Engineering Design
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
What is the weight of the Engineering Drawing Assessment in the final grade?
20% of the final grade.
When will the Engineering Drawing Assessment be completed?
During the registered Week 5 Workshop.
What is the duration of the Engineering Drawing Assessment?
95 minutes.
What should students review to prepare for the Engineering Drawing Assessment?
Workshop activities from Weeks 2 to 3.
What is one of the recommended resources for practice before the assessment?
Boundy Engineering Drawing (Chapter 6).
What items must students bring to the Engineering Drawing Assessment?
Student ID card, drawing implements (pencils, eraser, ruler), and a device to upload a digital copy.
What will be provided during the Engineering Drawing Assessment?
Drawing Paper, Drawing Kits, Digital Callipers, and Scrap paper.
What are the requirements for the Detail Drawing in the assessment?
Single Component, Sufficient Orthogonal Views, Optional Isometric view, Dimensions, Tolerances & Notes, Completed Title Block, Drafting Standard, Paper Size, Part Name or Number, Projection & Scale, Company, Drafter, Units, Materials & Finish, Date & Revision, Revision Table.
What is the purpose of the 'Design Intent' in engineering drawing?
To understand what the designer intended regarding dimensions and placements of features.
What are the criteria for the Drawing Assessment?
Views & positioning, Accuracy & cleanliness.
How many marks are allocated for Views & positioning in the Drawing Assessment?
6 marks.
What is the maximum allowable error for geometric accuracy in the drawing?
Less than 10% error.
What is the significance of including a Title Block in the drawing?
It provides essential information such as part name, drafter, date, and revision.
What is the importance of including dimensions in the drawing?
Dimensions specify the size and location of features on the part.
What is an optional view that can be included in the Detail Drawing?
Isometric view.
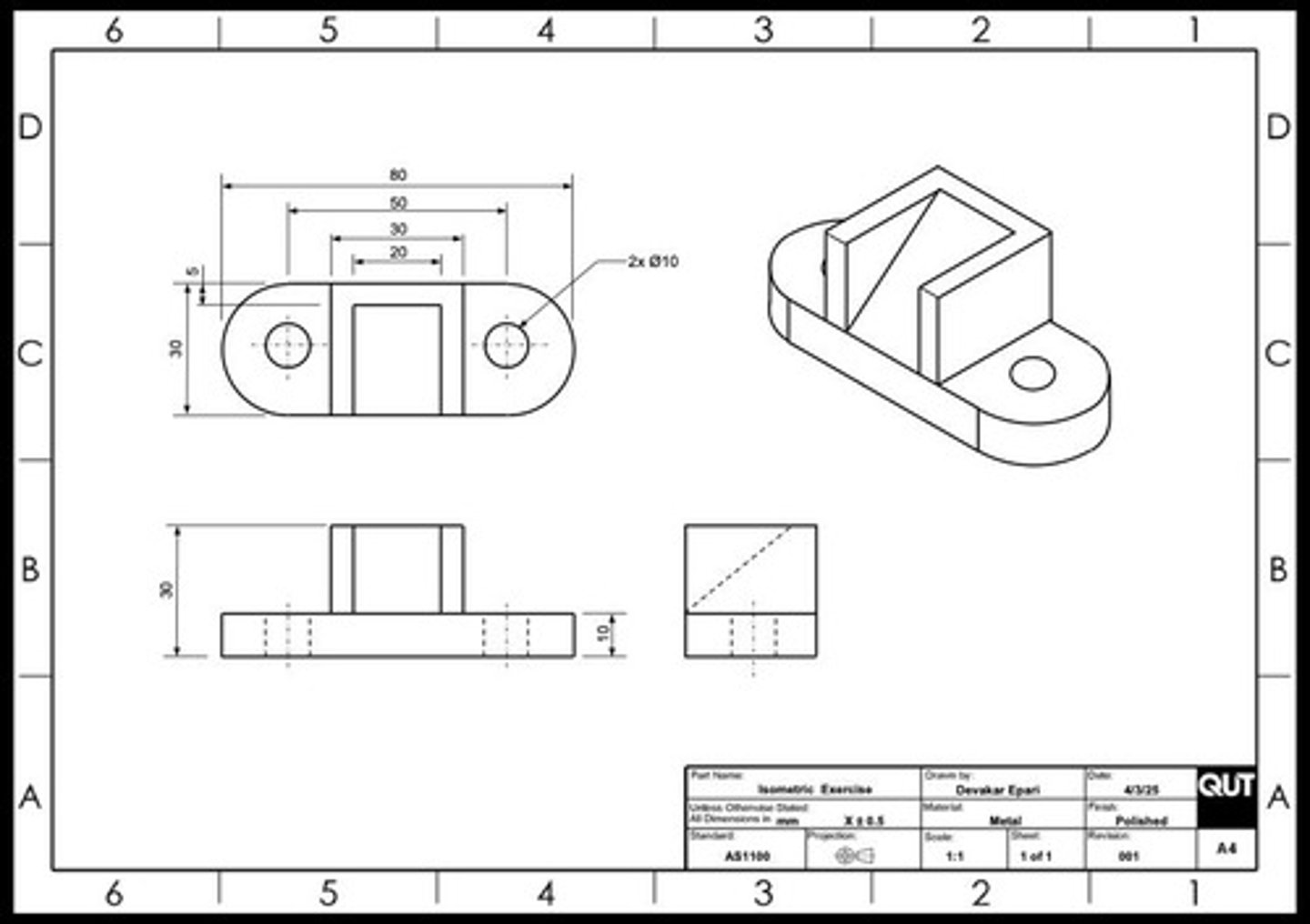
What should be included in the Revision Table of the drawing?
Details of revisions made to the drawing.
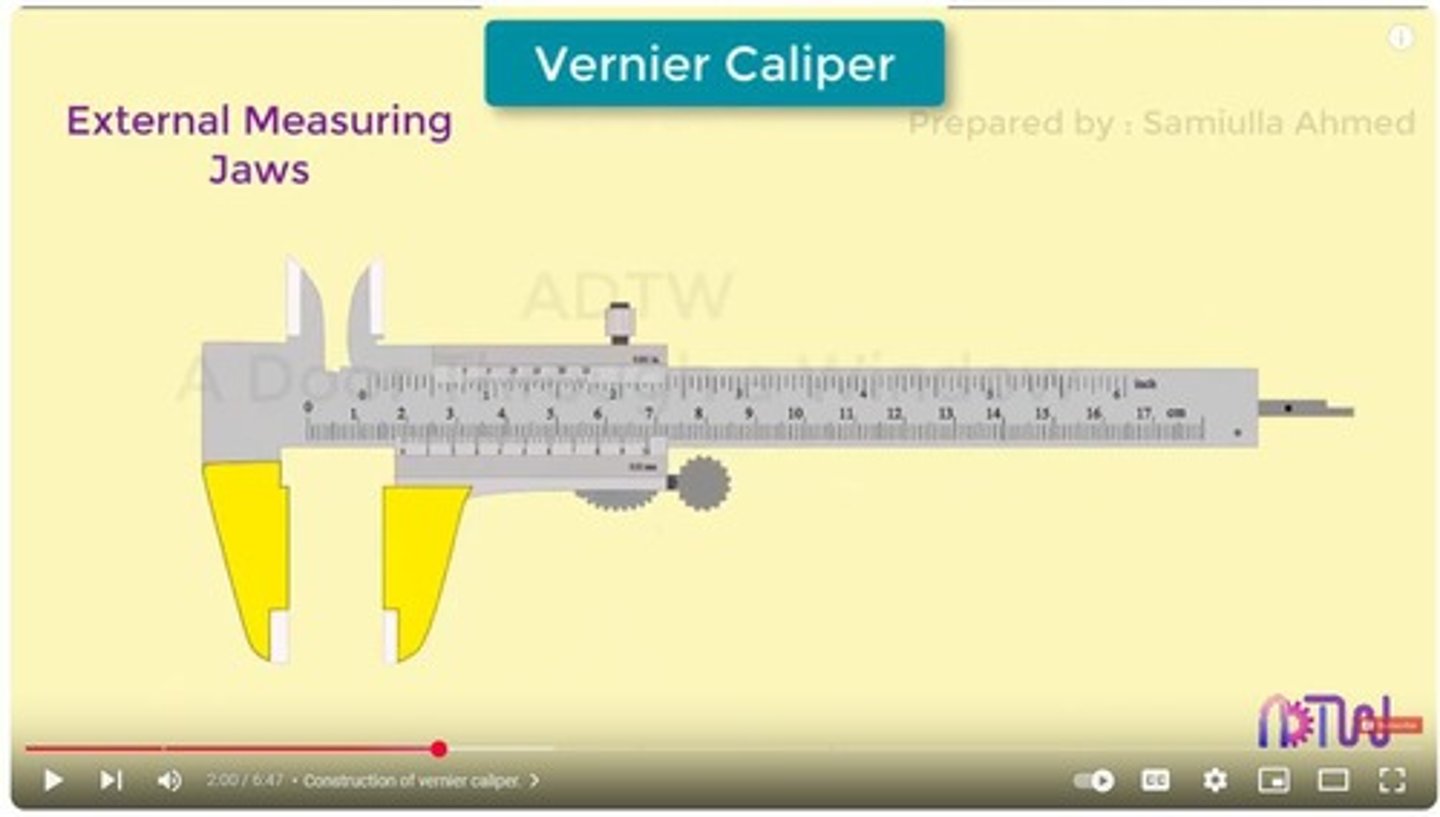
What is the purpose of using a Vernier Caliper in engineering drawing?
To measure dimensions accurately.
What does 'sufficient orthogonal views' refer to in the context of engineering drawing?
It refers to providing enough views (like front, top, side) to fully describe the component.
What is the significance of 'cleanliness' in the drawing criteria?
The drawing should be free of construction and projection lines for clarity.
What is the focus of the EGB125 Design for Manufacture course?
To teach students about engineering drawing, design projects, specifications, architecture, and teamwork.
What is the TEQSA Provider ID for the Australian University offering this course?
PRV12079.
What is the CRICOS No. for the Australian University?
00213J.
What is the first step in the reverse engineering process?
Specifications.
What should be included in the specifications during reverse engineering?
Marketing Specifications, Manuals and IFUs, Standards, and Bill of Materials.
What does the system architecture step in reverse engineering involve?
Functional Architecture.
What are the key components of risk management in reverse engineering?
Identify hazards, identify risk controls, and assess if the residual risk is acceptable.
What is the purpose of the requirements step in reverse engineering?
To reverse engineer and formulate requirements, create a traceability matrix, and describe the use case and user needs.
What is the focus of the engineering design step in reverse engineering?
Redesigning components, such as the front wheel hub, for modified use cases and assessing impacts on requirements and manufacturing.
What should be included in the title block of a technical drawing?
Dimensions, tolerances, units, drawing standard, projection, scale, part name or number, material, and finish.
What does clean drawing entail in technical documentation?
Removal of construction and projection lines.
How should dimensions be presented in a technical drawing?
Dimensions should be sufficient to fully define the part, accurate, and in the correct position.
What is the total score for the drawing quality assessment?
20
What is the significance of reverse engineering in design?
It helps understand design choices, identify functional components, and learn best practices.
What is the role of a traceability matrix in reverse engineering?
To connect requirements, specifications, and risks.
What is the expected outcome of the engineering design step regarding materials?
Determine if materials need to change and assess impacts on manufacturing.
What is the purpose of the risk analysis step in reverse engineering?
To identify hazards and establish risk controls.
What is the importance of including a Bill of Materials in specifications?
It lists all components required for the project.
What does the term 'functional components' refer to in reverse engineering?
The purpose of each part within the system.
What is the expected action during the requirements step of reverse engineering?
To formulate requirements based on reverse engineering findings.
What is the focus of the design project in EGB125?
To apply principles of design for manufacture.
What is the significance of understanding industry standards in reverse engineering?
It helps in learning best practices for design and manufacturing.
What is a key consideration when redesigning a component for modified use cases?
Assessing how requirements are impacted and what changes to form are required.
What is the expected outcome of creating an engineering component drawing?
To include dimensions and tolerances for the redesigned component.
What does 'red indicates change in language for further clarification' imply in the notes?
It signifies that changes or clarifications are highlighted in red.
What is the TEQSA Provider ID for the Australian University mentioned in the notes?
PRV12079
What is the CRICOS No. for the Australian University mentioned in the notes?
00213J
What course is associated with the School of Mechanical, Medical and Process Engineering?
EGB125 Design for Manufacture
What will be available from next week for the Design Project in EGB125?
Detailed Task Sheet and Criteria
What are the four requirements that design and development outputs must meet according to the notes?
a) Meet the input requirements; b) Adequate for subsequent processes; c) Include monitoring and measuring requirements; d) Specify essential characteristics for intended purpose.
What type of documented information must an organization retain regarding design and development outputs?
Documented information on design and development outputs.
What are examples of design and development outputs mentioned in the notes?
Engineering Drawings, Specifications, or Manufacturing Instructions.
What do design outputs describe according to the notes?
All the components and assemblies of your device.
What are the key design outputs in EGB125 Design for Manufacture?
Drawings, Material Specifications, Product Specifications, Packaging/Labelling Specifications, Manuals/IFUs, Production Specifications, Risk Analyses, Verification Results, Testing, Compliance with standards.
What is the significance of sheath length in the design output?
Sheath Length must be 400 mm ± 1mm to ensure the delivery system enables the graft to be positioned at the aneurysm site.
What are the components of a specifications template in EGB125?
1. Introduction 2. Product Description 3. Specifications 4. Raw Material List 5. Setlist 6. Overall Specifications.
What should be included in the specifications according to EGB125?
Identify relevant standards, reference the design inputs in the requirements, and include acceptance criteria.
What is the purpose of verification in the design process?
To ensure that the design outputs meet the specified requirements.
What is the purpose of validation in the design process?
To confirm that the design outputs fulfill the intended use and meet user needs.
What does the design input criteria specify for the delivery system?
The dimensions must enable the graft to be positioned at the aneurysm site.
What is the role of the 'Inspect Drawing' in the design output process?
To verify that the drawing meets the specified requirements and design criteria.
What type of test is mentioned in the design outputs to ensure usability?
Usability Test.
What does the term '000XXX Drawing' refer to in the design outputs?
It is a placeholder for the specific drawing of the stent delivery system.
What is the importance of compliance with standards in design outputs?
It ensures that the product meets regulatory and safety requirements.
What does 'Risk Analyses' involve in the context of design outputs?
Identifying and evaluating potential risks associated with the design and its use.
What is the expected outcome of the verification results?
To provide evidence that the design outputs conform to the specified requirements.
What is the significance of including a material specification in design outputs?
It details the materials to be used, ensuring they meet performance and safety standards.
What does 'Manuals/IFUs' stand for in design outputs?
Manuals/Instructions for Use.
What is the purpose of packaging/labelling specifications in design outputs?
To ensure that the product is properly packaged and labelled for safety and compliance.
What is the role of testing in the design outputs?
To evaluate the performance and safety of the product before it is released.
What does 'Production Specifications' entail in the design outputs?
Guidelines and standards for the manufacturing process of the product.
What is meant by 'Acceptance Criteria' in the specifications?
The specific conditions that must be met for the design outputs to be considered acceptable.
What does 'Design Input' refer to in the design process?
The requirements and criteria that guide the design outputs.
What is the relationship between design outputs and verification?
Design outputs must be verified to ensure they meet the design inputs and criteria.
What is the overall purpose of the EGB125 Design for Manufacture course?
To educate students on the principles and practices of designing products for manufacturability.
What is the purpose of design outputs in the design process?
Design outputs are specifications that result from the design input criteria and are used for verification and validation.
What standards are referenced for implantable stainless steel materials?
ASTM F138 and ISO 5832-1.
What is the significance of the V Model in systems engineering?
The V Model represents the relationship between different phases of development, emphasizing verification and validation.
What are the three types of system architecture mentioned?
Functional Architecture, Logical Architecture, and Physical Architecture.
What is the role of design controls in the design process?
Design controls ensure that user needs are met through design input, process, output, verification, and validation.
What is the purpose of design verification?
Design verification confirms that the design outputs meet the design inputs.
What is design validation?
Design validation ensures that the final product meets user needs and intended uses.
What is a Design History File?
A Design History File is a compilation of records that describes the design and development of a device.
How does reverse engineering relate to identifying requirements?
Reverse engineering helps identify functions that correspond to requirements.
What is the TEQSA Provider ID for the Australian University mentioned?
PRV12079.
What is the CRICOS number for the Australian University mentioned?
00213J.
What is the significance of implant materials in medical device design?
Implant materials must comply with specific standards to ensure safety and efficacy.
What is the relationship between functional architecture and system elements?
Functional architecture captures the relationships between different system elements.
What is the importance of user needs in the design process?
User needs drive the design input requirements and influence the overall design output.
What is the purpose of design reviews in the design process?
Design reviews assess the design progress and ensure alignment with user needs and specifications.
What does the term 'design input' refer to?
Design input refers to the requirements that guide the design process.
What is the role of MATLAB in the context of systems engineering as mentioned?
MATLAB is referenced for its content on functional architectures in systems engineering.
What does the term 'specifications' refer to in design outputs?
Specifications are detailed descriptions of the design outputs that must be verified and validated.
What is the significance of the 'identifying functions' in reverse engineering?
Identifying functions aids in determining the corresponding requirements for the design.
What does the design process encompass?
The design process encompasses design input, design process, design output, verification, and validation.
What is the purpose of the 'design process' in the context of design controls?
The design process ensures that all aspects of the design meet specified requirements and user needs.
What is the relationship between design output and validation?
Design output must be validated to ensure it meets the intended use and user needs.
What is the primary focus of EGB125 Design for Manufacture?
The course focuses on system architecture, functional architecture, and teamwork in the context of mechanical, medical, and process engineering.
What are the two types of electrical systems mentioned in the notes?
AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current).
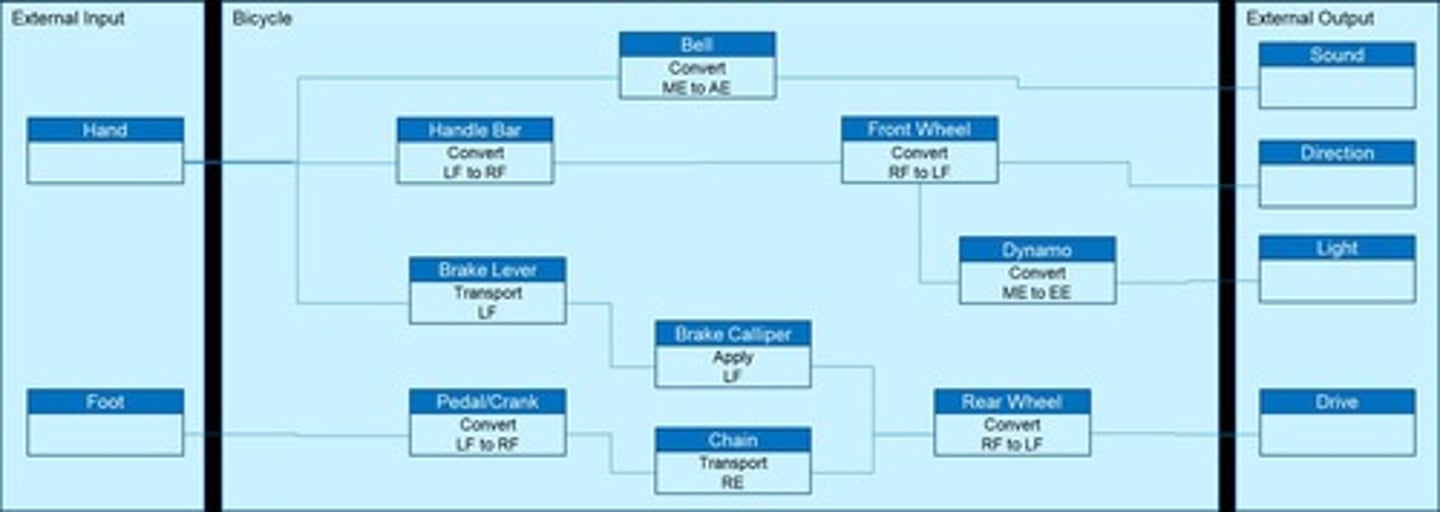
What are the main components of the physical architecture example provided?
Bicycle components such as Brake Lever, Bell, Handle Bar, Brake Calliper, Pedal/Crank, Front Fork, Frame, Chain, Dynamo, Rear Wheel, and Front Wheel.
What is an example of an external input and output in the functional architecture of a bicycle?
External Input: Bicycle; External Output: Handle Bar (Hand Direction).