Chapter 16 – Psychological Disorder
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Mental Disorders are Common
Fact: 1 out of every 5 Canadians suffers from a mental disorder (Clifford et al., 1996).
Fact: 1 in 5 are hospitalized due to psychiatric disorders (Public Health Agency, 2002).
Fact: Possibly underreported – up to 46.4% (Kessler et al., 2005).
Conclusion: Mental disorders are common, but many cases may go unreported.
What is Common or Abnormal?
A student drinking until she passes out
A man kissing another man on the lips
A parent slapping a child
Believing to be Jesus Christ
A woman refusing to eat for several days
A man barking like a dog
Feeling really sad
An elderly woman kicking others and screaming in the hospital
Note: These behaviors can be considered abnormal in certain contexts, but depend on cultural norms and individual situations.
What is Abnormal?
Distress or Disability/Dysfunction: Impairs social, cognitive, or occupational functioning.
Maladaptiveness: Hinders behavior or thoughts.
Irrationality: Example: Hearing voices.
Unpredictability: Behavior is erratic or inconsistent.
Unconventionality/Statistical Rarity: Example: High IQ.
Observer Discomfort: Behavior causes discomfort to others.
Violation of Moral and Ideal Standards: Deviates from cultural or moral norms.
Psychological Disorders
Psychopathological Functioning: Disruptions in emotional, behavioral, or thought processes that lead to personal distress or hinder goal achievement.
Abnormal/Clinical Psychology: The study of individual pathologies in mind, mood, and behavior.
Etiology of Disorders - Vulnerability Stress Mode
Model: Diathesis (vulnerability) + Stress (environmental stimulus) = Disorder.
Stressors: Loss of a job, divorce, death in the family, etc.
Note: Neither diathesis nor stress alone is sufficient to cause a disorder.
Historical Views
Psychological Theories: Psychological factors like stress caused problems (Freud’s unconscious conflicts).
Supernatural Theories: Early views linked disorders with evil forces, leading to harmful treatments like exorcism and witch hunts.
Biological Theories: The Four Humors (e.g., excess black bile leads to depression).
What is DSM-V?
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th edition).
classidies over 200 disorders
Recent Changes:
Removal of the multi-axial system.
Dimensional assessments added to measure symptom severity.
New diagnoses (e.g., Hoarding Disorder, Skin Picking Disorder).
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Chronic, excessive worry without specific threats.
Panic Disorder: Unexpected, severe panic attacks with physical and psychological symptoms.
Phobias: Persistent, irrational fears of specific objects or situations.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Re-experiencing traumatic events through flashbacks or nightmares.
Causes of Anxiety Disorders
Biological: Evolutionary preparedness, neurotransmitter imbalances (e.g., GABA).
Psychodynamic: Anxiety stems from unconscious conflicts.
Behavioral: Anxiety linked to reinforcement or conditioning.
Cognitive: Distorted perceptions of danger or fear.
Mood Disorders
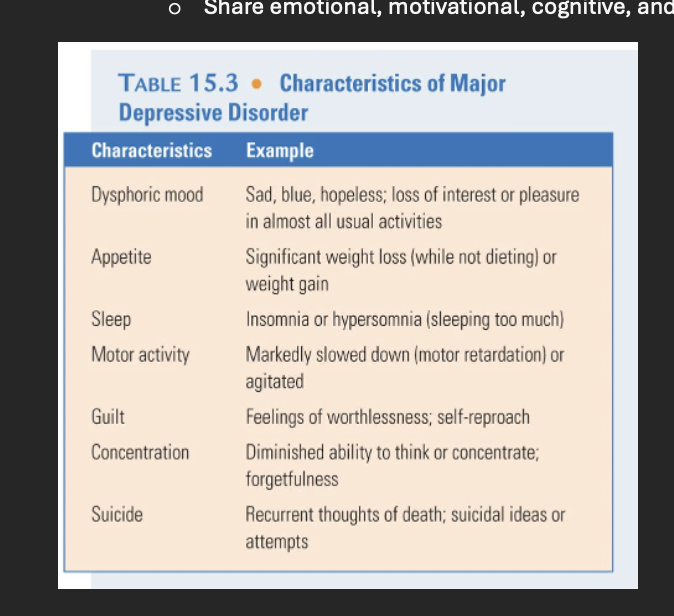
Major Depressive Disorder: Persistent sadness, low energy, and lack of interest in daily activities.
Bipolar Disorder: Extreme mood swings, including manic episodes (euphoria, high energy) and depressive episodes (low mood, lack of interest).
Causes of Mood Disorders
Biological: Neurotransmitter imbalances (serotonin, norepinephrine).
Psychodynamic: Unresolved early conflicts transferred to adult symptoms.
Cognitive: Negative thought patterns (Beck’s Cognitive Triad) contribute to depression.
Somatic Disorders
Anxiety Illness Disorder (Hypochondriasis): Preoccupation with being ill despite medical reassurance.
Somatic Symptom Disorder: Long history of unexplained physical symptoms.
Conversion Disorder: Loss of motor or sensory function with no physical cause
Dissociative Disorders
Dissociative Amnesia: Memory loss for important personal experiences due to psychological factors.
Dissociative Fugue: A person experiences amnesia and engages in wandering behavior, sometimes with a change in identity.
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID): Two or more distinct personalities within the same individual (formerly known as Multiple Personality Disorder).
Schizophrenia
Definition: Severe disorder characterized by disintegration of personality, distorted thoughts, perceptions, and emotions.
Symptoms:
Positive: Hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking.
Negative: Flat affect, reduced social engagement.
Onset: Can be gradual or sudden. Affects men more often and typically appears earlier than in women.
Causes of Schizophrenia
Biological Factors: Genetic predisposition (e.g., 46% risk for identical twins).
Environmental Stressors: Lack of support, emotional over-investment from parents (expressed emotion).
Diathesis-Stress Hypothesis: Genetic vulnerability combined with environmental triggers.
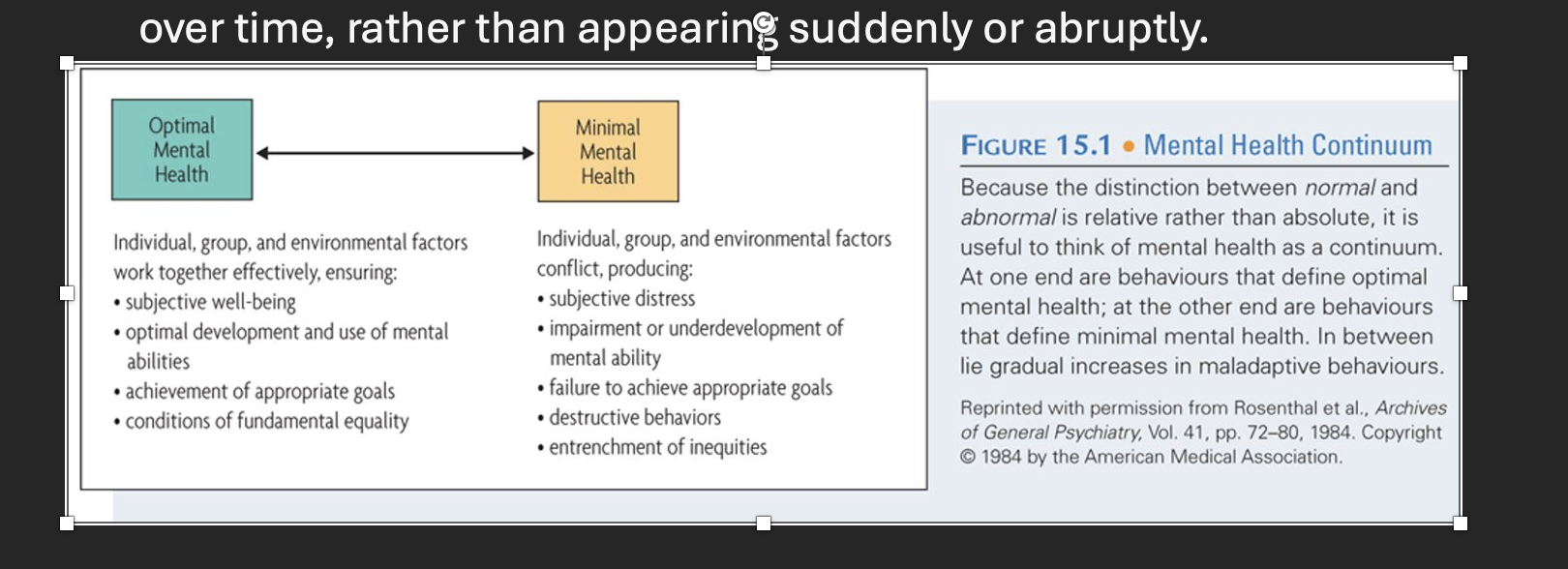
optimal mental health and minimal mental health
the five axes of DSM-IV-TR - classes of inromatio and description
charateristics of major depressive disorder with examples
types of schizopenoc disorders and major symptoms
