Chapter 9: Enthalpy + Hess's Law
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is enthalpy?
a measure of heat energy in a chemical system
which law alludes to energy changes?
the law of conservation of energy
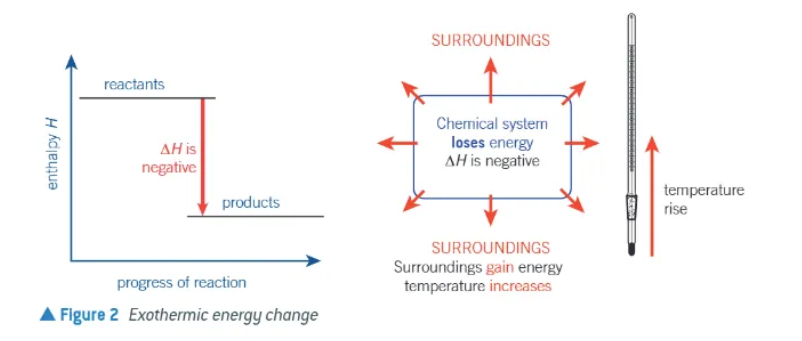
directions of energy transfer in an exothermic reaction:
∆H is negative
chemical system loses energy
surroundings gain energy
temperature of surroundings increases
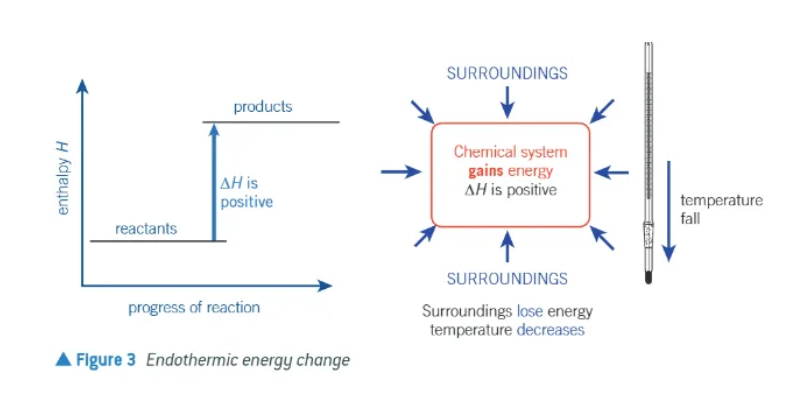
directions of energy transfer in an endothermic reaction:
∆H is positive
chemical system gains energy
surroundings lose energy
temperature of surroundings decreases
what is the activation energy?
the energy required to break bonds, acting as an energy barrier → Ea
the minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
in general, reactions with low activation energies are…
fast
list the 4 general standard conditions:
pressure → 100kPa
temperature → 298K
concentration → 1 mol dm-3
state → the physical state of a substance under standard conditions
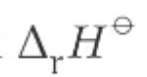
What is this?
the standard enthalpy change of a reaction → enthalpy change accompanying a reaction in the molar quantities shown in a chemical equation under standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states
what is the standard enthalpy change of formation?
∆fHϴ → enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions, with all reactants + products in their standard states
when balancing equations for enthalpy changes of formation, what do you need to make sure???
that a balancing number isn’t added in front of the product!!
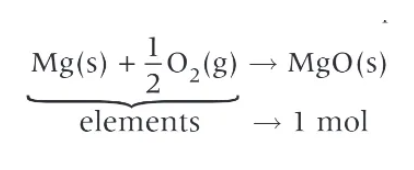
all elements have an enthalpy change of formation of ….
0 kJ mol -1
definition of the standard enthalpy change of combustion
∆cHϴ → the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a substance reacts completely in oxygen under standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states.
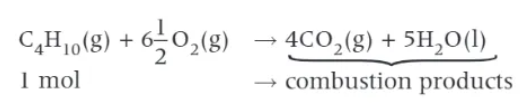
definition for the standard enthalpy change of neutralisation:
∆neutHϴ → the energy change that accompanies the reaction of an acid by a base to form one mole of H2O (l), under standard conditions, with all reactants and products in their standard states.
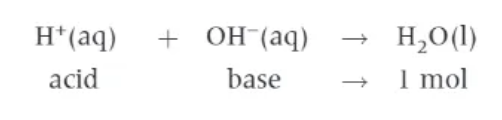
what is a specific heat capacity, or c ?
the energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1K.
good conductors of heat, such as metals, have a [what] specific heat capacity?
small
what is the specific heat capacity of water?
4.18 J g-1 K-1
units for specific heat capacity:
J g-1 K-1
0K = [what] degrees Celsius?
-273oC
what is the m in q = mc∆t?
the mass that changes temperature! NOT the mass of the reactants!!
units for q = mc∆t:
q = J
m = g
c = J g-1 K-1
∆T = K/C
4 reasons why combustion provides an inaccurate Q value:
heat loss to surroundings → could be to beaker, but mainly surrounding air
incomplete combustion of fuel → CO/C produced instead of CO2
evaporation of methanol (fuel) → burner isn’t weighed quick enough
non-standard conditions
lead to a value of ∆cH that is NOT exothermic enough!
how can a combustion reaction be altered to make it more accurate?
draught screens
input of oxygen gas
what kind of cup should be used to determine the enthalpy change of a reaction between 2 solutions (or a solid + solution)?
a polystyrene cup
a neutralisation reaction is normally between…
2 solutions
what is an average bond enthalpy?
the energy required to break one mole of a specific type of bond in a gaseous molecule
bond enthalpies are always…
endothermic → positive enthalpy value
limitation of average bond enthalpies:
it varied depending on chemical environment
is bond breaking endo/exothermic?
endothermic → ∆H is positive
is bond making endo/exothermic?
exothermic → ∆H is negative → think BMX!
when given bond enthalpies, how do we work out the ∆H of a reaction?
break - make
what does Hess’s Law state?
if a reaction can take place by 2 routes, and the starting and finishing conditions are the same, the total enthalpy change is the same for each