Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system + pharmacology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
α1 adrenoceptor function
Smooth muscle contraction (mostly vasoconstriction)
α2 adrenoceptor function
Control how much noradrenaline is in the body by blocking its release. Act almost as brakes to the sympathetic system
β1 adrenoceptor function
Increases heart rate and contractility
β2 adrenoceptor function
Relaxes smooth muscle (mainly in bronchi and blood vessels)
β3 adrenoceptor function
Stimulates lipolysis and relaxing bladder smooth muscle
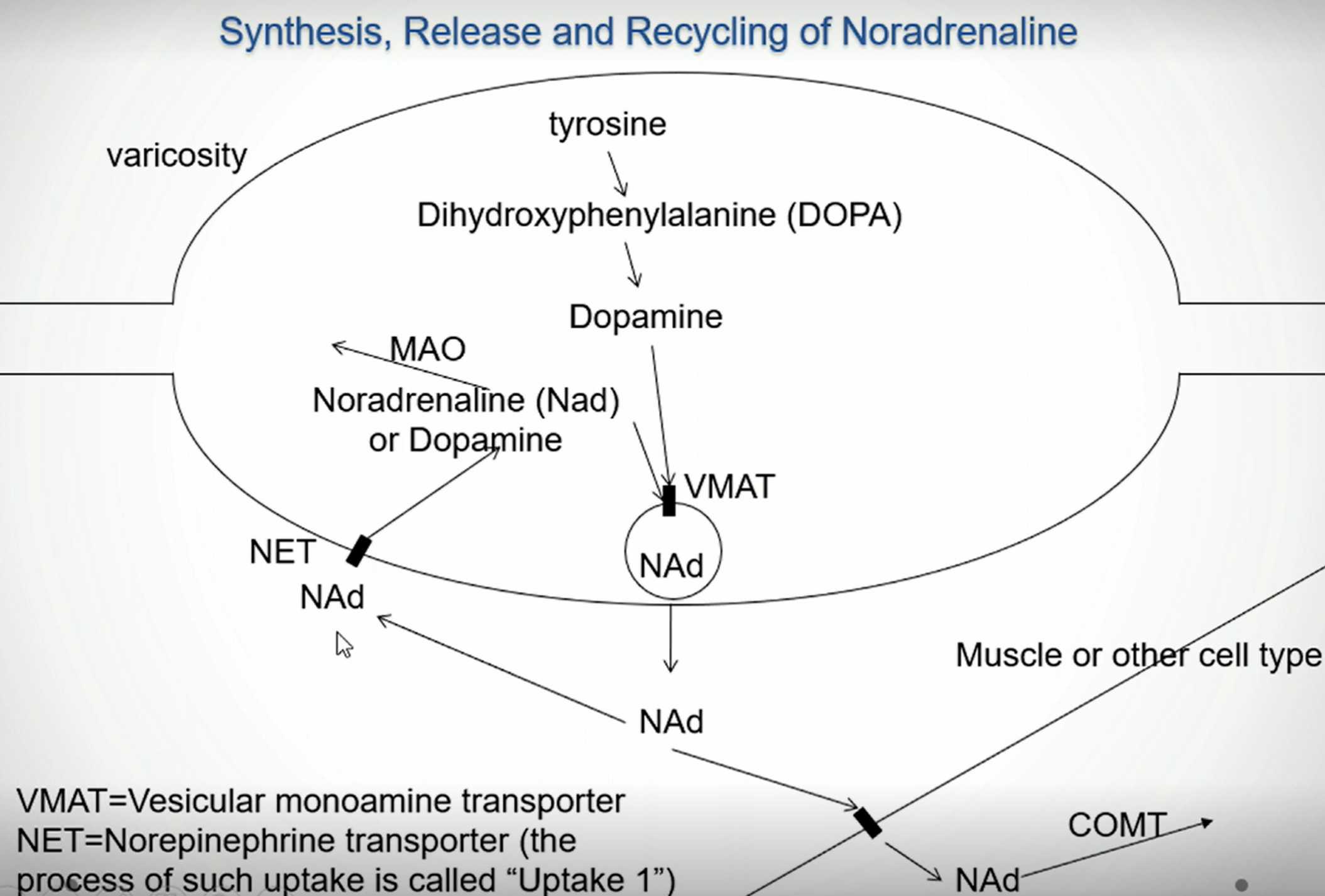
What effect will blocking the NET (norepinephrine transporter) have on the effect of noradrenaline (NA) on the body
It will increase the effect, as there is less reuptake of NA, so more remains in the extracellular space, allowing it to remain active for longer
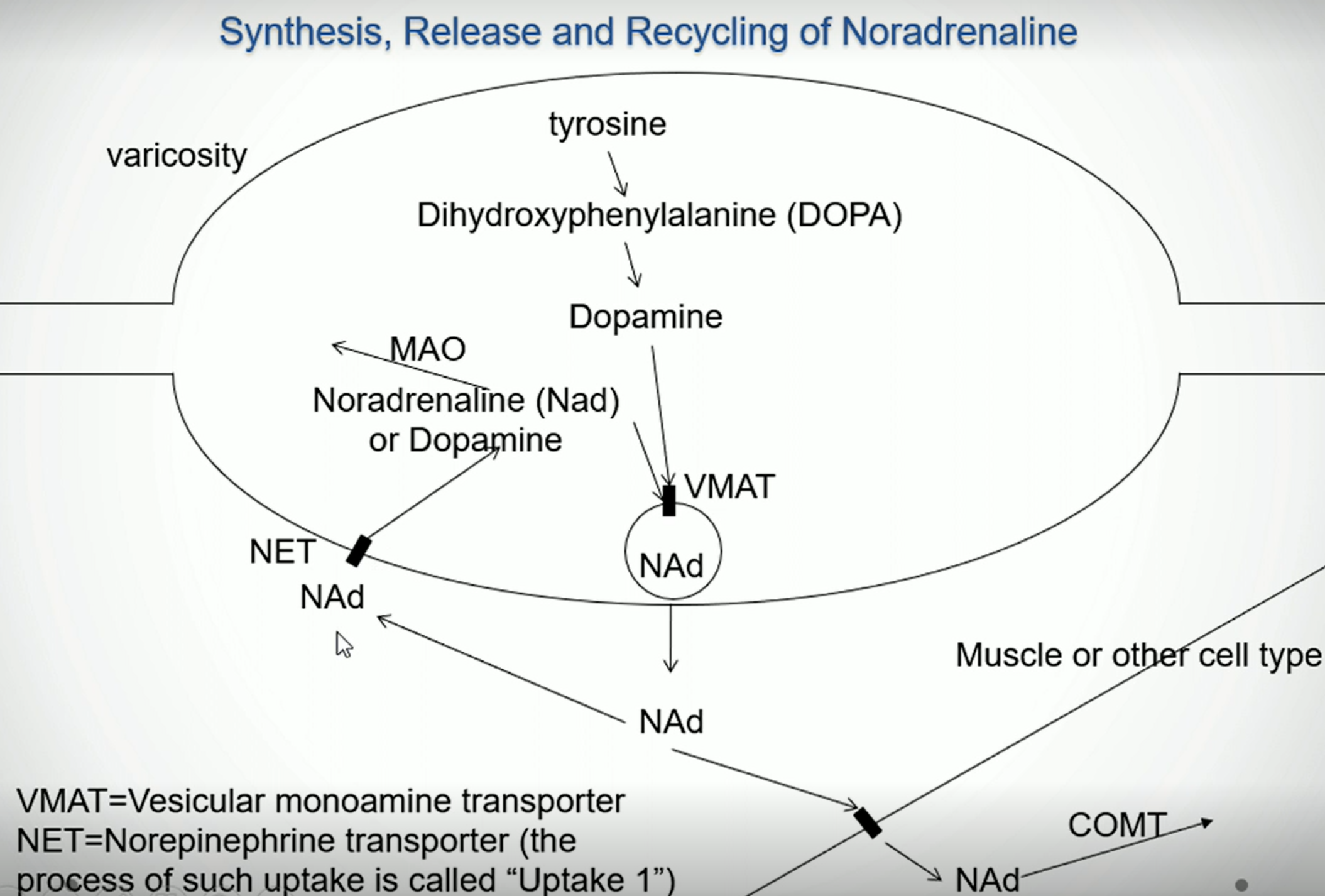
What effect will inhibiting MAO (monoamine oxidase) have on the effect of noradrenaline?
It will increase the effect, as MAO breaks down noradrenalin, and so it will only be able to go back into the extracellular space.
What ion is required to release ACh
Ca2+ , can be inhibited by botulism toxin to prevent ACh release

Main way ACh is removed from synaptic cleft?
Acetylcholinesterase irreversibly hydrolyses ACh
A cholinesterase inhibitor can be used to reverse action of nicotinic receptor antagonists (which would’ve caused paralysis). Hast he side effect of severely amplifying parasympathetic system.
Function of interstitial cells of Cajal?
Act as pacemakers for the gut, send electrical signals to tell gut muscles when to contract to ensure gut motility and peristalsis
What is the descending inhibitory reflex and the ascending excitatory reflex
Ascending excitatory reflex refers to a stimulus causing contraction of smooth muscle just above the stimulus, propelling it forward. Descending inhibitory is the relaxation of smooth muscle just below
What cells are stimulated to produce gastric acid (HCl)
Parietal cells
Main functions of submucosal plexus
Secretion, absorption, blood flow and minor function in certain muscle control and sensory input
Main functions of mesenteric plexus
Mostly involved in the muscle contraction and motility of the gut.
5 Step chain from sensing food to producing HCl
ACh
Gastrin
Histamine
Parietal cell
HCl
3 main acid releasing chemicals
Gastrin
Histamine
ACh