1. microbial techniques
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
CULTURING MICROORGANISMS
most microbes can’t be seen by naked eye
to investigate microbes we need to culture them
culturing- to grow them in large numbers so they can be measured in some way
need to be provided w/ nutrients and O2 and have right pH levels and temp for growth
CULTURING MICROORGANISMS- PRECAUTIONS
equipment sterile before culture started
once cultures are made they can’t leave lab
must also be disposed of by sealing them in plastic bags and sterilising at 121˚C for 15 mins under high pressure, before throwing them away- done in an autoclave
no ethical issues associated with culturing microbes but the danger of infecting people w/ pathogens should always be considered
CULTURING MICROORGANISMS- WHY PRECAUTIONS
always the risk that a mutant strain could arise which is pathogenic even if microbe is harmless
risk of contaminating culture w/ pathogenic microbes from env
when you grow a pure strain of microbe, entry of others from your skin or equipment will contaminate it
ASEPTIC CULTURE TECHNIQUES- MICROBE REQUIREMENTS
some microbes will grow on pure agar but most need added nutrients- nitrogen, carbon and specific minerals
most grow when a medium is enriched with a good source of protein like blood or yeast extract
by producing medium w/ specific ingredients you provide a selective medium- one which only a select group of microbes will grow in
important in identifying mutant strains and those bacteria with antibiotic resistance
ASEPTIC CULTURING TECHNIQUES- STEPS
nutrient medium can be in form of nutrient broth (liquid) or nutrient agar (solid)
agar is jelly extracted from seaweed- useful as although jelly sets at 50˚C it doesn’t melt until 90˚C
both media must be kept sterile until ready to use
once medium is ready, then introduce your microbes e.g. bacteria
can scrape bacteria from a source or dip loop into a suspension of bacteria
streak microbe onto agar or into broth- inoculation
GROWING A PURE CULTURE
to grow a pure culture, isolate organism by:
growing microbes under anaerobic conditions- only anaerobic bacteria will survive(same could be done w/ aerobic conditions)- but some can respire in both ways
use specific nutritional requirements- produce medium which favours microbes you want to grow and inhibit growth of ones you don't- could also use growth inhibitors, antibiotics or antifungals to do this
use indicator media- can cause certain types of bacteria to change colour- ones wanted can then be isolated and cultured
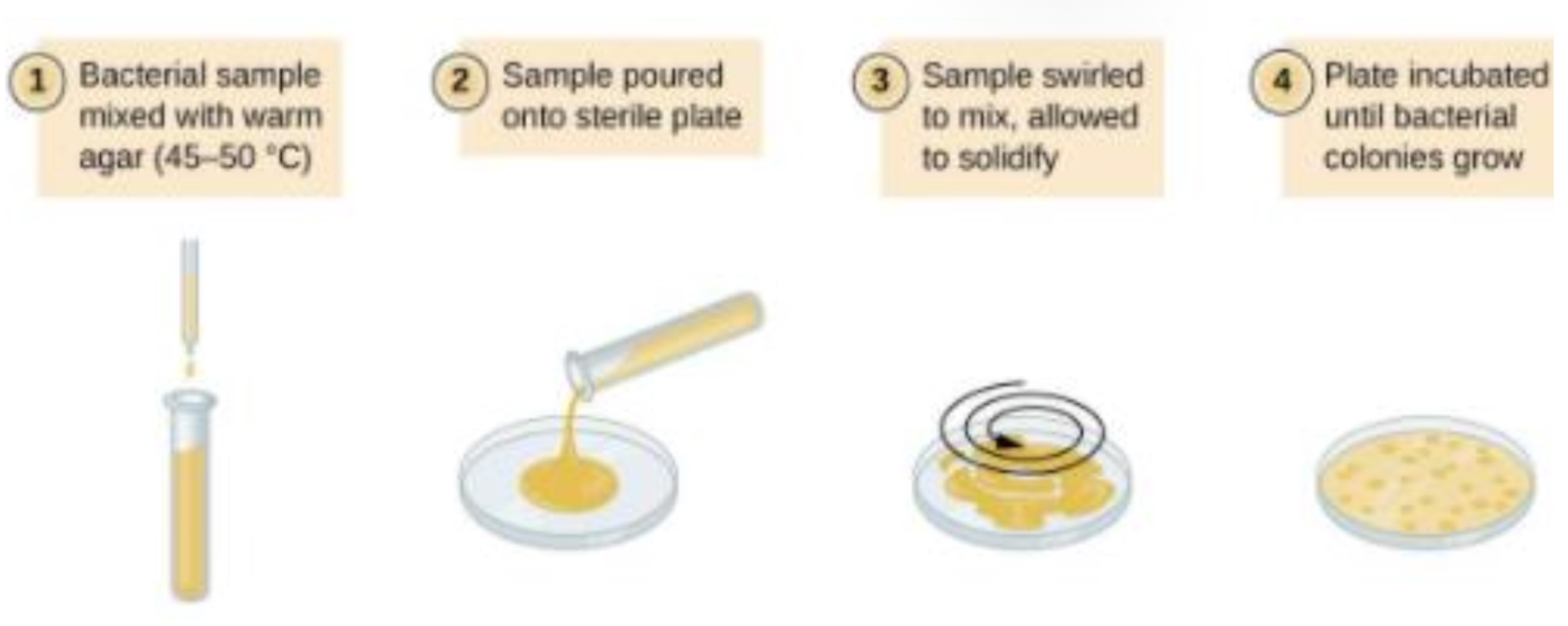
POUR PLATE- WHY USED
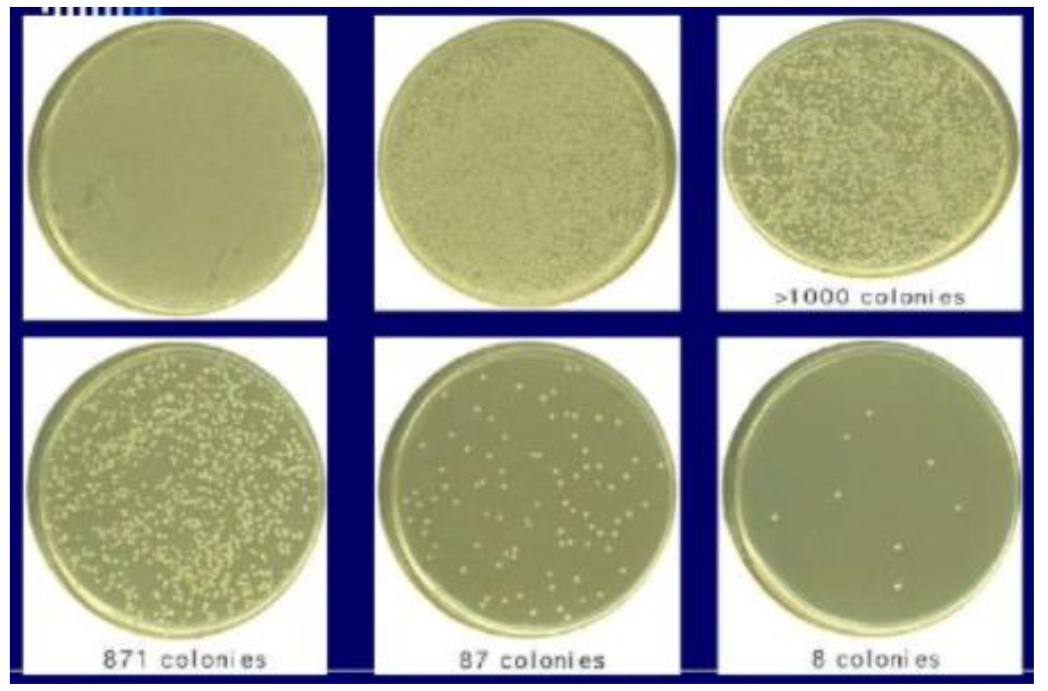
often used to count no. of microorganisms in a mixed sample
used to perform viable plate counts which let us create growth curves and calculate conc of cells in the tube a sample was plated from
POUR PLATE- TECHNIQUE
molten agar inoculated before it solidifies
molten agar should be cooled to 44˚C before plating otherwise it may kill organism
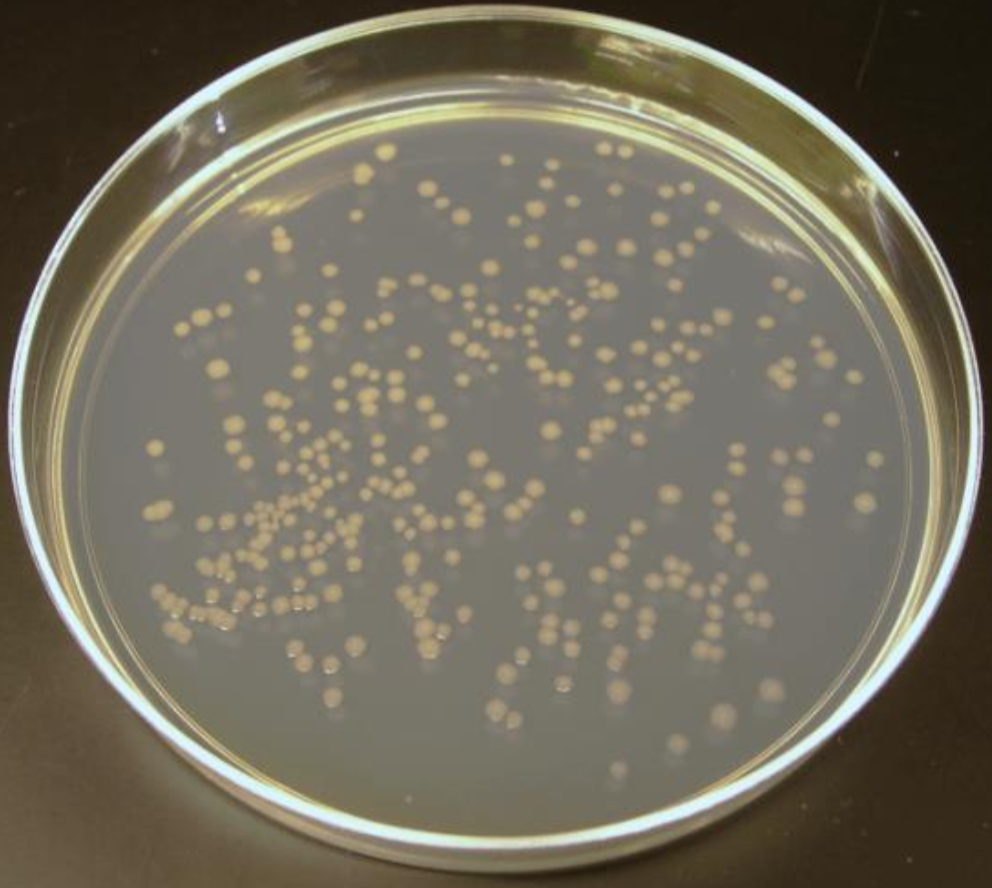
POUR PLATE- RESULT
colonies uniformly distributed throughout solid medium when appropriate sample dilution is plated
SPREAD PLATE- WHY USED
also is used to count no. of microorganisms in a mixed sample
used to help identify microorganisms based on how colonies look
can add antibiotic etc. to plates to look at selective growth
SPREAD PLATE- TECHNIQUE
culture is uniformly spread over surface of an agar plate
if not diluted enough, a lawn of bacteria is produced
antibiotics or agents can then be added to ‘clear’ zones so their effectiveness can be estimated
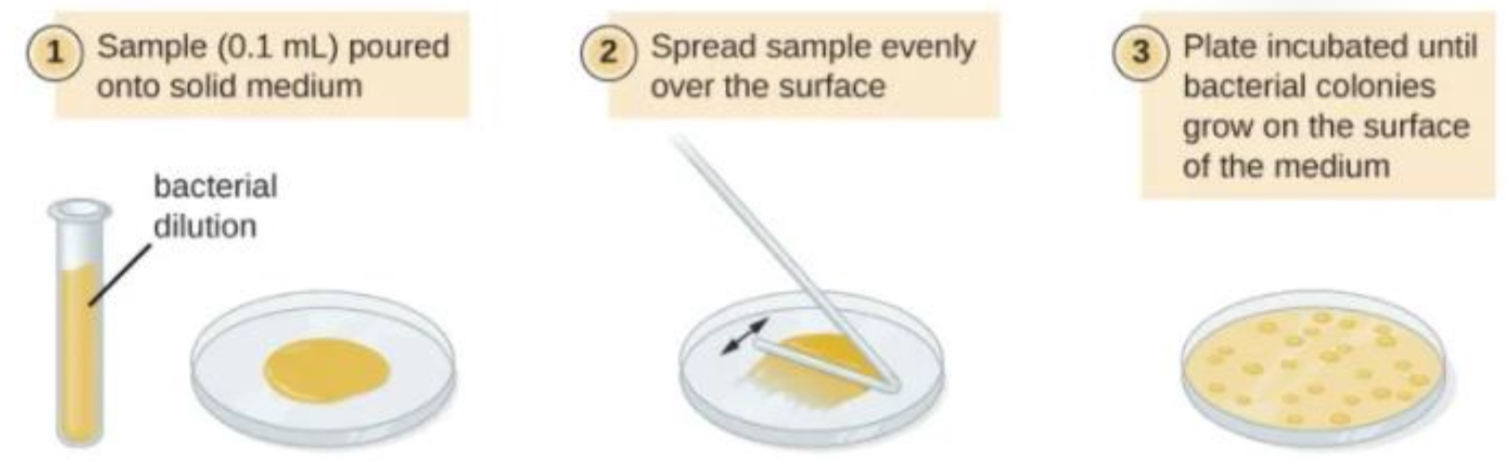

SPREAD PLATE- RESULT
isolated colonies distributed evenly across agar surface if appropriate conc of cells is plated
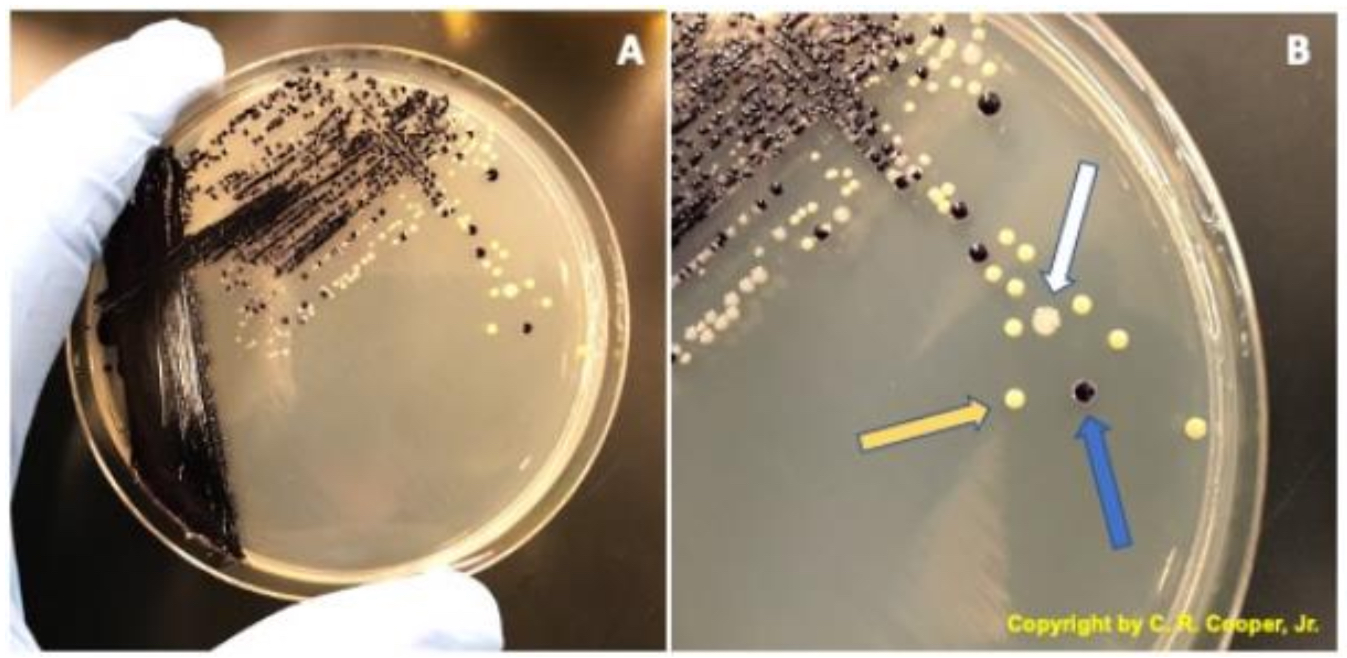
STREAK PLATE- WHY USED
used for obtaining a pure culture from a mixed culture or microbes
STREAK PLATE- TECHNIQUE
inoculating loop is used to add streaks of a culture onto plate
plate is quarter turned after each streak set
each new direction streak passes through older streak so sample is diluted as you go
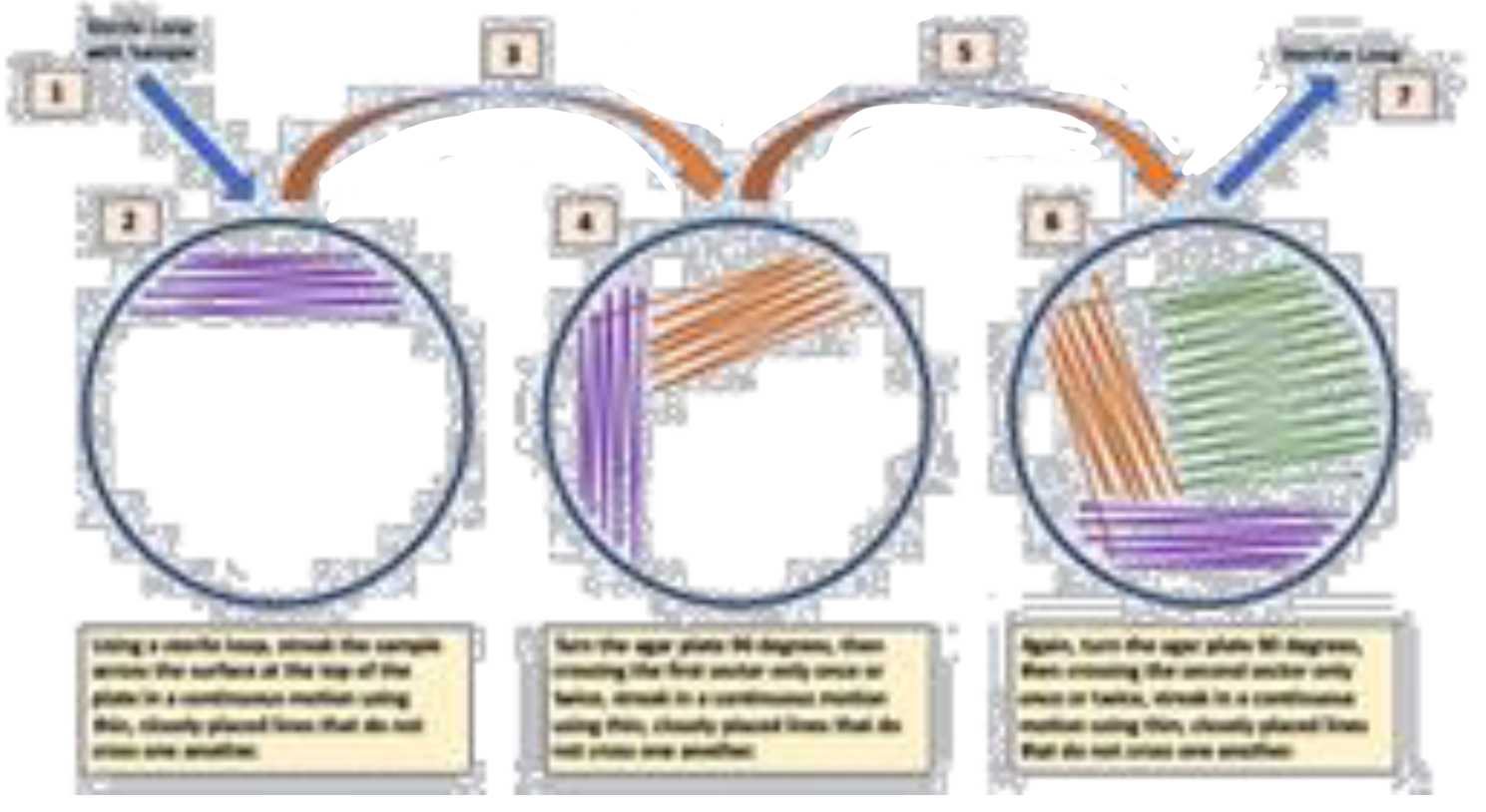
STREAK PLATE- RESULT
if original culture contained more than one bacterial species, colonies of each individual one can be identified and removed