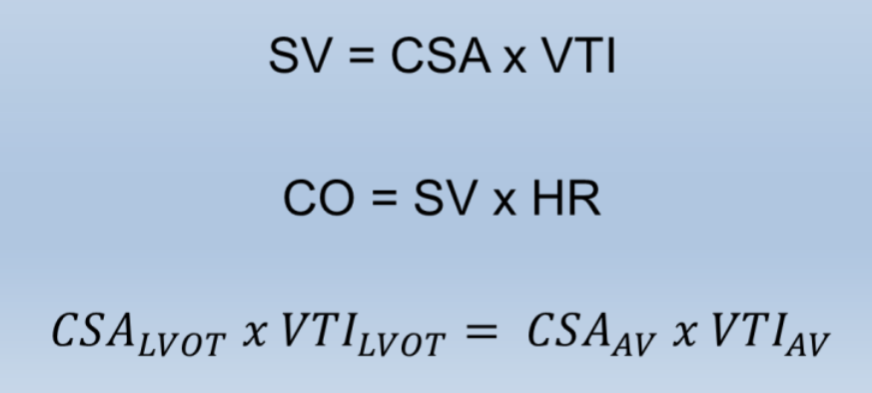
What measurements does the flow profile provide?
VTI
Peak velocity
Mean velocity
Peak pressure gradient
Mean pressure gradient
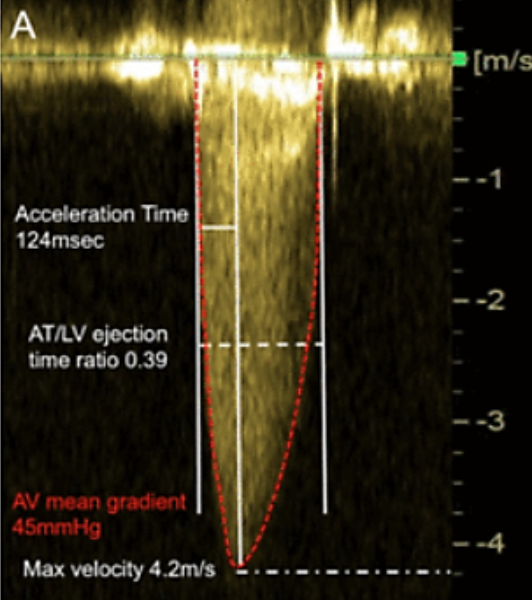
What is acceleration time?
Time from onset of flow to peak velocity
What is deceleration time?
Time from peak flow to end of flow
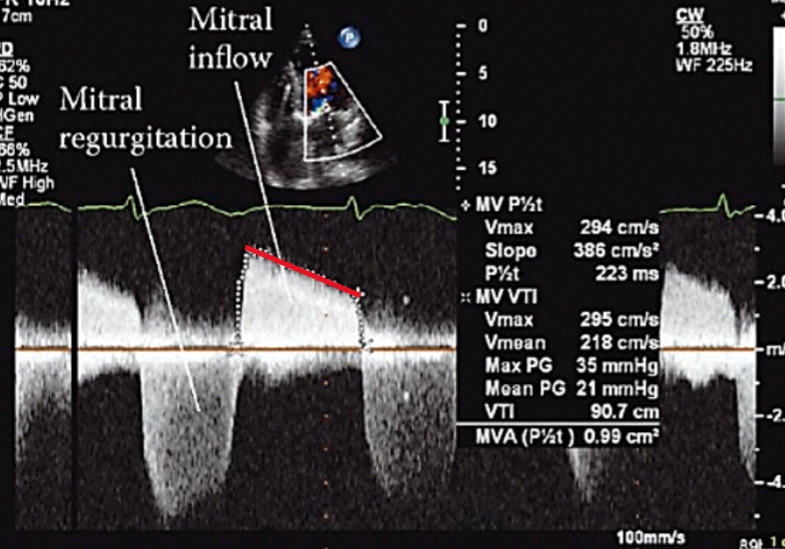
What is pressure half time (PHT)?
Time it takes for peak pressure to drop to half its original value
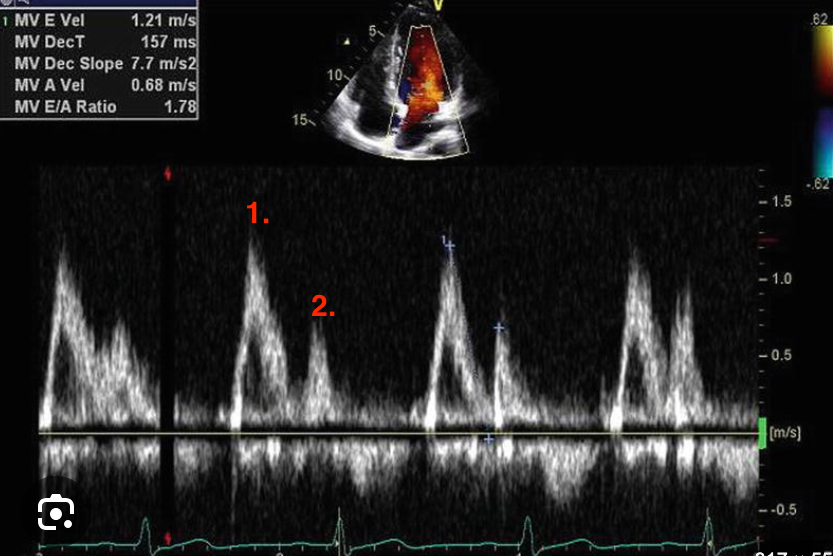
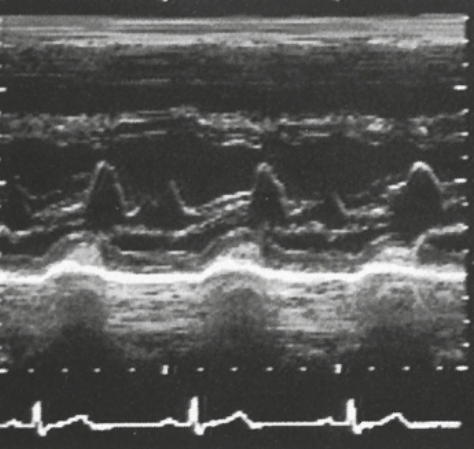
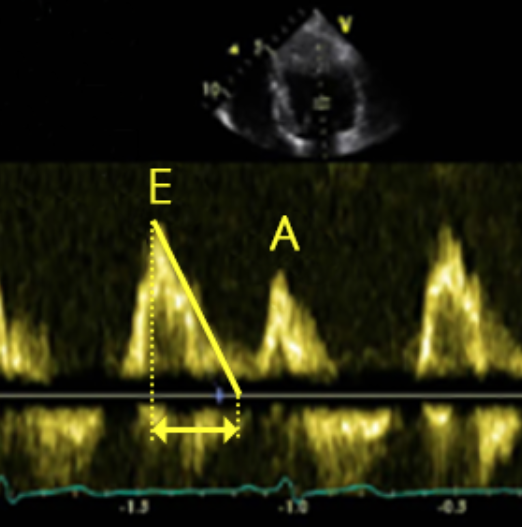
Identify this image.
Normal MV inflow
E-wave or diastolic filling
A-wave or atrial kick
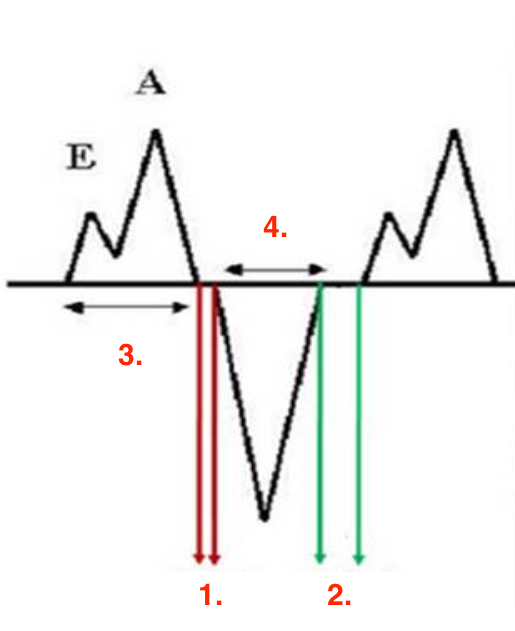
Identify this image.
IVRT
IVCT
IVRT
FT
ET or ejection time
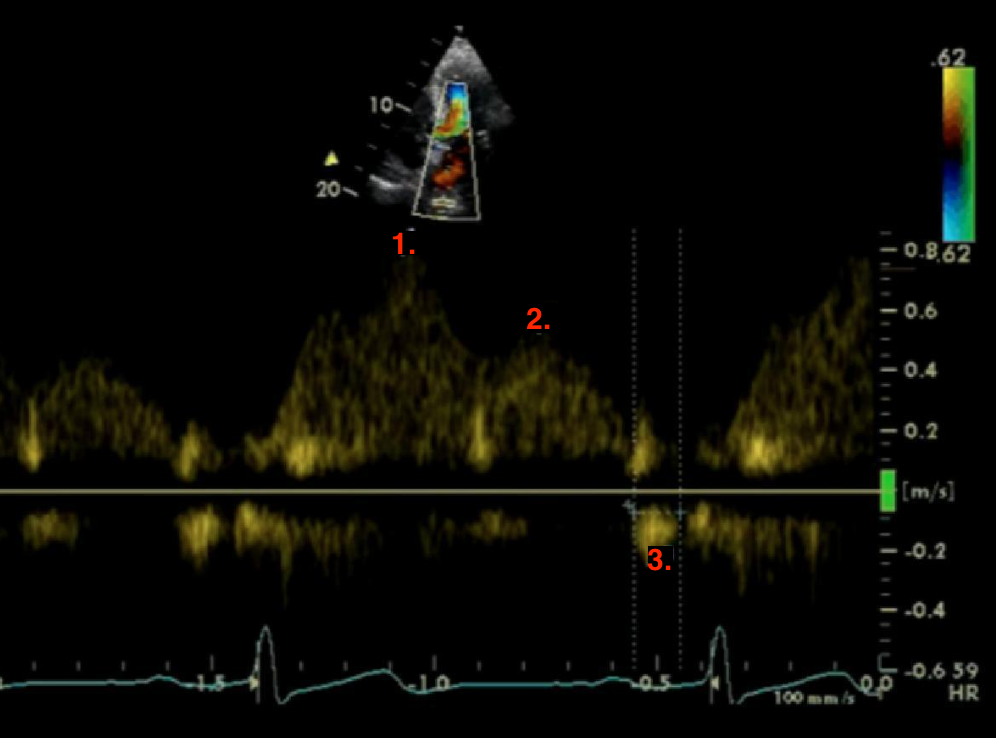
Identify this image.
Normal PV inflow
S-wave or PSV
D-wave or PDV
A-wave or peak atrial reversal velocity
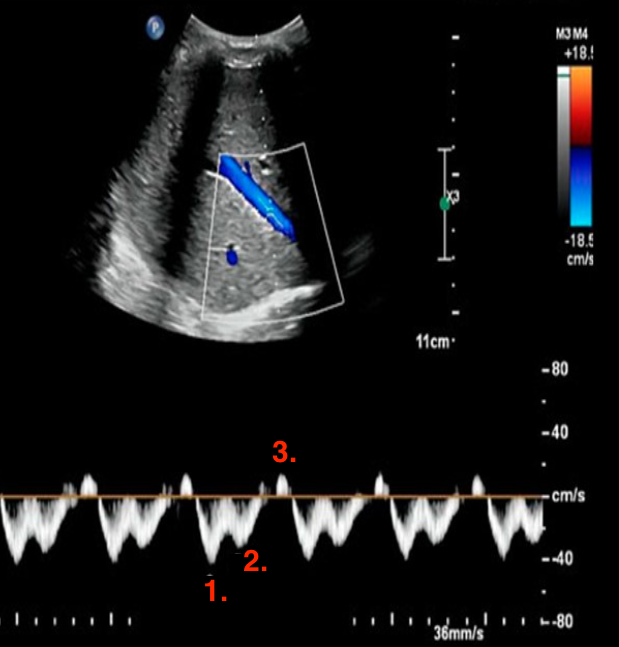
Identify this image.
Normal hepatic vein flow
S-wave or PSV
D-wave or PDV
A-wave or peak atrial reversal velocity