Management Accounting Set 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the difference between a percentage and a percentage point?
a percentage expresses a ratio relative to 100 (e.g. 20%)
A percentage point measures the absolute change between percentages (e.g. 10% —> 12% = +2 percentage points)
How do you calculate a percentage share of a total ?
Share (%) = Part/Total x 100
Formula for percentage variation (growth rate)?
Variation (%) = Final Value - Initial Value / Initial Value x 100
What is a negative percentage variation?
It means the value decreased. Example : From 100 → 90 → (90-100)/100=-0,1 × 100= -10%
Formula for Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
→ Measures average annual growth over time.
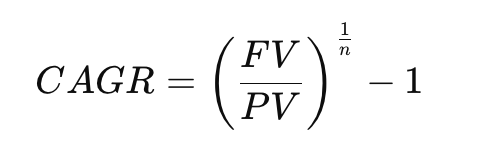
Formula for Future Value (FV)?
where i = growth rate or interest rate, n = number of periods
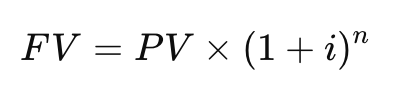
What’s the difference between simple and compound interest ?
simple interest : only on the initial principle
compound interest: on both the principal and accumulated interest
Why do interest rates exist ? (4 reasons)
Cost of availability (money tied up)
Cost of risk (possibility of default)
Compensation for inflation (loss of purchasing power)
Administrative cost (bank’s structure & profit)
What does inflation measure?
The decline in purchasing power of money — i.e. how many goods/services a currency can buy decreases as prices rise.
What is the breakeven point (BEP)?
The sales level at which total revenues = total costs —> no profit, no loss

What are fixed costs?
Costs that do not vary with sales volume (rent, salaries, website hosting)
What are variable costs ?
Costs that change directly with sales or production (raw materials, shipping, packaging)
What is gross margin?
Shows profitability before marketing or overhead costs.
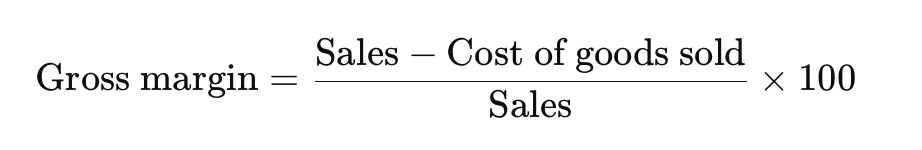
What is operating margin ?
Includes gross margin minus operating (marketing, admin) costs.
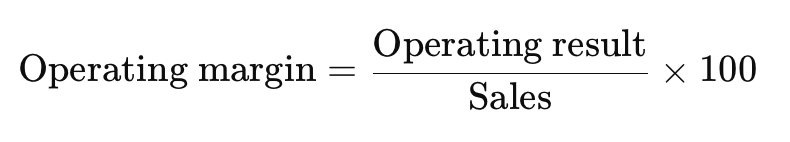
What is EBIT (Operating result)?
Earnings Before Interest and Taxes - a measure of the company’s core operating performance.
How do marketing and selling costs affect results ?
They impact the operating result but not the gross result, since they occur after gross profit in the income statement.
What are the main sources of difference between published and organic growth ?
Currency fluctuations
Changes in scope/perimeter (acquisitions, disposals)
how to calculate a selling price from a target gross margin ?
Selling price = Cost / 1- Target Margin
Converting Currencies
if €1 = $1.09 →
€100 000 = $109 000 (€ amount multiplied by 1.09)
€241 980= €222 000 ($ amount divided by 1.09)
What is the contribution margin (CM) ?
CM = Sales - Variable Costs
Shows how much each sale contributes to covering fixed costs and profit.
What is the contribution margin ratio (CMR)
CMR= CM/Sales
It expresses the CM as a % of sales.
Formula for breakeven sales (in €)
Breakeven sales = Fixed costs / CMR
Example: Fixed costs €25 000, CMR: 0.5 → BE= €50 000
Formula for breakeven quantity (units):
BE (units)= Fixed costs /CM per unit
What happens when fixed costs increase?
Breakeven point rises - you need more sales to cover costs.
What happens when contribution margin increases?
Breakeven point falls - you reach profit sooner.
What is the margin of safety ?
The % by which actual (or forecasted) sales exceed the breakeven point.

What is gross profit?
Sales - Cost of goods sold (COGS)
Shows profitability from core production before overheads
What is operating profit?
Gross profit - Operating expenses (marketing, admin, logistics)
What is net profit?
Operating profit - interest - taxes
Difference between markup and margin ?
Margin: profit as a % of selling price.
Markup: profit as a % of cost.
Example: Cost €100, Price = €150 → Margin = 33%, Markup = 50%
Formula for markup pricing:
Price Cost x (1 + Markup)
What’s a good way to improve operating margin?
Increase sales price, reduce variable costs, or optimize fixed costs (efficiency)
What is ROI (Return on Investment) ?
ROI = Operating profit/ Invested Capital x 100
Measures how efficiently the company uses its capital.
What is EBIT used for ?
Used to compare performance independently of financing structures (neutral measure of operations)
What is an exchange rate ?
The price of one currency in terms of another (e.g. €1 = $1.09)
What happens when your home currency strengthens?
your exports become more expensive abroad, and profits from foreign sales shrink when converted back.
Example: if €1 goes from $1.09 → $1.20, a $120 sale now brings only €100 instead of €110
What happens when your home currency weakens?
Foreign revenues translate into more home-currency income - good for exporters but increase import costs
What is currency risk?
the potenial gain or loss caused by exchange-rate fluctuations between the transaction date and the payment date.
How can companies reduce currency risk?
Through hedging (forward contracts, options) or natural hedging (matching costs and revenues in the same currency)
What is Cost-plus pricing ?
Adding a fixed markup or margin to a cost.
Example: Cost €200 + 25% markup → Price of €250
What is Value-based pricing?
Setting a price according to the perceived value to customers, not just cost.
Common in luxury: emotional value > functional cost.
What is Competition-based pricing?
Serves as a benchmark against market leaders or similar products: used when differentiation is limited.
What is dynamic pricing?
Adjusting prices frequently based on demand, season or customer data (e.g. travel, hospitality, or limited drops)
What is psychological pricing?
Using perception tactics like €990 instead of €1000 to suggest precision or value