Topic #6 - Object Recognition
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Facial Recognition in Different Species
it is not clear why you might want to do this but there is evidence of farmers able to do this with their livestock - could be just from expertise and familiarity to monitor their health
Species that spend a lot of time with _____ ____ may show individual recognition capabilities.
non conspecifics (different species); examples include domesticated pets and honeybees
Facial Recognition in Crows
species is neither domestic nor spends time with other species
capture crows by throwing a net over them and tying their legs off (unpleasant for the crow)
people doing the capturing are wearing masks
researchers walk along the route where the crows live, either wearing trapping masks (or dangerous variants) or masks not used in trapping
third case had 2 people walking the route simultaneously
if crows can recognize individuals, they should have a response to the people they like the least (the ones doing the banding)
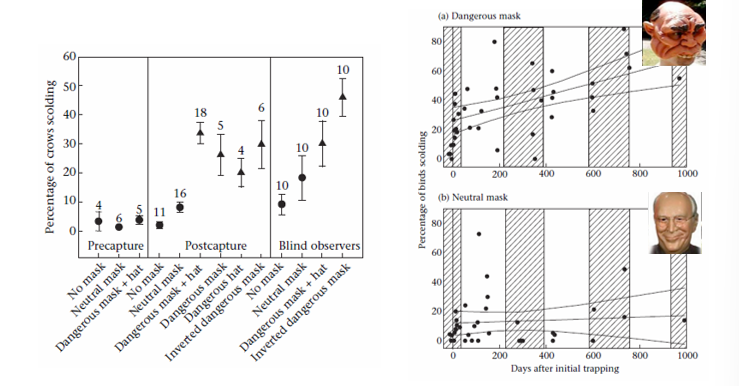
Results of Facial Recognition in Crows
only those wearing particular kinds of masks got scolded the most (circling and making calls) which lasted a long time after trapping happened → they recognized the individual faces and remembered them over time
Challenges to Object Recognition
going from 3D world to 2D representation of the object on the retina
viewpoint and orientation dependance: need to be able to recognize the same object regardless of the angle you view it from (think of music video he showed)
distinguishing objects that share features: same configuration, same arrangement, but can still disambiguate between similar things
recognizing objects without all parts visible: filling in information by learned behaviour
Gestalt Principles
we use heuristics to impose order on visual images to make sense of the world
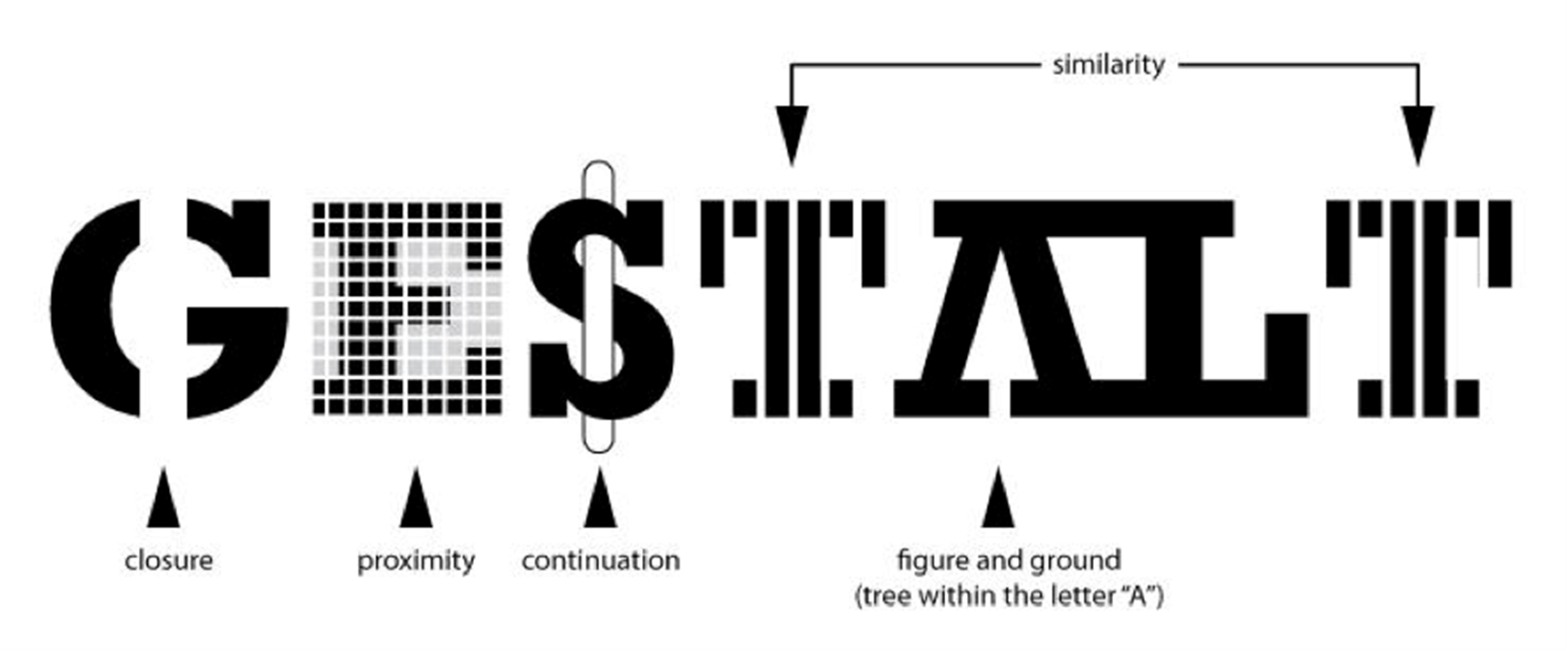
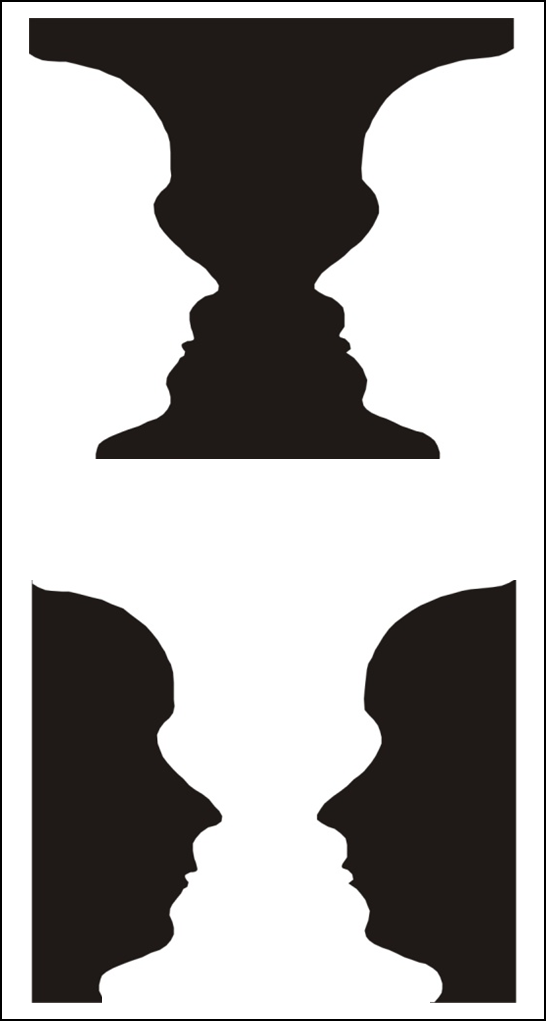
Examples of Figure Ground Separation
AL in the image, the dalmatian in the snow, the face/vase illusion

The brain is a predictive machine that uses ____ ____ of condensed representations to predict what will happen next.
mental models; we can’t predict all the sensory information we will get nor their changes
The brain can recognize objects independent of our own ______ or the ____ of the object.
viewpoint; orientation - called viewpoint/orientation independence
these are all the same car but are each very different on the retinal level
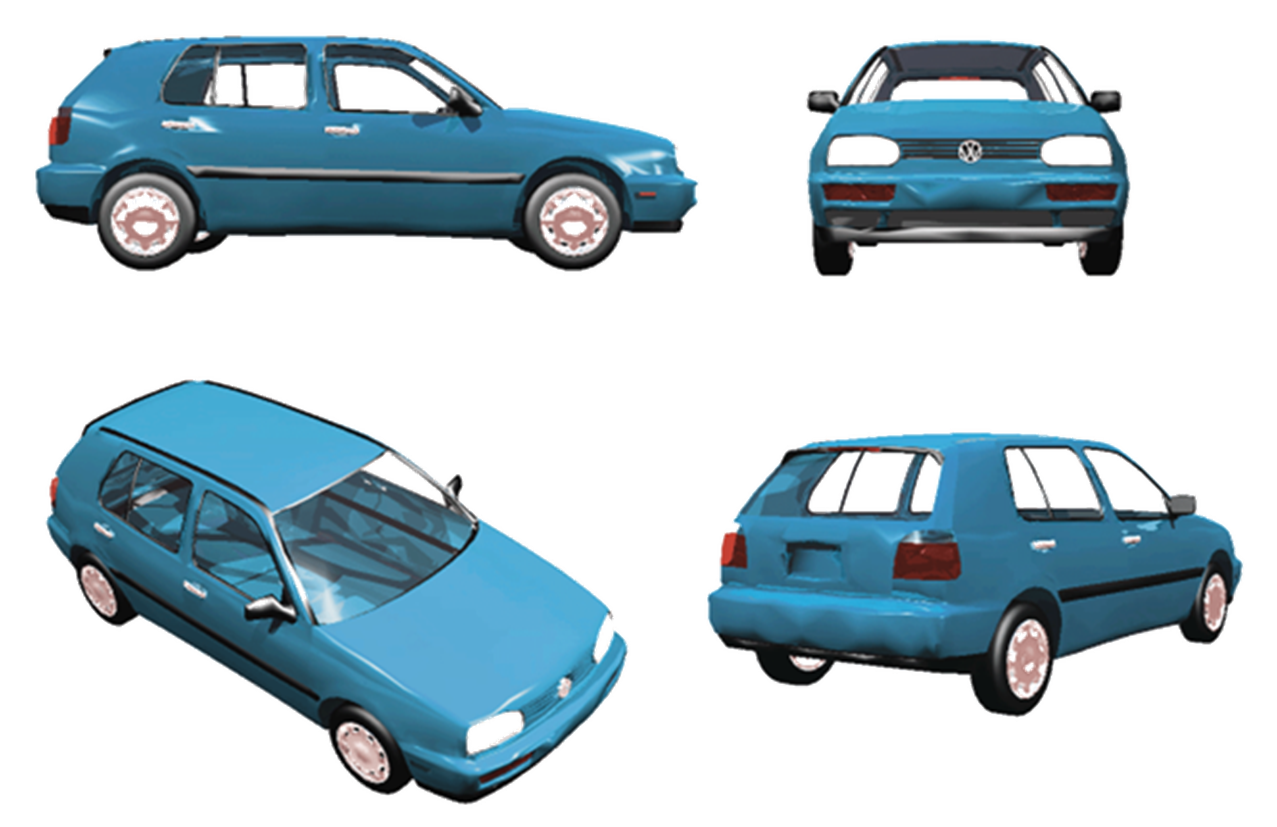

Unusual Views
we can recognize objects in viewpoints that we rarely see
right brain damage patients struggle to do this but are still able to recognize common views
Object Constancy
ability to recognize things in a stable manner despite changes in the retinal image
proven by unusual viewpoints, orientation, gestalt principles, etc.

Bistable Image
despite no changes at retina you can still interpret the image as different things
e.g. duck/rabbit
Vision is _____.
constructive; we use things like Gestalt principles to organize and make sense of the information we receive which enables object constancy
Ventral ‘What’ Pathway
components of the visual field are segregated and early parts (V1 and V2) process localized, low level properties like line orientation and luminance
MT/V5 (middle temporal in MONKEYS, V5 in humans) is critical for moving stimuli
MT/V5 (middle temporal in MONKEYS, V5 in humans) is critical for processing ____ ____.
moving stimuli
found in the inferotemporal cortex where cells show preferences to particular classes of objects
motion processing is critical for identity (ventral path) and action (dorsal path)
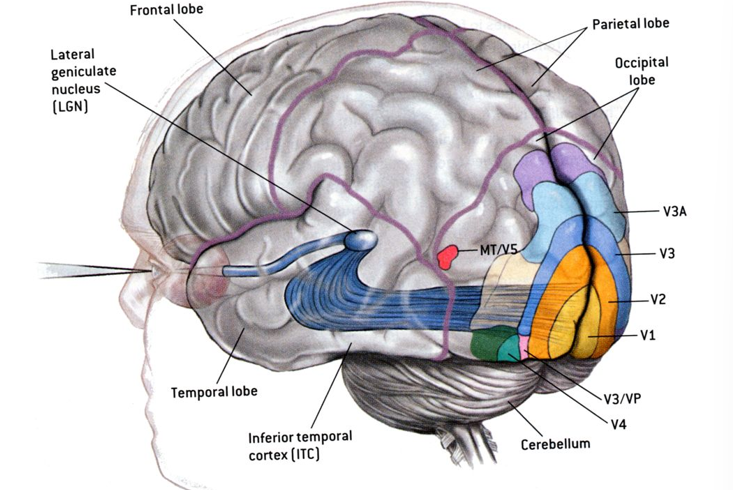
Building the Image
each part of the visual system processes something particular in a hierarchal way
receptive fields of many retinal ganglion cells map onto one single lateral geniculate cell
many LGN cells map onto a V1 cell - this makes up the receptive field of a single V1 cell
low level aspects on an image are processed in early stages, semantic processing only occurs at later stages of processing
The hierarchal arrangement of the visual pathway reflects higher levels ____ information from lower levels.
integrates; this has advantages for representing objects
Orientation Tuning
cells are ‘tuned’ to fire to specific orientations and directions of motion
orientation preferences are organized in columns in V1 - cells fire maximally to stimulus they prefer
low level processing
Ocular dominance columns respond ____ to one eye over the other.
more; not an on/off type switch, just a more maximal response from the eye that is preferred
similar to orientation columns but for eye preference
Where is columnar organization of cells found?
eyes, V5/MT
Preferences in the Ventral Stream
further forward in the system = more sophisticated preferences by populations of neurons
V4 and V8 - sensitive to colour
V5/MT- motion
lateral occipital complex (LOC) - object form
anterior inferotemporal cortex (AIT) - complex representations of objects
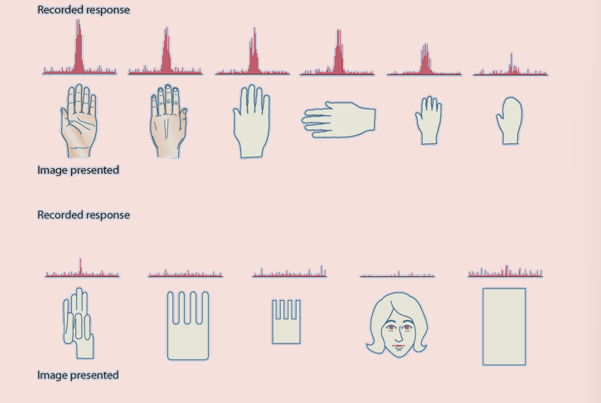
when inferotemporal firing was tested in monkeys, they were shown hands and hand outlines (like a mitten) and other not-hand images, some that were designed to look like hands → firing rates showed sensitivity to hands but had no response for non-hand objects
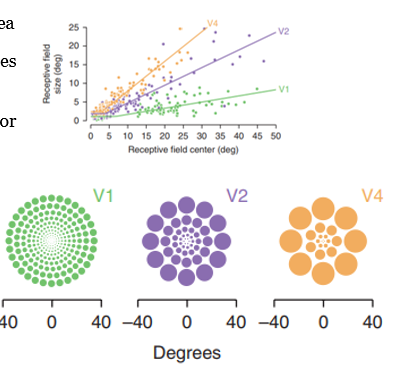
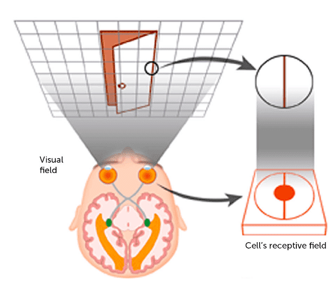
Receptive Field Size by Location
relative to fovea, cell density and receptive field (RF) changes → cell density is highest at fovea and RF size increases moving away from the fovea
RF size increases in more anterior parts of the temporal cortex
V1 has higher density (more cells) and a smaller RF since it processes fine-grain details , moving forward to V4 shows that receptive field gets larger
Most of our processing power goes towards the _____ _ _____ of the visual field.
central 4 degrees
Advantages of a Large Receptive Field (RF)
cells respond regardless of location or size
cells respond to global shape properties
supports object constancy
cells in IT always include fovea - anterior parts of the DORSAL stream have larger RFs but only 60% include the fovea
consequences of a small RF are shown in the image (only gives the brain information about a small portion of the image)
Synesthesia
experience of the world with an additional characteristic that we don’t see - stimulation of a sense or part of the body gives the impression of a sense in another part
grapheme-colour synesthesia is the most common - letter/number with colour, same association every time
breaks down the idea of modularity of vision due to the multifaceted percepts
Types of Synesthesias
grapheme-colour
shape-taste
space-time
object-personality
Theories Underlying Synesthesia
synaptic pruning - you have more synapses than you need when you are young so you get rid of the ones you don’t need as you get older → less synaptic pruning during development causes cross-linkage between the modules of vision
re-entrant activation -