ARC 1013 Test 1
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Architecture Appreciation Test 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Solids and Voids
The relationship between these creates architectural space
Visual Scale
The size or proportion that a building element appears to have relative to other elements of known or assumed size
Proportion
A quantified relationship among the parts of an element as well as the relationship of that element to the whole.
Golden Section
An irrational proportion with special mathematical and spatial relationships applicable to a wide variety of phenomena including aesthetics, art, music, and nature. Known since Greek mathematician Euclid
Magnitude of the Golden Section
approximately 8.5 or 1.6180340…
Le Corbusier’s Modulor
created a series of harmonic numbers: one being the average height of the human being, and the other being the height of a man with raised arms.
Massing
composing three-dimensional shapes or volumes into a building design
Acoustics
branch of physics that deals with production, control, transmission, reception, and effects of sound
Context
the built or natural environment that surrounds new buildings
Style
a particular or distinctive form of artistic expression characteristic of a person, people, or period
“God is in the details.”
Mies van der Rohe
Shed Roof
slopes to one side
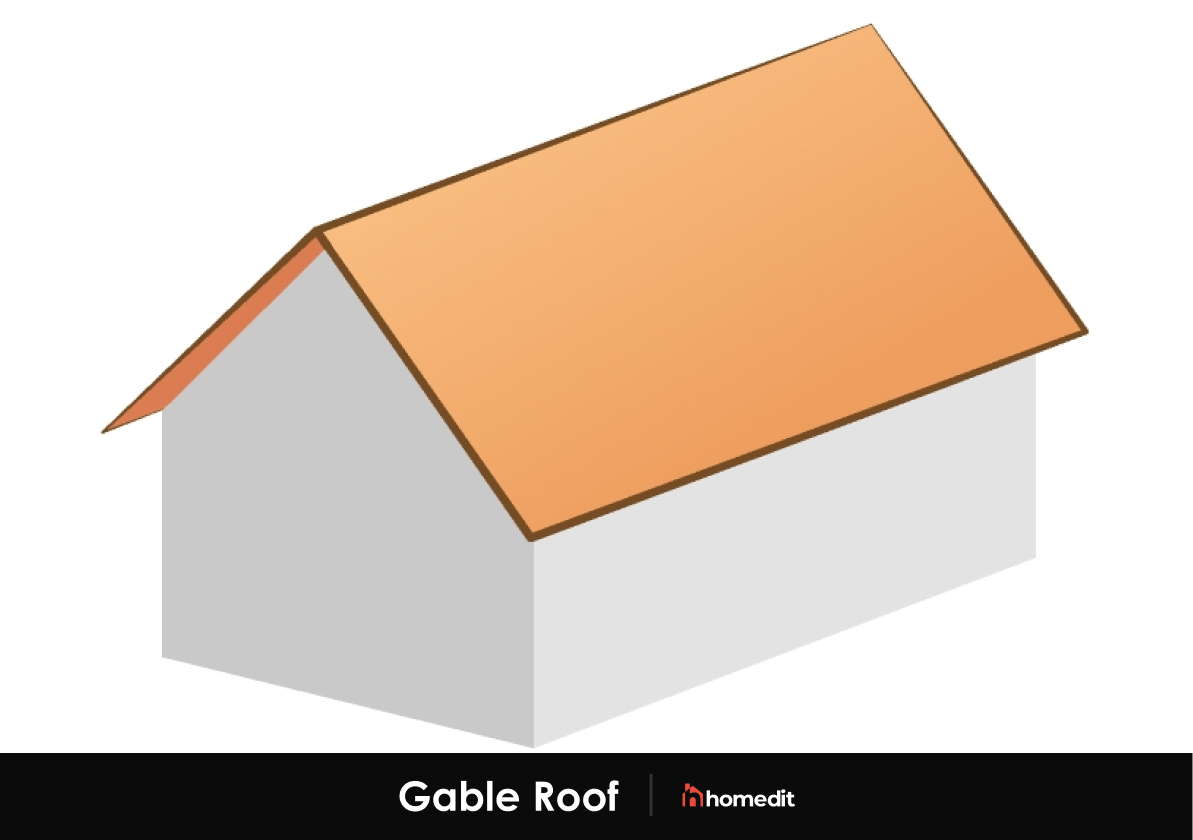
Gable Roof
A roof that slopes to two sides
Hipped Roof
a roof where the sloping ends and sides meet at a ridge

Pavilion Roof
a roof that’s shaped like a pyramid and is used to cover a square structure.

Barrel Vault
a semi-circular roof

Gambrel Roof
a roof that combines two different pitches below the ridge

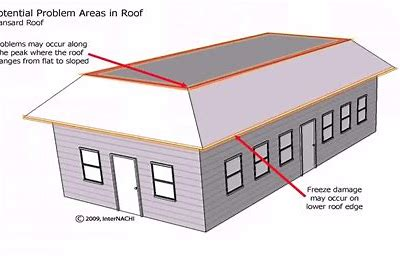
Mansard Roof
a roof that combines two different pitches below the ridge and is named after the French architect Francois Mansart
Rusticated Wall
a wall made of stone that is typically rough and raised of the wall surface

Half-timbered Wall
a wall that has timbered framework with the spaces filled with masonry or plaster

Clapboard Siding
a wall made of wood laid horizontally

Board and Batten siding
a wall made of wood laid vertically consisting of wide boards and narrow battens.

Stucco
a wall made of course plaster composed of cement, sand, and lime; mixed with water and used to cover exterior walls

Lancet Window
a window usually surrounded by decorative stonework. Has foils at the top

Palladian Window
windows consisting of a round-headed window flanked by two smaller windows

Double-hung window
a window that has two vertically hung sashes, each in separate tracks

Bay Window
a window that projects from the surface of a wall to allow light from three sides

Ribbon Window
horizontal bands of windows

Casement Window
a window sash opening on hinges that are generally attached to the vertical side of the frame

Transom Window
a window above a door(way)

Clerestory
a portion of an interior rising above adjacent rooftops that has windows to admit daylight

Pedimented Doorway
a doorway that has some type of arch or gable above the doorway

Venetian Door
a door with a semicircular window above it and flanked by vertical windows

French Door
a door that has rectangular glass panes extending throughout its length, often hung in pairs

Sliding Door
a door that operates or moves on a track

Building Type
an architectural form which has become accepted by society through repeated use. Ex: skyscrapers, cathedrals, data centers
Things required for any architectural project
Need, land, and financing
Program
the client’s list of practical requirements for a design project
Steps to become a licensed architect
BARC/MARC, minimum 3-year internship, and pass 6 parts ARE 5.0 exam
Basic architectural services consist of the following phases
schematic design, design development, construction documents, bidding and contract negotiation, and construction phase
Orthographic Plan Drawing
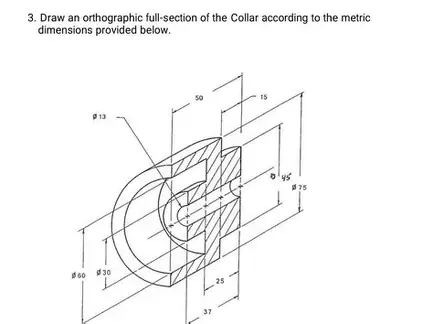
Orthographic Section Drawing
Orthographic Elevation Drawing
Axonometric Drawing
Perspective Drawing
