X-Rays
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Explain what is meant by a non-invasive technique
No cutting or incision of the patient's body, so no surgery is required.
State some of the advantages of using non-invasive techniques
Lower risk of infection;
Less trauma, such as bruising or bleeding
State the main properties of X-ray photons
They can travel in a vacuum;
They travel at the speed of light in a vacuum;
They have no charge;
They have no rest mass;
They are highly ionising.
Explain why an X-ray photon has greater energy than a photon of visible light
E = hf;
X-ray photons have a higher frequency than visible light photons, so they have a higher energy.
Describe briefly how X-rays are produced in an X-ray tube
Fast moving electrons hit a metal surface;
the loss in kinetic energy of the electrons produces X-ray photons.
Describe how X-ray photons are produced in a hospital X-ray machine
Electrons are accelerated through a high potential difference;
the high speed electrons hit a metal surface;
the loss in kinetic energy of the electrons produces X-ray photons.
State interaction mechanisms between X-ray photons and matter, and describe what happens during the mechanism to the X-ray photon interacting with a single atom
Simpler Scattering; The X-ray photon scatters (bounces) off an electron with no change to its energy as it does not have enough energy to remove the electron from the atom.
Photoelectric effect; the X-ray photon provides enough energy to remove a delocalised/free electron from the surface of a metal, and provides kinetic energy to the electron;
Compton scattering; the incoming X-ray photon collides with an electron in an atom. The electron is ejected from the atom and the photon is scattered with a lower energy;
Pair production; the incoming X-ray photon disappears and produces an electron-positron pair.
Describe Simple Scattering in terms of an X-ray photon
The X-ray photon scatters (bounces) off an electron with no change to its energy as it does not have enough energy to remove the electron from the atom.
Describe the Photoelectric Effect
in terms of an X-ray photon
The X-ray photon provides enough energy to remove a delocalised/free electron from the surface of a metal, and provides kinetic energy to the electron;
Describe the Compton Effect in terms of an X-ray photon
An X-ray photon interacts with an electron within the atom;
The electron is ejected and the energy of the scattered photon is reduced.
Describe Pair Production of an X-ray photon
The incoming X-ray photon disappears and produces an electron-positron pair.
Name an element used as a contrast material in X-ray imaging
Barium or iodine
Explain why contrast materials are used in the diagnosis of stomach problems
The contrast medium absorbs X-rays because it has a large attenuation coefficient (it has a larger atomic number);
This is ideal for imaging the outline of soft tissues, as if there is a hole then the barium will highlight this by flowing out of the hole, revealing problems with the tissue.
Describe the use of image intensifiers when X-rays are used to produce images of internal body structures
An Intensifier is used as X-rays would pass through the film
Intensifiers converts an X-ray photon in to many visible light photons, which are absorbed by the film;
Therefore, a lower exposure to X-ray radiation is needed.
Describe the operation of a computerised axial tomography (CAT) scanner
An X-ray beam passes through the patient at different angles as the X-ray tube rotates around the patient;
A thin fan-shaped beam is used;
Images of slices through the patient in one plane are produced, with the help of computer software;
X-ray tube / detectors are moved along the patient for the next image slice through the patient.
State an advantage of a CAT scan image over a conventional X-ray image
3D image: allows size, shape and position of tumours to be assessed better
Better contrast between different (soft) tissues.
Explain how the production of a CAT scan image differs from that of a X-ray image
A simple X-ray produces a single image;
whereas a CAT scan takes images at many different angles.
State some of the disadvantages of a CAT scan
CAT scan relies on x-rays and any exposure to ionising radiation carries some risks for patients.
Slower and more expensive that a traditional x-ray.
Requires the patient to remain very still during the scanning process (otherwise the image will be blurred) , which may be difficult for some patients (e.g youth children)
Suggest why, when producing an X-ray image, long-wavelength X-ray radiation poses a greater hazard to health than short-wavelength radiation.
Long-wavelength radiation is more likely to be absorbed in the body/less likely to penetrate through the body.
Distinguish between sharpness and contrast in X-ray imaging.
Sharpness: how well the edges of structures are defined.
Contrast: the difference in the degree of blackening between structures.
State the causes of loss of sharpness of an X-ray image.
Scattering of photons in tissue; not using a collimator; not using a lead grid; wide beam.
Explain why an aluminium filter may be placed in the X-ray beam when producing an X-ray image of a patient.
An X-ray beam contains many wavelengths. An aluminium filter absorbs long wavelength X-ray radiation that would be absorbed by the body (and not contribute to the image).
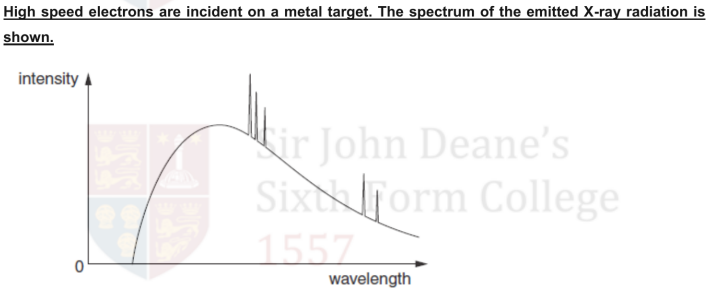
Explain why:
there is a continuous distribution of wavelengths;
Electromagnetic radiation is produced whenever charged particles are accelerated;
the electrons hitting the metal target have a distribution of accelerations.
there is a sharp cut-off at short wavelength.
The shortest wavelength corresponds to the greatest acceleration; College
as all of the electron's energy is given up in one collision and converted into a single photon.