Chemical equilibrium calculations
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
in the form of reactants to products and normal arrows (→)
in the form of ⇌
* the rates of forward and backward reactions are equal
* react and products are always present
* equilibrium can be approached from either side
* the concentration of reactants and products remains constant
reaction quotient formula
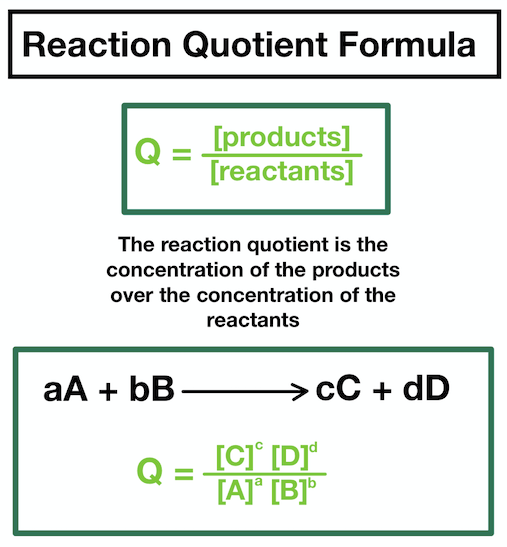
as the concentration becomes constant and the ratio becomes fixed at any given temperature this is when Kc occurs as the equilibrium has become constant
equilibrium constant formula
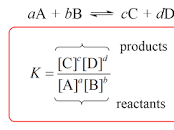
* products always over reactants
* when their is a number in front of the compound, write it as an indices outside of the bracket
* changes in concentration
* changes in pressure
* addition of a catalyst
IS:
* change in temperature
1. put into Kc form (product/reactant)
2. substitute the equilibrium concentrations into the expression
3. use calculator to calculate the answer
put a photo example pg. 247
1. substitute the value of Kc and the equilibrium concentration of known compounds
2. rearrange expression to make the missing concentration the subject
3. then calculate (don’t forget to square root if needed)
put photo example pg. 247
as if Q and Kc are not equal, the system is not at equilibrium
steps to determining whether a system is at equilibrium
substitute all concentrations of the compounds into the Q formula (same one as Kc)
calculate the value of Q from the equation and compare to Kc value given
if the values are not the same the system is not at equilibrium
state if the value is higher, lower or equal
what does the size/extent of Kc indicate
if it is more than 1 → favours the product (more products produced), moves to the right, forwards reaction
if it is less than 1 → favours the reactants (more reactants produced), moves to the left, backwards reaction
around 1 → equilibrium
the larger the value of Kc, the larger the product
what to do if there aren’t all values of Kc
rearrange values
what does the value of Kc demonstrate
how long the reaction has left
what is kC
the ratio of products over reactants
what does it mean if the value of Kc increases
it indicates that the ratio of product to reactants increases
what does it mean by the extent of a reaction in terms of what the value of Kc demonstrates
how many products and reactants
what side the equilibrium favours
use the value and size of Kc to describe