Cell Dynamics
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Definition of simple diffusion
The net movement of molecules or ions from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration down a concentration gradient as a result of the random movements of particles
Rate of diffusion depends on…
1) Difference of concentration of the substances on the two sides of the surface (greater, the faster)
2) Temperature (in terms of kinetic energy)
3) The greater the surface area, faster the diffusion (microvilli)
4) Bigger molecules diffuse slower than smaller molecules
5) SA/V ratio increases, diffusion increases
(The only exception is whether the volume is the same, if not, thinnest piece is faster)
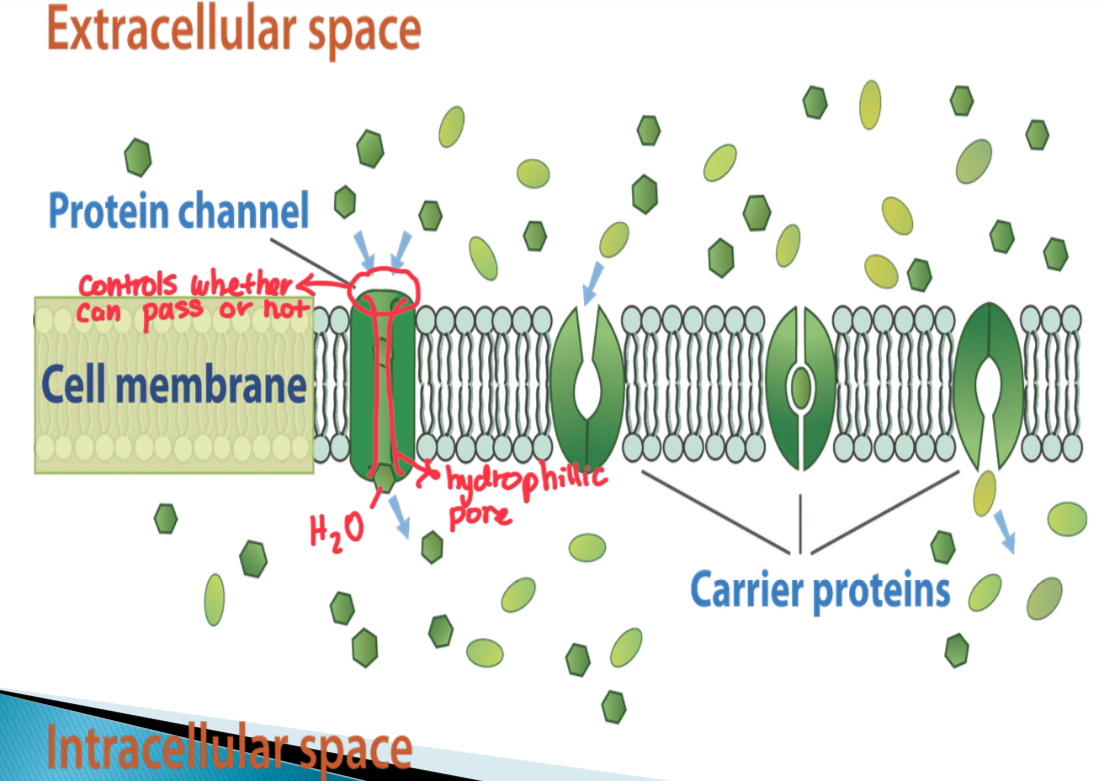
Process of facilitated diffusion
Involves both carrier and channel protein
Channel proteins are water filled pores and normally gated, meaning inside of the surface membrane will close and open like a gate
Carrier proteins constantly flip between two shapes
Definition of osmosis
The net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane via. random motion
Factors that affect water potential (normally measured in kPa) in cells
The higher the concentration of solutes, the lower the water potential (referred to as negative kPa value)
The presence of pressure makes the water potential become the least negative (referred to as positive kPa)
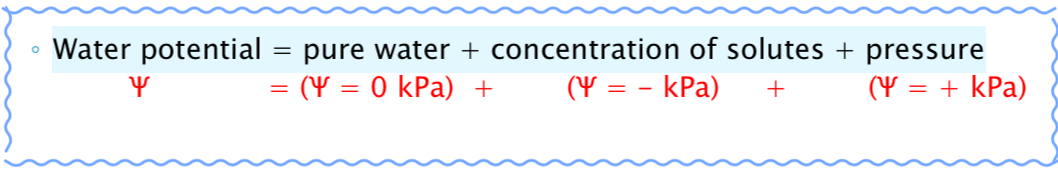
Water potential equation
Pure water + concentration of solutes + pressure
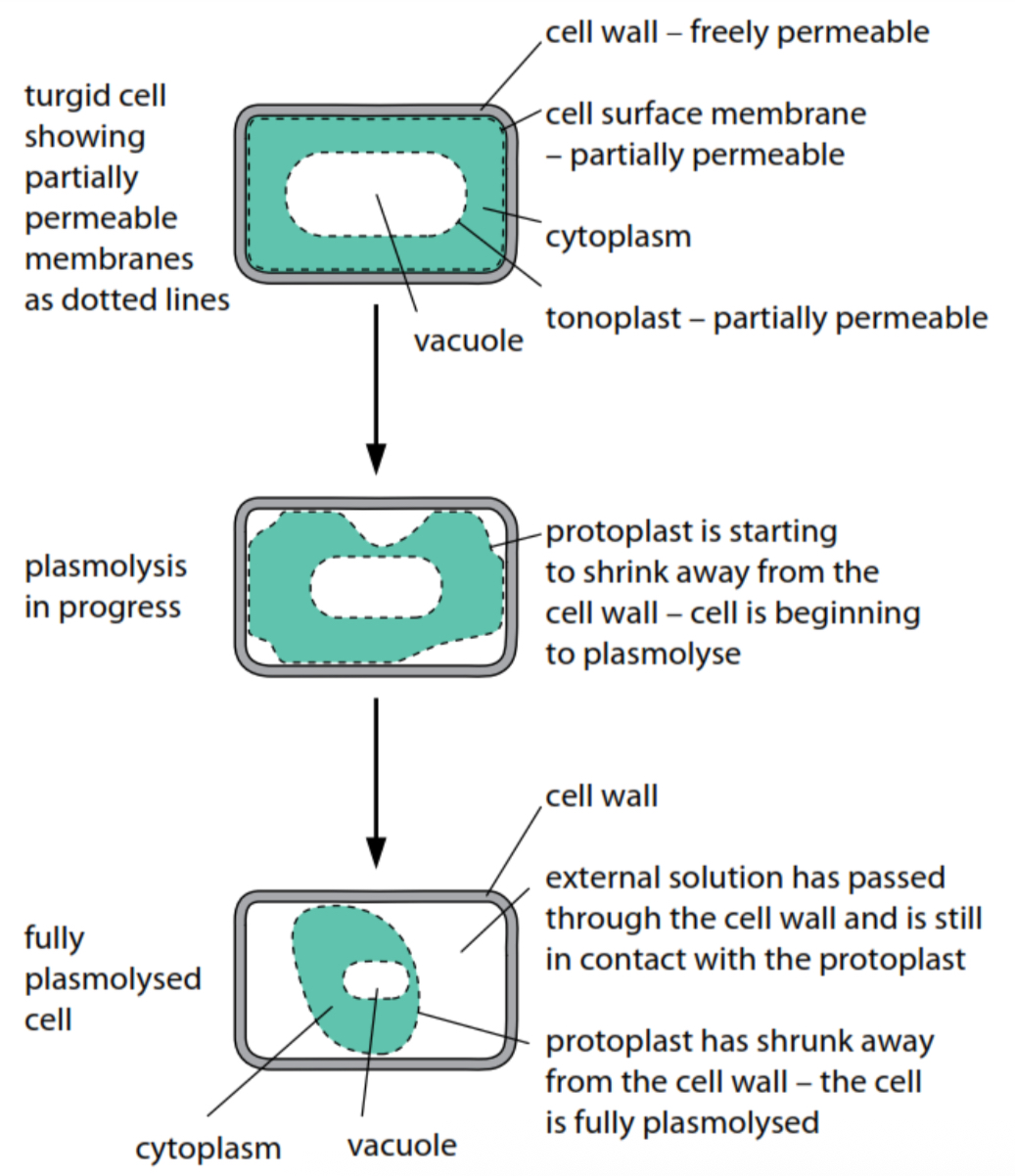
Plasmolysis in plant cells
Water drawn out from protoplasm, shrinks and exerts no more pressure at the cell wall. When the cell protoplasm fully detaches, it is fully plasmolysed
Process of active transport
Energy consuming transport of molecules or ions across a membrane against a concentration gradient by transferring energy from respiration
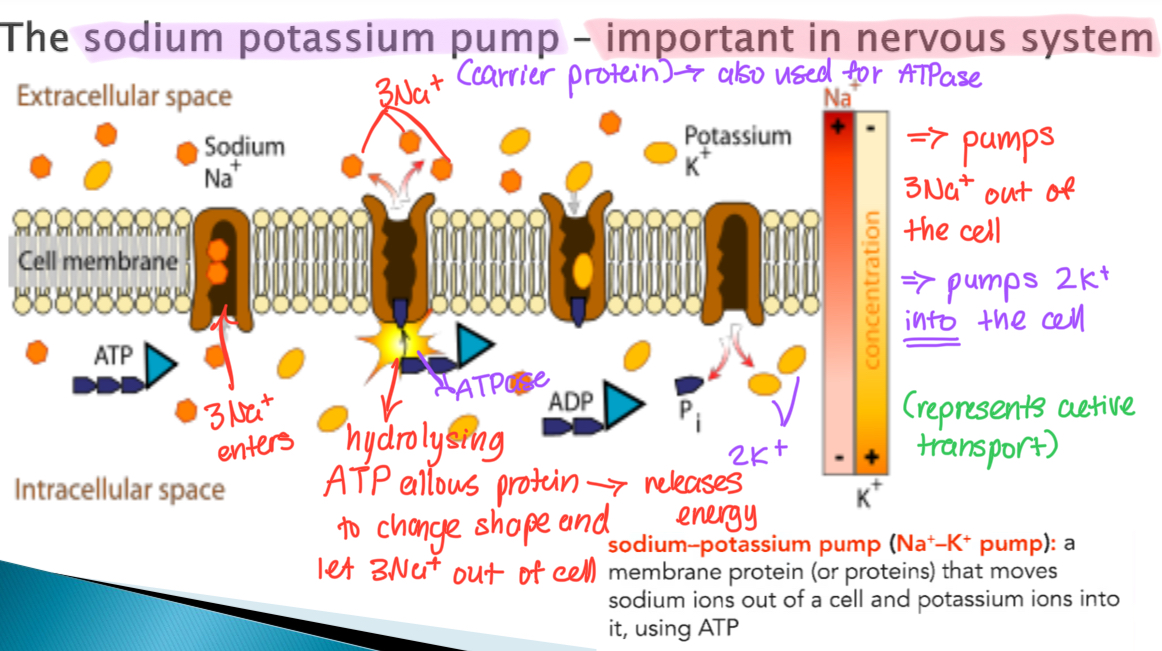
How the sodium potassium pump functions
1) 3Na+ enters carrier protein
2) Hydrolysing ATP via ATPase allows the protein to change shape and let 3Na+ out of cell
3) In turn, also pumps 2K+ into the cell
4) This process releases energy
Where is active transport also crucial?
Reabsorption in the kidney for ion and useful molecules back into the blood
Plants use this to load sugars from photosynthesis in the leaf and intake ions from soil to root.
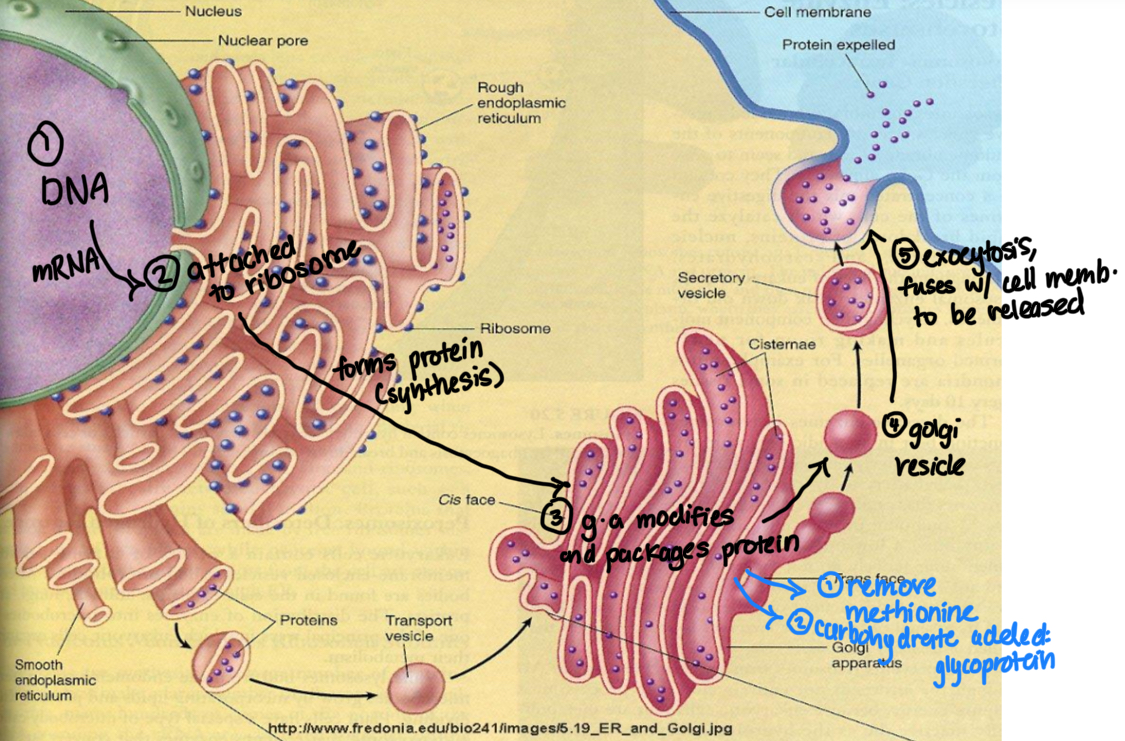
Bulk transport processes
Endocytosis: Involves engulfing of material by plasma membrane to form an endocytic vacuole
Exocytosis: Process of materials are removed from cells like enzymes, plant cells use this to get their cell wall building material to outside of plasma membrane