IPS1: Inorganic Chemistry Part 1 - Fundamentals - (A4) Quantum Numbers, Electron Configuration, Periodic Table
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proverbs 16:3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Quantum numbers
1. Principal QN (n)
2. Orbital QN (l)
3. Magnetic QN (ml)
4. Spin QN (ms) - for individual electrons
1. Principal Quantum Number
n = 1, 2, 3, ... (n)
orbital = shell or energy level
distance of electron from the nucleus; the higher the n, the higher the energy
2. Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l)
aka Azimuthal or Orbital Angular momentum Quantum number
l = 0, 1, 2, 3, ... (n-1)
orbital = subshell/sublevel
Shape of the orbital
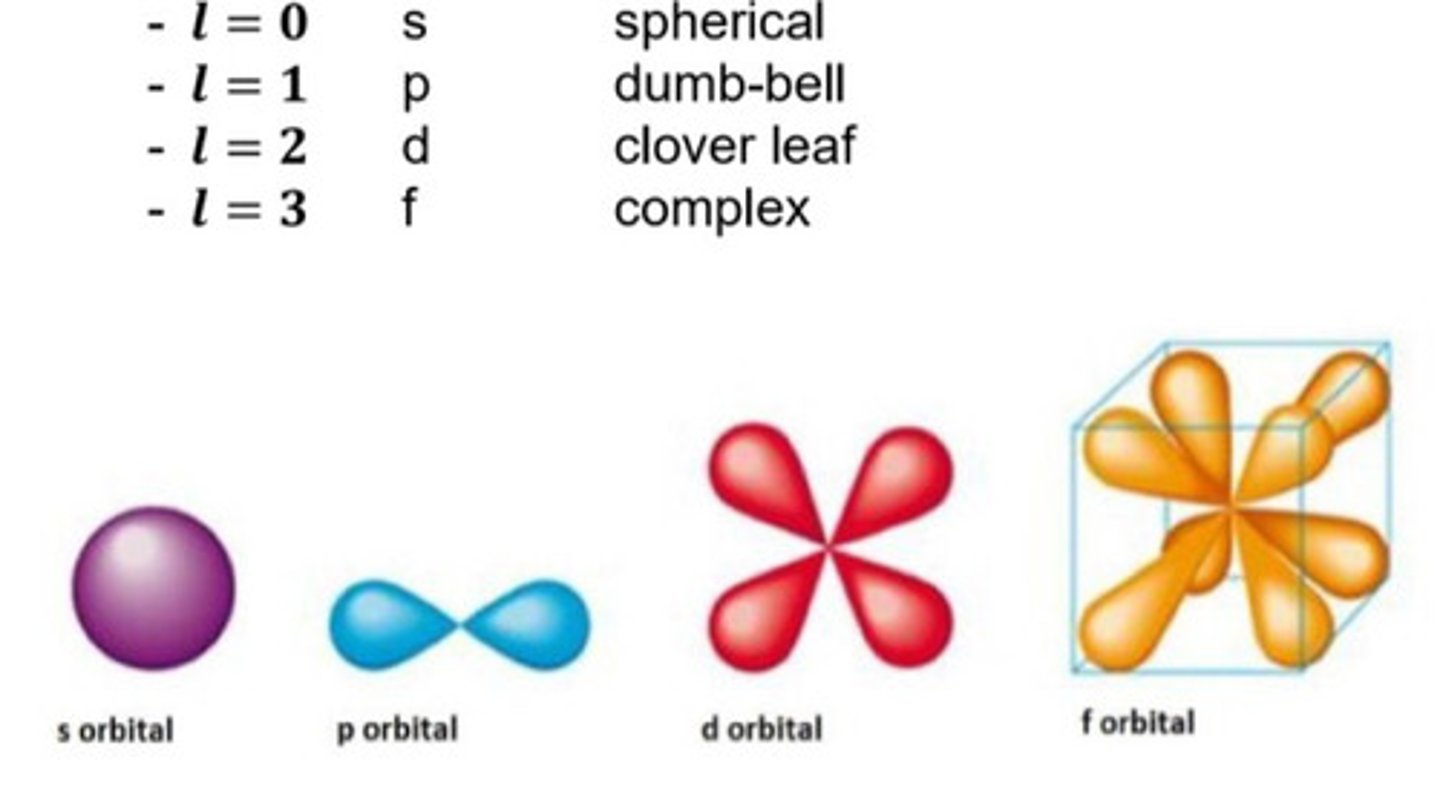
2. Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l)
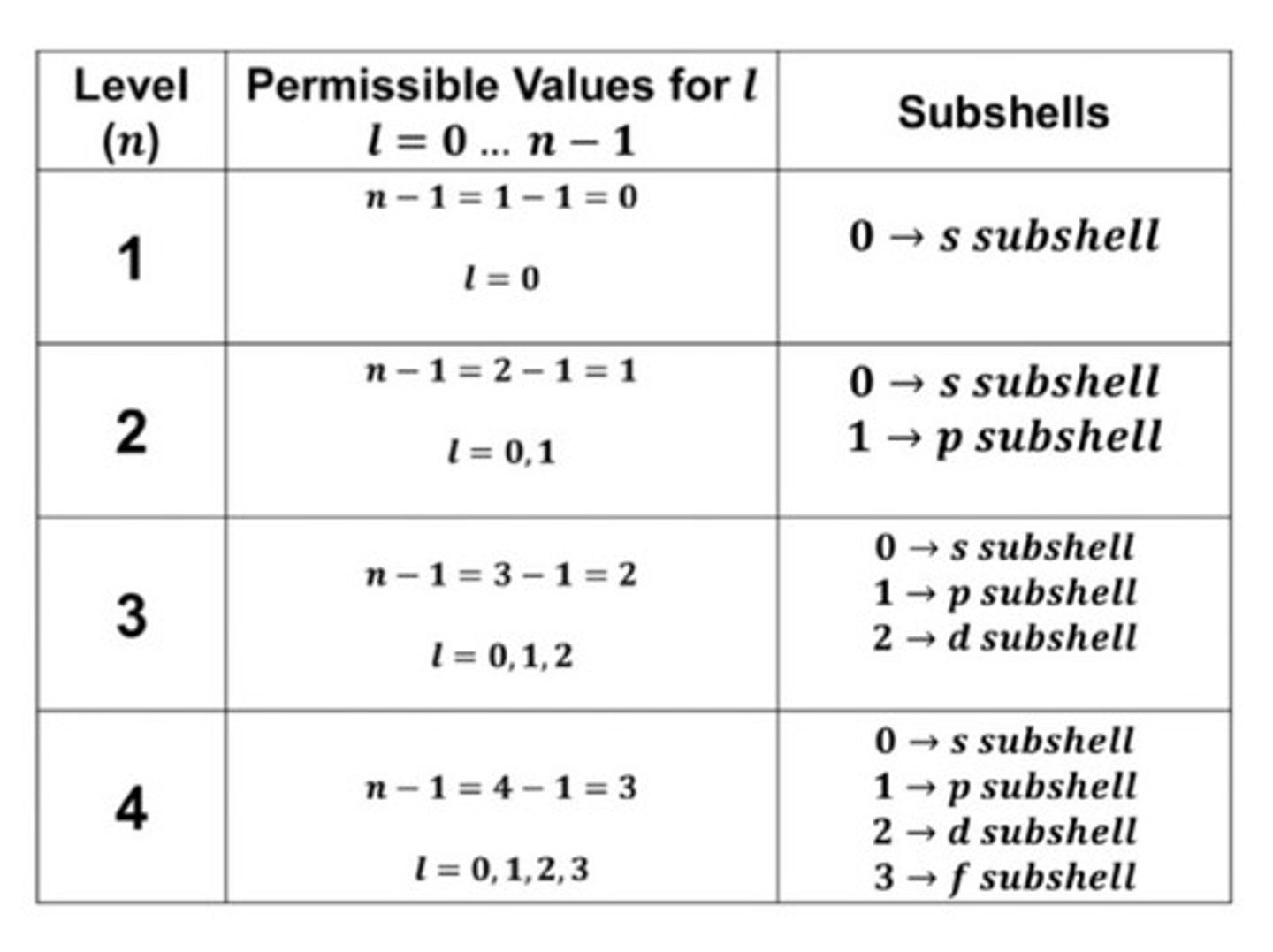
3. Magnetic Quantum Number
ml = -l ... 0 ... +l
orbital = specific orbital
orientation in space of the orbital

4. Spin Quantum Number (ms)
for each individual electron only
ms = +1/2 (upward; clockwise) or -1/2 (downward; counterclockwise)
Quantum Number and Electron Configuration

Electron Configuration
distribution electrons
describes the number and arrangement of electrons in orbitals, sub shells, and shells in an atom
Ground state
atom in its lowest energy or unexcited, state
Aufbau principle
orbitals fill in order of increasing energy, from lowest to highest
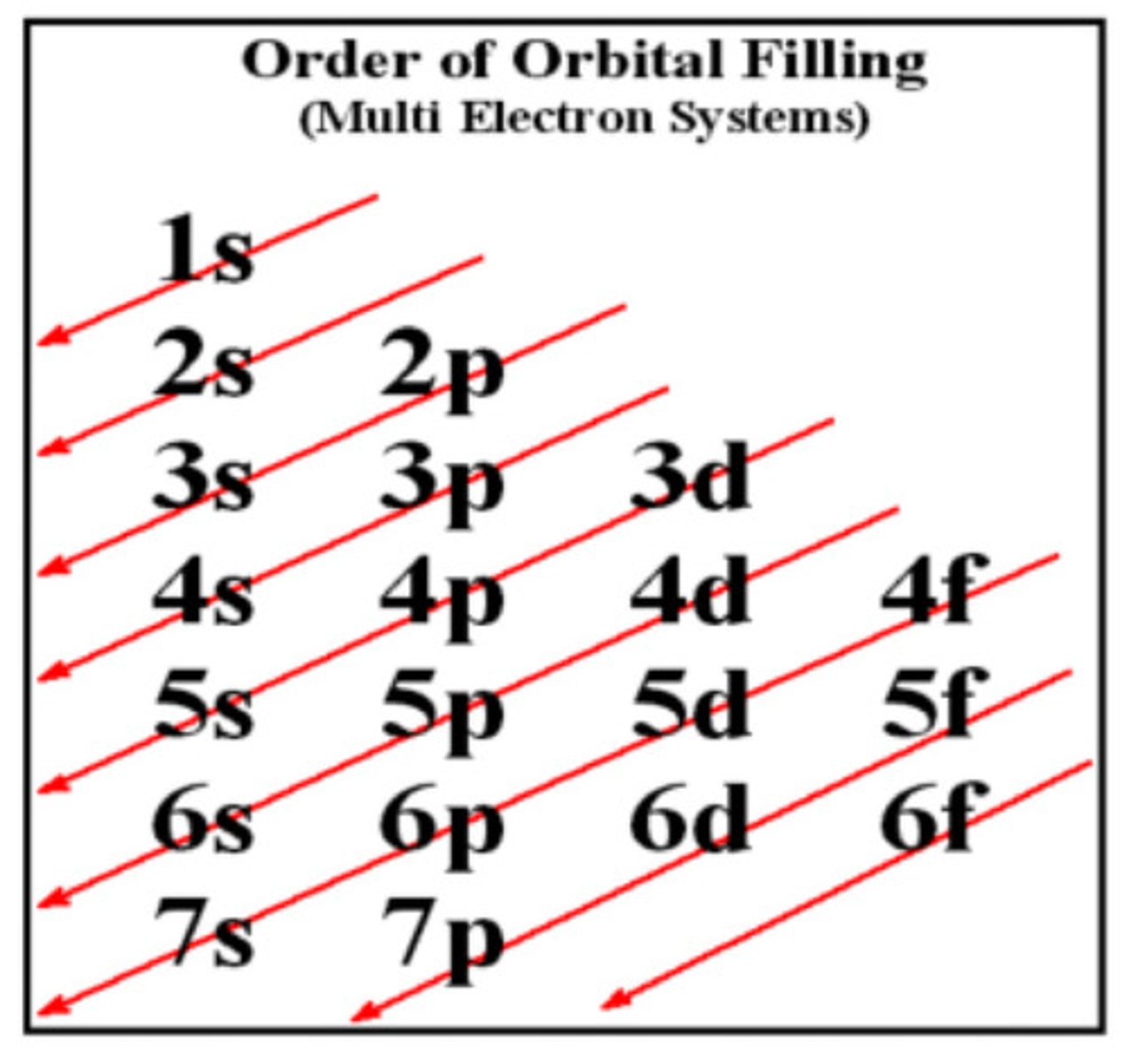
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No more than two electrons can occupy each orbital, and if two electrons are present, they must have opposite spins
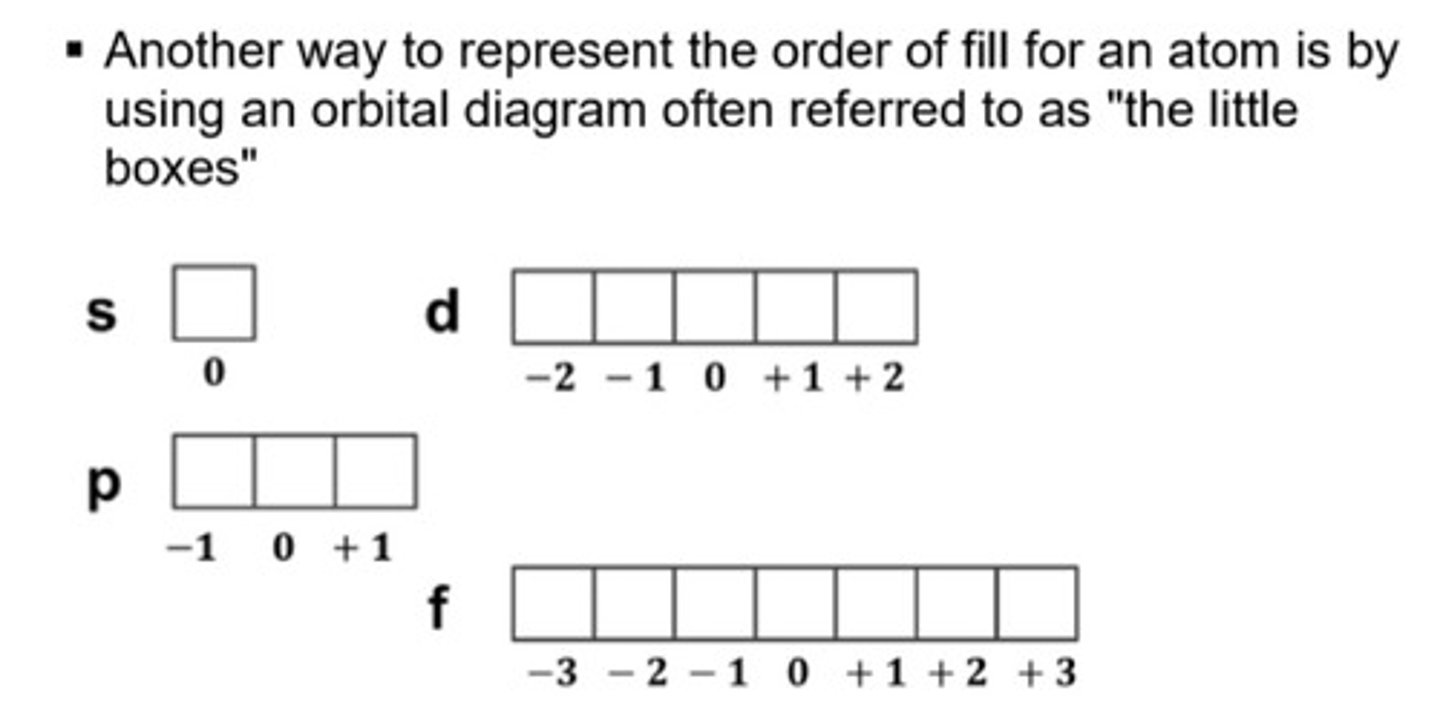
Orbital Diagrams
Noble Gas Configuration
an atom consists of the elemental symbol if the last noble gas prior to that atom followed by configuration of the remaining electrons
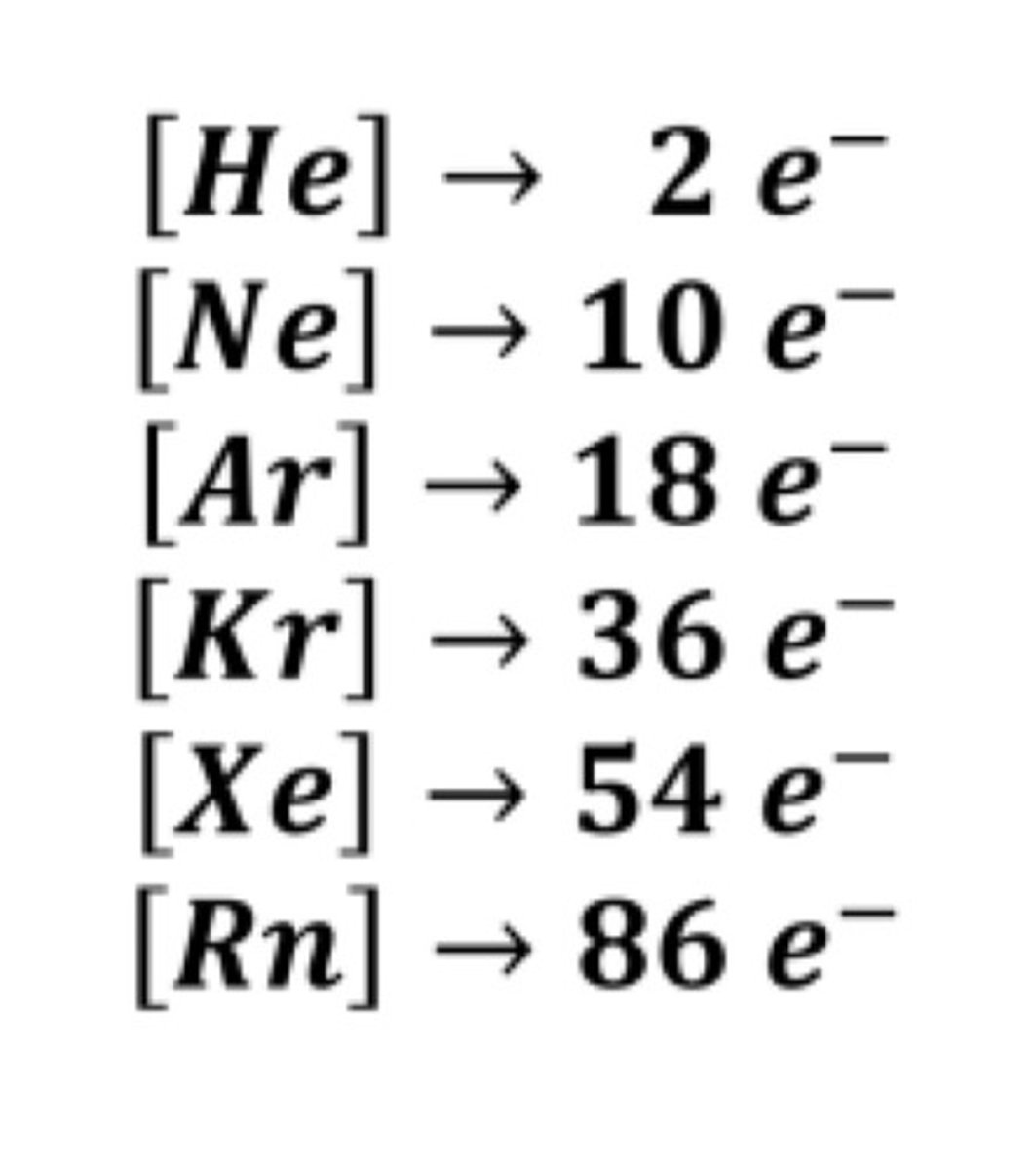
Hund's Rule
the order of fill is the same but as you can see from above the electrons are placed singly into the boxes before filling them with both electrons
a single electron will occupy an empty orbital first before pairing
Dimitri Mendeleev
concepts on periodic table based on chemical properties
Lothar Meyer
concepts on periodic table based on physical properties
Dimitri Mendeleev
Lothar Meyer
both emphasized the periodicity, or regular periodic repetition of properties with increasing atomic weight
Increasing atomic number
Elements are now arranged in the periodic table in order of
Periodic Law
the properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers
Vertical columns
group or families
Horizontal rows
periods
Group 1 (IA): Lithium group
H and Alkali metals
Group IIA: Beryllium group
Alkaline earth metals
1) Group IIIA
2) Group IVA
3) Group VA
4) Group VIA
5) Group VIIA
1. Scandium group
2. Titanium group
3. Vanadium group
4. Chromium group
5. Manganese group
Group 8,9,10 (VIIIB)
Iron group
Cobalt group
Nickel group
Group 11 (IB)
Coinage metals
Group 12 (IIB)
Zinc group
Group 13 (IIIA): Boron group
Triels; 3 valence electrons
Group 14 (IVA): Carbon group
Tetrels; 4 valence electrons
Group 15 (VA): Nitrogen group
Pnictogens; "to choke"
Group 16 (VIA)
Chalcogens; "ore"
Group 17 (VIIA)
Halogens: "salt"
Group 18 (8A): Helium or neon group
Noble gases
Properties of metals
forms cations by losing electrons
form ionic compounds with non metals
solid state characterized by metallic bonding
Properties of metals
high electrical conductivity that decreases with increasing temperature
high thermal conductivity
almost all are solids
malleable (can be hammered into sheets)
ductile (can be drawn into wires)
metallic gray or silver luster
Mercury (Hg)
Cesium (Cs)
Gallium (Ga)
liquid metals; melt at body temperature
Malleability
property to be hammered into sheets
Ductility
property to be drawn into wires
Copper (Cu)
Gold (Au)
metals that are not metallic gray or silver luster
Properties of non metals
poor electrical conductivity
good heat insulators (except C)
solid, liquid or gases
brittle in solid state
non ductile
non metallic luster
Properties of non metals
form anions by gaining electron
form ionic compounds with metals and molecular (covalent) compounds with nonmetals
covalently bonding molecules
Graphite (Carbon)
non metal that is good electrical conductor
Carbon
non metal that is not good heat insulator
Metalloid
show properties of both metals and non-metals
semiconductors
Lower
Metalloids are insulators at _____ temperature
Conductors
Metalloids are ______ at higher temperature
Metalloids
Boron (B)
Silicon (Si)
Arsenic (As)
Tellurium (Te)
Germanium (Ge)
Antimony (Sb)
Polonium (Po)
Astatine (At)
Atomic radii
half of the distance between the nuclei of neighboring atoms in the pure element
express in Angstroms (1Å = 10^-10 m)
Ionization Energy (IE)
the energy required to remove an electron from a gas-phase atom
Electron Affinity (AE)
the energy change that occurs when an electron is attached to an atom in the gas phase to form negative ion
Electronegativity
measure of the relative tendency of an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another atom
H and noble gases
excluded in the periodic trends
Periodic Trends
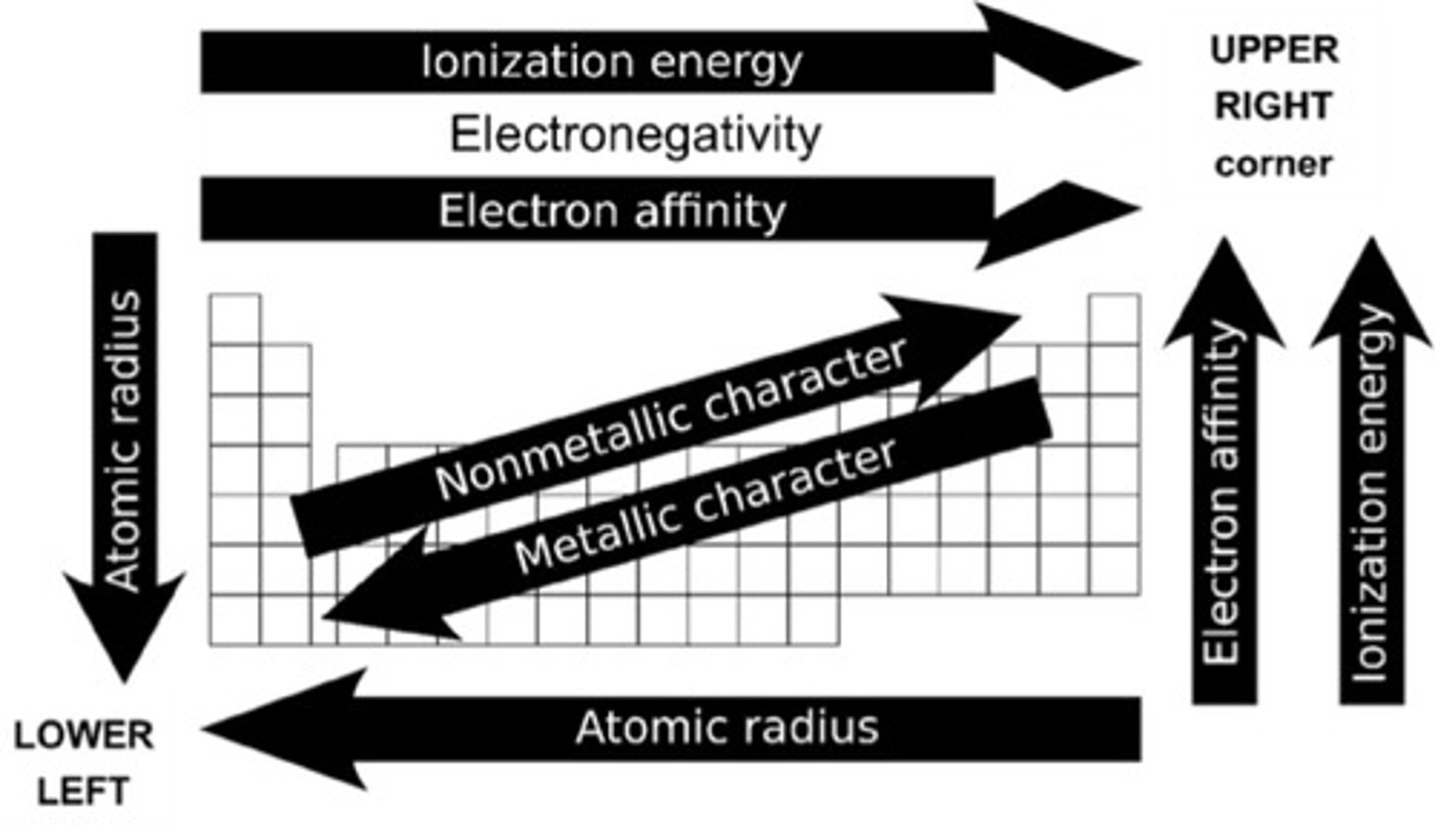
Increasing from left to right and down to top
Periodic trend: Ionization energy
Increasing from left to right and down to top
Periodic trend: Electron affinity
Increasing from left to right and down to top
Periodic trend: Electronegativity
Increasing from top to down and right to left
Periodic trend: Atomic radius
increasing from lower left to upper right
Periodic trend: Nonmetallic character
increasing from upper right to lower left
Periodic trend: Metallic character