Biology Quiz 1: Properties of Water
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
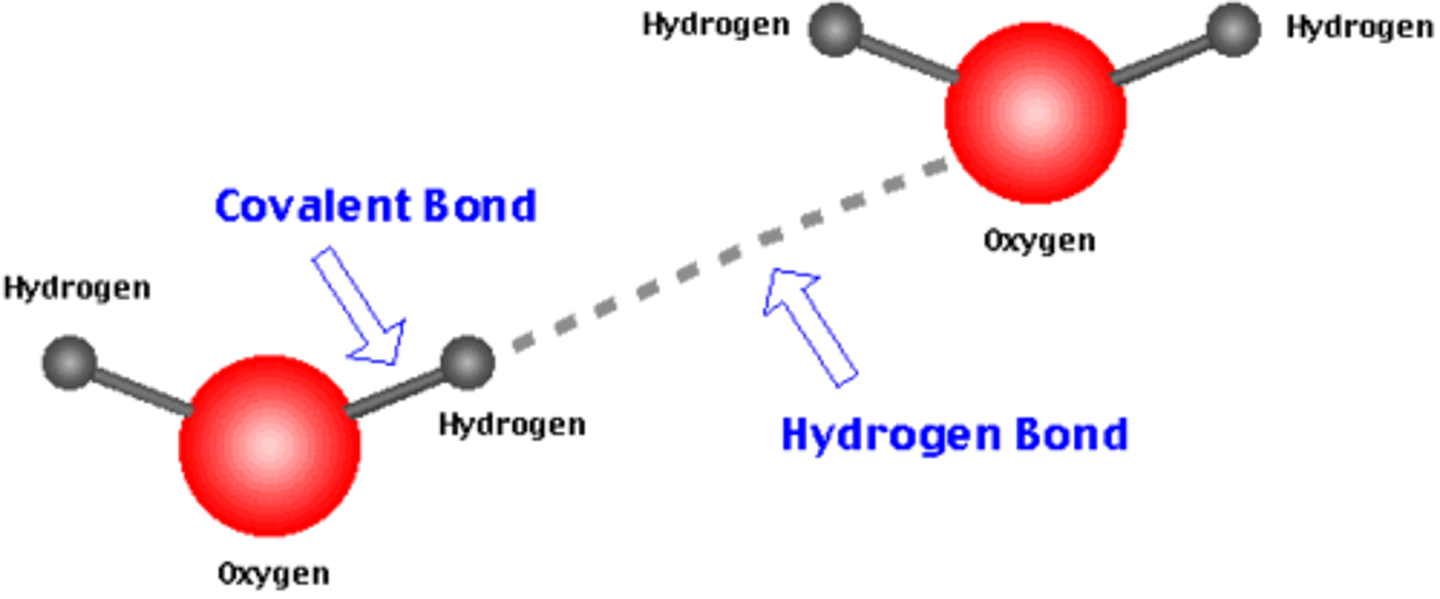
What type of bonds are within a water molecule?
covalent bonds (between atoms - intramolecular)
What is the polarity of water?
polar, this is because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen meaning there is an unequal sharing of electrons
Which element of water is negatively charged and which is positively charged?
Oxygen is negatively charged
Hydrogen is positively charged
What are the types of bonds between water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds (between molecules - intermolecular)
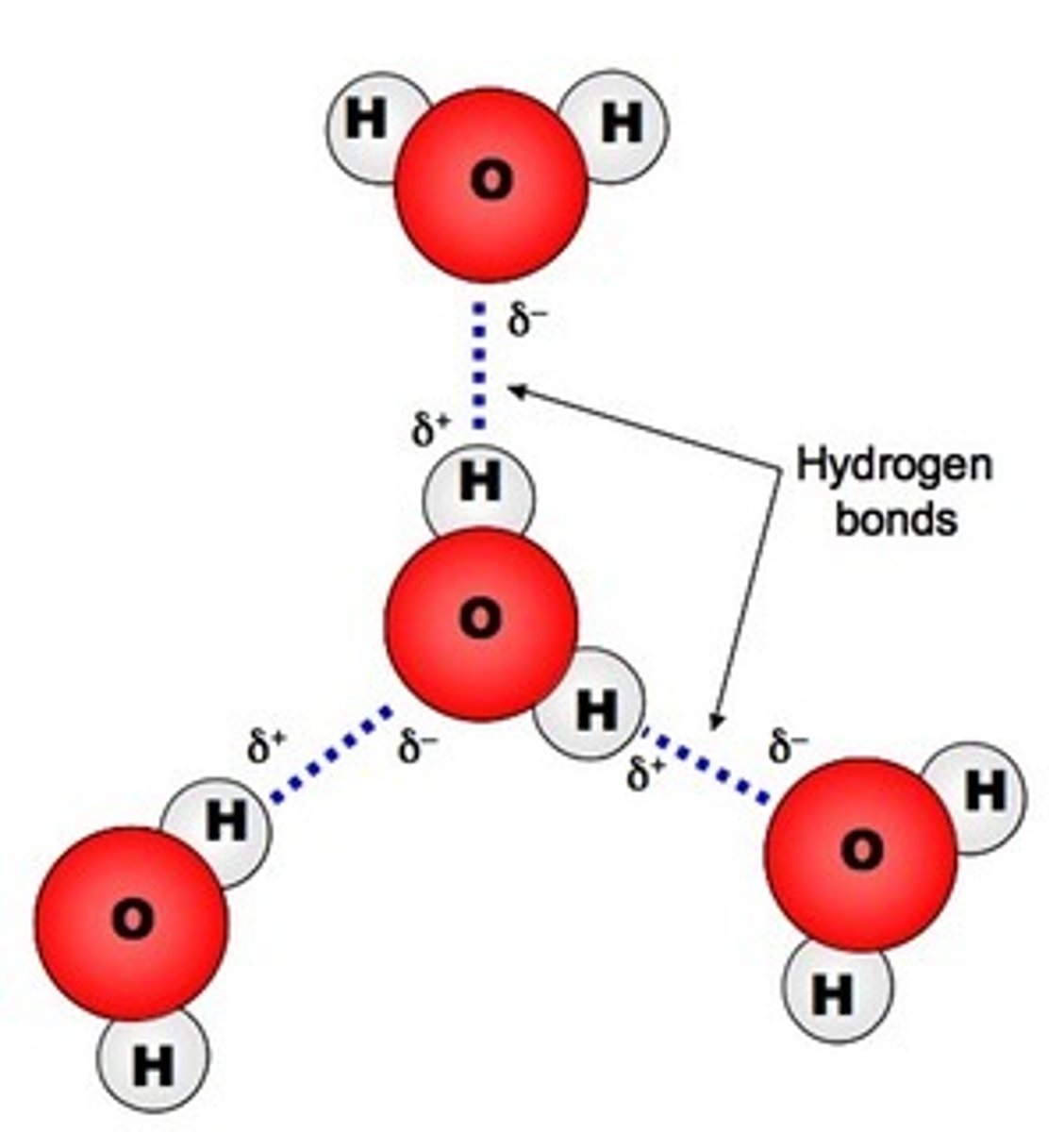
What is cohesion?
a property of water that allows molecules to stick to each other; creates surface tension
What is surface tension?
property that allows things to be supported on top of water, this is because of cohesion.
ex: water bugs, ice sheets on a lake
What is adhesion?
a property of water that allows water molecules to stick to other things that are polar or charged.
What is capillary action?
caused by adhesion, capillary action is the upward movement of water.
This is how plants can get water from their roots to their leaves
What is specific heat?
the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature by 1 degree Celsius.
What is the specific heat of water?
4.187 kJ/kgK this is very high which is a good thing because it allows for the temperature of an underwater environment to be stable
What is latent heat of evaporation?
the energy that must be added to a substance to change the state of being a liquid to a gas.
What is the latent heat of evaporation for water?
2,270 kJ/kg this means water absorbs a lot of heat when it evaporates (evaporative cooling - sweating)
What can water dissolve?
any polar or charged particle can dissolve in water (exception to this is oxygen, this is only because oxygen is such a small atom)
What does hydrophobic mean?
water fearing; if a molecule is hydrophobic it means that it does not attract to water, all things that are hydrophobic have to be non-polar like waxpaper
What does hydrophilic mean?
water loving; the molecule is attracted to water, all things that are hydrophilic are polar or charged like glass
What is the density of water based on?
temperature; this is why ice is less dense then water
Molecules and their Method of Transport
Glucose
polar and carried in blood plasma
amino acids
positively and negatively charged and carried in blood plasma
oxygen
non-polar but very small; Hemoglobin carries the majority of oxygen. A small amount is dissolved in blood plasma, which becomes concentrated with oxygen quickly.
Fats
large and non-polar; carried in lipoprotein complexes
Cholesterol
mostly hydrophobic with a small hydrophilic region; carried in lipoprotein complexes
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
ionic (charged); dissolved in blood plasma