HENRETTA APUSH Chapter 14
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
"fire eaters"
Refers to a group of extremist pro-slavery politicians from the South who urged the separation of southern states into a new nation, which became known as the Confederate States of America.
Confederate States of America (CSA)
On Dec. 20, 1860, after Lincoln's election to president, a special convention to dissolve the union voted unanimously made South Carolina the first to secede from the Union. By February 1861 Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas also seceded. They declared their new nation the CSA.
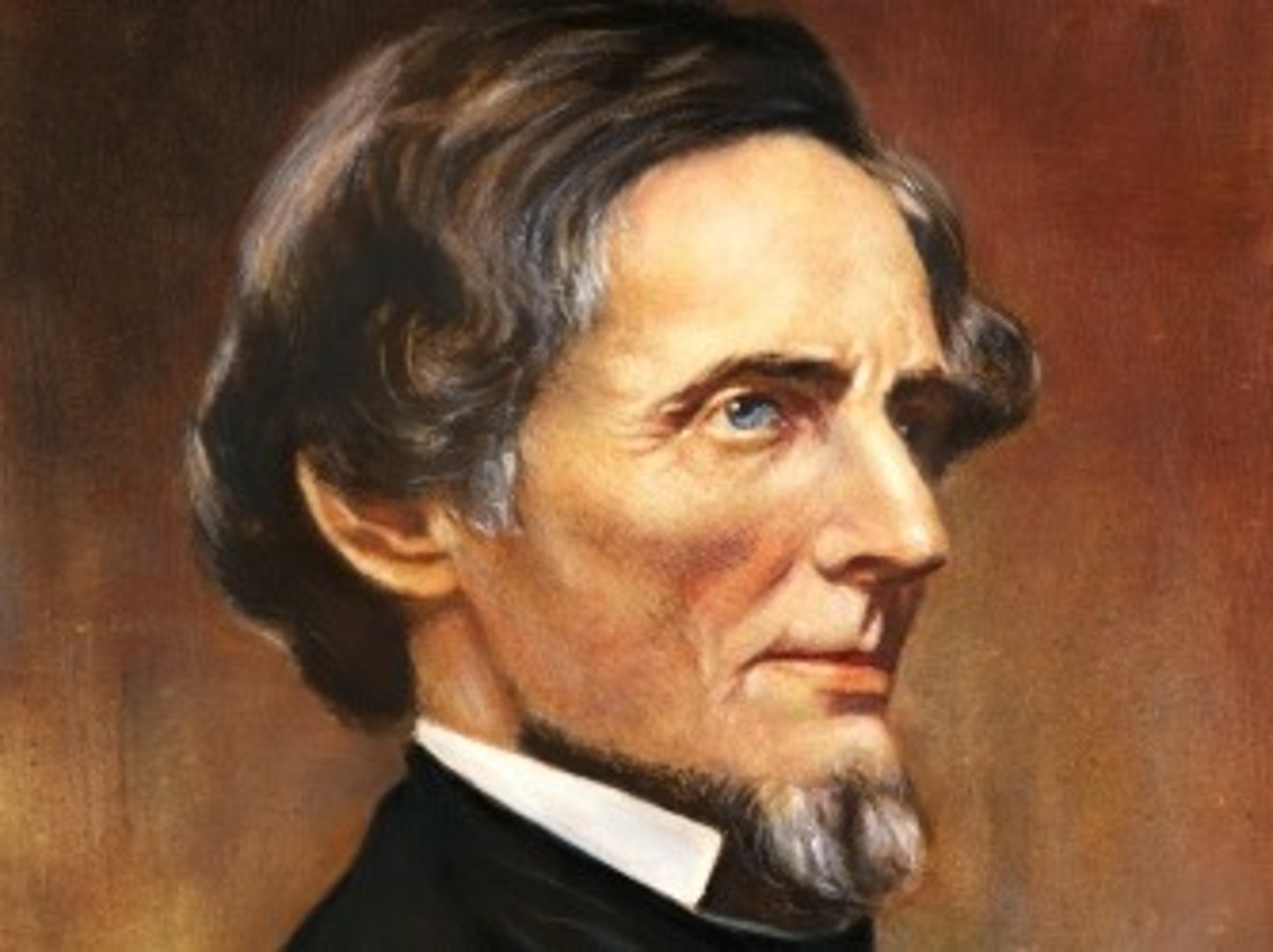
Jefferson Davis
An American statesman and politician who served as President of the Confederate States of America for its entire history from 1861 to 1865.

The Crittenden Compromise
A plan proposed by Senator John J Crittenden for a constitutional amendment to protect slavery from federal interference in any state where it already existed and for the westward extension of the Missouri Compromise line to the Canadian border. A. Lincoln rejected it as a betrayal of Republican principles.
Abraham Lincoln
(1809-1865) Sixteenth president of the United States (from 1861 to death 1865), he opposed the extension of slavery into the territories and defended the power of the federal government to rule on slavery in the territories. He was determined to preserve the Union and issued the Emancipation Proclamation. He was assassinated in 1865.
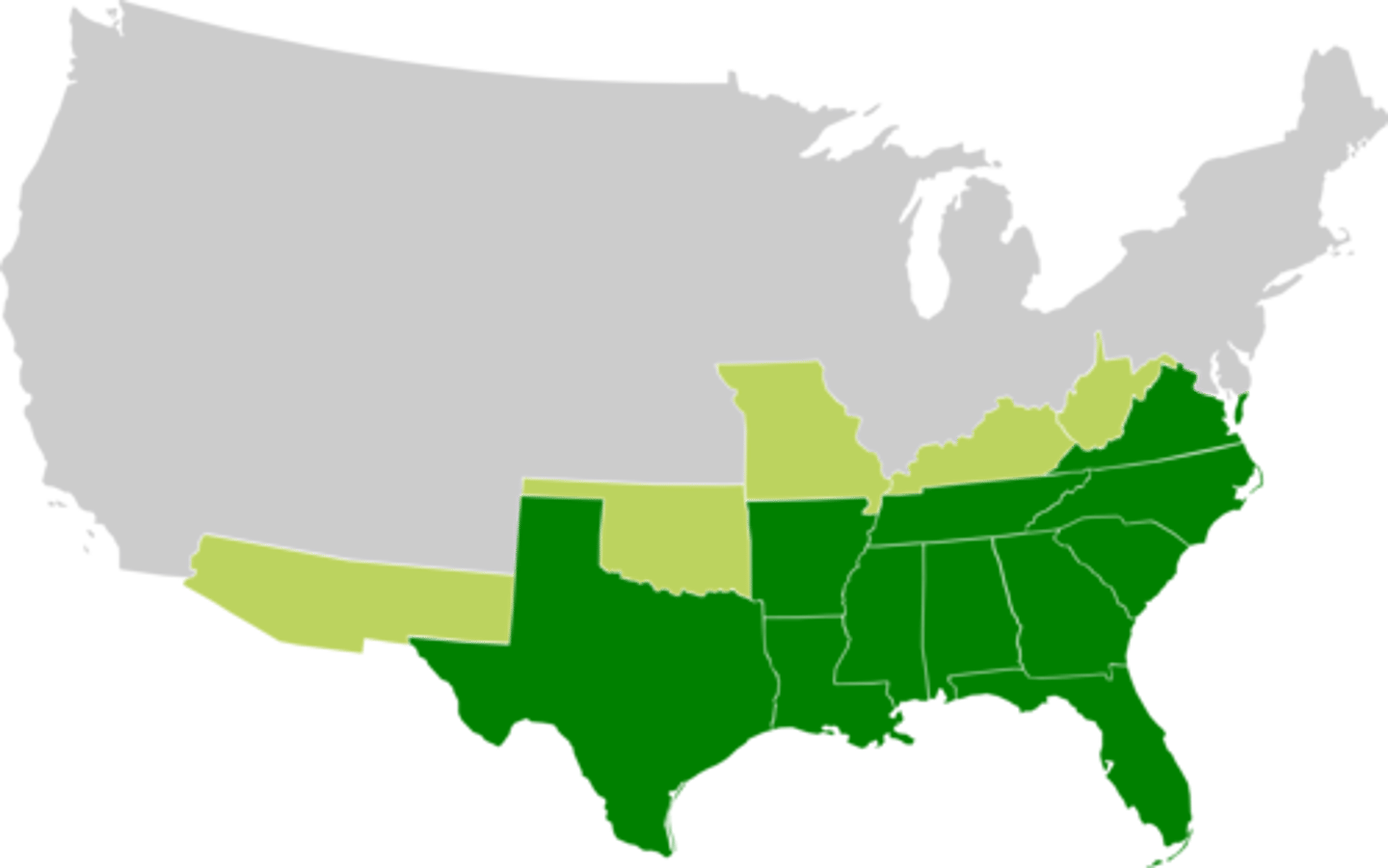
Seceded States & Border States in Union
Slave states that remained in the union: OK (was unorgnaized territory in 1861), MO, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware, (breakaway) West Virginia, New Mexico territory. Slave states that left the Union SC, Miss., Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia (part of VA refused breaking away into W.Virginia), Arkansas, Tennessee, and N.Carolina.
Ft. Sumter
SC fired the first shots of the Civil War against the U.S. Federal fort in the harbor of Charleston, SC in April, 1861. No one was killed, but the outbreak of violence convinced several upper south to states to secede, unwilling to wage war against their fellow southerners.
West Virginia
Having few slaves and no cotton crop, the citizens of the hill country of Virginia seceded from the state and formed the new Union non-slave state of West Virginia in 1863.
Richmond, VA
Capital of Virginia; was capital of the confederacy during the Civil war.
Battle of Bull Run/Manassas
in the summer of 1861, the first major battle of the armies of the Union and the CSA about 50 miles west of Washington, D.C. It became a humiliating Union route and the first indication that the war was not going to end soon.
Robert E. Lee (CSA)
American soldier, he refused Lincoln's offer to head the Union army and agreed to lead Confederate forces. He successfully led several major battles until his defeat at Gettysburg, and he surrendered to the Union's commander General Grant at Appomattox Courthouse.
Ulysses S. Grant (USA)
An American general and the eighteenth President of the United States (1869-1877). He achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War.

"total war"
All-out war that affects civilians at home as well as soldiers in combat; military, economic, political, & social war; destruction of resources was vital. The lives and property of enemy civilians were legitimate objects of attack.
conscription
A forced enlistment of citizens of a country to fight for their country. "The draft."
Confederate Congress
The Congress in the south during the Civil War, they were the first to pass conscription (draft) law. Southern law that declared that all able-bodied men between 18-35 were eligible for three years of military service. Substitutes were allowed but the in the South the price was uncontrolled, rising to $10,000 in Confederate money. The most disliked part of the law was the provision exempting one white man on each plantation with twenty 20 or more slaves.
habeas corpus
A court order requiring authorities to bring a prisoner before the court so that the court can determine whether the prisoner is being held legally. Constitutional protection against unlawful imprisonment.
Enrollment Act of 1863
The first Northern draft act, declaring all able-bodied males between the ages of twenty and forty-five liable for military service; promptly contradicted itself by permitting those who could afford to do so to hire substitutes or even purchase outright exemptions from military service for $300.
Clara Barton (USA)
"Angel of the Battlefield"--American Civil War; known for her compassionate care; founder of the American Red Cross.
King Cotton
Southern confidence was bolstered by their belief that European factories and economies would die without adequate supplies of cotton; in their desperate need for cotton, these countries would recognize and send aid to the CSA. In actuality, most European firms had anticipated the Civil War, stockpiled cotton before the war, and began to purchase cotton from Egypt and India.
Homestead Act of 1862
Enacted during the US Civil War to encourage agricultural output. It allowed citizens to gain 160 acres of land for $30 as long as they lived on it for 5 years and made some sort of improvements to the land.
Union Pacific and Central Pacific Railroad
The railroad companies were chartered in 1862 to work together to create the first transcontinental railroad. This development far surpassed Henry Clay's plans in the old American System plans for government subsidized transportation expansion. One side was to begin in Omaha, Nebraska, and end in California. Irish men were the main labor force. The other began in California and Chinese men laid the tracks.

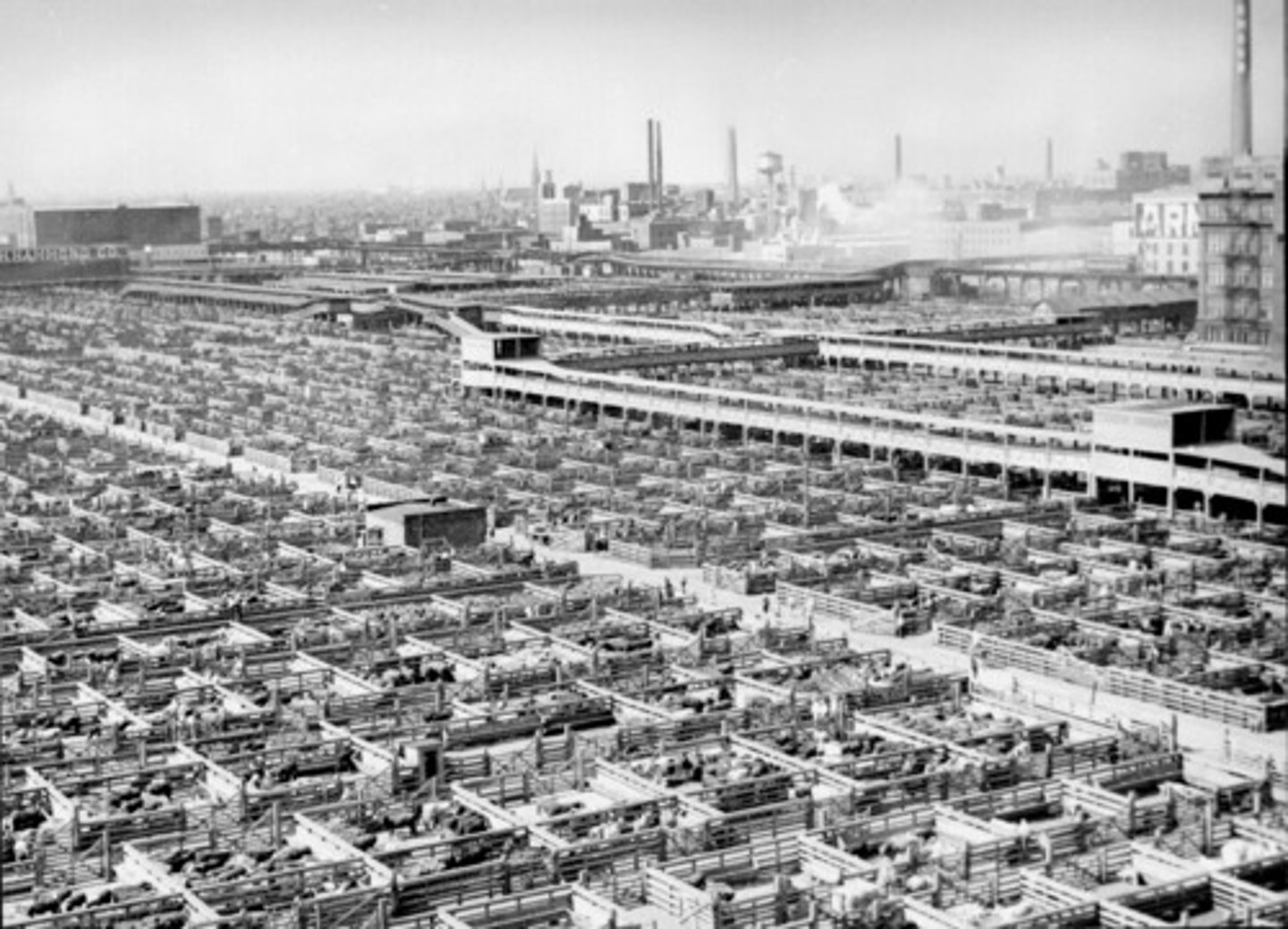
Chicago Stockyards & Meatpacking
To meet the demand of feeding the Union army, the Chicago railroads carried thousands of hogs and cattle to mega-stockyards and slaughter houses in Chicago. By 1862, Chicago surpassed Cincinnati as the meat-packing capital of the nation.

greenbacks
Name for Union paper money not backed by gold or silver. Value would fluctuate depending on status of the war.

contrabands
Term used by Union generals early in the war for escaped slaves. Some returned them to their masters, but most were allowed to live and work behind Union lines. So many slaves escaped that Lincoln listened to their pleas and finally freed them and allowed them to fight for their relatives' freedom.
Battle of Antietam
Civil War battle in which the North succeeded in halting Lee's Confederate forces in Maryland. Was the bloodiest battle of the war. resulting in 25,000 casualties
Confiscation Act
Series of laws passed by fed gov. in 1862 designed to liberate slaves in seceded states; authorized Union seizure of rebel property, and stated that all slaves who fought with Confederate military services were freed of further obligations to their masters; virtually emancipation act of all slaves in Confederacy.
Radical Republicans
A faction in the Republican party led by Charles Sumner and Thaddeus Stevens who began to use wartime legislation to destroy slavery, beginning with D.C. After the Civil War, the Radical Republicans supported black suffrage and equality. They supported the abolition of slavery and a demanding reconstruction policy during the war and after.
Emancipation Proclamation
Lincoln, acting in his capacity as the military commander-in-chief, issued a proclamation on January 1, 1863, after a crucial victory at Antietam, freeing all slaves in areas under rebellion; this excluded the border states, keeping them on the side of the Union, prevented foreign powers from entering the war for slavery, provided a rationale for the war, and allowed blacks to enlist in the army.
Battle at Gettysburg
July 1 - 3, 1863. This was one of the worst battles fought in the North. General Lee tried to attack Washington, D.C., and his army ran into the Union near this location. They fought for 3 days and 50,000 soldiers were killed. The North won. (See above Lincoln's "Gettysburg Address" delivered Nov. 1863.)

Battle of Vicksburg
1863 Union victory under General Grant in Mississippi River town, completed the Union control of the vital Mississippi River, divided the CSA in two, and provided a vital lifeline for northern supplies to its forces in the south.
Black Infantry
In 1862, President Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation opened the door for African Americans to enlist in the Union Army. Although many had wanted to join the war effort earlier, they were prohibited from enlisting by a federal law dating back to 1792. President Lincoln had also feared that if he authorized their recruitment, border states would secede from the Union. By the end of the war, approximately 180,000 African-American soldiers had joined the fight. By 1865, 200,00 Af-Am soldiers were serving in the Union army.
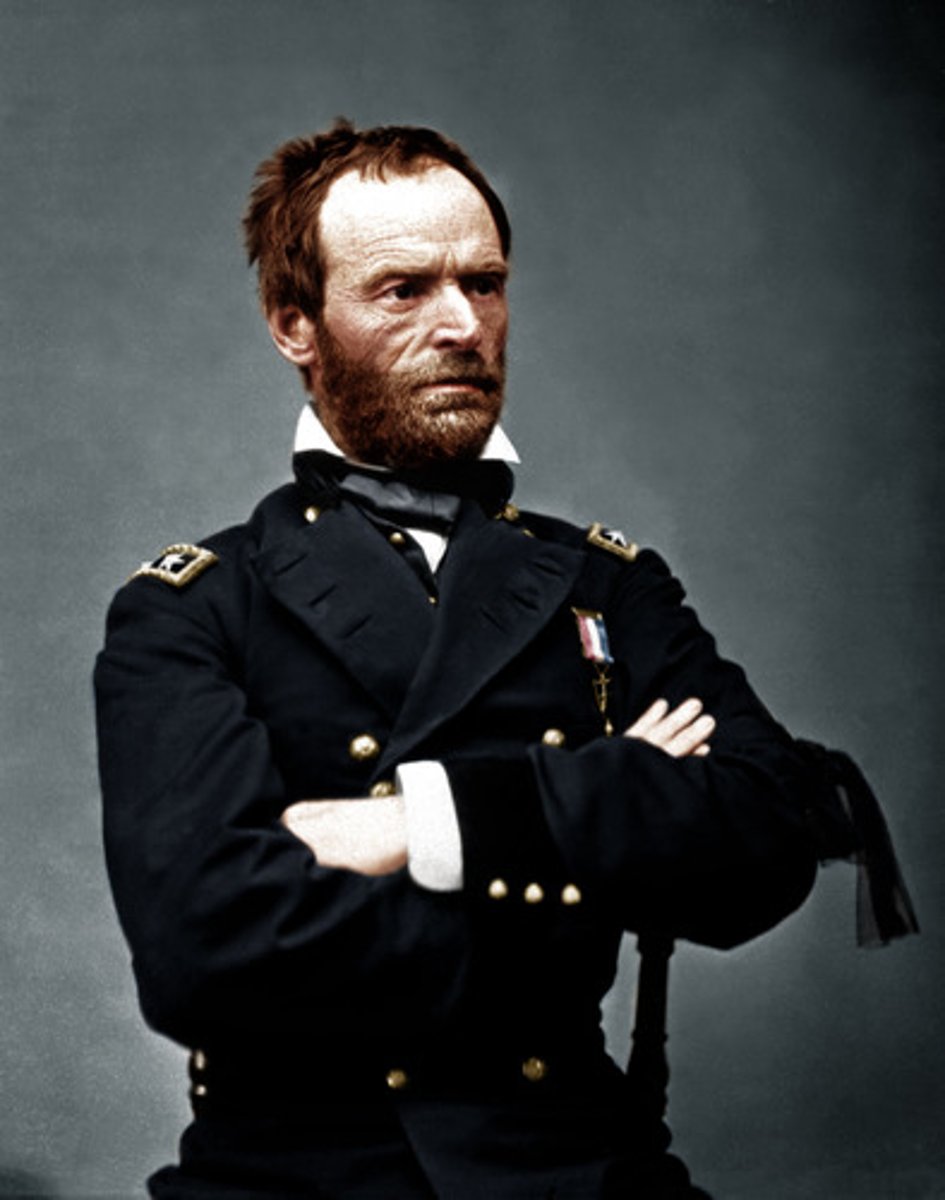
General William Tecumseh Sherman (USA)
Union General who defeated the Confederate forces in Atlanta, GA; He led the "March to the Sea" in the fall of 1864 during which his troops caused great destruction--destroying everything in their path.

Copperheads
"Peace Democrats" who urged both parties to declare a ceasefire and negotiate a settlement instead of pursuing more bloodshed. They were regarded by their enemies as "snakes in the grass", hence, "copperheads."
Thirteenth Amendment
1865 constitutional amendment that abolished slavery.
Special Field Order No. 15
military orders issued during the American Civil War, on January 16, 1865, by Major General William Tecumseh Sherman, were intended to address the immediate problem of dealing with the tens of thousands of black refugees who had joined Sherman's march in search of protection and sustenance. This order was designed to give 40 acres for an average southern black family and a mule.

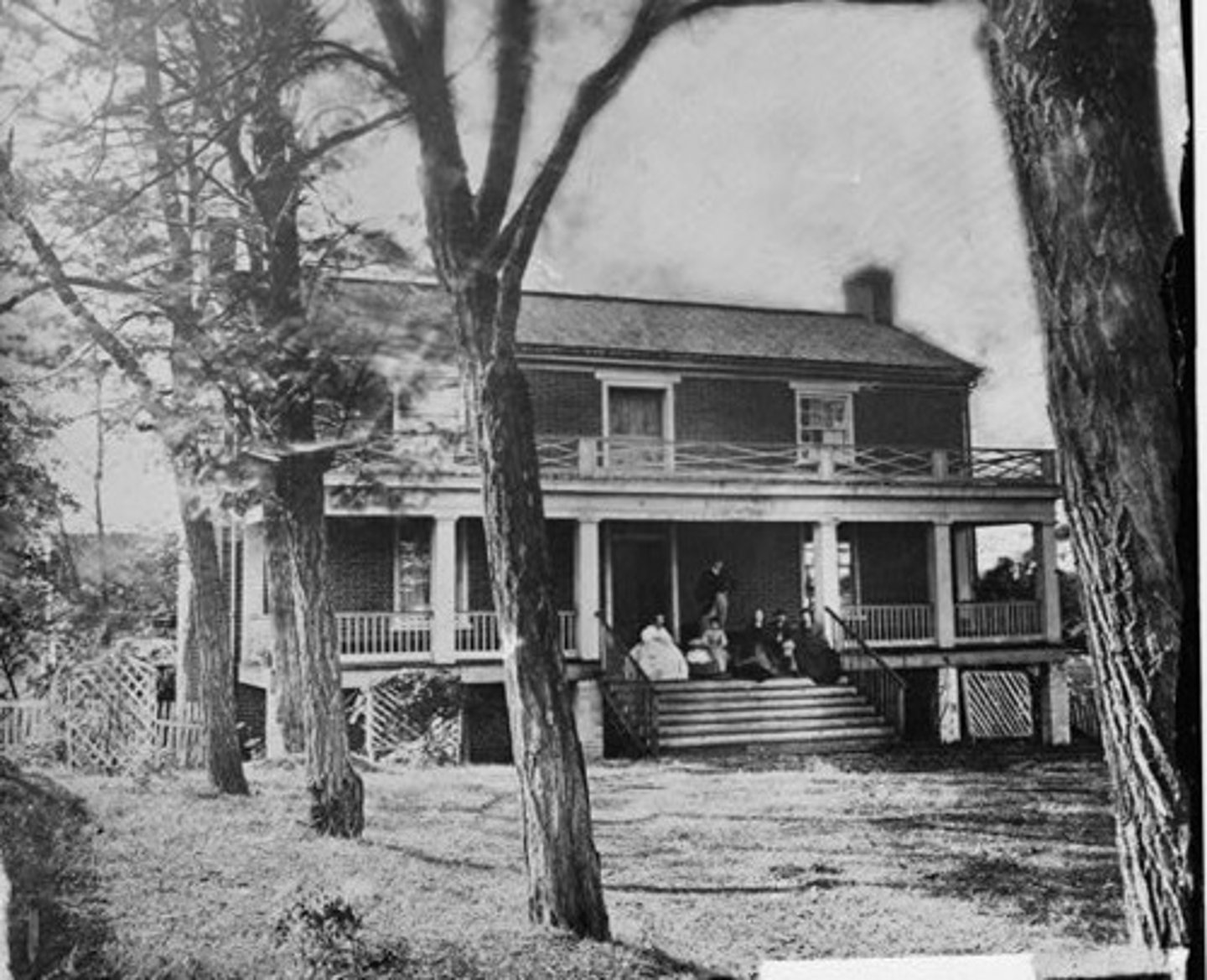
Appomattox Courthouse
Site where Robert E. Lee surrendered to Ulysses S. Grant on April 9, 1865 after almost a year of brutal fighting throughout Virginia in the "Wilderness Campaign."
