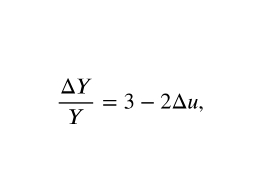Macro Theory Chapter 3- Labor Market
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the production function?
This is the function that is used to measure the relationship between the inputs and outputs of the economy.
What is the equation for the production function?
Y= A x F(K,N)
Y= real output
A= number measuring total productivity
K= capital stock or quantity of capital
N= Labor
F= represents the function that relates quantities of capital and quantities of labor to each other that increases output.
What is the Cobb-Douglas Production Function?
Y= AK0.3 N0.7 where it could also be written as A= Y/K0.3 N0.7
K has the power of 0.3 to represent the elasticity in output produced by Capital (1% increase in capital results in a 0.3% increase in output)
N has the power of 0.7 to represent the elasticity in output produced by labor
(1 % increase in labor results in a 0.7%) increase in output
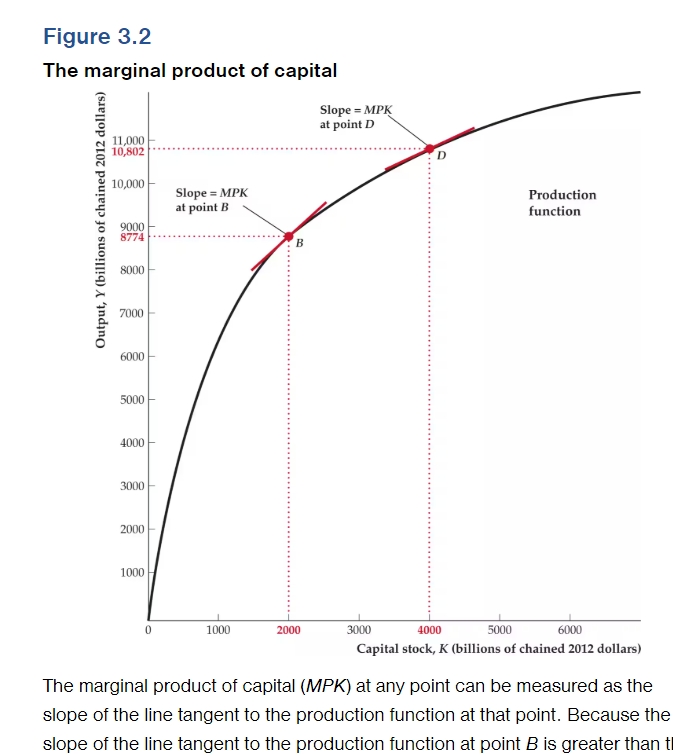
What is the marginal Product of Capital? (MPK)
This is the increase in output that results from a 1 unit increase in capital stock represented by change in Y over change in K.
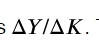
What is the marginal product of labor?
The increase in output that results from a 1 unit increase in labor (hiring an additional worker). Measured as change in Y over change in N
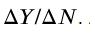
What is the principle of diminishing marginal productivity?
This is when the marginal product of capital or labor increases by smaller and smaller increments, the production function of the labor market gets flatter as productivity increases. When you hire more workers or increase capital stock, you get less gain as you did before (still better off, just by a smaller amount).
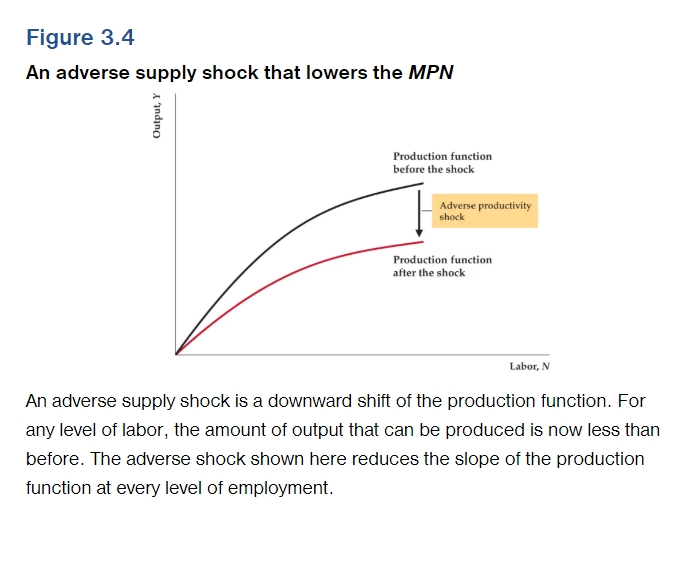
What is a supply shock? (Productivity Shock)
This refers to a change in an economy’s production function. Positive supply shocks raise the amount of output that can be produced given quantities of capital and labor. Negative supply shocks decrease the amount of output that can be produced given quantities of capital and labor.
What are the assumptions about Demand for Labor?
All workers are alike
Wages of workers are decided by competitive market and are viewed as such by firms
Firms are looking to maxmize profit
What is the Marginal Product of Revenue? (MRPN)
This is the real wage for workers represented as
w= W/P (real wage equals nominal wages over prices), firms want to hire employees’ whose MPN > MRPN because the amount of output given for this type of employee will allow firms to maximize profit.
What is the substitution effect of higher real wage?
When real wage increases for a short-term time, people will substitute more hours of leisure in exchange for labor. (i.e.- overtime pay for working on your time off)
What is the Intra-Temporal Substitution effect?
w increases, N increases, C increases, and Leisure decreases (work more now while real wage increases as opposed to relaxing more)
What is the Inter-Temporal Substitution effect?
w increases, N increases, Lf increases (work more now to increase leisure in the future when real wage increases)
What is the income effect of a higher real wage?
When real wages increases for a long-term time, a worker will either increase labor overtime to increase income or a worker will decrease labor overtime to maintain income.
What is the difference between the income effect and substitution effect?
The income effect is a long term effect on wages, while the substitution effect is a short term effect on wages.
What is Labor market equilibrium?
this is defined by the classical approach as when real wages and prices adjust to have full employment output (or sometimes called potential output) represented by the equation shown in the image
when Y bar equals full employment output, N bar equals full level employment, anything that changes N bar will change Y bar.
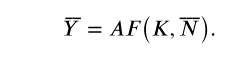
What assumption does the classical approach make about unemployment?
That the unemployment rate will reach zero (even though it will never reach zero due to the natural rate of unemployment)
What factors make up the labor force?
Employed workers and unemployed workers, discouraged workers are not part of the labor force.
What does the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) survey to find the rate of unemployment?
Households, they specifically measure the amount of people as opposed to the amount of jobs available. Around 60,000 households are surveyed.
How does The Employment Situation find the rate of unemployment?
uses the household and establishment surveys, however, this isn’t the official measurement of unemployment since it measures both people through households and jobs through establishment surveys, which leads to conflicting information
What is someone who is not in the labor force defined as?
Someone who didn’t work the past week and didn’t look for work within the past four weeks.
What is an unemployed worker defined as?
A person who didn’t work the past week but looked for work within the past 4 weeks
What makes up the unemployment rate? (The U3 measure of unemployment- official unemployment rate)
The fraction of people who are unemployed in the labor force. Unemployed People in Labor Force/ People in the Labor force.
What is the U1 measure of unemployment?
This measure only counts people as unemployed if they have been unemployed for 15 weeks or more.
What is the U2 measure of unemployment?
Only counts people as unemployed if they are job losers, or only held temporary positions, it doesn’t count people who have quit their jobs.
What is the U4 measure of unemployment?
Discouraged workers are added to both the unemployment rate and the civilian labor force. (DWs are people who think that they cannot find a job).
What is the U5 measure of unemployment?
Discouraged and marginally attached workers (MAWs are people who don’t have a job, but looked for one in the past 12 months) are added to the civilian labor force and to the number of the unemployed.
What is the U6 measure of unemployment?
Discouraged, marginally attached (are added to civilian labor force) and part time workers for economic reasons are added to the unemployment rate. (Part Timers for economic reasons refer to people who want to work full time but had to settle for a part time schedule).
What is a employed worker defined as?
A person who worked full time or part time last week (in case they were sick or on vacation from the job)
What is the participation rate?
the fraction of adults employed over the amount of adults in the labor force. Adults employed/ Adults in labor force
What is the employment ratio?
This is the fraction of adults employed over the adult population. Adults employed/ adult pop.
What is an “unemployment spell”? What is “duration”?
A unemployment spell is when a worker cannot find a job, the amount of time that this period lasts is known as duration.
What is frictional unemployment?
This is the reason why unemployment never reaches zero, it occurs when workers are looking for jobs while firms are looking for suitable workers
What is structural unemployment?
This is long term employment that exists even when the economy is not in a recession (chronic unemployment)
What is the natural state of unemployment?
This unemployment occurs when output and employment levels are at their full level.
What is cyclical unemployment?
This is equal to actual unemployment - natural unemployment
Positive when real output is less than full level employment levels
Negative when real output is greater than full level employment levels
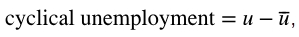
What is Okun’s Law?
The gap between an economy’s full employment and output and it’s actual level of output increases by 2 percent points for each percent the unemployment rate increases represented by the function.
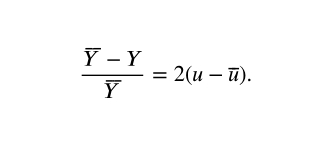
What is implied by Okun’s Law?
actual output will be 2% lower than full unemployment while also being 2 times the cyclical unemployment rate, it also implies that the natural rate of unemployment increases leading to less real output (less than 3% output on average), represented by the function shown