Chapter 10 (Glencoe Biology)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Heredity
Passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring.
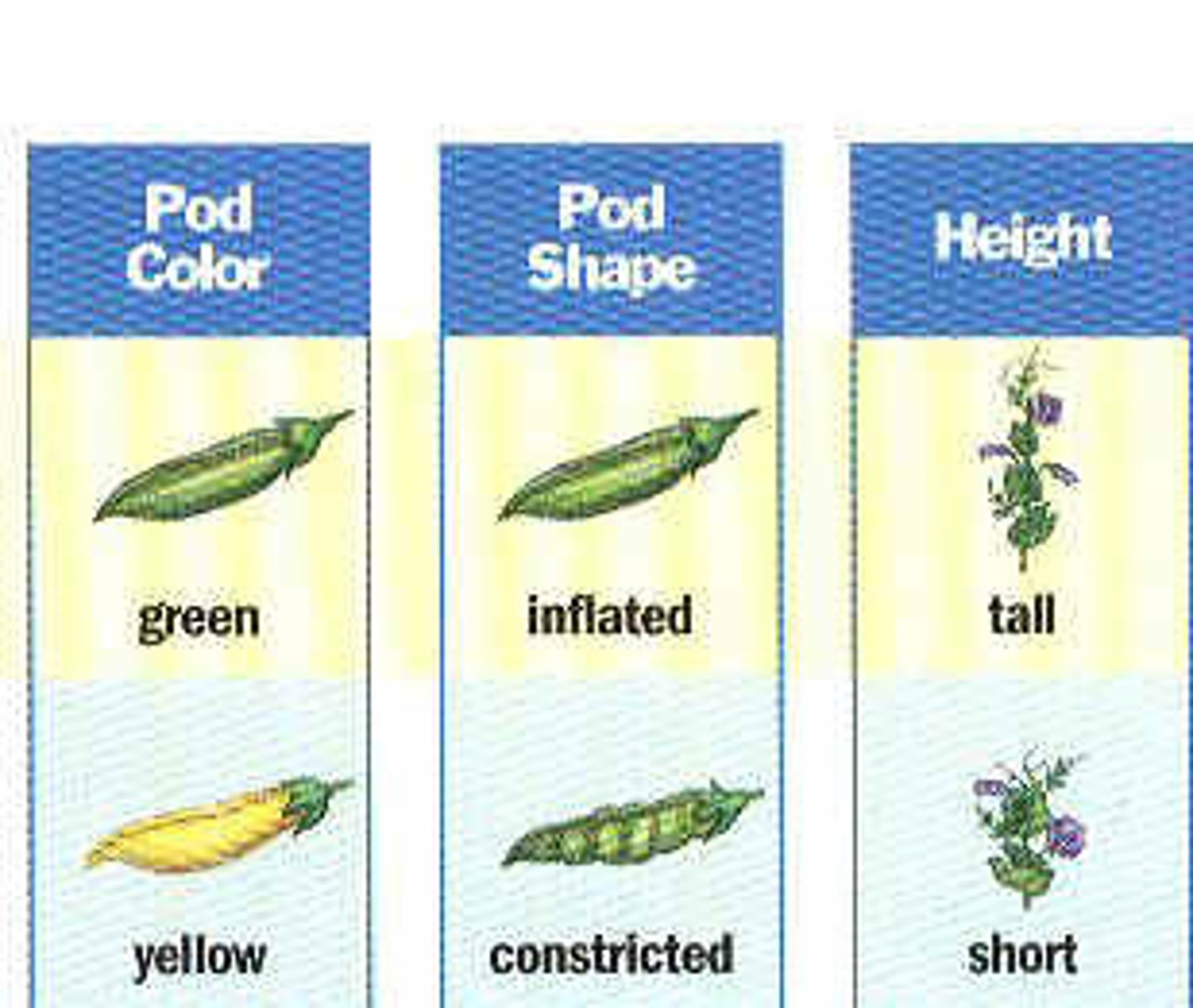
Trait
Characteristic that is inherited; can be either dominant or recessive.
Genetics
Branch of biology that studies heredity.
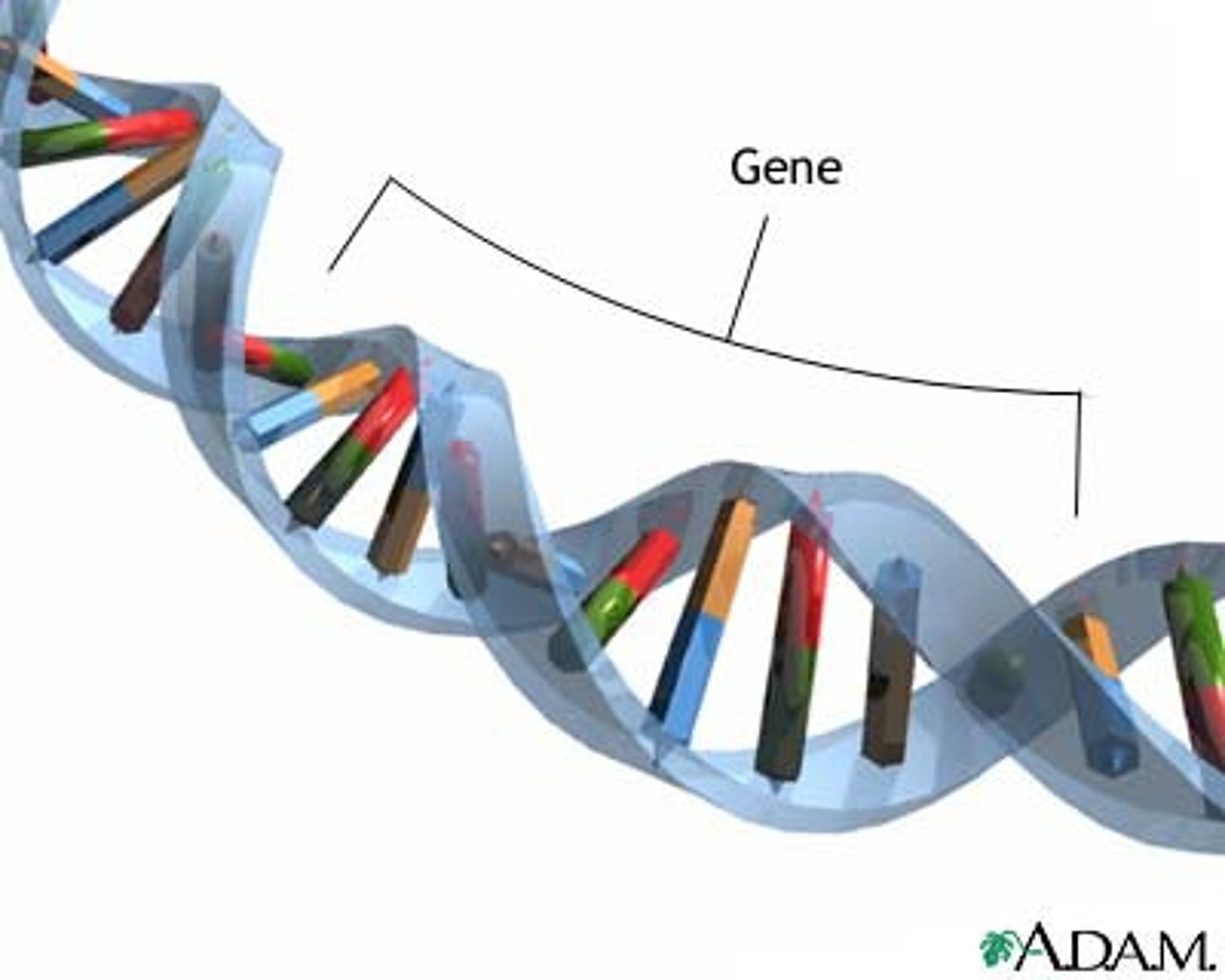
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Allele
Alternative forms of a gene for each variation of a trait of an organism.
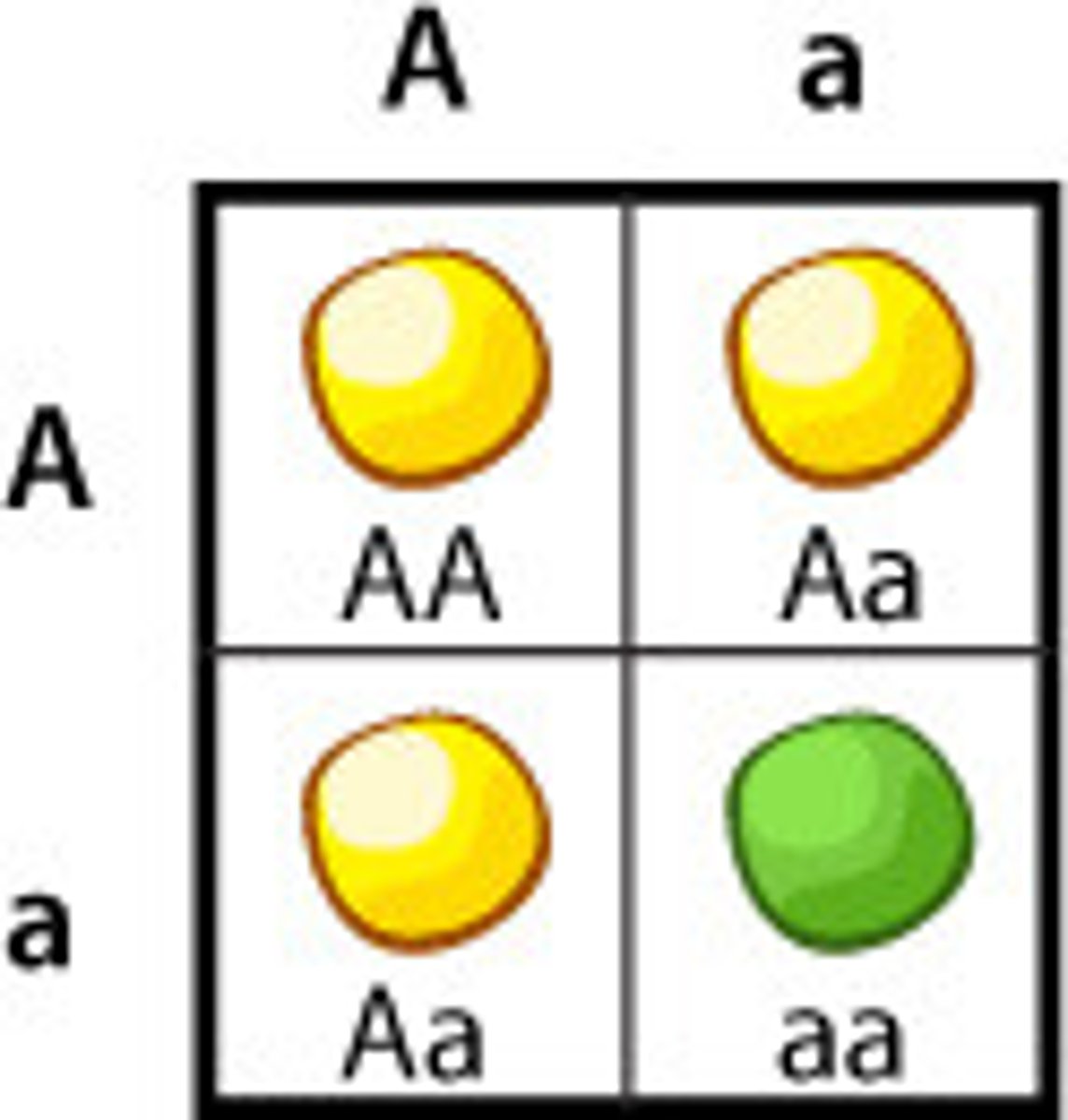
Dominant
Observed trait of an organism that masks the recessive form of a trait.
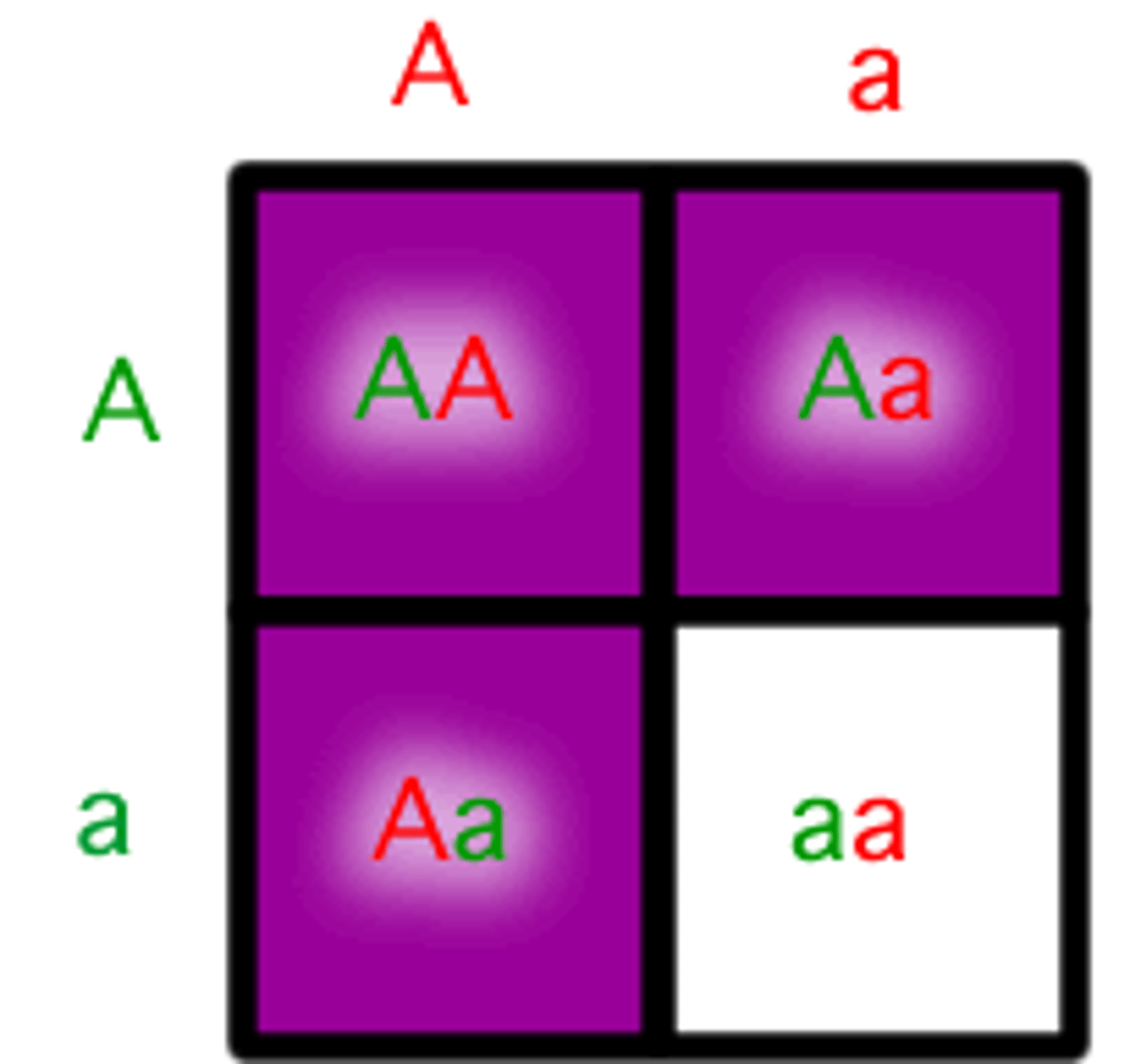
Recessive
Trait of an organism that can be masked by the dominant form of a trait.
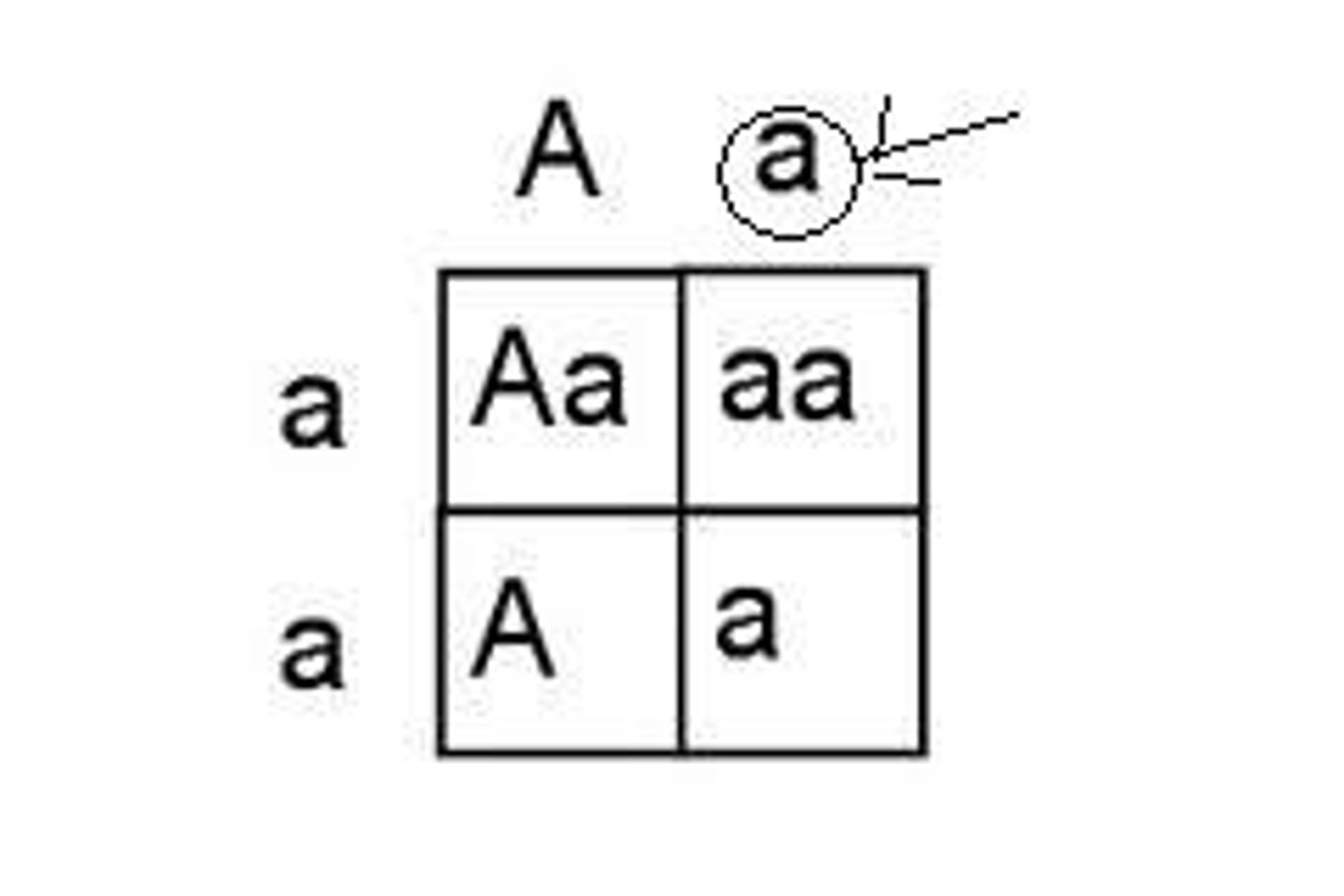
Law of segregation
Mendelian principle explaining that because each plant has two different alleles, it can produce two different types of gametes. During fertilization, male and female gametes randomly pair to produce four combinations of alleles.
Phenotype
Outward appearance of an organism, regardless of its genes. PHysical appearance
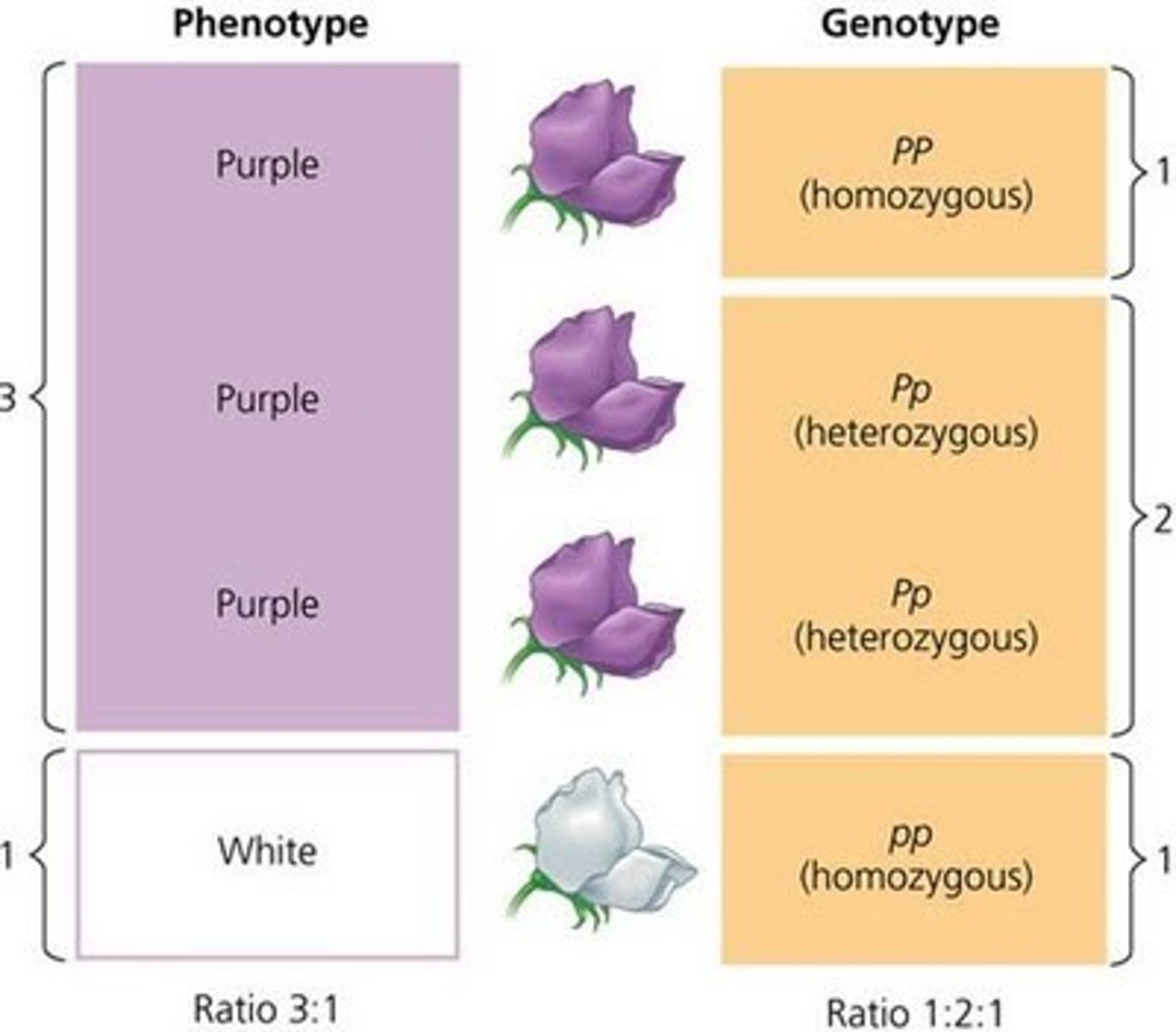
Genotype
Combination of genes in an organism. What the letters are in a punnet square.
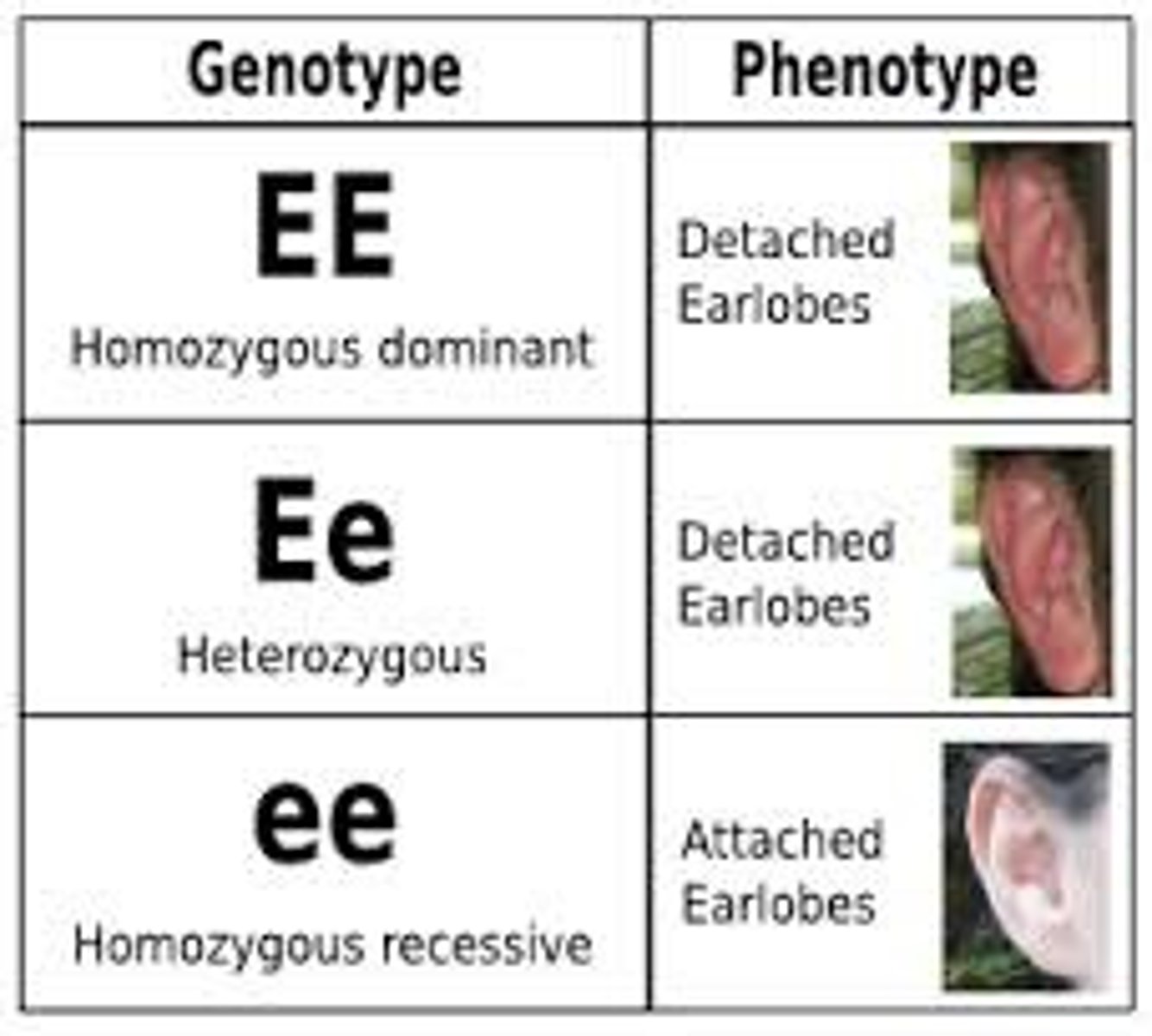
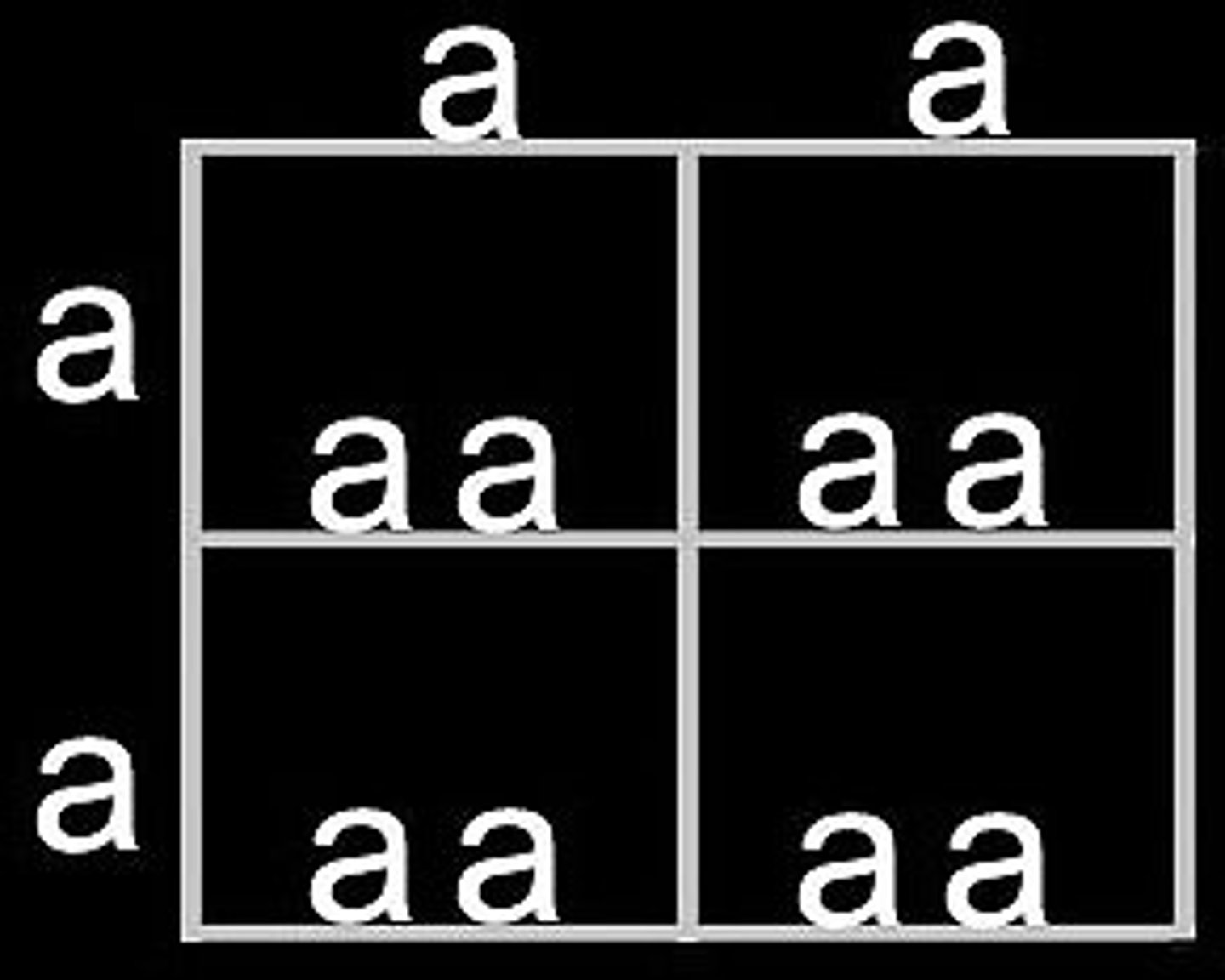
Homozygous
When there are two identical alleles for a trait. Same letters
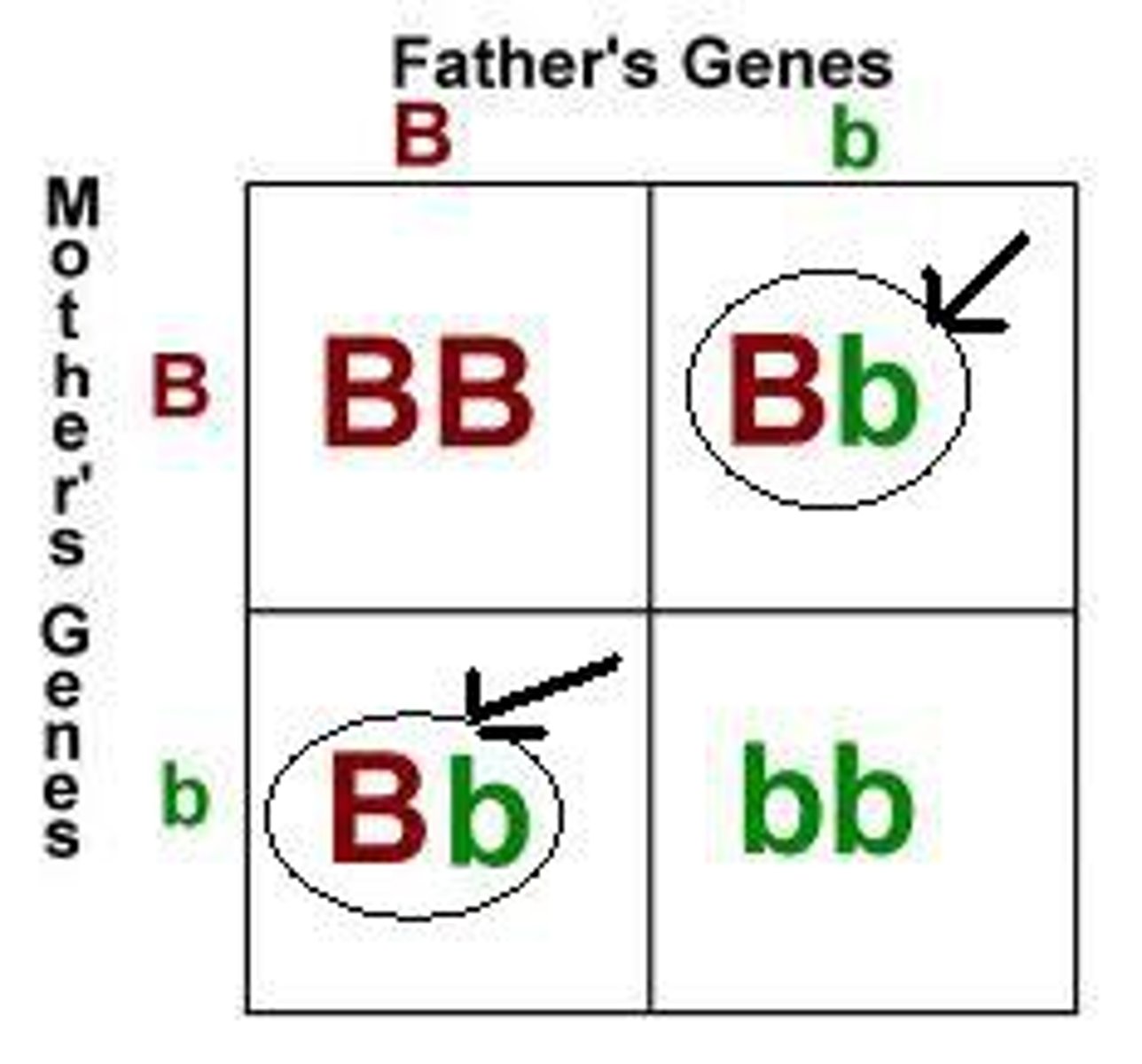
Heterozygous
When there are two different alleles for a trait. Different letters
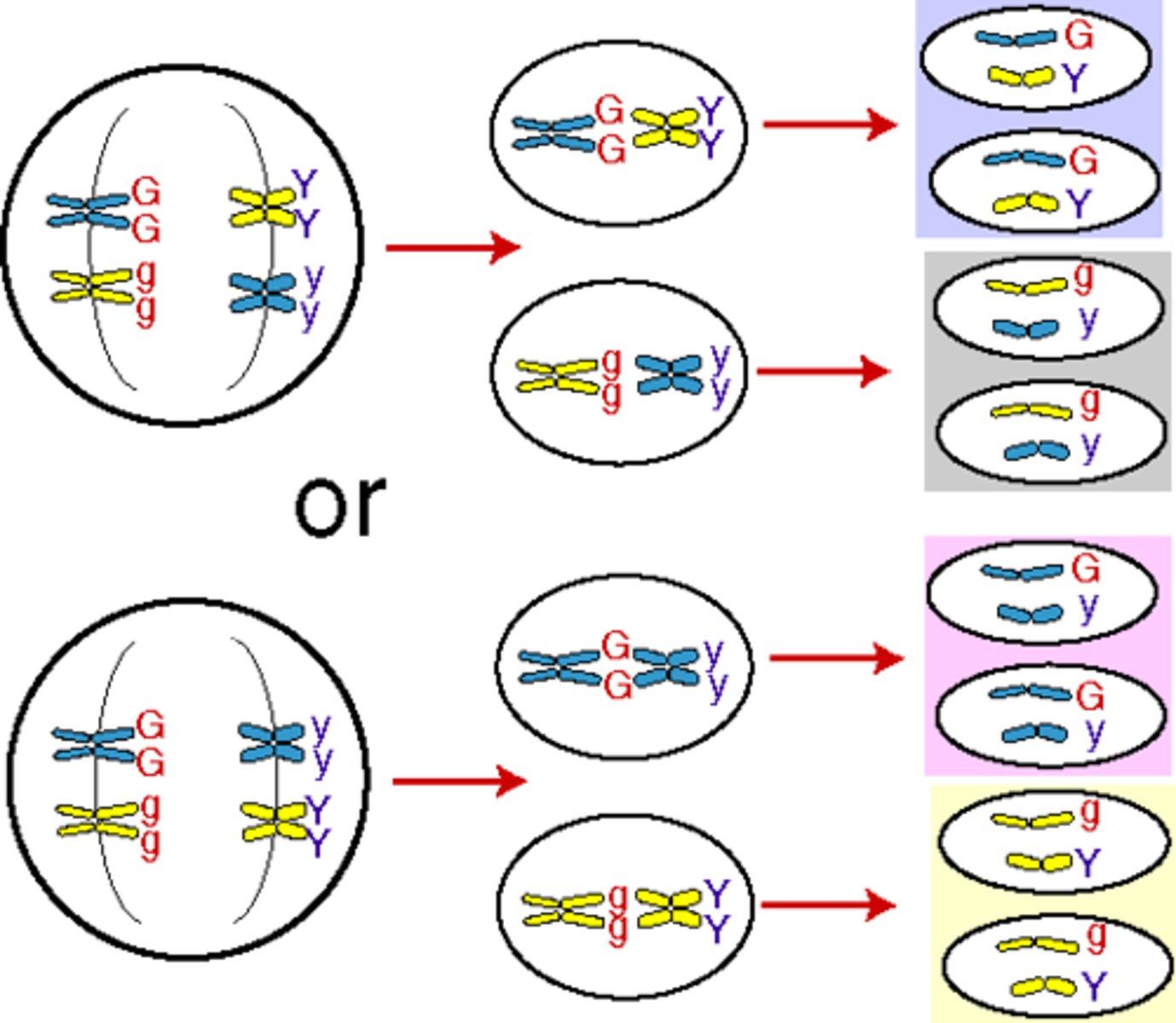
Law of independent assortment
Mendelian principle stating that genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other.
Hybrid
Offspring formed by parents having different forms of a trait.
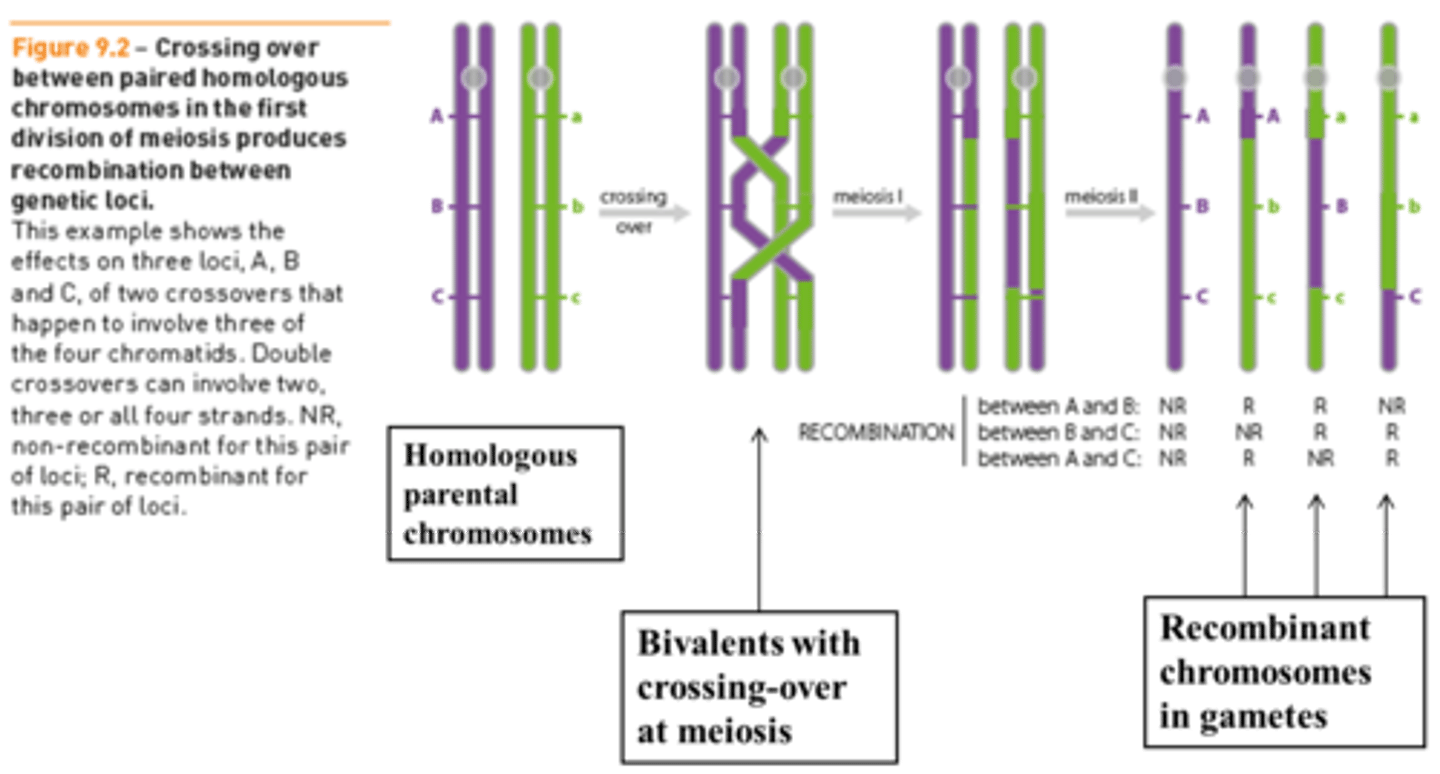
Genetic recombination
Major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by re-assortment or crossing over during meiosis.
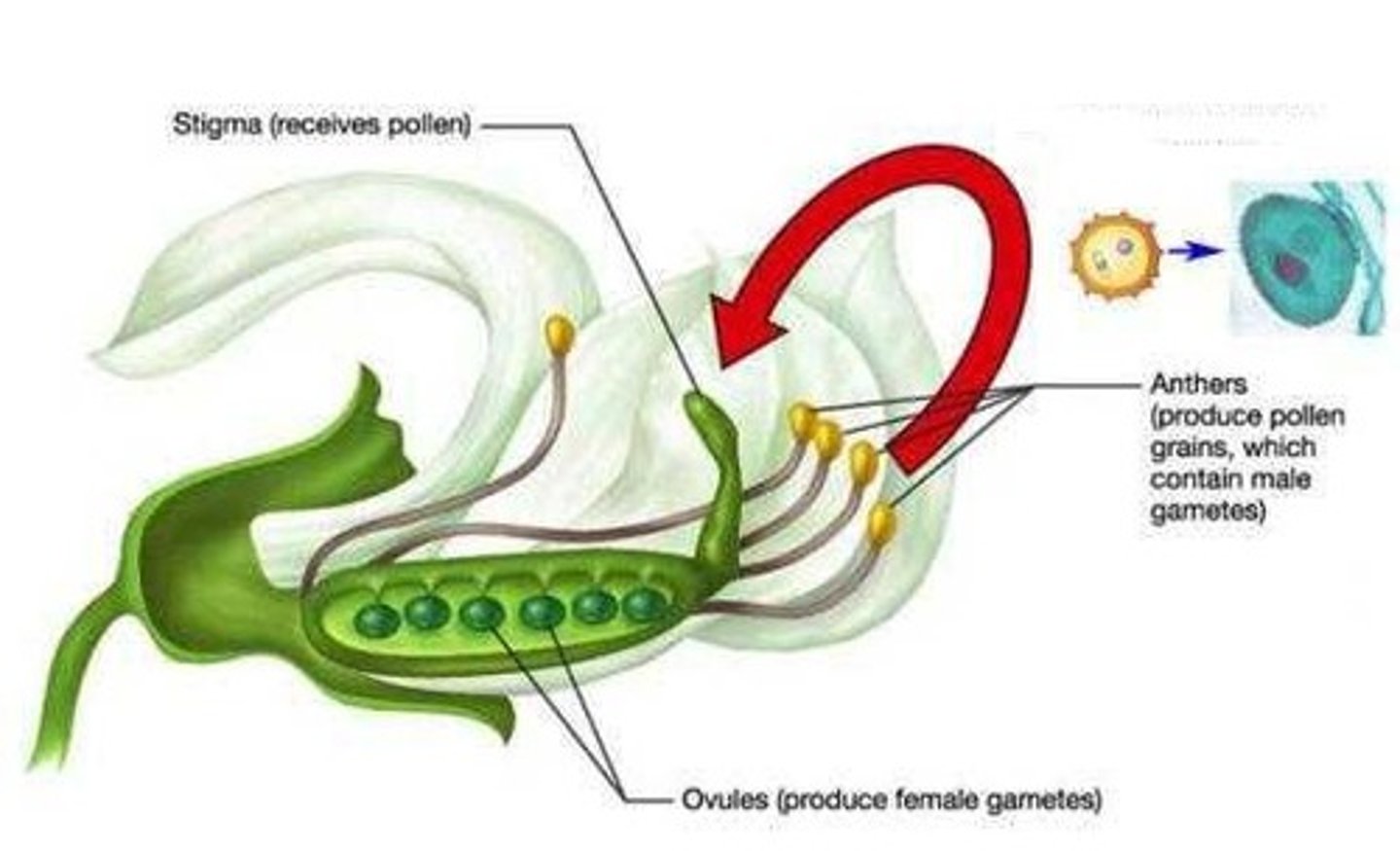
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structures in plants