14: Carbonyl compounds
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
How are carboxylic acids formed?
Oxidation of aldehydes using acidified potassium dichromate
Under reflux
Why can carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition?
The carbon has a delta positive charge and is electron deficient
So its attracted to a nucleophiles as they have a high electron density
The C=O bond is unsaturated and very reactive
How is a pi bond formed in the C=O group?
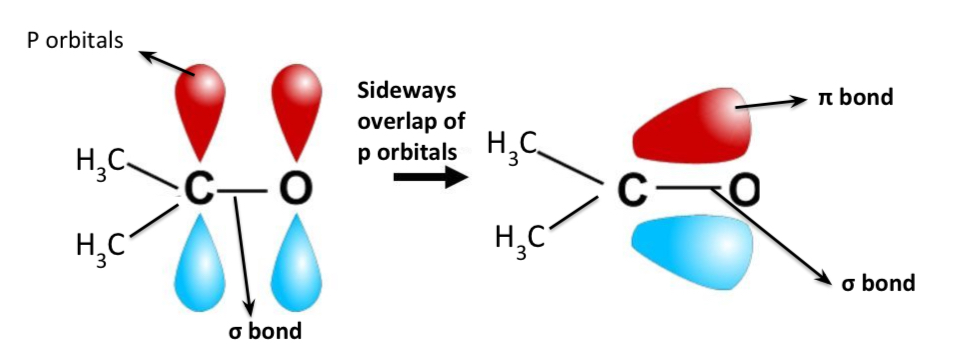
What are examples of nucleophiles?
:OH-
H2O:
:NH3
Cyanide :-C=N
Hydride :H-
What is the general mechanism for nucleophilic addition?
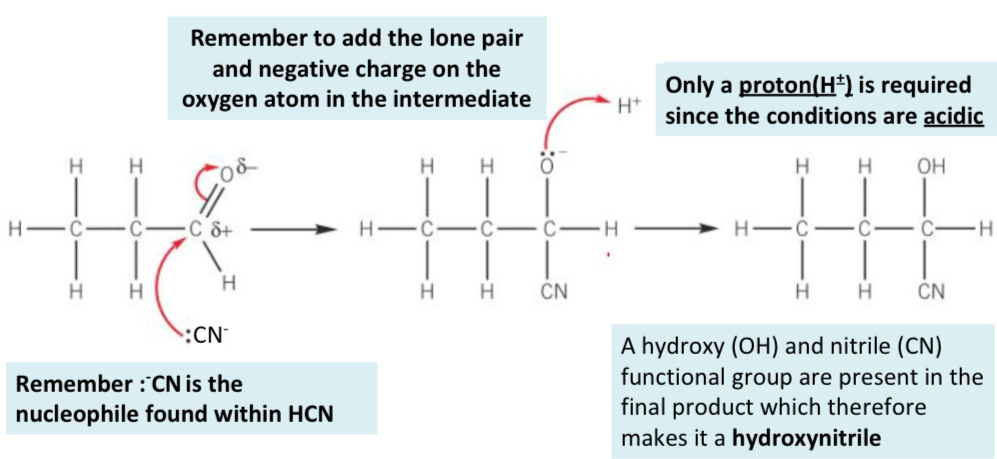
1) The lone pair of electrons on the nucleophile is donate to the delta positive carbon atoms of the carbonyl bond, forming a dative covalent bond
2) The pi bond in the C=O bond breaks by heterolytic bond fission
3) A negatively charged intermediate is formed
4) The lone pair on the oxygen atom of the intermediate is donated to the hydrogen atom in a water, alcohol or hydrogen cyanide molecule. A dative covalent bond is therefore formed
5) The intermediate is protonated to form an alcohol or a hydroxynitrile
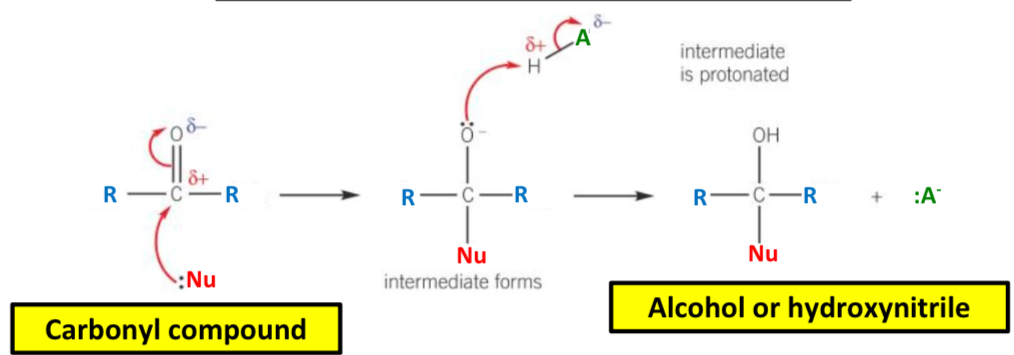
What is the reducing agent in the reduction of carbonyl compounds to alcohols?
Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) actsa as reducing agent
The BH4- acts as source oh hydride ions
THE HYDRIDE ION IS THE ONLY SPECIES INVOLVED IN THE NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
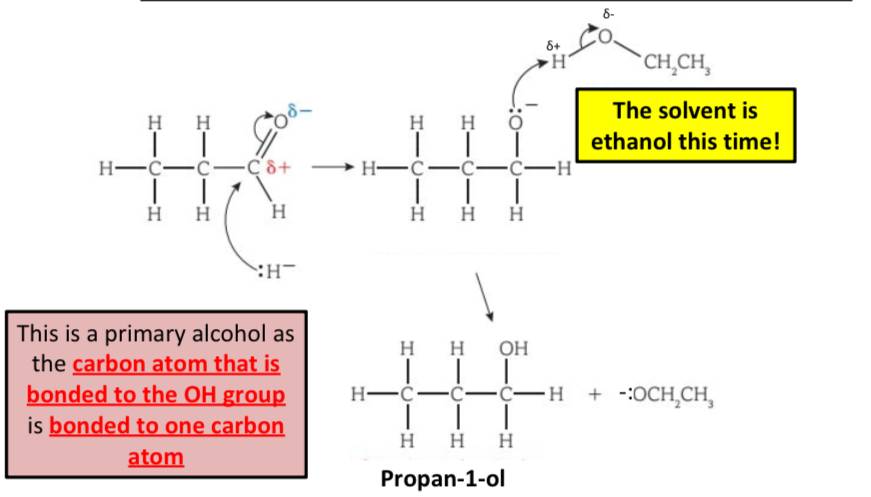
Aldehydes are reduced by sodium borohydride to form what?
Primary alcohols
What is the reducing agent represented with in an equation?
[H]
How many moles of reducing agent are needed for aldehydes to be ruled to primary alcohols by NaBH4?
2
What are ketones reduced to by NaBH4? How many moles of the reducing agent are needed?
Secondary alcohols
2
The NaBH4 needs to be what?
In aqueous solution
NaBH4/H2O
What is the reaction mechanism for the reduction of ketones?
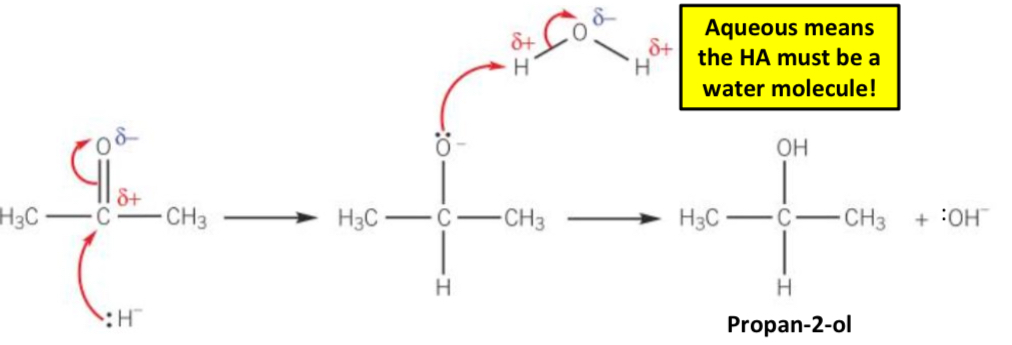
What is the reaction mechanism for the reduction of aldehydes?
What are the nucleophiles used in the formation of hydroxynitriles?
Hydrogen cyanide: a weak acid that will partially ionise in solution to form a nucleophiles called a cyanide ion. HCN is a poisonous gas
Sodium cyanide: a salt that will completely ions to form a cyanide ions. It is safer to use
what is the mechanism for the formation of hydroxynitriles?
What are the reagents for the formation of hydroxynitriles?
NaCN(aq) and H+ (aq)