Crude oil, hydrocarbons and alkanes .1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
what is the only compound that contains hydrogen and carbon atoms only
Hydrocarbons
what is a crude oil and where is it found
Crude oil is a finite resource
that is found in the Earth’s crust. (It is the remains of organisms that lived and died millions of years ago - mainly plankton which was buried in mud)
what is crude oil
Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons.
how are the carbon atoms joined in hydrocarbons
The carbon atoms in these molecules are joined together in chains and rings
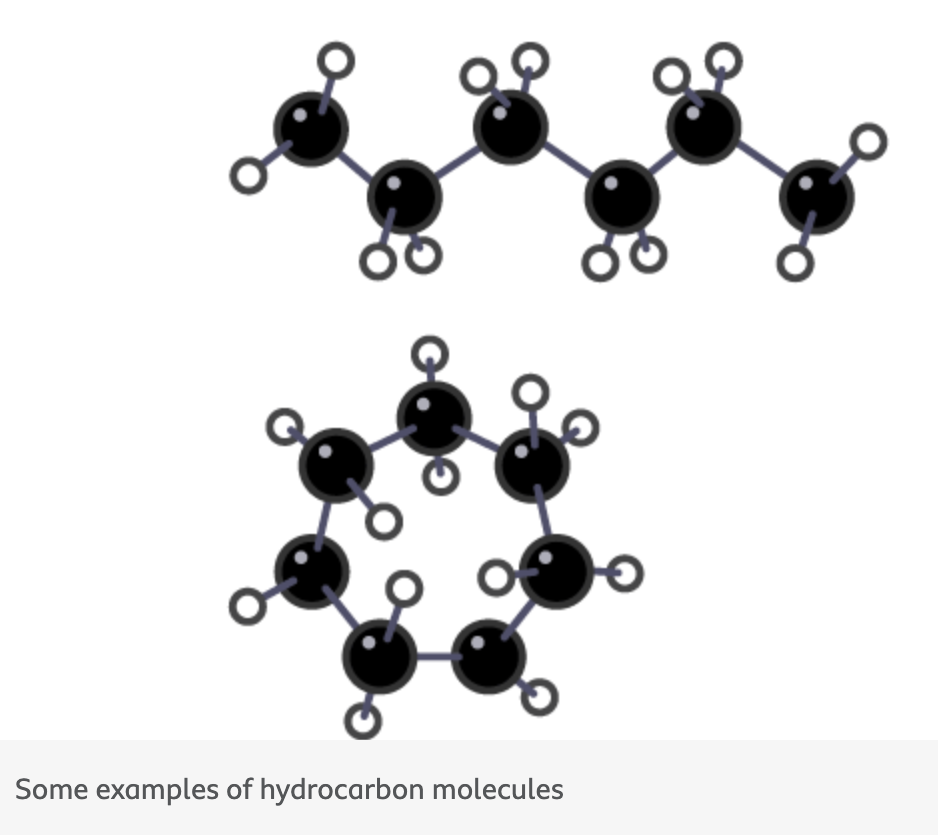
what is crude oil is an important source of (2)
fuels such as petrol, diesel, kerosene, heavy fuel oil and liquefied petroleum gases
feedstock for the petrochemical industry
what is a feedstock
A feedstock is a raw material used to provide reactants for an industrial reaction.
what is a petrochemical and give and example
substance made from crude oil using chemical reactions.
eg. ethene produced from crude oil.
used as feedstock to make poly(ethene), a polymer
what do alkanes form
a homologous series
Like all homologous series, what do the alkanes have the same (4)
have the same general formula
differ by CH2 in molecular formulae from neighbouring compounds
show a gradual variation in physical properties, such as their boiling points
have similar chemical properties
what is the general formula for the alkanes
CnH2n+2,
what is n in the general formula for alkanes
n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
what are examples of 4 alkanes
methane
ethane
propane
butane
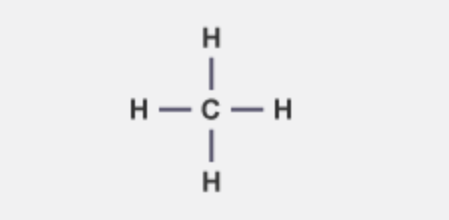
what is the molecular formula and structural formula of methane
CH4
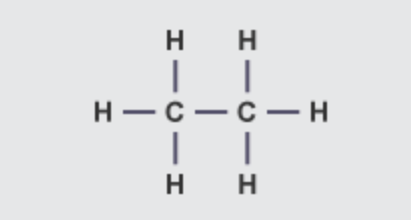
what is the molecular formula and structural formula of ethane
C2H6
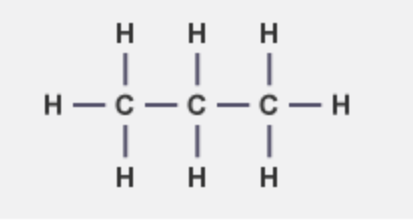
what is the molecular formula and structural formula of propane
C3H8
what is the molecular formula and structural formula of butane
C4H10
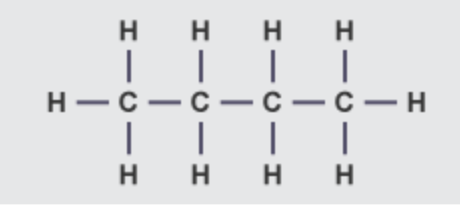
what are the alkanes
The alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons:
why are the alkanes hydrocarbons
because they are compounds containing hydrogen and carbon only
why are the alkanes saturated
because their carbon atoms are joined by C-C single bonds
what is Fractional distillation used for
to separate crude oil into simpler, more useful mixtures
why can the Fractional distillation method be used
because different hydrocarbons have different boiling points
what happens during the fractional distillation of crude oil (4) - bbc bitesize one
heated crude oil enters a tall fractionating column, which is hot at the bottom and gets cooler towards the top
vapours from the oil rise through the column
vapours condense when they become cool enough
liquids are led out of the column at different heights
process of fractional distillation
oil is heated until most of it has turned into gas - gases enter a fractionating column (and liquid bit is drained off)
in column theres a temp gradient (hot at bottom, cool at top)
longer hydrocarbons have high boiling points. they condense back into liquids and drain out the column early on, when they are near the bottom. shorter hydrocarbons have lower boiling point so condense much later on, near to the top of the column where its cooler
you end up with the crude oil mixture seperated out into different fractions. each fraction contains a mixture of hydrocarbons that all contain a similar number of carbon atoms so have similar boiling points
what is the structure (how are they held together/built) of Small hydrocarbon molecules and how does this affect them during the fractional distillation of crude oil
have weak intermolecular forces
so they have low boiling points
They do not condense, but leave the column as gases
what is the structure (how are they held together/built) of Long hydrocarbon molecules and how does this affect them during the fractional distillation of crude oil
have stronger intermolecular forces
so they have high boiling points
They leave the column as hot liquid bitumen
what are fractions and why are they called this
The different, useful mixtures are called fractions
This is because they are only part of the original crude oil
at the bottom of the fractionating tower what molecules are found and what are the properties of the molecules found here
hottest part
large molecules found here
high boiling point
not very volatile
does not flow easily
does not ignite easily
at the top of the fractionating tower what molecules are found and what are the properties of the molecules found here
coolest part
small molecules found here
low boiling point
very volatile
flows easily
ignites easily
what is the temperature of the fractionating tower at the top
coolest part
25 degrees
what is the temperature of the fractionating tower at the bottom
hottest part
350 degrees
how many parts is the fractionating tower spilt in
4
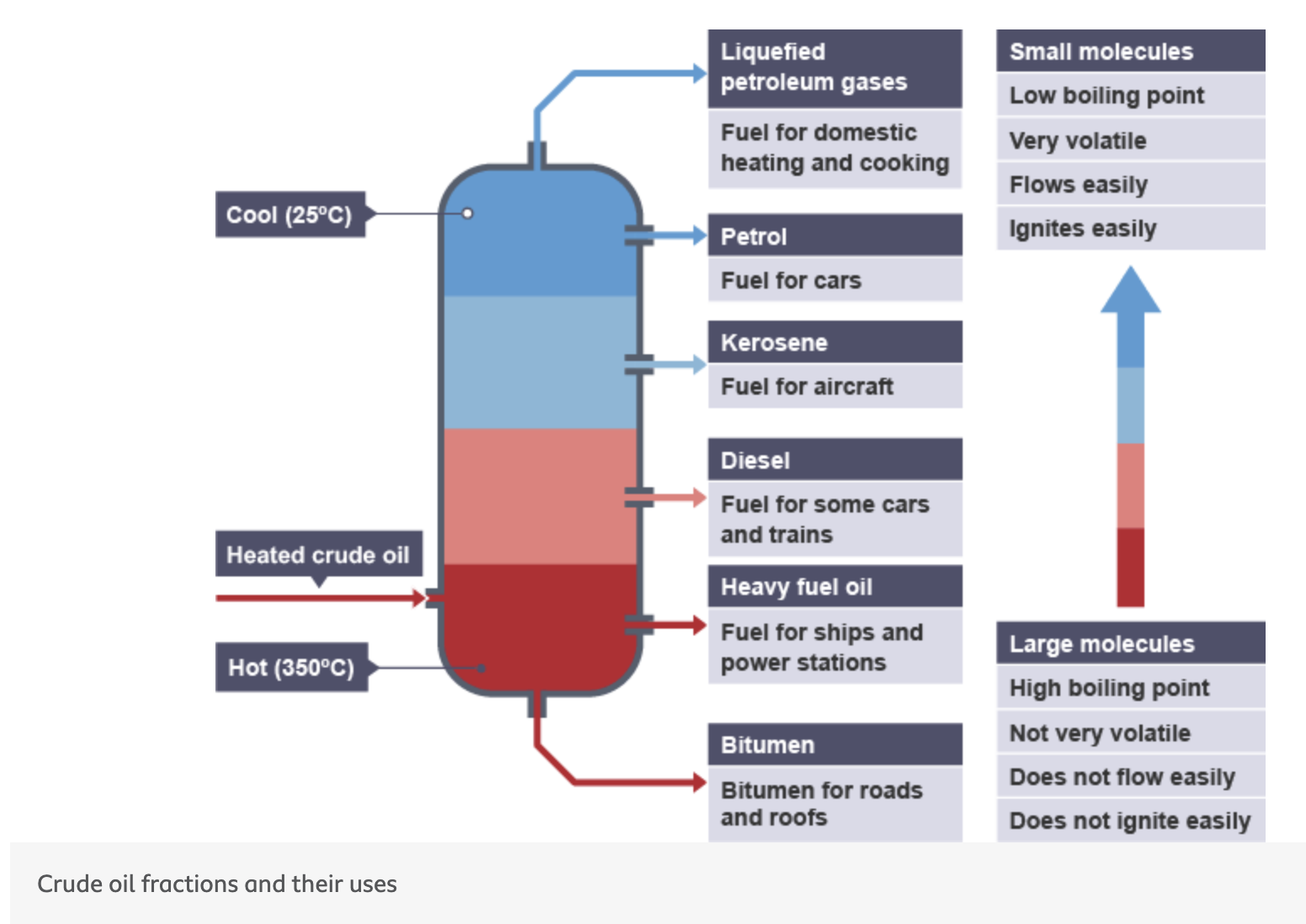
what are the crude oil fractions and their uses from top to bottom of the fractionating tower
liquefied petroleum gas
petrol
kerosene
diesel
heavy fuel oil
bitumen
what is liquefied petroleum gas use
fuel for domestic heating + cooking
what is petrol use
fuel for cars
what is kerosene use
fuel for aircrafts
what is diesel use
fuel for some cars + trains
what is heavy fuel oil use
fuel for ships + power stations
what is bitumen use
bitumen for roads + roofs
what is one way to remember the names of the fractions
Lazy
Penguins
Keep
Drinking
Hot
Beer
what does each crude oil fraction contain
a mixture of hydrocarbons
what are the hydrocarbons in a fraction mostly
alkanes
what do the alkanes in each fraction have similar but not identical (4)
numbers of hydrogen and carbon atoms in their molecules
boiling points
ease of ignition
viscosity
what do the gases fraction containing hydrocarbons with one to four carbon atoms have (properties 3)
These have:
boiling points below room temperature
they are very flammable
have a low viscosity
what does the hydrocarbons in the bitumen fraction containing hydrocarbons with more than 35 carbon atoms have as its properties in comparison to the previous factor with 1-4 carbon atoms (3)
These have:
boiling points well above room temperature
are very difficult to ignite
have a high viscosity
what can Hydrocarbon fuels can undergo and what does it depend on
complete combustion or
incomplete combustion
depending on the amount of oxygen available
when does complete combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel happen
when there is a good supply of air
what type of reaction happens when carbon and hydrogen atoms in the fuel react with oxygen and what is the product
an exothermic reaction
carbon dioxide and water are produced
the maximum amount of energy is given out
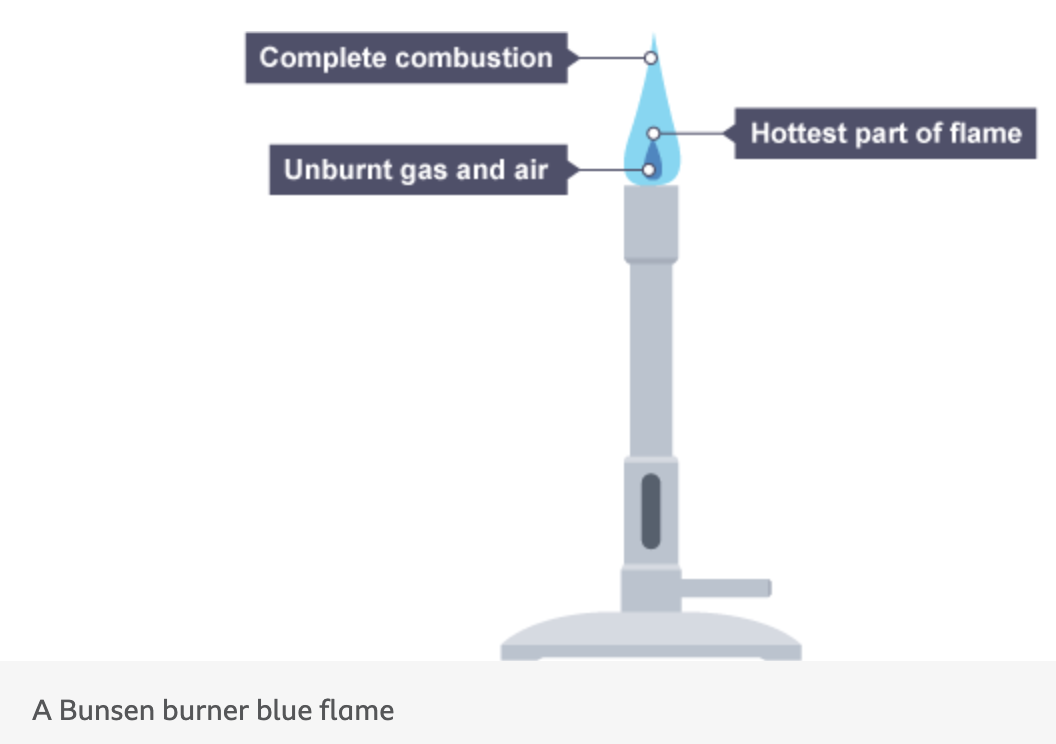
when does complete combustion happen in a bunsen burner
this occurs when the air hole is fully open
what is the general equation for the reaction
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
what is the equation for the complete combustion of propane, used in bottled gas
propane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
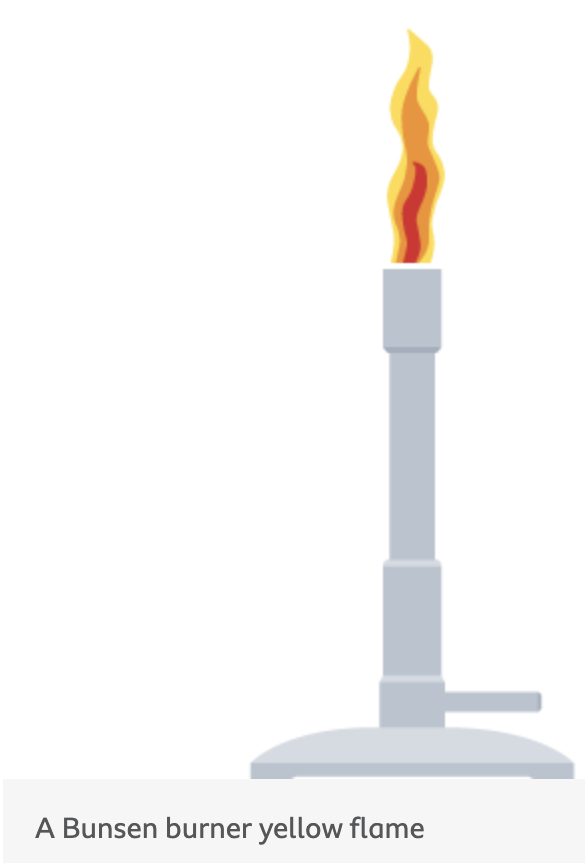
when does Incomplete combustion happens
when the supply of air or oxygen is poor
what is produced during incomplete combustion and what is the overall energy released
Water is still produced
but carbon monoxide and carbon are also produced
Less energy is released than during complete combustion
when does a incomplete combustion occur in a bunsen burner
incomplete combustion occurs when the air hole is closed

what is cracking + what are the unsaturated substances involved
a reaction in which larger saturated hydrocarbon molecules are broken down into smaller, more useful hydrocarbon molecules, some of which are unsaturated:
the original starting hydrocarbons are alkanes
the products of cracking include alkanes and alkenes, members of a different homologous series
what can hexane be cracked to form + state the word equation + equation
hexane can be cracked to form butane and ethene:
hexane → butane + ethene
C6H14 → C4H10 + C2H4
during cracking how is the formula/equation of each substance/product known
The starting compound will always fit the rule for an alkane, CnH2n+2.
The first product will also follow this rule.
The second product will contain all the other C and H atoms.
The second product is an alkene, so it will follow the rule CnH2n.
what is the alkene general formula
CnH2n
question : C16H34 is an alkane which can be used as the starting chemical in cracking. One of the products of cracking this compound is an alkane which has 10 carbon atoms in it. Write a balanced symbol equation for this cracking reaction.
C16H34 will be the first part of the equation
question says 10 carbon atoms and we know the first product in a chemical cracking is a alkane and the formula for that is CnH2n+n so it would be C10H22
then the second part of the product is a alkene and its whats left over so for carbon you would do 16-10=6 and for the hydrogen 34-22=12
the final answer would therefore be
C16H34 → C10H22 + C6H12
what are one of the 2 methods for cracking
Catalytic cracking
Steam cracking
what is cracking
thermal decomposition reaction - breaking down molecules by heating them
what is catalytic cracking
uses a temperature of approximately 550°C and a catalyst known as a zeolite which contains aluminium oxide and silicon oxide
what is steam cracking
uses a higher temperature of over 800°C and no catalyst
process of catalytic cracking. bbc bitesize one
The structure of hexane
The hexane is passed over a hot catalyst
Butane and ethene are produced
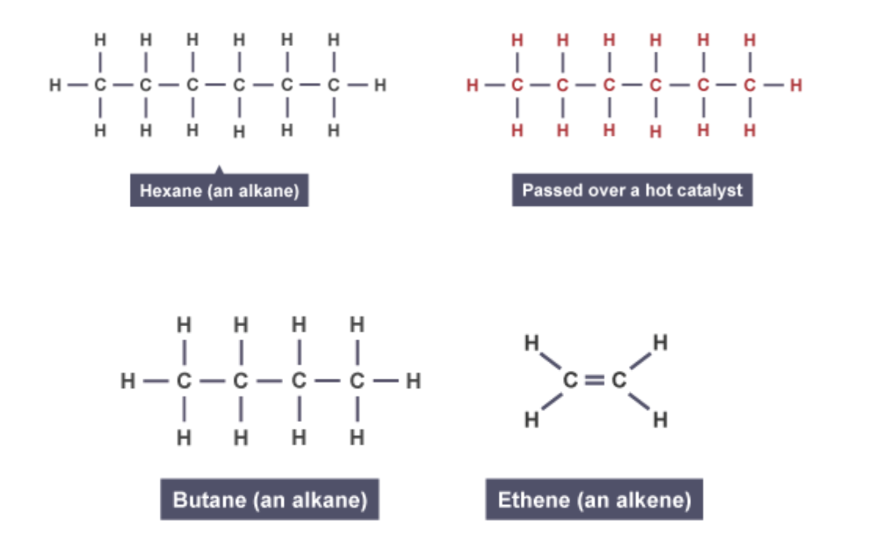
process of catalyctic cracking
heat the long chain hydrocarbons to vapourise them (turn them into gas)
vapour is then passed over a hot powered aluminium oxide catalyst
long-chain molecules split apart on the surface of the specks of catalyst
process of steam cracking
heat the long chain hydrocarbons to vapourise them (turn them into gas)
mix them with steam
then heat them at very high temperatures
why is cracking important (2)
It helps to match the supply of fractions with the demand for them.
It produces alkenes, which are useful as feedstock for the petrochemical industry.
what is the supply (definition)
The supply is how much of a fraction an oil refinery produces.
what is the demand (definition)
The demand is how much of a fraction customers want to buy.
what does fractional distillation of crude oil produce very often
produces more of the larger hydrocarbons than can be sold
and less of the smaller hydrocarbons than customers want
wha are smaller hydrocarbons more useful as than larger hydrocarbons
as fuels
what does cracking do to larger hydrocarbons and how is this good
converts larger hydrocarbons into smaller hydrocarbons
the supply of fuels is improved
This helps to match supply with demand
what do Alkanes and alkenes both form a series of
Alkanes and alkenes both form homologous series of hydrocarbons
what is the difference between alkenes and alkanes and what does this result to (2)
alkanes are saturated, their carbon atoms are only joined by C-C single bonds
alkenes are unsaturated, they contain at least one C=C double bond
As a result, alkenes are more reactive than alkanes. Alkenes can take part in reactions that alkanes cannot
what will ethene molecules react together to form
poly(ethene), a polymer.
what will happen when alkenes react with bromine water and how is this useful for testing
turn it from orange/brown to colourless.
This is the way to test for a double C=C bond in a molecule.