Final Prep
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
A metabolic uncoupler like Dinitrophenol has an ionizable group and works by
A) forming pores in the mitochondrial inner membrane
B) intercepting electrons that are being passed between electron carriers in the electron
transport chain
C) diminishing the electrochemical gradient across the outer membrane of the mitochondria
D) being small and hydrophobic enough to easily pass through biological membranes
E) all of the above
D) being small and hydrophobic enough to easily pass through biological membranes
Which statement describes an aspect of how ATP synthase works?
A) The beta subunits may all be in the empty conformation at the same time.
B) The term “Conformational change” refers specifically to the change in the shape of ADP when it is converted to ATP.
C) The movement of protons through the F0 subunit induces rotation of the c subunits.
D) The gamma subunit associates with all three beta subunits at the same time.
E) All of the above describe aspects of how ATP synthase works
C) The movement of protons through the F0 subunit induces rotation of the c subunits.
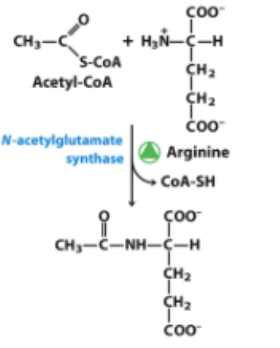
The reaction below is directly involved in the regulation of which pathway?
A) Urea Cycle
B) Gluconeogenesis
C) Citric Acid Cycle
D) Glycolysis
E) Amino acid synthesis
A) Urea Cycle
The electron transport chain (ETC) involves _____.
A) Electron transfer from NADH to Complex I of the ETC.
B) Electron transfer from Succinate to Complex I of the ETC.
C) Electron transfer from Complex I to Complex II of the ETC.
D) All the above.
E) None of the above.
A) Electron transfer from NADH to Complex I of the ETC.
You are working on understanding the respiratory chain in a rare eukaryotic organism that is not well studied. You think you have found a protein that is involved in the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). Which of the following pieces of experimental information is least conclusive in determining whether this protein is a respiratory chain protein?
A) Removal of the protein from the mitochondrial membrane (leaving all other components
intact) results in the rate of electron transport dropping to zero
B) One can observe oxidized and reduced forms of the protein when the ETC is active
C) When added to a mitochondrial suspension in a test tube, the protein is taken up very
rapidly and specifically by the mitochondria
D) When electron transfer within Complex IV is inhibited by addition of a chemical, the protein
becomes completely reduced.
E) When ATP synthase function is inhibited, this protein is no longer seen in the oxidized form
C) When added to a mitochondrial suspension in a test tube, the protein is taken up very
rapidly and specifically by the mitochondria
Glutamate is considered a “collection point” in amino acid catabolism because
A) Glutamate is stored as an energy source to use in fasting or starvation conditions
B) Glutamate is exported from extrahepatic tissue for further catabolism in the liver
C) Catabolism of a variety of amino acids in the liver produces glutamate
D) Glutamate is used as a substrate in the urea cycle to “collect” amino groups
E) Skeletal muscle is broken down as fuel when needed and glutamate travels to the liver from
the muscle for further catabolism
C) Catabolism of a variety of amino acids in the liver produces glutamate
You are studying a new life form from Mars that has something similar to our electron transport
chain. You find that there are four proteins that pass electrons from one to the other and you want to determine the order in which they do this. You name the proteins Em, Mac, Dre, and Snoop. In the lab, you use an electron flow inhibitor on these cells and find that Em is reduced, while the rest are oxidized. You can assume the cells have a source of electrons to feed into the chain and a final electron acceptor like oxygen. Which of the conclusions below can you make from your observations?
A) Em is likely the last member of the electron transport chain
B) Em is likely the first member of the electron transport chain
C) Em is likely somewhere in the middle of the electron transport chain
D) Em is probably not part of the electron chain.
E) Em must have an iron containing heme prosthetic group
B) Em is likely the first member of the electron transport chain
Which component of the electron transport chain does not pump protons across a mitochondrial membrane?
A) Ubiquinone
B) Complex II
C) Cytochrome c
D) A and C only
E) A, B, and C
E) A, B, and C
Based on the information provided below, what is the ΔG’° for the spontaneous electron transfer between Ubiquinone and Succinate?
Ubiquinone + 2H+ + 2e− → ubiquinol + H2 ΔE’° = 0.045 V
Fumarate2− + 2H+ + 2e− → succinate2− ΔE’° = 0.031 V
A) −2.702 kJ/mol
B) −2.316 kJ/mol
C) +2.702 kJ/mol
D) +2.316 kJ/mol
E) None of the above
A) −2.702 kJ/mol
Which of the following statements about flavoproteins is true?
A) The standard reduction potential of flavoproteins is −0.219 V
B) NAD+ is associated with flavoproteins and can accept 1 or 2e − .
C) Flavoproteins are primarily involved in phosphorylation reactions.
D) Flavoproteins are coenzymes.
E) None of the above.
E) None of the above.
If electron transfer in the mitochondrial electron transport chain is blocked at Complex III in
the presence of oxygen, then
A) ATP synthesis will continue but the rate will decrease slightly
B) ATP production from ATP synthase will stop
C) ATP synthesis will increase to compensate for the lack of Complex III function.
D) Complex I and II will pump more protons across the inner membrane to compensate for the
lack of Complex III function.
E) Complex IV will pump more protons across the inner membrane to compensate for the lack
of Complex III function.
B) ATP production from ATP synthase will stop
What is the driving force for ATP synthesis in oxidative phosphorylation?
A) The speed of glycolysis
B) The movement of protons that are pumped across the outer mitochondrial membrane
C) The pH difference across the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) ATP synthase uses ATP hydrolysis to make ATP
E) The malate-aspartate shuttle
C) The pH difference across the inner mitochondrial membrane
You discover a cancer drug that targets tumor cells in the liver -- it inhibits glycolysis but does
not affect gluconeogenesis. Which of these enzymes could this drug be allosterically regulating?
A) Phosphohexose isomerase
B) Pyruvate kinase
C) Pyruvate carboxylase
D) Enolase
E) Two or more of the above
B) Pyruvate kinase
You discover a new protein that is allosterically activated when energy is plentiful in a liver cell
(i.e. [ADP] << [ATP]). You name this protein MO, after your favorite biochem professor. Which of the following statements is true about MO?
i. You would expect glycogen synthesis to be increased by active MO
ii. You would expect glycogen synthesis to be decreased by active MO
iii. You would expect ATP-producing processes to be activated by MO
iv. You would expect ATP-producing processes to be inhibited by MO
A) ii, iii
B) i, iii
C) i, iv
D) ii, iv
E) ii, iii, v
C) i, iv
The activity of phosphofructokinase 1 is increased by the binding of
A) ATP
B) citrate
C) ADP
D) acetyl CoA
E) two or more of the above
C) ADP
Hexokinase I is the isozyme of hexokinase that is found in muscle. Which statement is true
about Hexokinase I?
A) It has a high affinity for its substrate as compared to Hexokinase IV.
B) It has a lower Km ([S] at ½ vmax) than Hexokinase IV.
C) Hexokinase I will have high phosphorylation activity even at low substrate levels.
D) The activity of Hexokinase I is directly related to maintaining blood glucose levels.
E) Two or more of the above are true.
E) Two or more of the above are true.
Which of the following is an example of regulating enzyme activity by covalent modification?
A) Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase by a kinase activates the phosphorylase.
B) ATP binds to phosphofructokinase and inhibits its activity.
C) Glycogen phosphorylase is tagged with ubiquitin and targeted for degradation.
D) A transcription factor binds to DNA and induces expression of the gene for the E1 of the PDC.
E) The mRNA encoding the E1 of PDC is degraded so a ribosome cannot use it for translation.
A) Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase by a kinase activates the phosphorylase.
In the context of amino acid catabolism, which of the following cofactors plays an important role in amino group transfer reactions?
A) Biotin
B) Tetrahydrofolate
C) S-Adenosylmethionine
D) Pyridoxal phosphate
E) All the above
D) Pyridoxal phosphate
A mammalian hormone that is functionally very similar to insulin is discovered. Which of the
following effects would this hormone likely have?
A) increase in fatty acid synthesis in the liver
B) decrease in gluconeogenesis in the liver
C) increased glucose uptake in the muscle
D) increased glycogen synthesis in the liver
E) All of the above could be likely triggered by this hormone
E) All of the above could be likely triggered by this hormone
Ammonium produced in extrahepatic tissues from amino acid breakdown is transported to the
liver in the form of _____.
A) Ammonia
B) Glutamate
C) Glutamine
D) All of the above
E) Amino acid catabolism never occurs in extrahepatic tissue
C) Glutamine
How is ammonia transported out of the mitochondria in the urea cycle?
A) Incorporated into carbamoyl phosphate, which is transported to the cytosol then
dephosphorylated into citrulline
B) Incorporated into ornithine, which is then transported to the cytosol
C) It is not transported out of the mitochondria
D) Incorporated into carbamoyl phosphate, which reacts with ornithine to form citrulline,
which is then transported to the cytosol
E) Concentrated into urea, which is then transported to the cytosol
D) Incorporated into carbamoyl phosphate, which reacts with ornithine to form citrulline,
which is then transported to the cytosol
Entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle is decreased when
A) the ratio of [ATP]/[ADP] is high
B) the ratio of [NADH]/[NAD+] is high
C) [ADP] or [AMP] is low
D) [citrate] is high
E) all of the above
E) all of the above
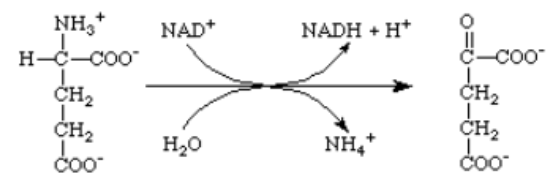
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes this reaction?
A) glutamine synthetase
B) glutamate synthase
C) glutamate dehydrogenase
D) aspartate aminotransferase
E) glutamate aminotransferase
C) glutamate dehydrogenase
Which of the following statements does not describe a purpose of amino acid catabolism?
A) To provide energy sources, particularly during starvation
B) To provide carbon skeletons for use in glucose production
C) To breakdown amino acids into compounds such as fumarate, acetyl-CoA or acetoacetate
D) To generate ATP from the oxidation of carbon skeletons into CO2 and H20
E) All of the above describe a purpose of amino acid catabolism
E) All of the above describe a purpose of amino acid catabolism
Consider the following characteristics of hormones in mammals. Which combination of
characteristics correctly applies to glucagon?
I. is made from amino acids
II. is made from sterols
III. binds to cell surface receptors
IV. is membrane permeable and enters the cell
V. is secreted from the pancreas
A) I, IV, and V only
B) II, III, and V only
C) II and IV only
D) I, III, and V only
E) I and III only
D) I, III, and V only
Which of the following compounds are produced from the breakdown of glucogenic aminoacids?
A) acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA
B) acetyl CoA and acetone
C) oxaloacetate and fumarate
D) only acetyl CoA
E) phenylalanine and leucine
C) oxaloacetate and fumarate
What metabolite is found in both the citric acid cycle and the Urea cycle?
A) Ornithine
B) Oxaloacetate
C) Arginino-succinate
D) Fumarate
E) Malate
D) Fumarate
Proline is synthesized from Glu in a pathway that involves the following reaction:
Pyrroline 5 carboxylate + NAD(P)H + H+ ---> Proline + NAD(P)+
Which enzyme below catalyzes this reaction?
A) Pyrroline 5 carboxylate reductase
B) Proline reductase
C) Pyrroline 5 carboxylate dehydrogenase
D) Proline isomerase
E) Proline phosphatase
A) Pyrroline 5 carboxylate reductase
The Nitrogen cycle describes
A) the creation of nitrogen containing compounds in a variety of organisms, including bacteria
and plants
B) the creation of nitrogen compounds in various oxidation states in a single organism
C) how amino acids travel from the muscle to the liver for catabolism
D) the excretion of amino groups in the form of urea
E) the metabolic pathway that creates cyclic nitrogen containing compounds
A) the creation of nitrogen containing compounds in a variety of organisms, including bacteria
and plants
What can the brain use to generate energy?
A) Acetyl-CoA from the breakdown of fatty acids in the brain.
B) β-hydroxybutyrate from the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver.
C) Glucose from gluconeogenesis in the brain.
D) Phosphocreatine
E) All of the above
B) β-hydroxybutyrate from the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver.
Which of the following changes are likely to happen shortly after you have a meal?
A) decrease in glycogen phosphorylase activity
B) decrease in phosphofructokinase 1 activity
C) increase in PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) carboxykinase
D) increase in glucagon concentration in the bloodstream
E) all of the above
A) decrease in glycogen phosphorylase activity
As a doctor, you are monitoring a person on a fast. After two weeks of not eating any food at all, which of the following things would you observe in your patient?
A) Triglyceride synthesis would be occurring at high levels to store energy for later use.
B) Acetone would be a primary fuel for the body.
C) [Beta hydroxybutyrate] > [glucose] in the blood
D) Protein synthesis would be occurring at high rates.
E) Most of the acetyl CoA in the liver cells will be used by the liver in the citric acid cycle.
C) [Beta hydroxybutyrate] > [glucose] in the blood
Which of the following occurs in the movement of electrons through the respiratory chain?
A) hydride ions are passed from one carrier to another
B) direct transfer of electrons between ions
C) electrons are moved as part of a hydrogen atom
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D) all of the above
Which of the following six statements about mitochondrial respiration are true?
1. The electron carriers of the respiratory chain are present in the cytoplasm of the cell
2. The final electron acceptor is water
3. The electron carriers are arranged in order of decreasing reduction potential.
4. During electron transport, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the
intermembrane space.
5. Ubiquinone and cytochrome C transport electrons between the respiratory chain complexes
6. Complex II may receive electrons from succinate or NADH.
A) 2, 3, 4, 6 only
B) 1, 2, 4, 5 only
C) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 only
D) 4, 5 only
E) 2, 4, 5 only
D) 4, 5 only
Which of the statements below about the metabolism of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids in
mammals is true?
A) Blood sugar levels impact the metabolism of all three types of molecules.
B) The metabolism of all three are affected by the hormone glucagon.
C) All three are precursors for more complex molecules.
D) The liver is capable of catabolizing all three types of molecules.
E) All of the above are true
E) All of the above are true
Where do the two nitrogen atoms in urea come from?
A) One from oxidative deamination of glutamate, the other from aspartate
B) One from arginine, the other from ammonium
C) One from carbamoylphosphate, the other from citrulline
D) One from glutamate from oxidative deamination, the other from uric acid
E) One from aspartate, the other from citrulline
A) One from oxidative deamination of glutamate, the other from aspartate
Entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle is decreased when
A) the ratio of [ATP]/[ADP] is high
B) the ratio of [NAD + ]/[NADH] is high
C) [AMP] is high
D) [citrate] is low
E) all of the above
A) the ratio of [ATP]/[ADP] is high
Which of the following statements about hexokinase isozymes is false?
A) Hexokinase IV in the liver has a lower affinity for glucose than Hexokinase I in the muscle
B) Hexokinase I and IV are both inhibited by glucose 6 phosphate
C) At low glucose concentrations, hexokinase IV will have low phosphorylation activity
D) Hexokinase I in the muscle has a high affinity for glucose, which promotes entry of glucose into
glycolysis
E) Hexokinase I and IV catalyze the same reaction
B) Hexokinase I and IV are both inhibited by glucose 6 phosphate
What is the closest value to the ∆G°’ for the following reaction:
NADH + H + + ½ O 2 ---> H 2 O + NAD +
A) -220 kJ/mol
B) -112 kJ/mol
C) 210 kJ/mol
D) 110 kJ/mol
E) need more information to calculate this
A) -220 kJ/mol
What would likely be the consequence of a biochemical defect in which glucagon was secreted in excess?
A) increased accumulation of triacylglycerols in adipocytes
B) decreased rate of urea excretion
C) lowered concentrations of ketone bodies circulating in the blood stream
D) inhibited glycolysis in the liver and depleted glycogen stores
E) all of the above
D) inhibited glycolysis in the liver and depleted glycogen stores
List the following in order of increasing tendency to accept electrons: (a), alpha-ketoglutarate + CO2 (yielding isocitrate); (b) oxaloacetate; (c) O2 ; (d) NADP+
A) c,b,d,a
B) b,a,c,d
C) a,d,b,c
D) d,c,a,b
E) b,d,a,c
C) a,d,b,c
You are studying the respiratory chain in a eukaryotic microorganism that was recently discovered. You find that there are four proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane that pass electrons from one to the other and you want to determine the order in which they do this. You name the proteins alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. In the lab, you use an electron flow inhibitor on these cells and find that gamma is reduced, while the rest are oxidized. You provide the cells with a source of electrons to feed into the chain and a final electron acceptor like oxygen. Which of the conclusions below can you make from your observations?
A) Gamma is likely the last member of the electron transport chain
B) Gamma is likely the first member of the electron transport chain
C) Gamma is likely somewhere in the middle of the electron transport chain
D) Gamma is probably not part of the electron chain.
E) Gamma is probably the final electron acceptor.
B) Gamma is likely the first member of the electron transport chain
A metabolic uncoupler like Dinitrophenol has an ionizable group and works by
A) forming pores in the mitochondrial inner membrane that allow protons to pass through
B) intercepting electrons that are being passed between electron carriers in the electron transport
chain
C) diminishing the electrochemical gradient across the outer membrane of the mitochondria
D) being small and hydrophobic enough to easily pass through biological membranes
E) all of the above
D) being small and hydrophobic enough to easily pass through biological membranes
If electron transfer in the mitochondrial electron transport chain is blocked at Complex III in the
presence of oxygen, then
A) ATP production will continue but the rate will decrease slightly
B) ATP synthase activity will stop
C) ATP synthesis will increase to compensate for the lack of Complex III function.
D) Complex I and II will pump more protons across the inner membrane to compensate for the lack of Complex III function.
E) Complex IV will pump more protons across the inner membrane to compensate for the lack of Complex III function
B) ATP synthase activity will stop
Which of the following statements is true about ATP synthase?
A) at any given moment, the three Beta subunits may be all attached to ATP
B) turning of the c subunits is driven by protons traveling up their concentration gradient
C) conformational change of beta subunits is associated with binding to ADP, ATP, or neither
D) the gamma subunit associating with a beta subunit induces ATP binding
E) the active site where catalysis occurs is on the gamma subunit
C) conformational change of beta subunits is associated with binding to ADP, ATP, or neither
Which of the following statements about flavoproteins is true?
A) The standard reduction potential of FAD is not always -0.219 V.
B) NAD+ is associated with flavoproteins and can accept 1 or 2e − .
C) Flavoproteins are primarily involved in phosphorylation reactions.
D) Flavoproteins are coenzymes.
E) All of the above are true
A) The standard reduction potential of FAD is not always -0.219 V.
Which complex does not contribute to the proton motive force?
A) Complex I
B) Complex II
C) Complex III
D) Complex IV
E) all of them contribute
B) Complex II
Which of the following enzymes are most likely to be regulated in glycolysis?
A) all enzymes in glycolysis are potential regulation points
B) enzymes that catalyze reversible steps are most likely to be regulated
C) hexokinase and pyruvate kinase
D) the first three enzymes of the pathway, since regulation is most efficient if it occurs at the
beginning of a pathway
E) enzymes like aldolase, which catalyze big chemical changes like cleavage of C—C bonds
C) hexokinase and pyruvate kinase
If a person did not eat for two weeks, which of the following statements would most likely be true?
A) Glucose and ketones will be present at similar concentrations in the blood.
B) Acetone would be a primary fuel for the body.
C) The concentration of Beta hydroxybutyrate would be higher than the concentration of glucose in the blood
D) Protein synthesis would be occurring at high rates.
E) Most of the acetyl CoA in the liver will enter the Citric Acid Cycle in the liver to generate ATP
for the body
C) The concentration of Beta hydroxybutyrate would be higher than the concentration of glucose in the blood
Where does the carbon in urea come from?
A) Decarboxylation of citrulline
B) Carboxylation of arginine, followed by arginine hydrolysis into urea and ornithine
C) Carbamoylation of aspartate, followed by cleavage of argininosuccinate
D) High concentration of bicarbonate in the mitochondrial matrix
E) None of the above
D) High concentration of bicarbonate in the mitochondrial matrix
Flux through a metabolic pathway can be regulated by _____.
A) altering the number of enzyme molecules that are made.
B) altering the catalytic activity of enzymes that are present.
C) controlling the degradation of enzymes.
D) covalently attaching certain functional groups to enzymes.
E) all the above
E) all the above
Which of the following is an example of regulating enzyme activity by covalent modification?
A) ATP binds to an allosteric site on the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and inhibits its activity.
B) Glycogen phosphorylase is targeted for degradation.
C) Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase by a kinase activates the phosphorylase.
D) A transcription factor binds to DNA and induces expression of the gene for the E1 of the PDC.
E) All of the above are examples of covalent modification.
C) Phosphorylation of glycogen phosphorylase by a kinase activates the phosphorylase.
Nitrogen is excreted from animals in which of the following forms?
A) urea only
B) urea, uric acid, and NH 4+
C) glutamine and glutamate
D) carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate
E) only NH 4+
B) urea, uric acid, and NH 4+
You are studying the enzyme regulation of an allosterically regulated step in glycolysis. Which of the following is least likely to be an allosteric inhibitor of this enzyme?
A) ATP
B) citrate
C) ADP
D) acetyl CoA
E) succinate
C) ADP
The electron transport chain (ETC) involves _____.
A) Electron transfer from NADH to Complex I of the ETC.
B) Electron transfer from Succinate to Complex I of the ETC.
C) Electron transfer from Complex I to Complex II of the ETC.
D) Complex IV pumping H + into the mitochondrial matrix.
E) Two or more of the above
A) Electron transfer from NADH to Complex I of the ETC.
Which of the following statements about the mitochondrial respiratory chain is false?
A) The respiratory chain contains multiple types of electron carriers.
B) One protein in the mitochondrial respiratory chain is not part of a protein complex.
C) In the mitochondrial respiratory chain, ubiquinone is a soluble protein that functions as an e−carrier.
D) In the mitochondrial respiratory chain, prosthetic groups often facilitate electron transfer.
E) Electrons are passed from a carrier with lower reduction potential to a carrier with higher
reduction potential
C) In the mitochondrial respiratory chain, ubiquinone is a soluble protein that functions as an e−carrier.
In the context of amino acid catabolism, which of the following cofactors play(s) an important role in amino group transfer reactions?
A) Biotin
B) Tetrahydrofolate
C) S-Adenosylmethionine
D) Pyridoxal phosphate
E) All the above
D) Pyridoxal phosphate
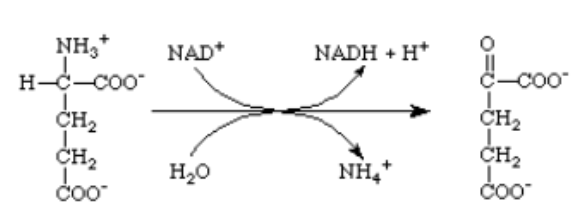
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes this reaction?
A) glutamine synthetase
B) glutamate synthase
C) glutamate dehydrogenase
D) aspartate aminotransferase
E) glutamate aminotransferase
C) glutamate dehydrogenase
Ketogenic amino acids can be broken down to form
A) Lysine
B) Acetyl-CoA
C) Fumarate
D) Oxaloacetate
E) All the above
B) Acetyl-CoA
ATP synthase utilizes rotational catalysis to facilitate ATP synthesis. Rotational catalysis specifically refers to _____.
A) the rotation of α (alpha) and β (beta) subunits of the F1 domain.
B) the rotation of substrates binding the active sites in the beta subunits of ATP synthase.
C) the rotation of protons as they travel across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
D) the rotation of the γ (gamma) subunit of the F1 domain.
E) the rotation of all F 0 domain proteins
D) the rotation of the γ (gamma) subunit of the F1 domain.
You decide to add a protein supplement (eg. a protein shake) to your breakfast and lunch in addition to what you normally eat. Which of the following biochemical responses would you expect to see in your body?
A) decreased urea production
B) decreased transcription of arginase
C) decreased levels of N-Acetylglutamate
D) increased activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
E) two or more of the above would occur
D) increased activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
You have discovered a modified electron transport chain in the mitochondria in a new species of yeast that you are studying. You observe that this chain has an additional ETC complex, which you name Complex X. You find that Complex X has a single cytochrome with a standard reduction potential of 0.27 V. Which part of the ETC do you predict Complex X receives electrons from, assuming that the chain contains all of these electron carriers?
A) cytochrome c
B) cytochrome a
C) cytochrome b
D) cytochrome c1
E) ubiquinone
A) cytochrome c
Which of the following molecules are substrates for an enzyme that uses Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) as a cofactor?
A) glutamate and NAD +
B) carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine
C) serine and alpha-ketoglutarate
D) glutamate and ATP
E) alanine and NAD+
C) serine and alpha-ketoglutarate
Glutamate is considered a “collection point” in amino acid catabolism because
A) Glutamate is stored as an energy source to use in fasting or starvation conditions
B) Glutamate is exported from extrahepatic tissue for further catabolism in the liver
C) Catabolism of a variety of amino acids in the liver produces glutamate
D) Glutamate is used as a substrate by a urea cycle enzyme
E) Skeletal muscle is broken down as fuel when needed and glutamate travels to the liver from the muscle for further catabolism
C) Catabolism of a variety of amino acids in the liver produces glutamate
You discover a new amino acid and name it “Monine” (after your favorite biochem teacher). Monine
is synthesized from Glutamate in a pathway that involves the following reversible reaction:
Monine carboxylate + NADH + H + <---> Monine + NAD +
Which enzyme below would catalyze this reaction?
A) Monine reductase
B) Monine dehydrogenase
C) Monine carboxylate dehydrogenase
D) Monine isomerase
E) Monine phosphatase
B) Monine dehydrogenase
Consider the following characteristics of hormones in mammals. Which combination of characteristics correctly applies to glucagon?
I. is made from amino acids
II. is made from sterols
III. binds to cell surface receptors
IV. is membrane permeable and enters the cell
V. is secreted from the pancreas
A) I, IV, and V only
B) II, IV, and V only
C) II, III, and V only
D) I, III, V only
E) I and III only
D) I, III, V only
The Nitrogen cycle describes
A) the creation of nitrogen containing compounds in various oxidation states in a single organism
B) how amino acids travel from the muscle to the liver for catabolism
C) the excretion of amino groups in the form of urea
D) the creation of nitrogen containing compounds in a variety of organisms, including bacteria and plants
E) the metabolic pathway that creates cyclic nitrogen containing compounds
D) the creation of nitrogen containing compounds in a variety of organisms, including bacteria and plants
After ingestion of a carbohydrate-rich meal, increased concentration of glucose in the blood is
associated with many changes in the metabolism of humans. Which change would NOT be expected?
A) a decrease in the secretion of glucagon from the pancreas
B) an increase in glycogen phosphorylase activity
C) an increase in the secretion of insulin from the pancreas
D) increased synthesis of storage triacylglycerols in adipose cells
E) increased glycolysis in the liver
B) an increase in glycogen phosphorylase activity
Inhibiting which of the following enzymes slows down the catabolism of valine in extrahepatic
tissues?
A) Valine aminotransferase
B) Branched-chain aminotransferase
C) Valine dehydrogenase complex
D) Coenzyme A
E) Glutamate dehydrogenase
B) Branched-chain aminotransferase
What can the brain use to make ATP?
A) Acetyl-CoA from the breakdown of fatty acids in the brain.
B) β-hydroxybutyrate from the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver.
C) Glucose from gluconeogenesis in the brain.
D) Phosphocreatine
E) All of the above
B) β-hydroxybutyrate from the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver.
Which of the following changes in enzyme activity is likely to happen by the release of insulin from the pancreas?
A) decrease in glycogen phosphorylase activity
B) increase in phosphofructokinase 1 activity
C) decrease in PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) carboxykinase
D) increase in acetyl CoA carboxylase
E) two or more of the above
E) two or more of the above
Which reaction in the urea cycle requires ATP?
A) Transport of ornithine into the mitochondrion
B) Hydrolysis of arginine to urea
C) Export of citrulline out of the mitochondrion
D) Cleavage of argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate
E) Condensation of aspartate and citrulline
E) Condensation of aspartate and citrulline