Genes and inheritance
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is a locus?
A part of the genome
What is the blending hypothesis vs particulate hypothesis?
Blending: genes (or parents substance) is uniformly and forever mixed
Particulate: despite mixed appearance there are still individual particles within the person
What is mendel’s first law?
Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characteristics
Words to know: allele, phenotype, genotype
What is mendel’s second law?
For each characteristic, an organism inherits two copies of a gene, one from each parent
Words to know: heterozygotic, homozygotic
What is Mendel’s third law?
If the two alleles at a locus differ, then the dominant allele, determines the organisms appearance
Words to know: dominant, recessive
What is mendel’s fourth law?
Two alleles for a heritable character segregate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes - the law of segregation
The law of independent assortment
Each pair of alleles segregate independently of each other pair of alleles
Dominant, recessive
Each individual characteristic is inherited 3:1 ratio
Degrees of dominance
If a red and a white flower were to be crossed together, it would result in a pink flower. Afterwards the 1st generation pink flower would be crossed with itself and you would get 1 red flower, 1 white flower and 2 pink flowers.
Pleiotropy
1 genetic change that has a large number of phenotypic outcomes; one genotype affects multiple phenotypes
Phenotype
The expression of the trait
Genotype
Pair of alleles
Epistasis
The phenotypic expression of a gene at one locus alters that of a gene at a second locus
Polygenic inheritance
The converse of pleiotropy
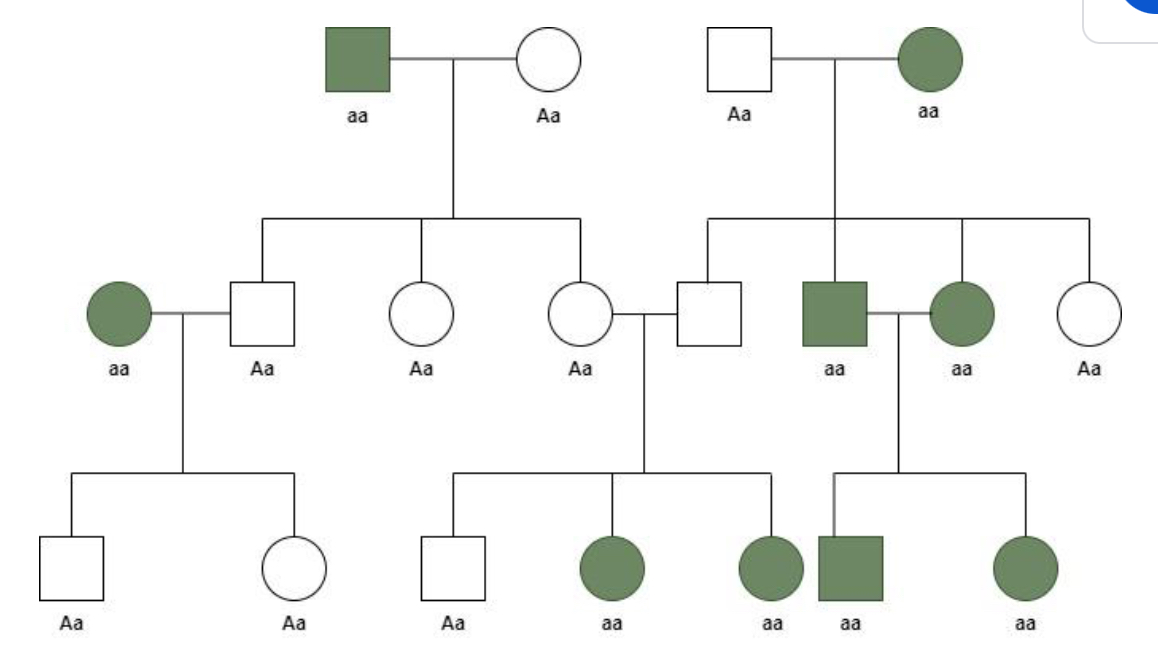
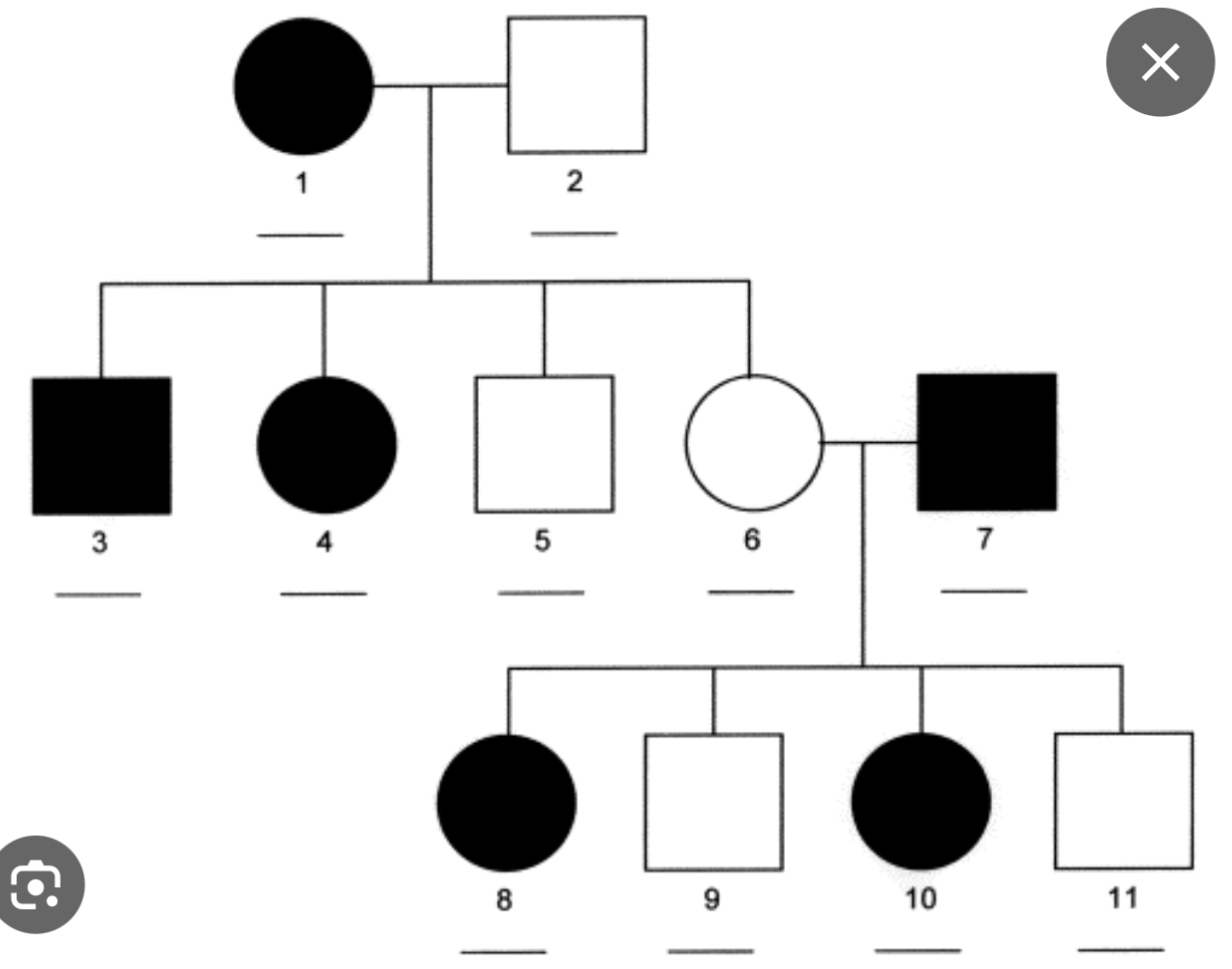
Autosomal recessive
^e.g. cystic fibrosis (Cl- ions cannot go through the channel, therefore there is a build up of ions one one side which leads to a build up of mucous, and the person cannot breathe)
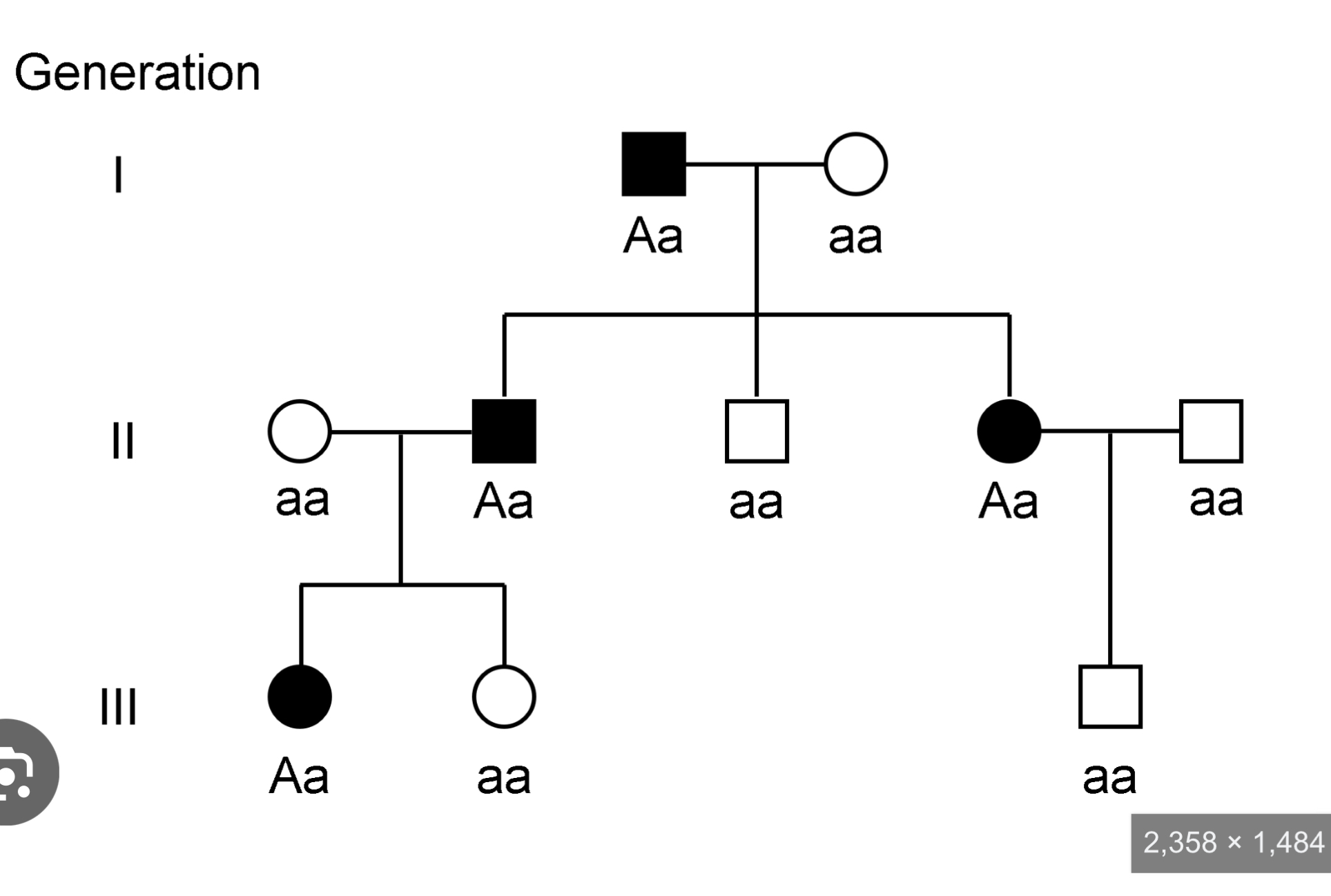
Autosomal dominant
^e.g. Huntington’s disease (enlargement of the frontal horns of the lateral vesicles)
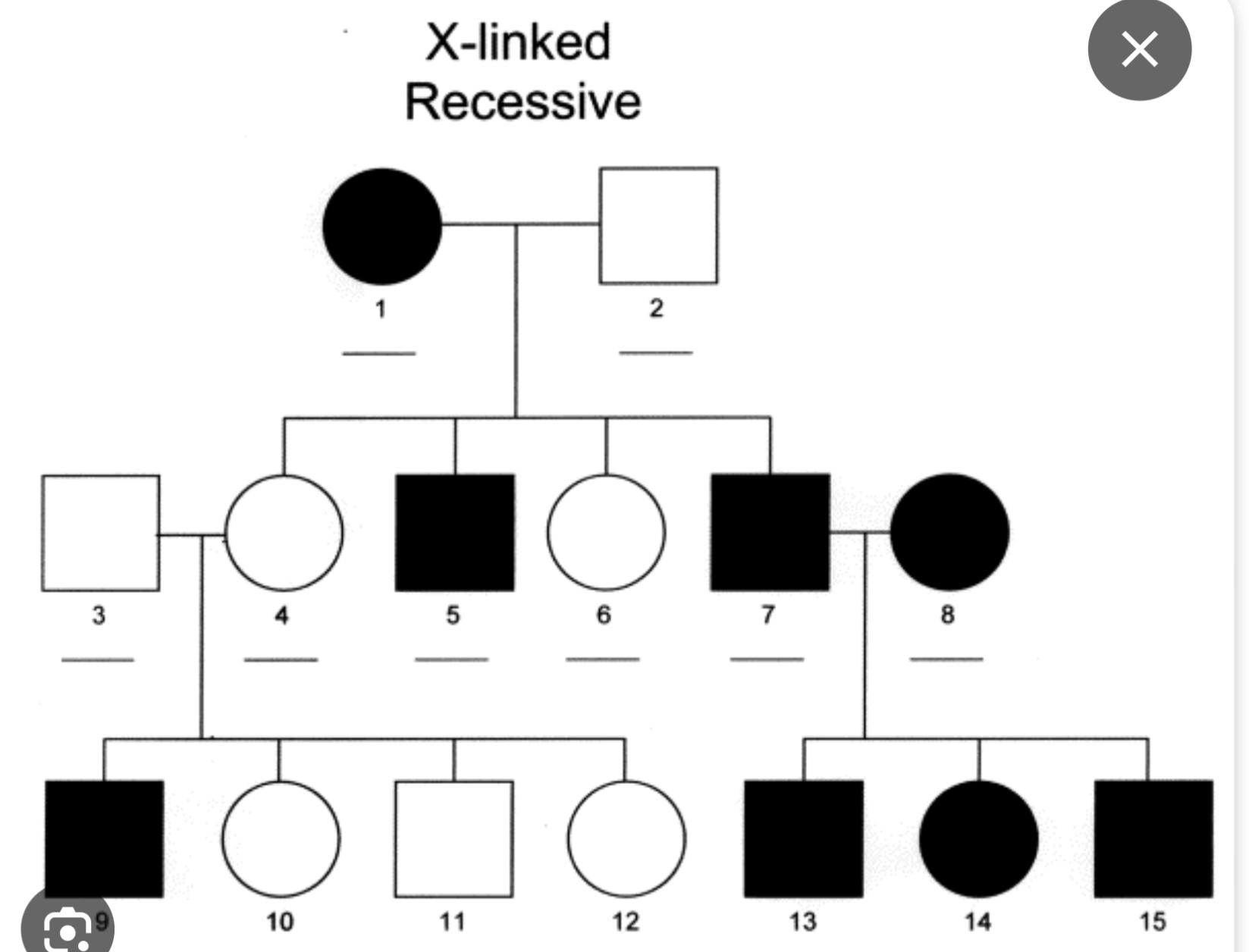
X-linked recessive
^ Red-green colour blindness
X-linked dominant
^ X-linked hypophosphatemia
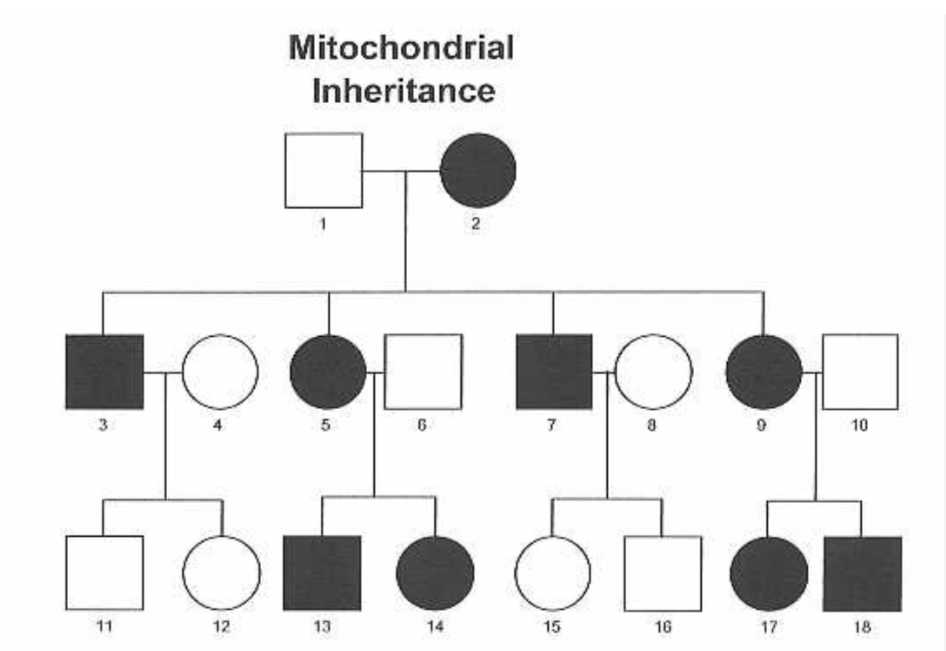
Mitochondrial inheritance
^
Equations
X = population mean
S² = population variance
s² = the sum of (Xk — X)² / (n—1)
S = population standard deviation
s = sqrt (s²)
What percentage of a trait is genetic and what percentage of a trait is environment?
Phenotype (P) = Genotype (G) + Environment (E)
What does Novel mean in genetics?
It means that it is the first occurrence in the family.
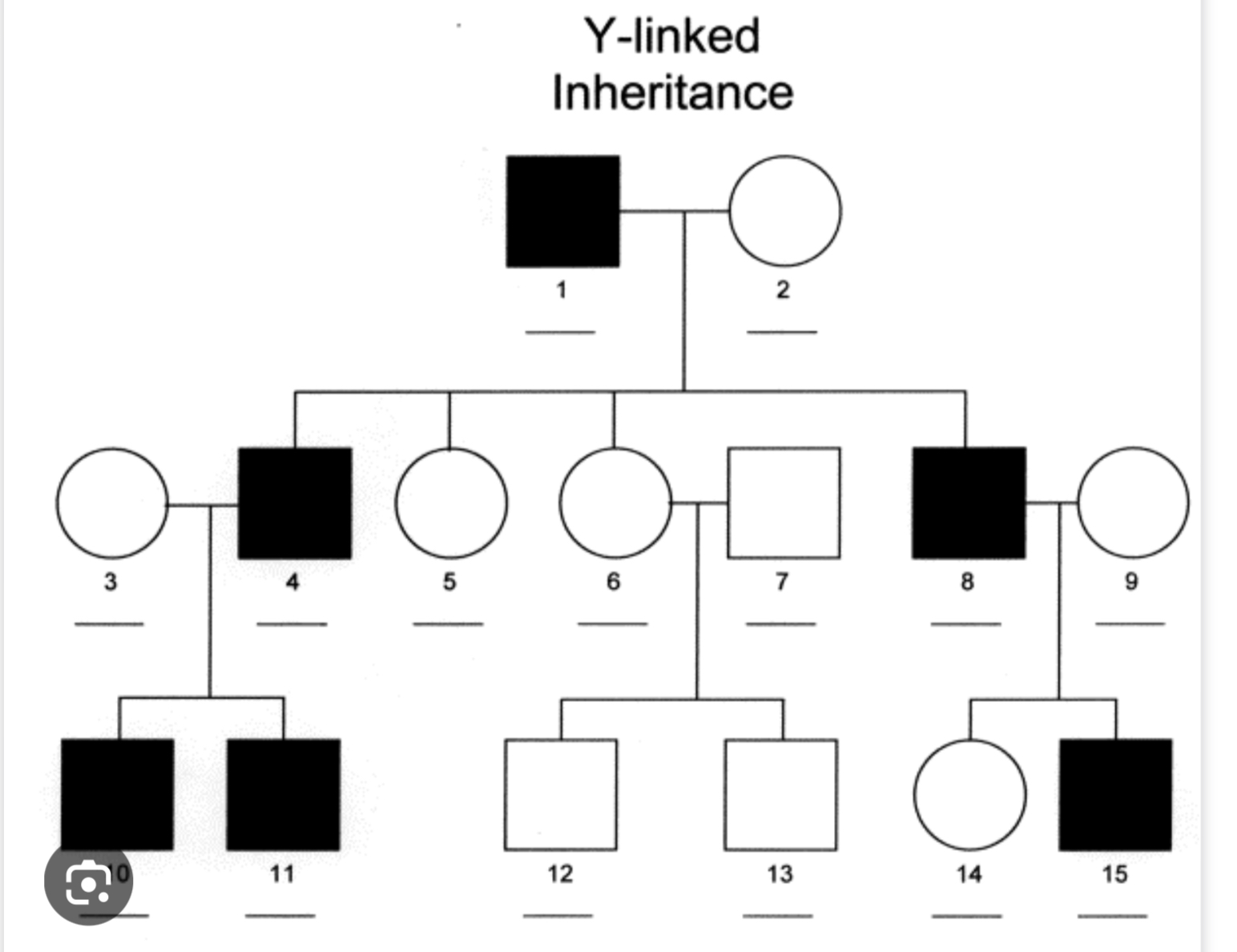
Y-linked inheritance
Direct line of paternal inheritance
Y-chromosome likely contains between 70-200 genes (very small amount)
Deletion of these genes cause highly penetrative disorders,