Chapter 6 Microbiology 2460
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Viruses
Obligate intracellular and acellular pathogens.
Do not have cells but possess genetic materials.
Microscope used to observe Viruses
TEM/SEM
What part of the host cell do virus’s hijack
Cellular machinery
Why are virus’s not included in tree of life,
Because they do not have cells or ribosomes to grp genetically
Host or Cell type specificity
a particular virus can only infect certain types of cells within a specific host organism.
Where is the genetic material of virus
surrounded by capsid
T or F
Virus usually have DNA or RNA not both
TRUE
Bacteriophages
Kind of virus that can infect eukaryotes or prokaryotes
Infection of virus can be obtained: Direct contact
From infected individual
Infection of virus can be obtained: Indirect w/ fomites
Eating utensil, doorknobs, bedding, etc.
Infection can be obtained: Mechanical vector
organism carries the virus on outside of body cockroaches, flies, etc.
Infection can be obtained: Biological vector
organism carries virus inside (ticks, mosquitoes, biting flies, etc.)
Virions
Viral particles assembled in infected host cells
Range of size for virions
20-900nm
Dmiti Ivanoski
Created Chamberland filter used porcelain to filter out virus with 0.1 μm pores, now used to remove all material except viruses from cell cultures.
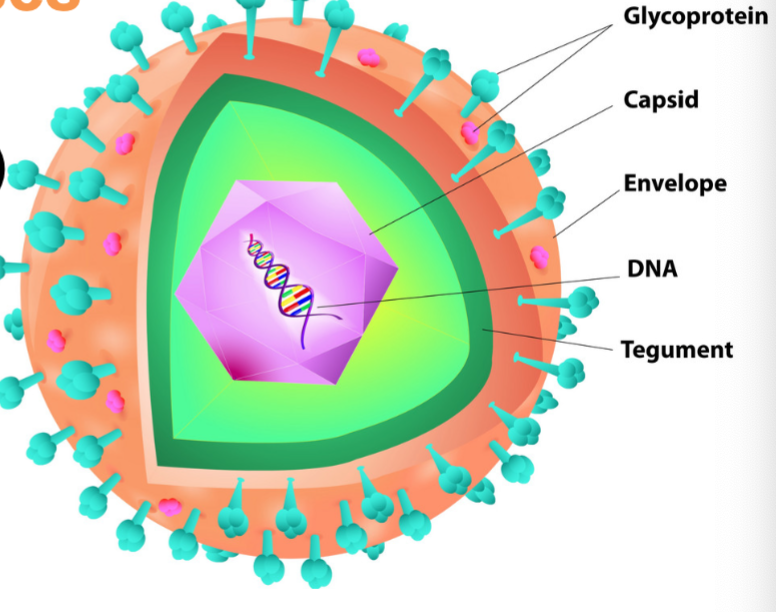
Component of Viruses:
capsid (capsomere-subunit),
Genomic material (rna or dna),
envelope and spikes (not all have)
What is used to classify Virus’s
Capsid Shape, Envelope and Genomic material
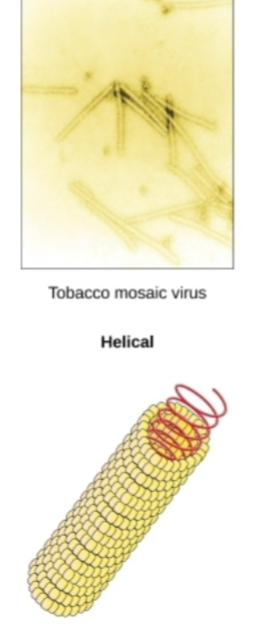
Type of Capsid shape this Virus exhibits?
Helical
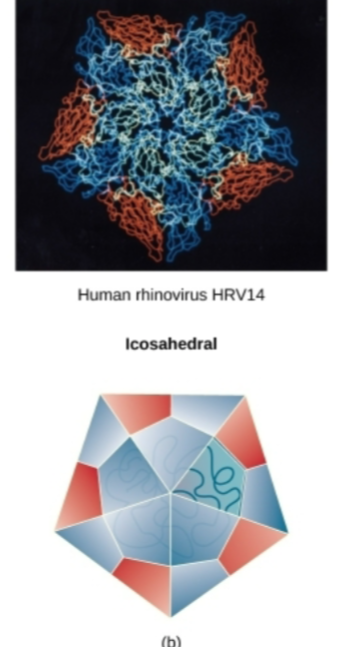
Type of Capsid shape this Virus exhibits?
Icosehedral
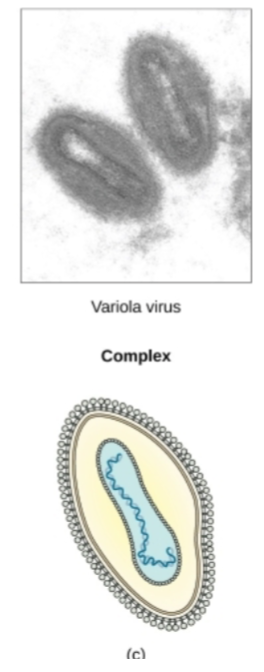
Type of Capsid shape this Virus exhibits?
Complex
Where is Virus genome
Polyhedral head (USUALLY DNA)
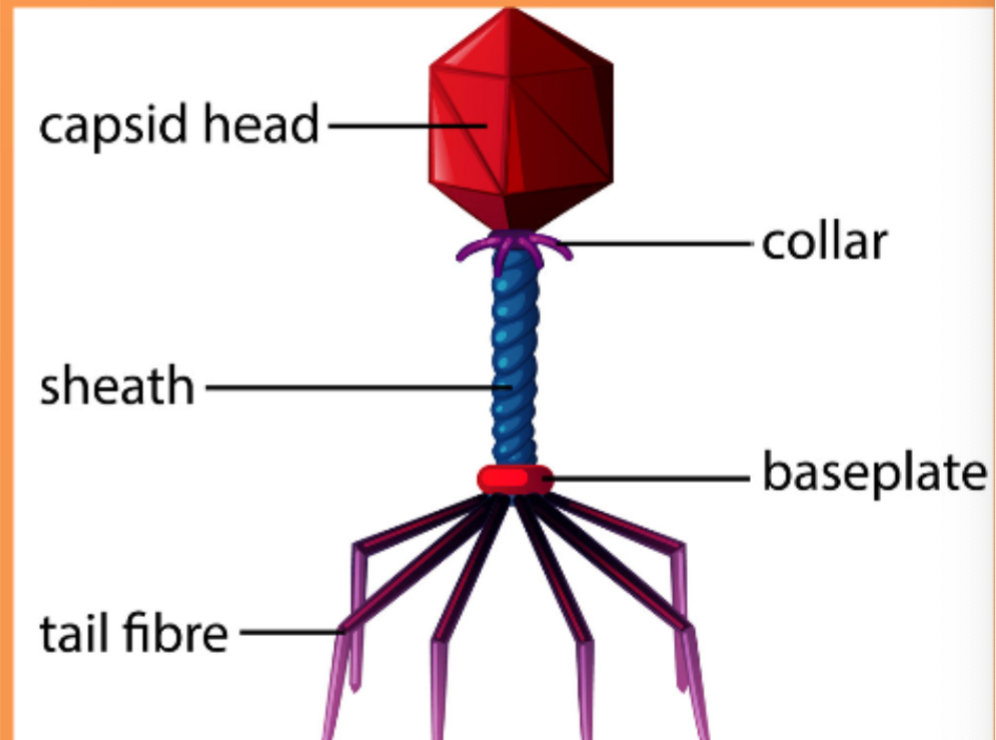
What does the bacteriophage virus use to attach to bacterial host
Tail fibers and pins
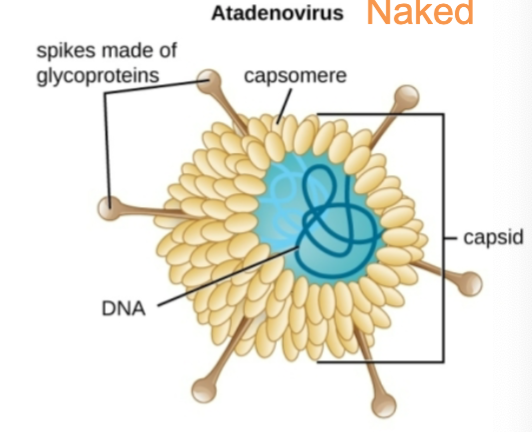
Viral grouping: Naked Viruses
Capsid only with not envelope
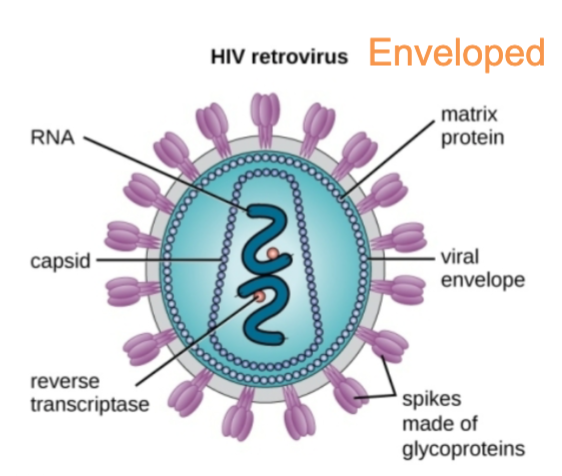
Viral grouping: Viral envelope
Phospholipid membrane surrounding capsid
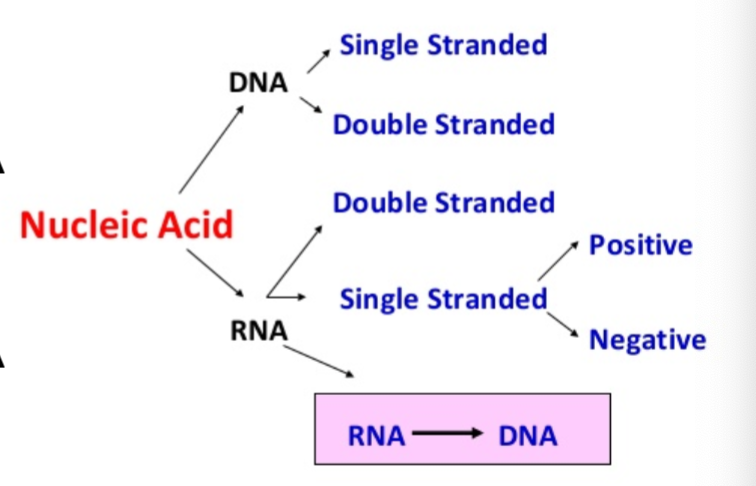
Viral grouping by genomic material
Single stranded DNA and RNA
Double stranded RNA and DNA
Who maintains “taxonomy” of viruses not in tree of life but still needing classification
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)
ICTV classify virus based on ?
genetics, chemistry, morphology, & mechanism for replication
With the use of binomial nomenclature with Virus’s the Family is
Virdiae
With the use of binomial nomenclature with Virus’s the genus is
Virus
Ttl Number of Orders families and genera of Virus
7 orders, 96 families & 350 genera
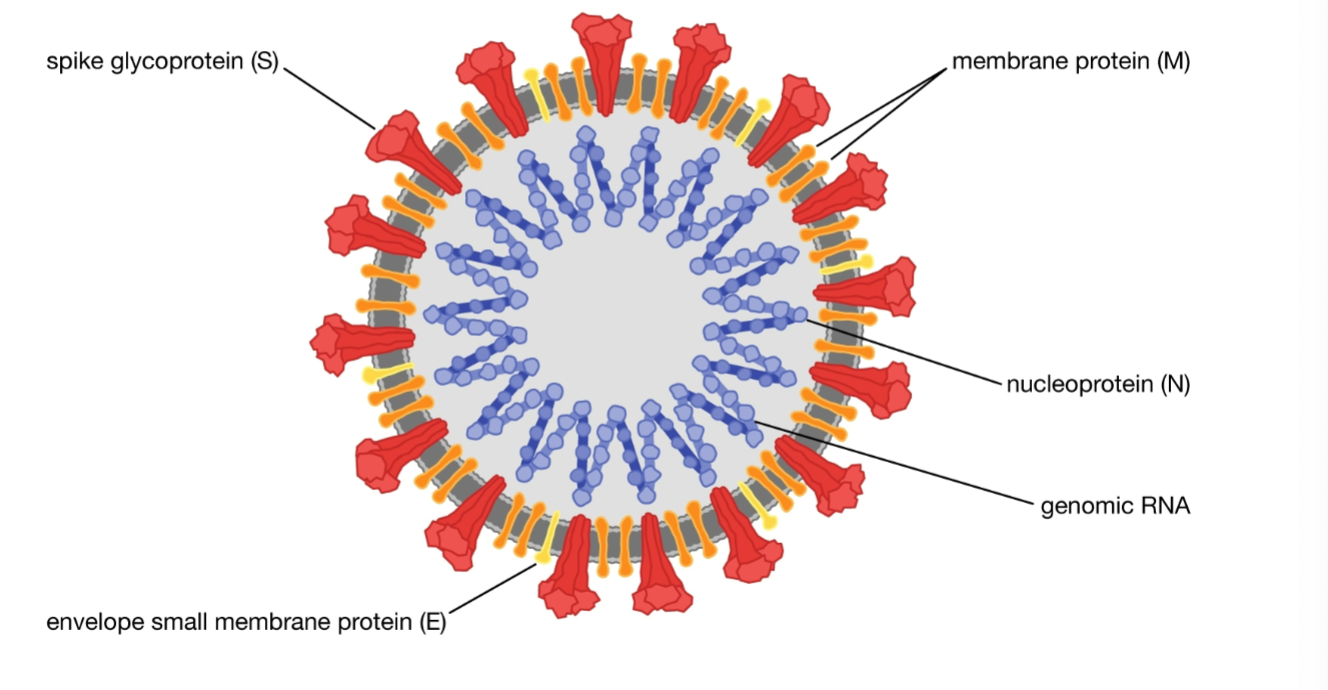
ID this Virus with spikes and genomic RNA
Sever acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 SARS-CoV-2
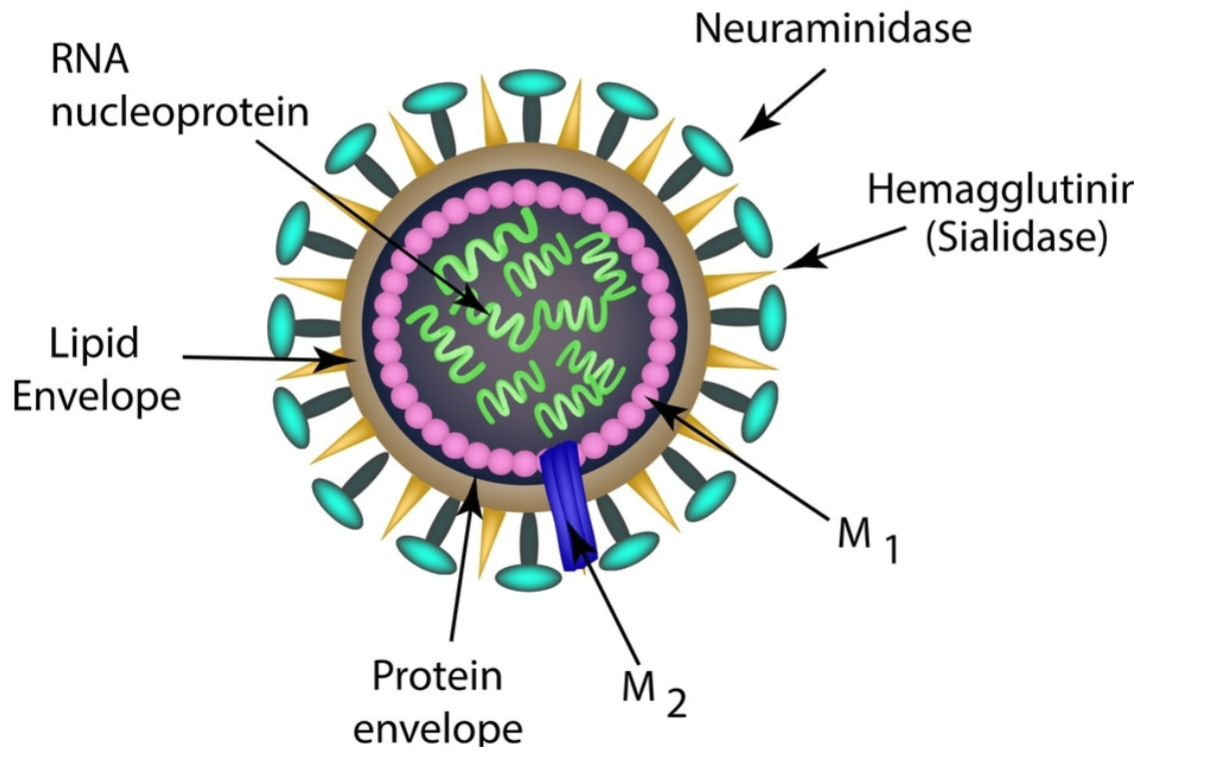
ID this Virus containing Neuraminidase, no spikes, and RNA nucleoprotein.
Inflluenza Virus
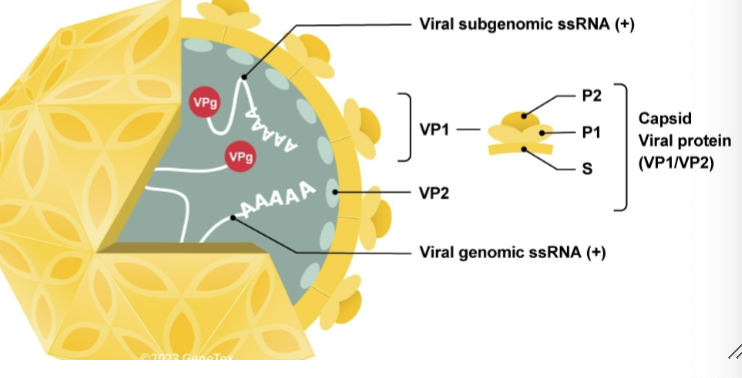
Norovirus
Under caliciviridae family
is a foodborne virus causing gastroenteritis
Naked +single stranged RNA
The goal of Virus
Invade host cell, hijack machinery to make proteins and replicate
____________ have been a model for viral life cycle studies
Bacteriophages
Virulent phages
This virus life cycle phage lead to death of host cell thru lysis
Temperate (latent) phages
This virus life cycle phage become part of host genome until induced to start making viral particles
In Host #1 what phages occur
Temperate → virulent phage
In host #2 what viral phages occur
Temperate phage
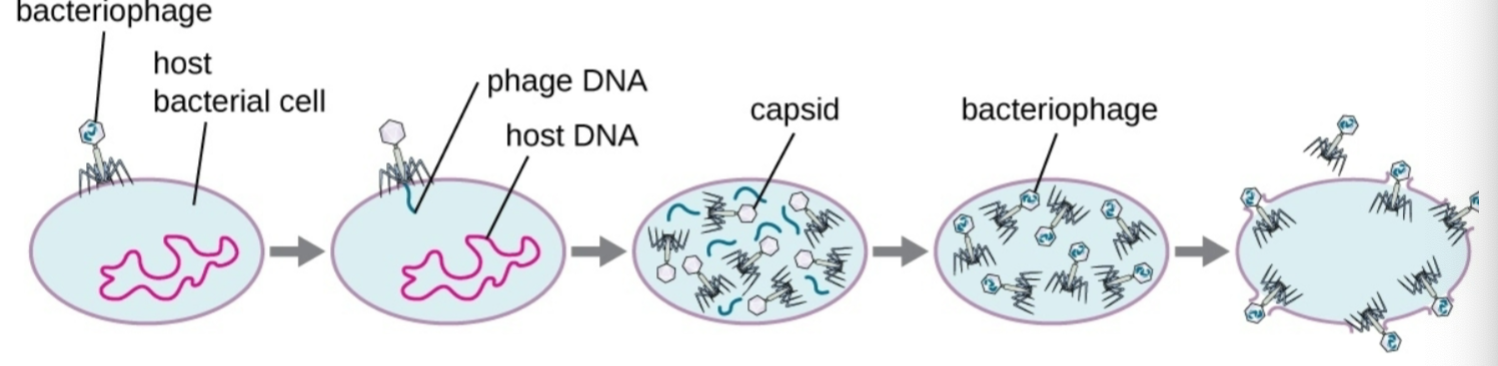
Describe the Lytic cycle of virulent phages
This cycle starts by:
the phage attaches (Attachment) to host surface and viral DNA entering host cell (Penetration)→
Phage DNA then replicates (biosynthesis) making phage proteins resulting in new phage particles (maturation) →
(3) Eventually lysis releases the newly made phages (lysis)
Describe the Lysogenic virulent phages
This phage starts by:
The phage infects a cell and DNA becomes incorporated into host genome → The cell divides and prophage DNA is passed on to daughter cells → Under stressful conditions DNA is excised from bacterial chromosome and enters the lytic cycle →
Phage DNA then replicates (biosynthesis) making phage proteins resulting in new phage particles (maturation) → Eventually lysis releases the newly made phages (lysis)
What can contribute to virulence; as seen in V cholerae and C. botulinum being less virulent w/o phages due to missing toxin genese
Lysogeny
Phage Transduction
Genetical material can be transferred btw bacterial cells via this
Generalized transduction
DNA is random when transferred during lytic cycle
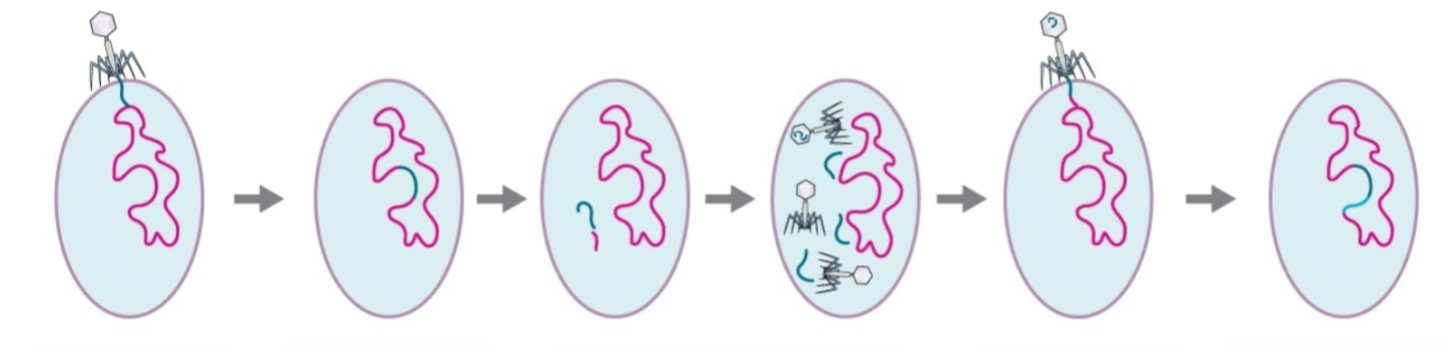
Specialized transduction
Occurs at end of lysogenic cycle and can transfer host DNA too.
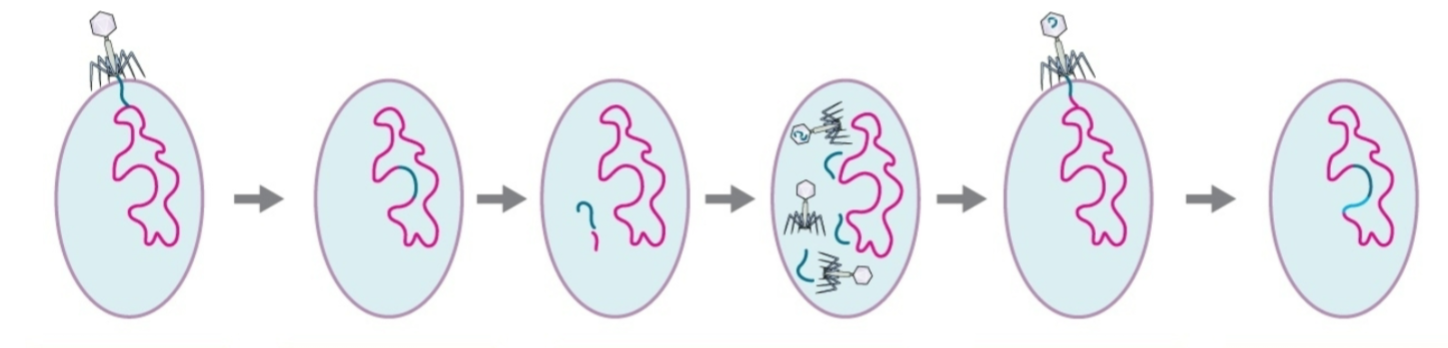
During the excision stage of Specialized phage transduction what occurs
The phage is excised from the bacterial chromosome along with short piece of bacterial DNA, The DNA is then packaged into newly formed capsids
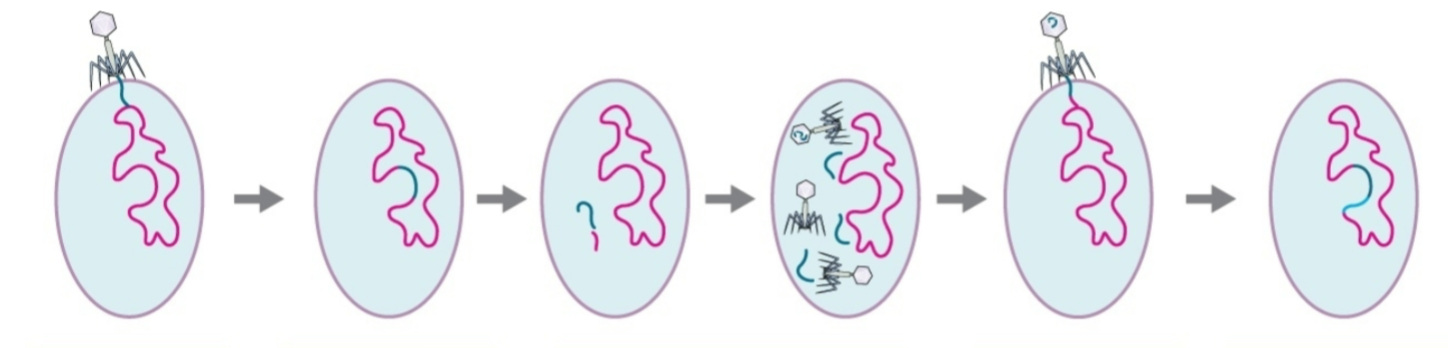
During the Infection stage of Specialized phage transduction what occurs
Phage containing both viral and bacterial DNA infect a new host cell.
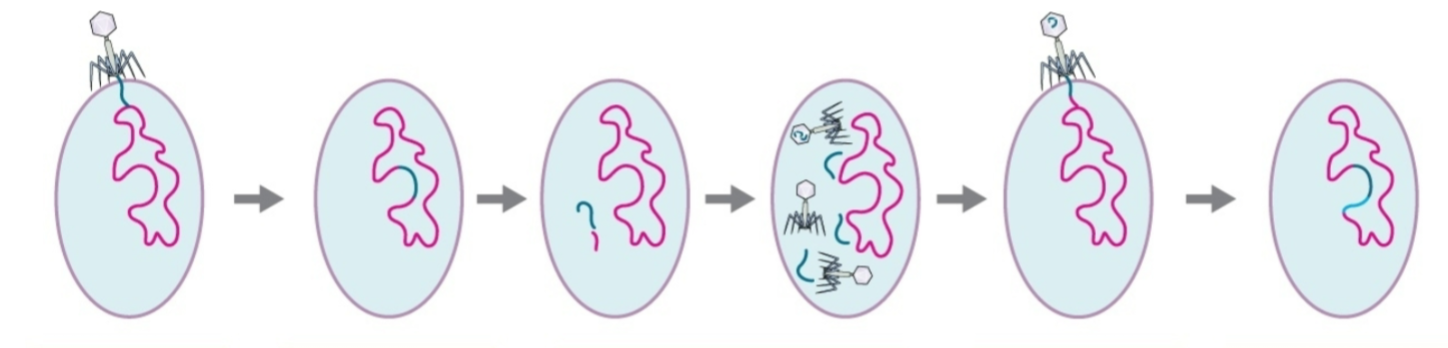
During the recombination stage of Specialized phage transduction what occurs
The phage DNA along with attached bacterial DNA are incorporated into new cell.
The Eukaryotic viruses are like 5 stages of phage life cycle EXCEPt
mechanism of penetration, nucleic acid biosynthesis and release of viral particles (lysis or budding)
During influenza life cycle how does the cell take in the virus
Endocytosis
After the Influenza virus has successfully tricked the cell to engulf does it goes to the nucleus to be
replicated by the viral rna polymerase
What is used to make viral proteins during the life cycle of influenza virus
Viral mRNA
During the influenza life cycle where does the new viral particle go after being made
released into the extracellular fluid
How are bacteriophage life cycle different from Eukaryotic virus life cycle of influenza
The cell is not killed (lysed) but continues to make new virus
What dictates how protein and nucleic acid are replicated in Eukaryotic virus’s
The 4 types of genomes
When virus has Double stranded DNA what occurs during biosynthesis
normal flow of host cell
When virus has single stranded DNA what occurs during biosynthesis
complementary strand is synthesized and then normal flow occurs
When virus has POSITIVE single stranded RNA what occurs during biosynthesis
Acts like normal mRNA and delivers piece of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein into a person’s cell and makes ribosomes which produce viral protein.
+ssRNA virus examples
SARS COv-2, HIV
When virus has NEGATIVE single stranded RNA what occurs during biosynthesis
-ssRNA is converted to +ssRNA through special RNA polymerase and then delivers piece of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein into a person’s cell and uses ribosomes to make more viral proteins
What is the special RNA polymerase that converts -ssRNA to +ssRNA
RdRp= viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
T or F -ssRNA can alternate btw positive and negative using RdRP ViralRNA dependent RNA polymerase
TRUE
Example of -ssRNA virus’s
Influenza and Ebola
Retroviruses
+ssRNA viruses, single stranded RNA viruses such as HIV.
Exhibit an alternative mechanism for viral nucleic synthesis
Reverse transcriptase
+ssRNA virus such as HIV carry this special enzyme within the capsid; it synthesizes a complementary ssDNA copy using +ssRNA genome as a template.
Ultimately allowing the ssDNA to be made into dsDNA which integrates into host cell and becomes a permanent part of the host
Provirus
Integrated viral genome of a retrovirus that can remain in the host cell or a long time to establish a chronic infection and does not undergo excision after splicing into the genome.
Persistent infection
occurs when a virus is not completely cleared from the system of the host but stays in certain tissues or organs of the infected person. eg latent and chronic infection
Latent Infection
type of Persistent infection whereby virus remain hidden in host cell after initial infection eg. Herpes simplex virus
Chronic infection
Type of persistent infection that occurs when host cannot successfully eradicate virus, HIV become chronic after latency period.
T or F
Plant viruses are more similar to eukaryotic viruses than prokaryotic viruses
TRUE
Most plant viruses have what type of genetic material
+ssRNA genomes
How are most plant plant viruses transferred
Via insect or fungal mechanical vectors.
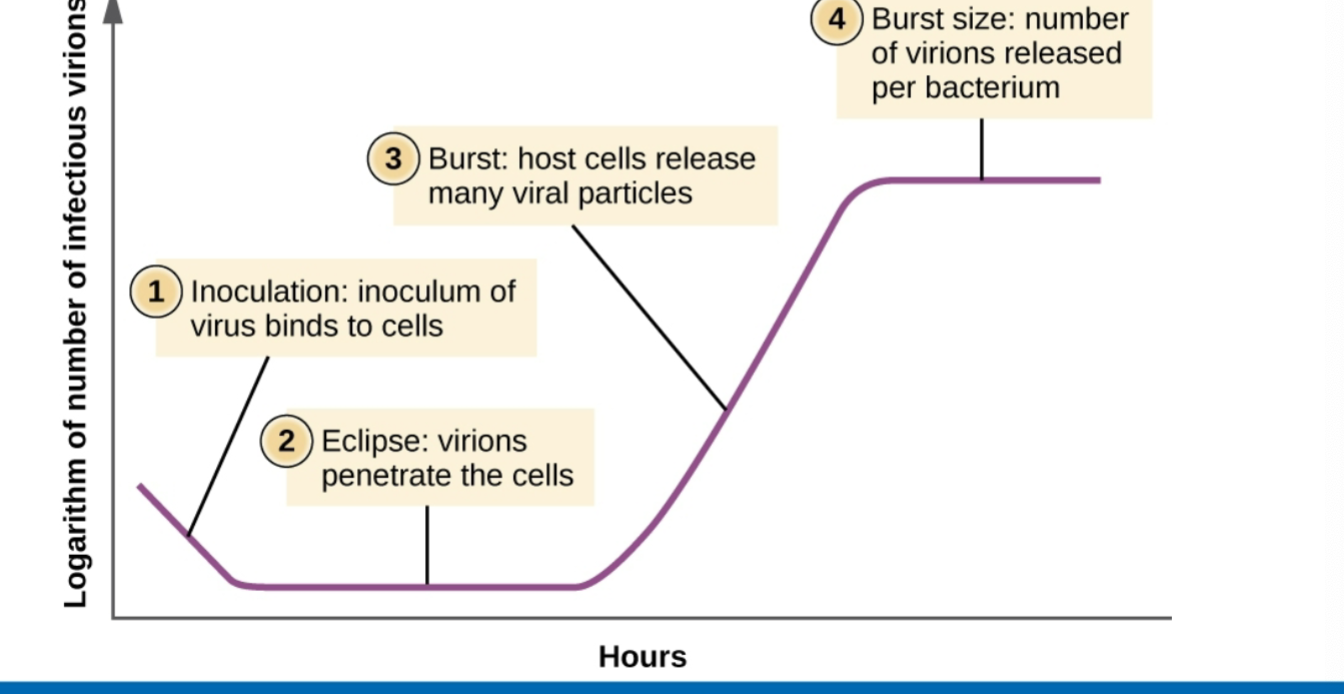
Viruses do not grow on their own but growth can still be measured; when does the number of infectious virions peak?
When host cells burst and release viral particles
When virus’s are grown in an organism either bacterial or animal cell cultures this is called ?
in vivo
When Virus’s are grown in vitro outside of an organism this is called
In vitro
Why do we grow animal virus cultures
ID pathogenic viruses, produce vaccines and for basic virology research
What animals or embryos can be used as incubators for viruses (in vivo)
eggs
When the influenza vaccine is being produced researchers infect flu strain 1 and 2 into chicken egg which produces many gene combinations, why is this important?
Can be used to predict the next influenza strain
Primary cell lines
Used for in vitro growth of viruses, whereby lines are obtained from desired tissue and cells are grown in petri dishes to allow attachment.
During In vitro growth in petri dishes mitosis is allowed to continue but is limited due to
Contact inhibition.
He La cell
Immortal cell line obtained from cervical cancer patient Henrietta lacks in 1951 these cells continued to grow and did not undergo contact inhibition.
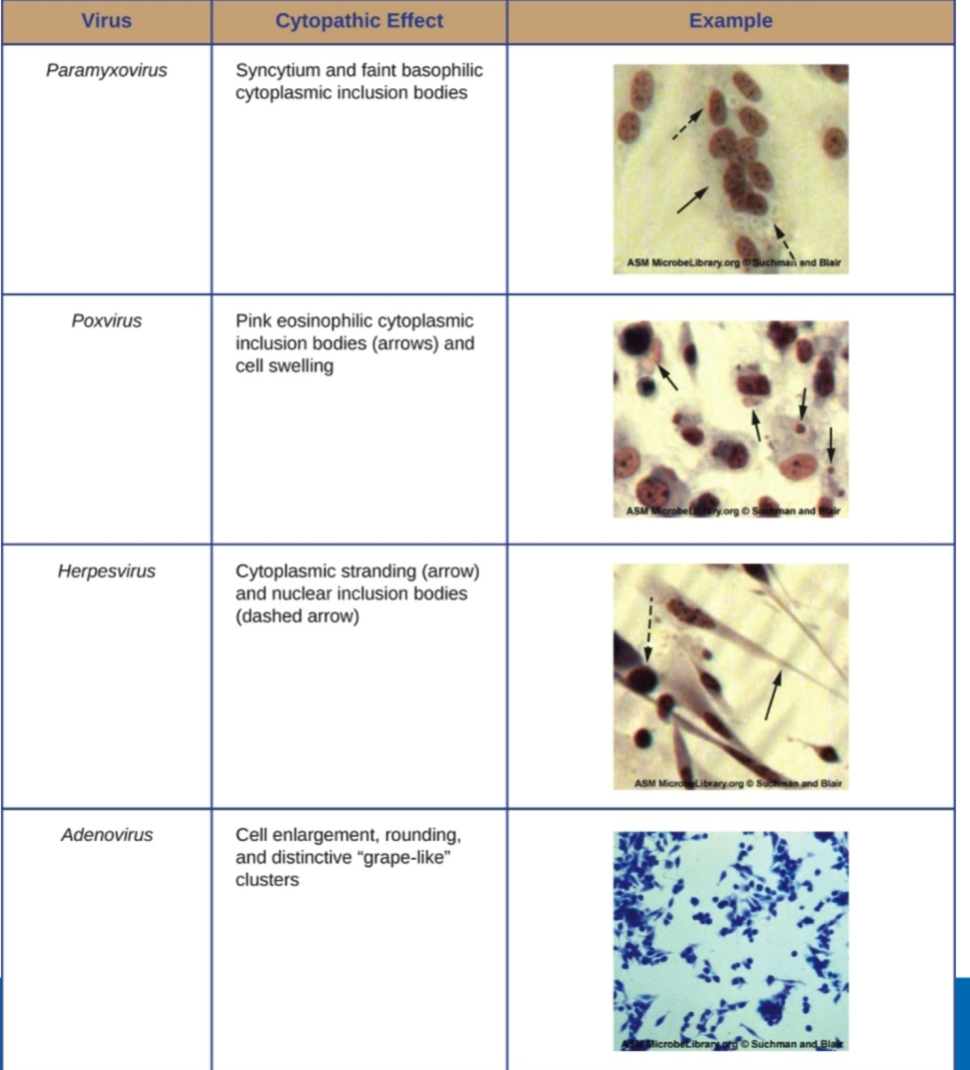
This method of virus detection use observable cell abnormalities such as Loss of adherence, Change to cell shape, Shrinkage of nucleus, Vacuoles formed, Fusion of cytoplasmic membranes to form multiple
nuclei, Inclusion bodies and Cell lysis (death)
Cytopathic effects CPEs
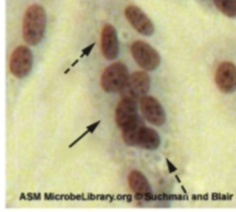
Which type of virus does CPE detect faint basophilic cytoplasmic inclusion bodies
Paramyxovirus
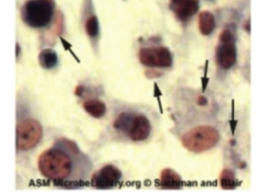
Which type of virus does CPE detect pink eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion bodies arrows and cell swelling
Poxvirus
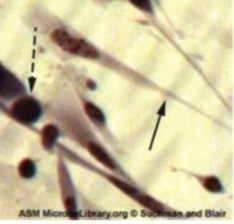
Which type of virus does CPE detect cytoplasmic stranding arrow and nuclear inclusion bodies (dashed arrow)
Herpesvirus
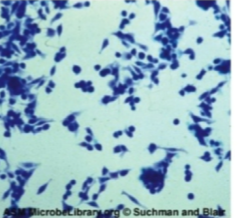
Which type of virus does CPE detect, cell enlargement rounding and distinctive grape-like clusters.
Adenovirus
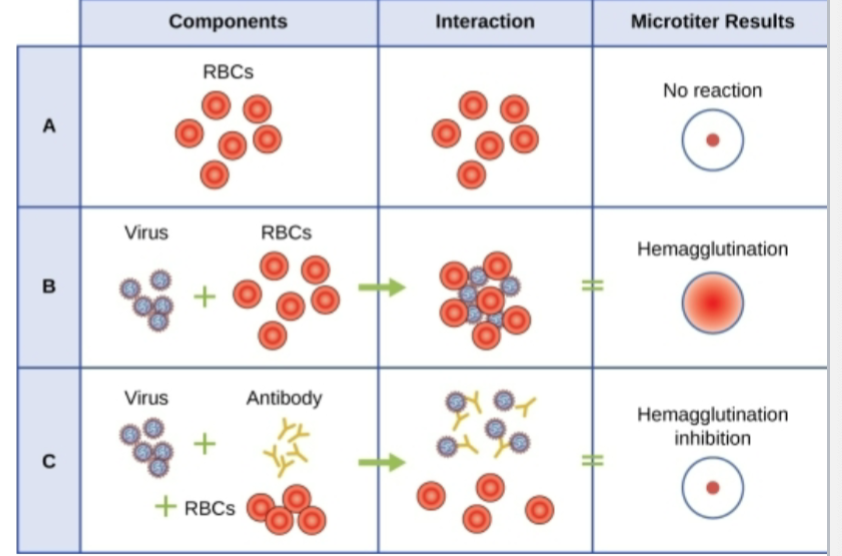
Hemagglutination Assay
Type of Detection of virus or antibodies from patient serum, either observes clumping (agglutination) of red blood cells
Some rapid COVID tests are agglutination
What is the positive outcome of a HIA test (detection of virus)
Hemagglutination
Nucleic Acid test
Taking by a nasal swab and results in Both PCR and RT-PCR used to detect and confirm the presence of the viral nucleic acid in patient specimens.
polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for DNA
reverse transcriptase PCR for RNA
What is the gold standard for covid infection
RT-PCR
Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA)
This Virus Identifier relies on the ability of antibodies to detect and attach to specific biomolecules called antigens with a high degree of specificity, colorless enzyme attached to the detecting antibody.
The enzyme acts as a tag on the detecting antibody and can interact with a colorless substrate, leading to the production of a colored end product.
Other acellular pathogens that are not viruses
Viroids, Virusoids and Prions
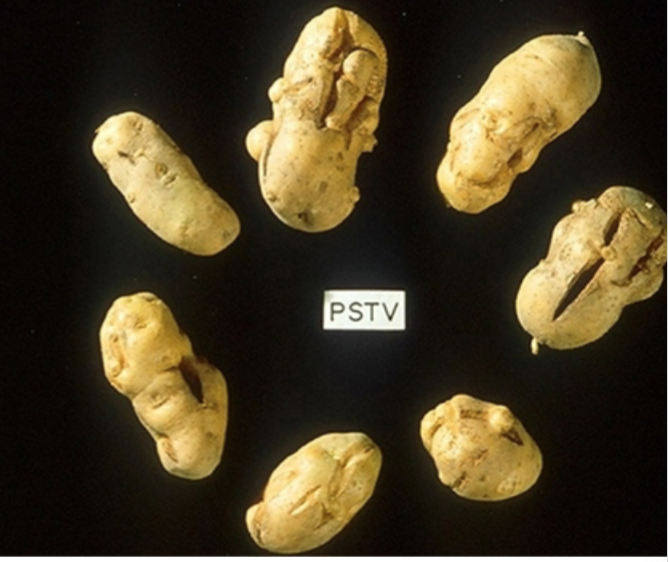
Viroids
Virus-like but not virus.
Circular RNA that can self replicate (No DNA conversion and no protein coating, capsid) eg. potato tuber spindle disease.

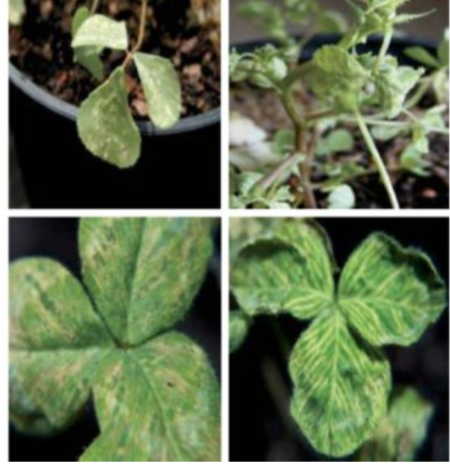
Virusoids
A second type of pathogenic RNA that can infect commercially agricultural crops. they require that the cell also be infected with a specific “helper” virus. eg. subterranean clover mottle virus

T or F
Prions have genomic material
FALSE
Prions
No genomic material; misfolded proteins that can cause others to become misfolded. eg transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (i.e.
mad cow disease)