Working memory model
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the working memory model?
a representation of short-term memory, it suggests that STM is a dynamic processor of different types of information using sub-units coordinated by a central decision making system
Who came up with the working memory model and why?
Baddeley and Hitch (1974) after they felt that the multi-store model of memory doesn’t explain much about STM
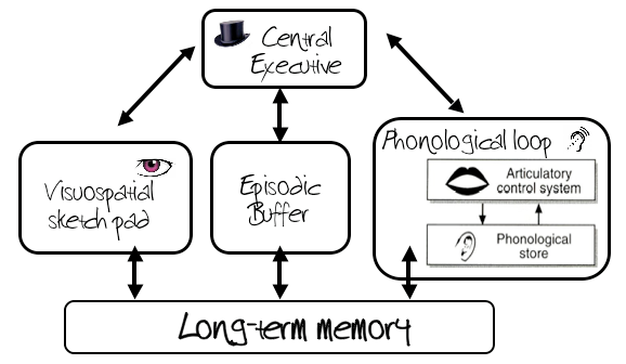
What is the role of the Central Executive?
decision making processes that monitors incoming stimuli and allocates tasks to the slave system
What is the capacity of the Central Executive?
Very limited
What is the coding of the Central Executive?
all types of information (auditory, visual….)
Example of a task relying on the CE.
Switching attention between tasks or problem-solving
What is the purpose of the phonological loop?
temporary store system for auditory and verbal information
What is the phonological loop divided into?
phonological store and articulatory process
What is the phonological store’s function?
stores the words you hear
What is the purpose of the articulatory process?
to process speech production and rehearses/stores verbal information
What is the capacity of the phonological loop?
About 2 seconds of what can be said
What is the coding of the phonological loop?
Acoustic
What is the purpose of the visuo-spatial sketchpad?
stores visual/spatial information e.g how many windows are in your house
What is the visuo-spatial sketchpad split into?
visual cache and inner scribe
What does the visual cache store?
Visual details such as colour and shape
What does the inner scribe do?
records the arrangement of objects in visual field i.e spatial awareness
What is the capacity of the visuo-spatial sketchpad?
3 - 4 objects
What is the coding of the visuo-spatial sketchpad?
visual
What is the role of the episodic buffer?
Integrates information from the CE, PL, VSS (other slave systems) into a single memory/episodes. It also provides a bridge between working memory and LTM
What is the capacity of the EB?
4 chunks
What is the coding of the epsiodic buffer?
all types of information (auditory, visual….)
Draw out the working memory model.
Who studied KF and why?
Shallice and Warrington as he had amnesia as a result of suffering brain damage from a motorcycle accident
What could KF do and not do?
he couldn’t recall someone reading out a sentence (phonological loop) but he could recall the sentence if he read it out (visuo-spatial sketchpad)
How does the case study of KF support the WMM?
the idea that these are two separate and independent components of working memory
How is the fact that there is research to support the phonological loop being roughly 2 seconds of what you can say a strength of the WMM? (+counter/development)
as these findings support the model’s view that the phonological loop has limited capacity which is determined by how many words can be vocalised within about two seconds, giving the WMM credibility.
C: however, it can be argued that Baddeley’s study is not valid enough to support the WMM as he conducted 8 experiments with 76 students in this research. 76 students is a small sample size that can’t be generalised to the target population and so it lack population validity
Give an example of this strength.
For example, Baddeley et al found that participants recalled shorter words (i.e touch, crab, tent) better than longer ones (i.e elephant, celery) as predicted by the WMM
How is the fact that there is further research support for the WMM from Baddeley’s research into dual task performance a strength?
as it shows how demands given at the central executive will overwhelm our cognitive load
Give an example of this strength.
Baddeley found that ppts have more difficulty doing two visual tasks (tracking a light and describing the letter F) than doing both a visual and verbal task at the same time
How is the fact that the WMM is supported by case study evidence a strength?
as by demonstrating that it is possible to have a deficit in the Pl while the VSS remains in tact, this affirms the idea that they are two separate and independent components of WMM
Give an example of this strength
for instance, clinical evidence from Shallice and Warrington (1970) show that the patient KF had a damaged phonological loop but other areas of memory i.e visuo-spatial sketchpad were intact
How is the fact that there is a lack of clarity over the nature of the central executive a weakness of the WMM?
as it means that the CE is an unsatisfactory component and this challenges the integrity of the WMM
Give an example of this weakness
for example, Baddeley himself recognised this when he said ‘ the central executive is the most important by least understood component of working memory.’ The CE needs to be more clearly specified