Chapter 4: Goods and Services Selection
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
to provide goods or services to society
Why do organizations exist?
great products
What is the key to success?
core customers
Top organizations typically focus on what?
satisfaction
Customers buy ————, not just a physical good or particular service
the goods and services it offers
The essence of an organization is
closely tied to an organizations strategy
Product and service design - or redesign- should be
Product Life Cycle Management
A systematic approach to managing the series of changes a product goes through, from its conception to its end-of-life.
may be any length from a few days to decades
How long are product life cycles?
Operations Function
must be able to introduce new products successfully
the higher the percentage of sales from the last 5 years, the more likely the firm is to be a leader
What do we learn from this graph?
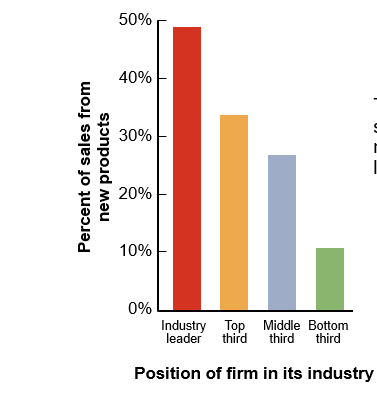
Traditionally
A champion
Team approach
Japanese “whole organization” approach
What are the 4 way of organizing for product development?
Traditionally
are distinct departments where duties and responsibilities are defined and it is difficult to foster forward thinking
A Champion
product manager drives the product through the product development system and related organizations
Team approach
Product development teams, design for manufacturability teams, and value engendering teams because they are cross functional and use representatives from all disciplines or functions
Japanese “whole organization” approach
no organizational divisions
differentiation
low cost
rapid response
What are the 3 Product Strategy Options?
Differentiation Example
Shouldice hospital
Low cost example
taco bell
Rapid response example
toyota
understanding the customer
economic change
sociological and demographic change
technological change
political and legal change
competition
cost/availability
What are the reasons corporations generate new products?
is there a demand for it
can we do it?
what level of quality is appropriate
does it make sense from an economic standpoint
What are the key questions of product and service design?
the potential market size and demand profile
What is considered in the question “is there a demand for it?”
Demand profile
will the demand be short or long term and will it grow slow or fast
Manufacturability and Serviceability
What is considered in the question “can we do it?”
Manufacturability
the capability of an organization to produce an item and an acceptable profit
Serviceability
the capability of an organization to provide a service at an acceptable cost or profit
customer expectations, competitor quality, fit with current offering
What is considered in the question “What level of quality is appropriate?”
liability issues, ethical considerations, sustainability issues, costs and profits
What is considered in the question “does it make sense from an economic standpoint?”
anywhere in the supply chain
Where does idea generation come from?
customers, suppliers, distributors, employees, maintenance and repair personnel
who can generate ideas?
Reverse engineering
dismantling and inspecting a competitor’s product to discover product improvements
Research and Development (R&D)
organized efforts to increase scientific knowledge or product innovation
Basic research
has the objective of advancing the state of knowledge about a subject without an near-term expectation of commercial applications
Applied research
has the objective of achieving commercial applications
Development
converts the result of applied research into useful commercial applications
Product liability
the responsibility a manufacturer has for any injuries or damages caused by as fault product
litigation, legal and insurance costs, settlement costs, costly product recalls, reputation effects
what are some of the concomitant costs of product liability?
Uniform Commercial Code
Under the ————, products carry an implication of merchantability and fitness
speed up the design process and cut costs
Designers are often under pressure to
Robust Design
A design that results in products or services that can function over a broad range of conditions
the less likely it will fail due to a change in environment in which it is used or performed
the more robust a product or service….
Standardization
extent to which product or service lacks variety and every customer or item processed receives the same service
Modular Design
a form of standardization in which component parts are grouped into modules that are easily placed or interchanged
easier diagnosis and remedy of failures
easier repair and replacement
simplification of manufacturing and assembly
training costs are low
adds flexibility to both production and marketing
what are the advantages of modular design?
limited number of possible product configurations
limited ability to repair a faulty module; the entire module must often be scrapped
what are the disadvantages of modular design
Delayed Differentiation
the process of producing, but not quite completing, a product or service until customer preferences are known
produce a piece of furniture, but do not stain it; the customer chooses the stain
What is an example of delayed differentiation?
Concurrent Engineering
Bringing engineering design and manufacturing personnel together early in the design phase. The purpose is to achieve product designs that reflect customer wants as well as manufacturing capabilities
Component Commonality
When products have a high degree of similarity in features and components, a part can be used in multiple products
product quality
shorter design time
production cost reductions
database availability
new range of capabilities
Computer Aided Design Benefits of CAD/CAM
Cradle-to-Grave & End of Life
the assessment of the environmental impact of a product or service throughout its useful life
End-of-Life (EOL) Programs
deal with products (business and consumer) that have reached the end of their useful lives. The goal of such programs is to reduce the dumping or incineration of products (e.g electronics) which may pose hazards to the environment
Remanufacturing
refurbishing used products by replacing worn-out or defective components
Design for disassembly (DFD)
designing a product so that used products can be easily taken apart
Design for recycling (DFR)
product design that takes into account the ability to disassemble a used product to recover the recyclable parts
Bill of Material BOM
lists the components of a product
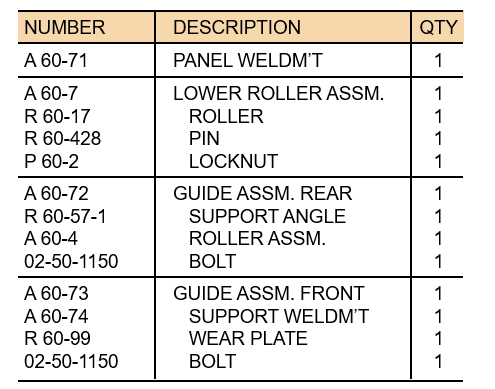
Operations Strategy
Effective product and service design can help the organization achieve competitive advantage