temporal lobe function + dysfunctions
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
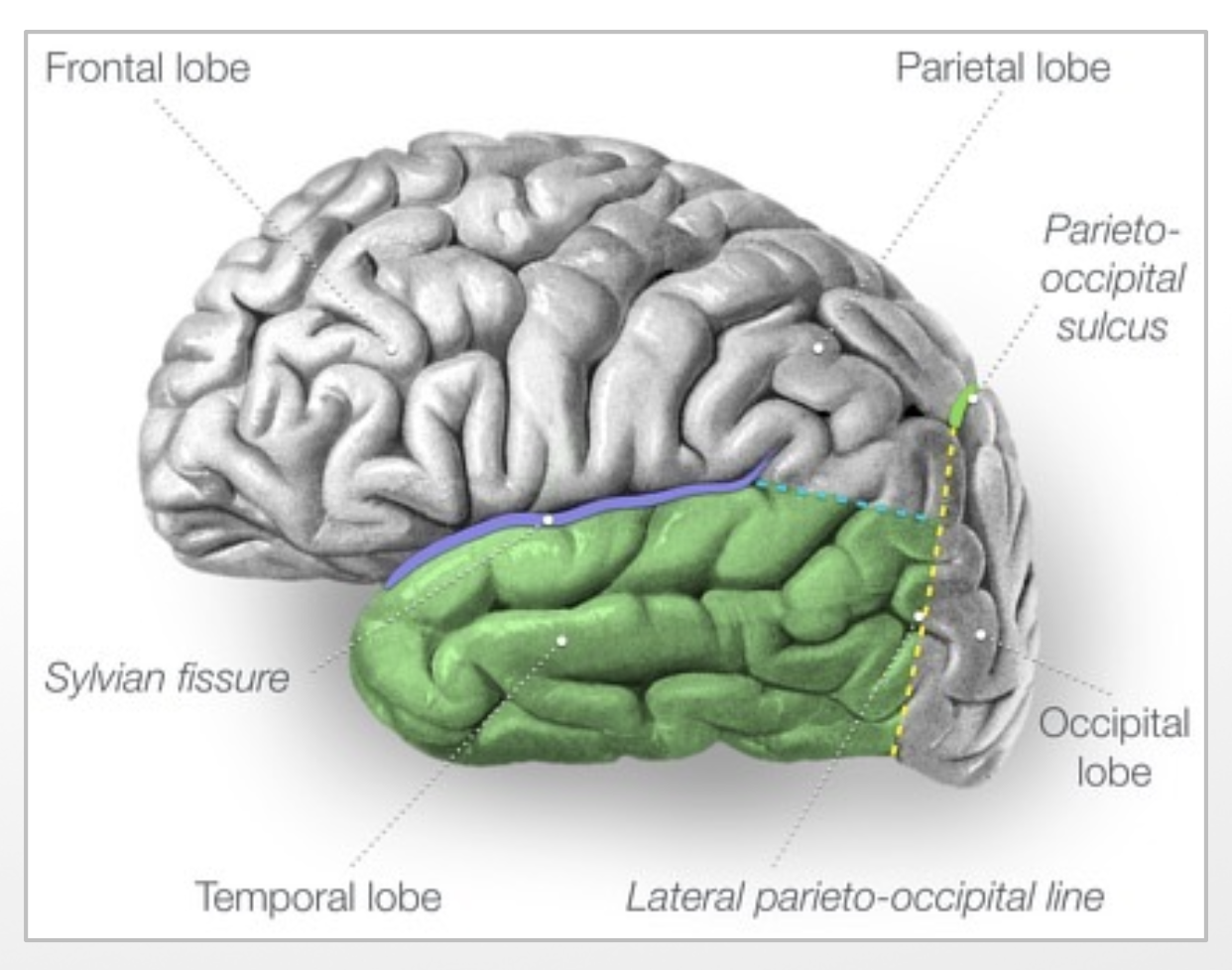
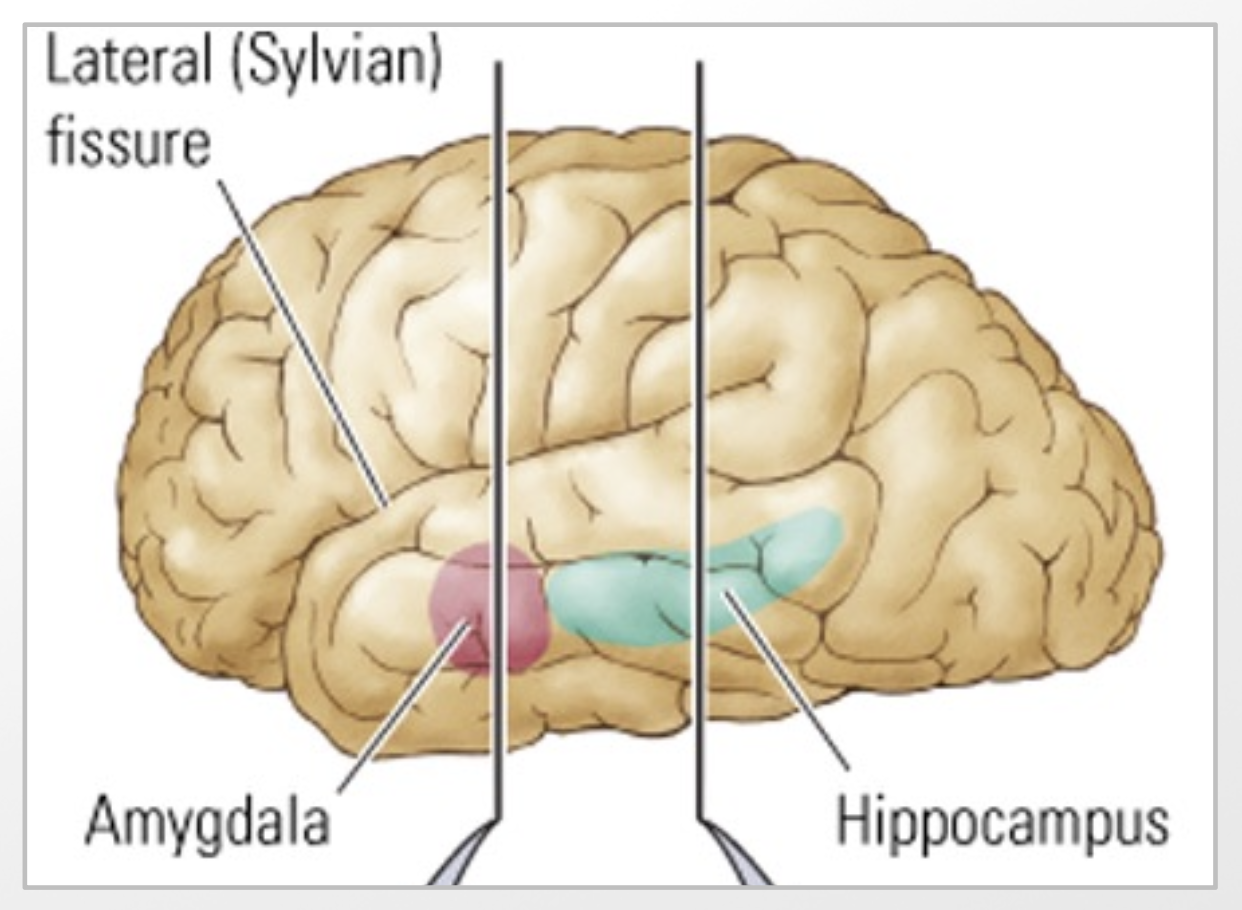
the temporal lobe is inferior to the ____ and anterior to the ____
Sylvian fissure
occipital cortex
functions of the temporal include: (3)
auditory + visual perception
object recognition
long-term memory (medial temporal)
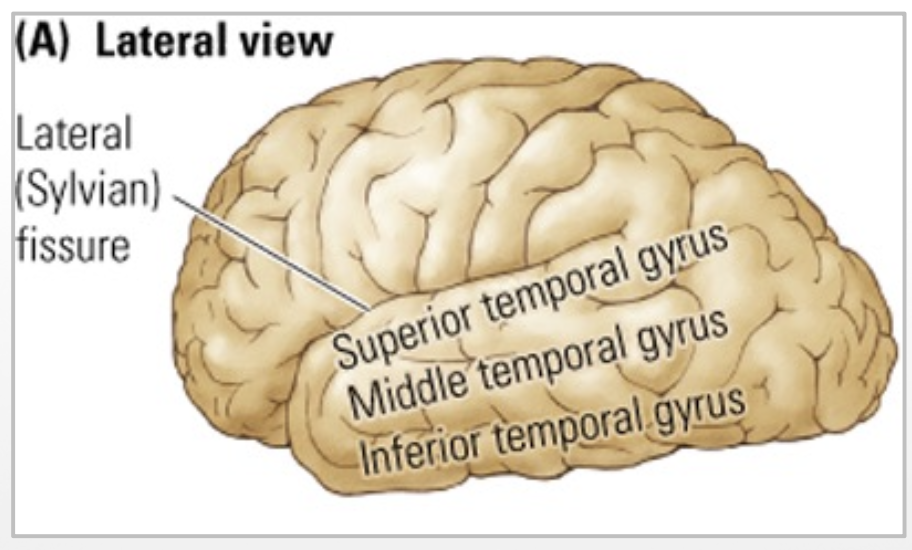
lateral surface of the temporal cortex is divided into: (3)
superior temporal gyrus
middle temporal gyrus
inferior temporal gyrus
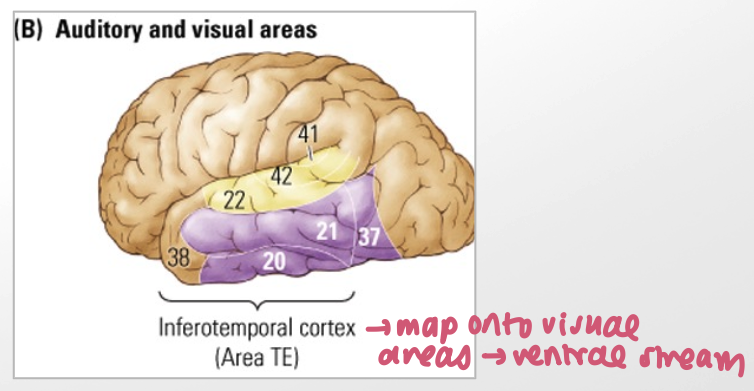
visual areas → _____ stream in the ___ part of the temporal cortex
ventral
inferior part
auditory areas of the lateral surface of the temporal lobe (3)
1º auditory cortex (tonographically organized) → (A1)
2º auditory cortex
Wernicke’s area (posterior superior)
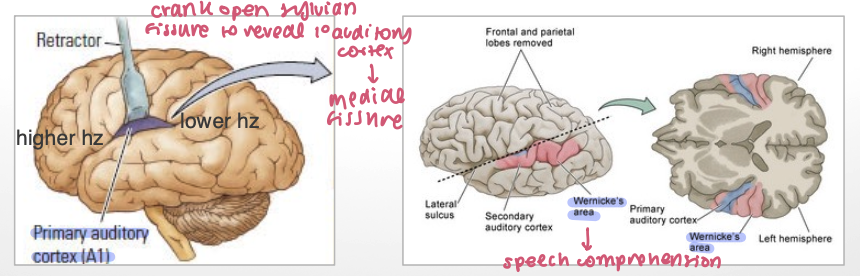
Wernicke’s Area responsible for ____
speech comprehension
anterior A1 is for ___ hz and posterior A1 is for ___
higher
lower
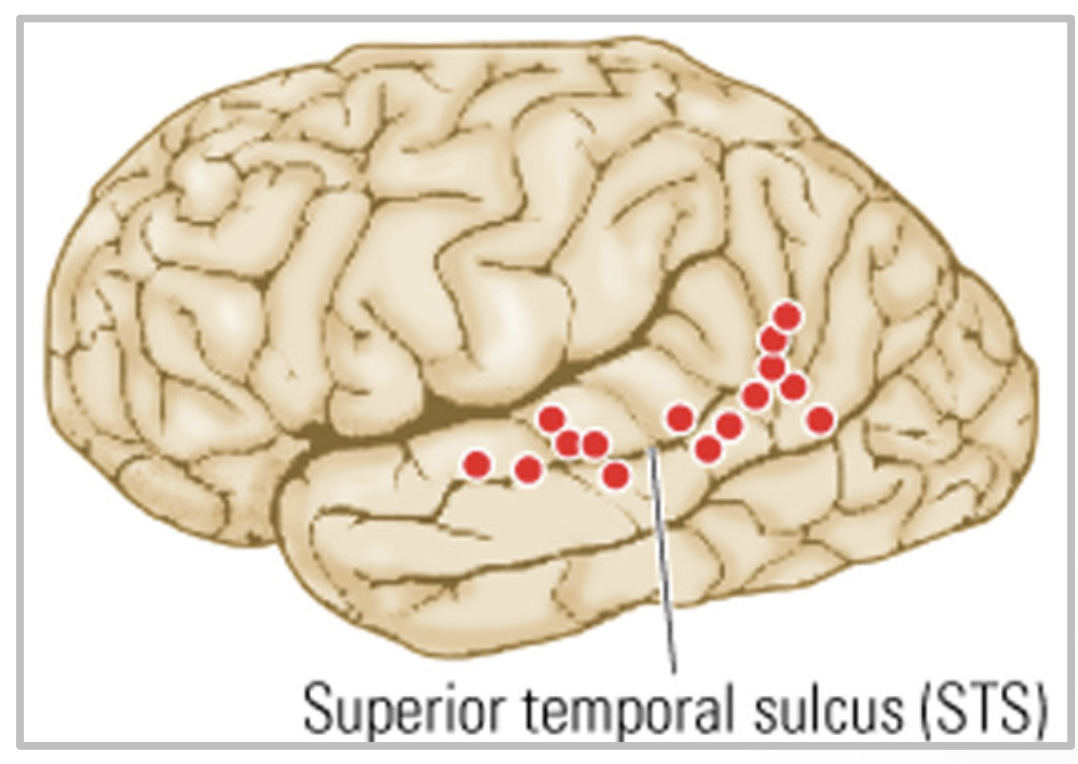
superior temporal sulcus (STS) (3)
polymodal region
takes inputs from multiple sensory regions + polymodal regions
visual, auditory, somatosensory
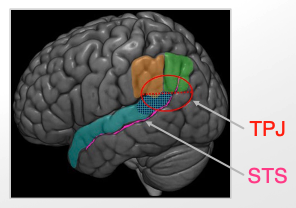
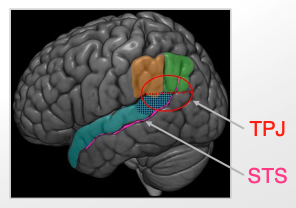
temporo-parietal junction (TPJ) responsible for 2:
attention
social processing
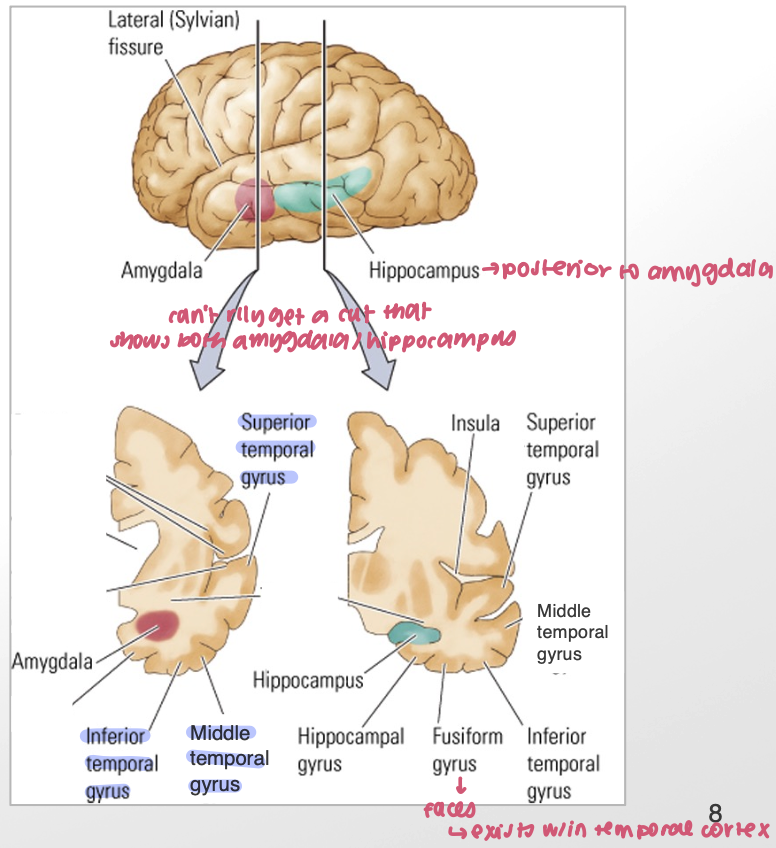
medial and subcortical areas of the temporal cortex (5)
amygdala
hippocampus
fusiform gyrus
insula
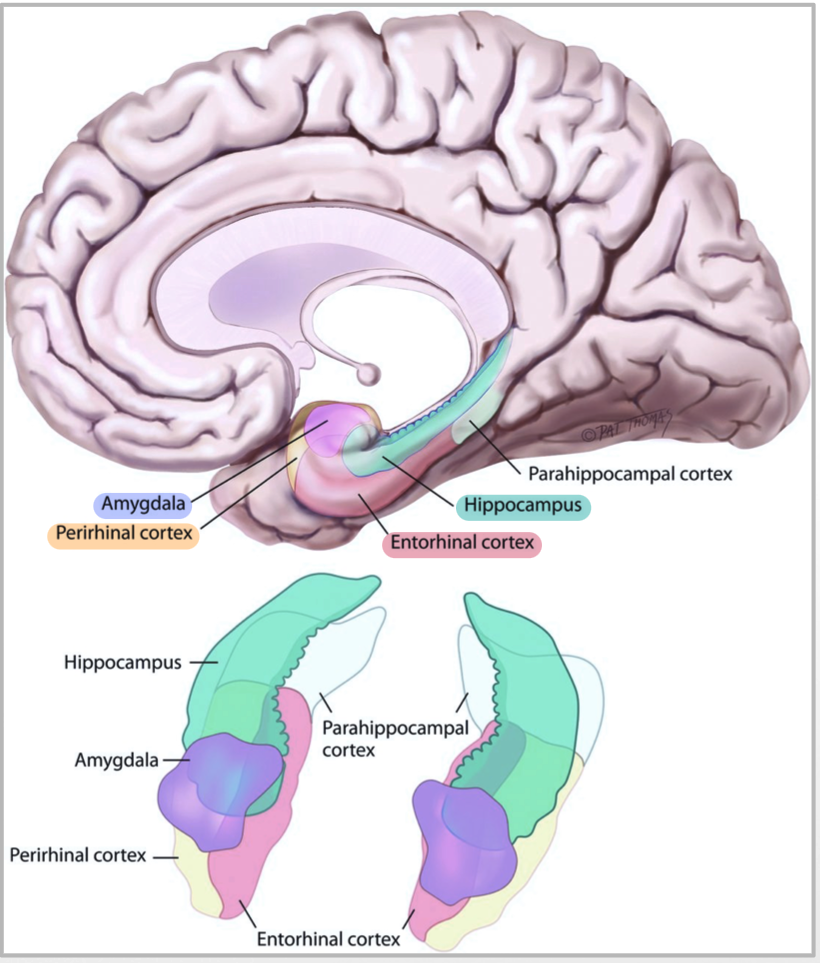
areas below hippocampus (3)
areas that lie below//wrap around hippocampus (3)
parahippocampal cortex
entorhinal cortex
perirhinal cortex
afferent projections into the temporal come from:
sensory systems
auditory, visual, somatic regions
efferent projections (sends info to) (3):
frontal + parietal association regions
limbic system
basal ganglia
hierarchical sensory pathway (A) (2)
ends up in temporal pole → most anterior part of temporal
function: stimulus recognition
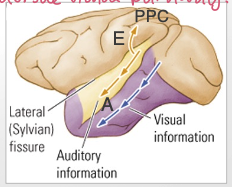
dorsal auditory pathway (E) (4)
ends up in posterior parietal cortex
v. similar to dorsal visual pathway
function: detection of spatial location → movement of sound
where in space sound is coming from
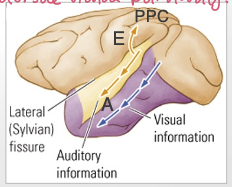
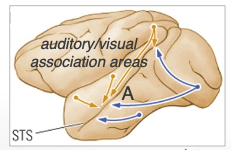
polymodal pathway (A) (3)
function: stimulus categorization
visual + auditory input
ends up in the superior temporal sulcus (STS)
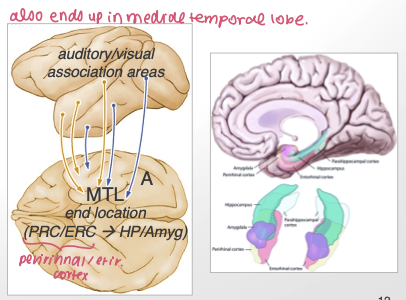
medial temporal projection (A)
also ends up in medial temporal lobe
function: learning + LT memory
frontal lobe projection (E)
ends up in frontal lobe
function: movement control, working memory, affect
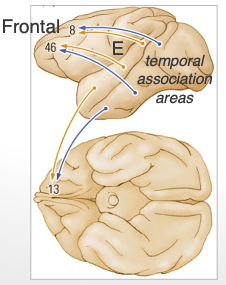
you lose your phone and a friend calls to help find it → what pathway is involved?
dorsal auditory pathway (E)
you are trying to keep up w the lecturer + write notes (remember what they are saying while you write) → what pathway is involved
frontal lobe projection (E)
overview of functions of the lateral regions of the temporal lobe (4)
process speech (L hemisphere), music (R) + other auditory stimuli
1º+2º auditory cortex
visual object recognition
2º visual areas → ventral pathway
identification + categorization of stimuli
inferior temporal cortex
cross-model matching
STS

overview of medial + subcortical regions functions of the temporal lobe
affective response (esp. fear)
amygdala (emotions in general)
encoding info. into long-term memory
hippocampus, perirhinal cortex
spatial navigation
hippocampus
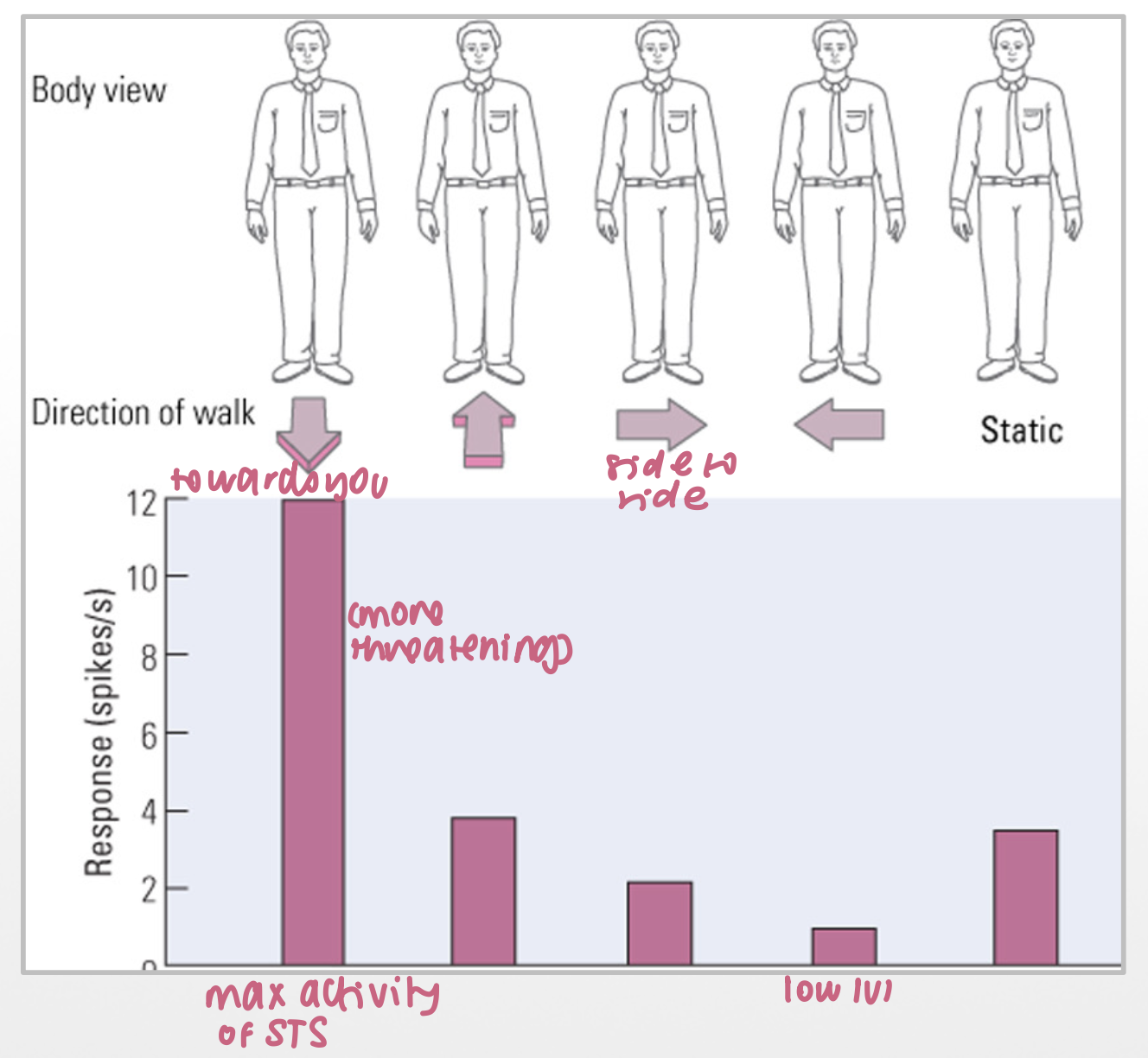
STS and biological motions
movement relevant to species
important for social cognition
in monkeys, ____ cells respond to eye gaze, ______, facial expression
STS
mouth movement
theory of mind
attributing intentions/beliefs/desires to ourselves + others
ie. I won’t talk about a certain thing excessively if I know the person I am talking to doesn’t like that thing
which direction of walking stimulates the STS the most?
towards you bc more threatening
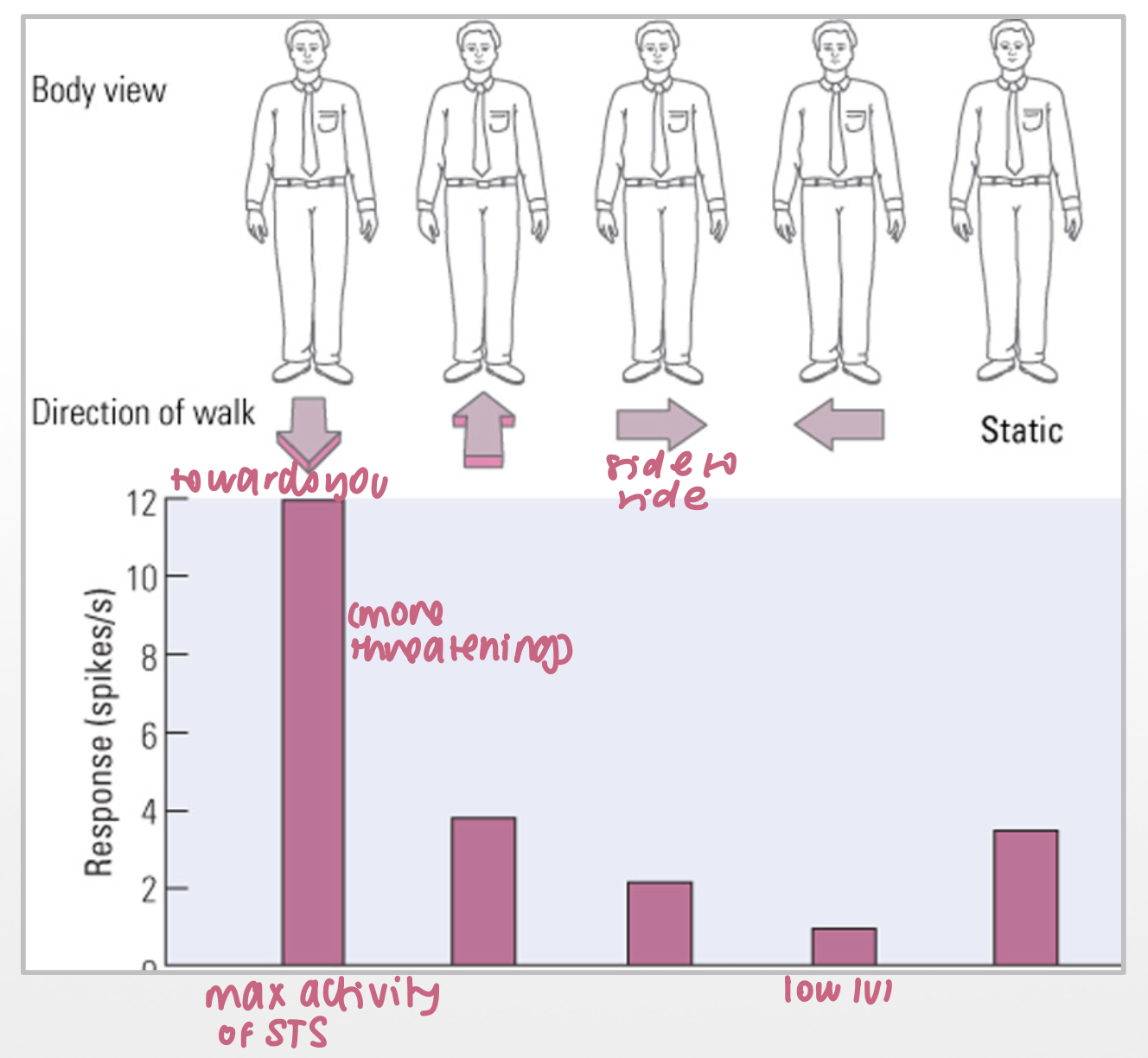
why are dots used to represent biological motion?
motion element singled out vs other visual input stimulating other areas
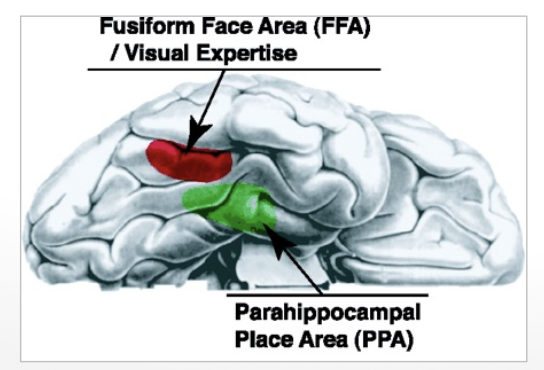
visual precessing areas
fusiform face area (FFA) → faces
parahippocampal place area (PPA) → scenes/places
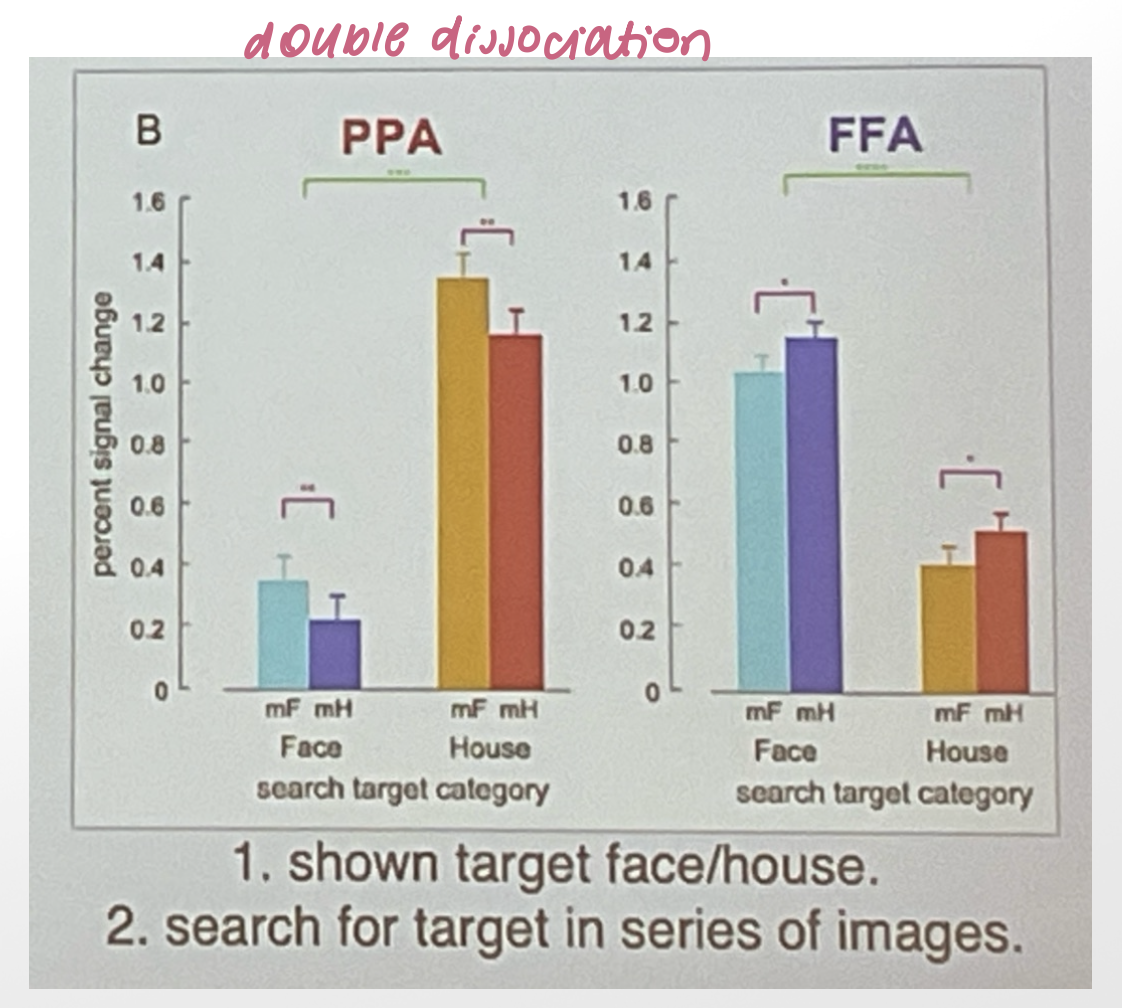
temporal regions for visual processing activate to ____ versus _____ → highlighting ______
faces
scenes
double dissociation
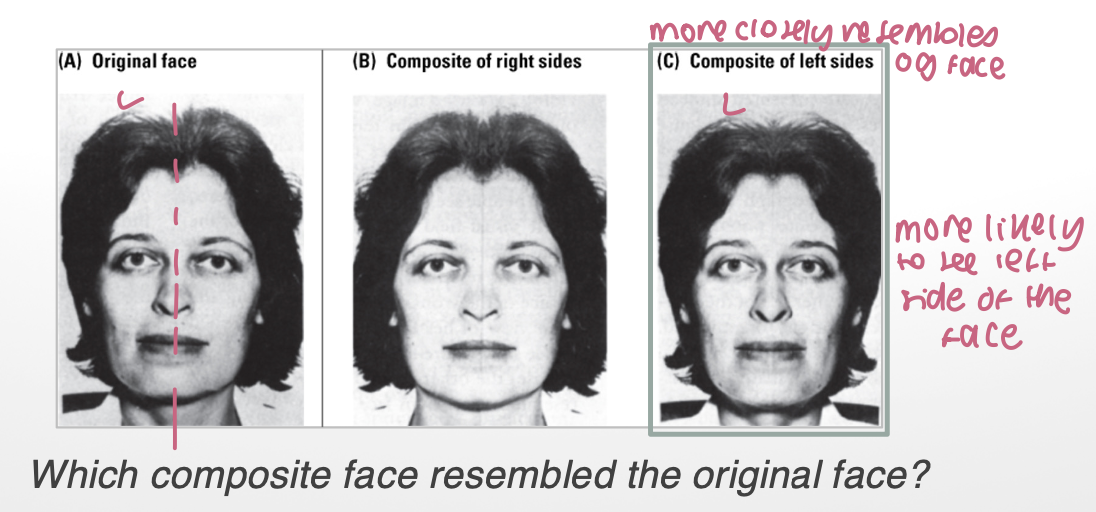
face processing (4)
selective activation of FFA
especially right hemisphere
shown in lesion + non-lesion individuals
distributed network that processes different aspects of face
how does speech differ from other sounds? (4)
Wernicke’s area → speech comprehension area in left temporal lobe
restricted range of frequencies tuned to perceive speech frequencies
same perception despite differing contexts → the ‘T’ in travel, Toronto, tea sound different but are all the letter ‘T’
speech sounds processed v. rapidly (30 vs 5 segments/s)
four characteristics of music perception
loudness
timbre
pitch
rhythm
loudness
magnitude of sensation judged by an individual
timbre
distinctive characteristic of sound
pitch
position of sound in musical scale (prosody/tone in speech)
rhythm
sound duration grouping and temporal regularity (beat)
temporal lobe lesion symptoms (3)
attention selection disturbances
language comprehension problems
disorders of memory
auditory disturbances (3)
cortical deafness
problems in discriminating speech sounds
Wernicke’s area
auditory hallucination → common symptom of schizophrenia
A1, Broca’s area, speech zones in left temporal cortex, hippocampus, amygdala
music perception disorders (3)
pitch discrimination → right posterior STG
meter discrimination → right/left anterior STG
amusia: tone deafness → inability to produce/comprehend musical sounds
music as pots and pans
imparements in visual perception (3)
impaired:
object + complex pattern recognition
biological motion recognition → STS
abnormal face perception → right temporal lobe (FFA)
prosopagnosia
altered personality + affect (6)
disrupted fear response → amygdala lesion
temporal lobe “personality”
egocentricity
perseveration
paranoia
proneness to aggression
evidence from lesion + stimulation studies
association btw sensory input + emotion
Klüver Bucy Syndrome
damage to bilateral amygdala + inferior temporal lobe
hyperphagia: strong sensation of hunger/desire to eat
hypersexuality: abnormal preoccupation w sexual fantasy
hyperorality: excessive oral activities
visual agnosia
loss of normal fear/anger responses
memory loss
Temporal lobe epilepsy
epileptic source is the temporal lobe
treatment: medication → or surgery
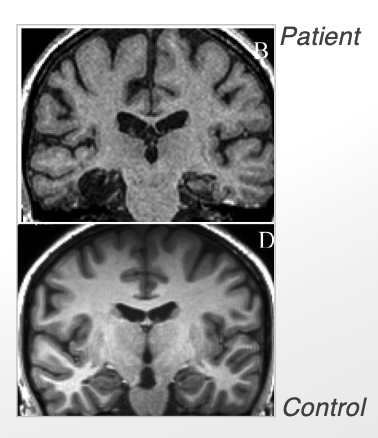
what does surgical removal of selective regions in temporal lobe say about temporal lobe function? (3)
left temporal lobectomy led to greater loss in verbal memory
nonverbal memory loss is comparable btw left/right temporal lobectomies
medial temporal lobe lesion led to impaired precision in spatial navigation towards targets in a virtual navigation task