Comprehensive Social Psychology & Self-Concept Study Guide
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What is social psychology?
The scientific study of how people think about, influence, and relate to one another.
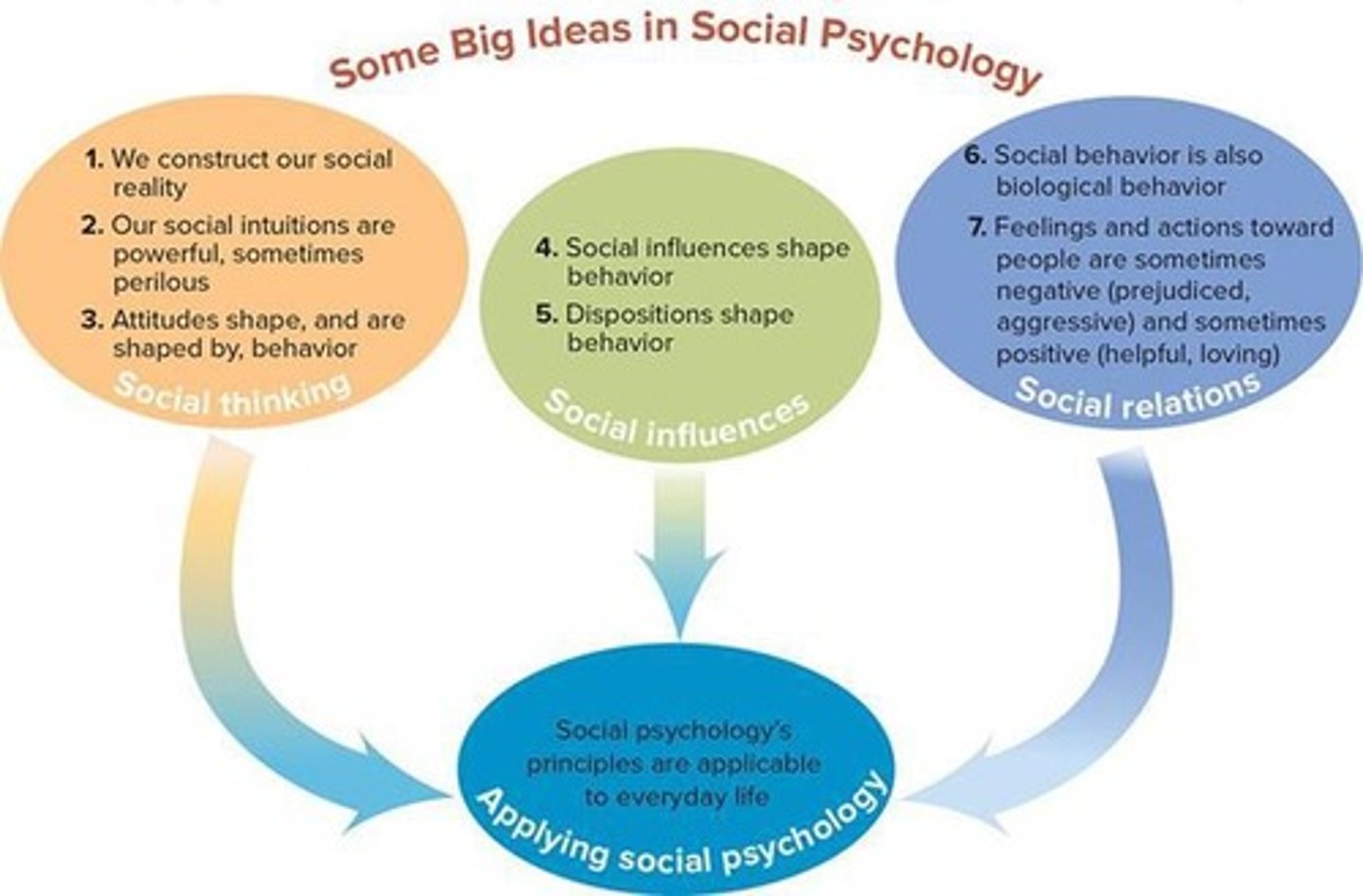
What are the three main areas of social psychology?
Social Thinking, Social Influence, and Social Relations.
How do human values influence social psychology?
They shape attributions, reactions, and interpretations of social situations.
What is the significance of attributions in social psychology?
Attributions help people make sense of behavior, making it seem orderly and predictable.
What is dual process theory in social psychology?
It suggests that social intuitions can shape fears and impressions, often leading to erroneous judgments.
How do social influences shape our behavior?
Social situations can have a powerful effect on behavior, as seen in historical examples like Nazi influence during WWII.
What role do personal attitudes play in shaping behavior?
Internal attitudes affect behavior, such as voting and susceptibility to peer pressure.
What is social neuroscience?
A field that explores the neural bases of social and emotional processes and behaviors.
How do social psychology principles apply to everyday life?
They help in understanding oneself, influencing others, and addressing important societal issues.
What are the four central themes of social psychology?
1. How we construe our worlds; 2. How social intuitions guide us; 3. How behavior is shaped by social factors; 4. Application of social psychology principles.
What is hindsight bias?
The tendency to see events as having been predictable after they have already occurred.
What are common criticisms of social psychology?
It is sometimes seen as trivial for documenting the obvious or dangerous for its potential to manipulate people.
What is the relationship between attitudes and behavior?
Attitudes often follow behavior; people tend to believe strongly in what they have committed to.
What is the importance of critical thinking in social psychology?
Critical thinking helps restrain impulsive intuitions when accuracy matters.
What are some methods used in social psychology research?
Forming and testing hypotheses, sampling, correlational research, and experimental research.
How does culture influence social behavior?
Culture helps define social situations, influencing standards of behavior like promptness and openness.
What is the impact of personality dispositions on social behavior?
Personality traits can lead individuals to react differently to similar situations.
What is the significance of the Princeton-Dartmouth game example?
It illustrates how individual beliefs and values can shape perceptions of objective reality.
What does it mean to be a bio-psycho-social organism?
It refers to the interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors in shaping human behavior.
What is the relevance of social psychology to judicial procedures?
Social psychology principles can influence juror decisions and understanding of human behavior in legal contexts.
What is a theory in the context of research?
An integrated set of principles that explain and predict observed events.
Define hypothesis.
A testable proposition that describes a relationship that may exist between events.
What is a sample in research?
The people who will participate in a study.
What is a random sample?
A sample in which every person in the population has an equal chance of inclusion.
Why does sample size matter in research?
It affects how closely the sample represents the population under study.
What is framing in survey questions?
The way a question or an issue is posed.
What is correlational research?
Research that examines naturally co-occurring phenomena to describe the nature of associations.
What is the goal of experimental research?
To establish a cause-effect relationship by intentionally intervening in the relationship between phenomena.
What does correlation (r) quantify?
The degree of linear relationship between two factors.
What does an r value of -1.0 indicate?
An inverse (negative) association.
What is random assignment in experimental research?
The process of assigning participants to conditions such that all have the same chance of being in experimental vs control groups.
What is replication in research?
Repeating a study to determine whether a finding can be reproduced.
List one advantage of correlational research.
It often uses real-world settings.
List one disadvantage of experimental research.
Some important variables cannot be studied with experiments.
What ethical principle requires participants to be informed about a study?
Informed consent.
What is deception in research?
When participants are misinformed or misled about the study's methods and purposes.
What is the purpose of debriefing in research?
To provide a full post-experimental explanation of the study to participants.
What is the difference between mundane realism and experimental realism?
Mundane realism refers to superficial similarity to everyday situations, while experimental realism involves participant engagement in the experiment.
What does the acronym WEIRD stand for in research contexts?
Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, and Democratic; referring to the limited diversity of research participants.
What is self-concept?
Self-concept is what you know and believe about yourself.
What is self-esteem?
Self-esteem refers to the evaluation of one's own worth.
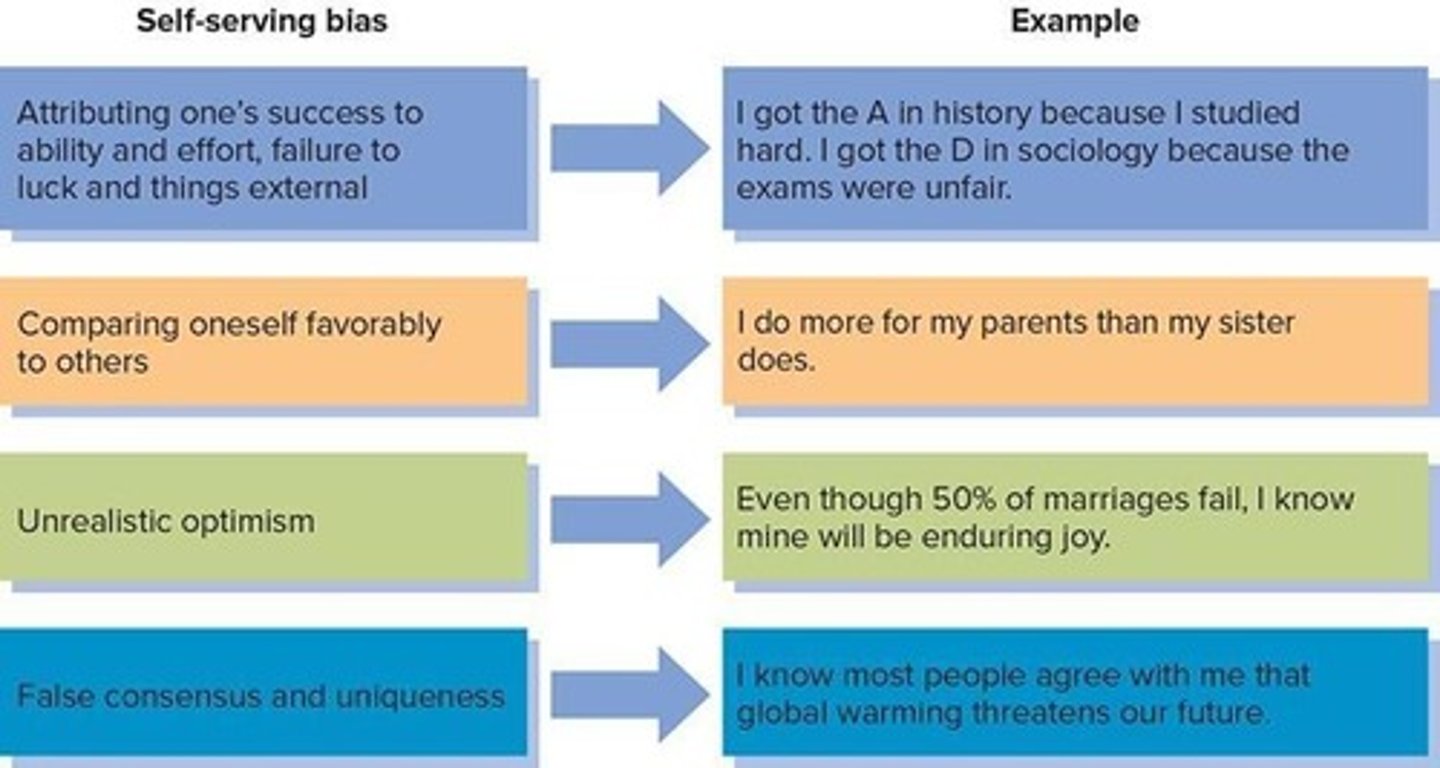
What is self-serving bias?
Self-serving bias is the tendency to attribute positive outcomes to oneself and negative outcomes to external factors.
What is self-presentation?
Self-presentation is the process of controlling how one is perceived by others.
What is the spotlight effect?
The spotlight effect is the belief that others are paying more attention to our appearance and behavior than they actually are.
What is the illusion of transparency?
The illusion of transparency is the belief that one's emotions can be easily observed by others.
How do surroundings influence self-awareness?
Surroundings can affect how we perceive ourselves and our behaviors.
What are self-schemas?
Self-schemas are mental templates that organize how we perceive and remember information about ourselves and others.
How can social comparison inform self-schemas?
Social comparison involves evaluating one's opinions and abilities by comparing oneself with others, which can shape self-schemas.
What is the looking-glass self?
The looking-glass self is the concept that we form our self-concept based on how we believe others perceive us.
What is individualism?
Individualism prioritizes one's own goals over group goals and defines identity in terms of personal attributes.
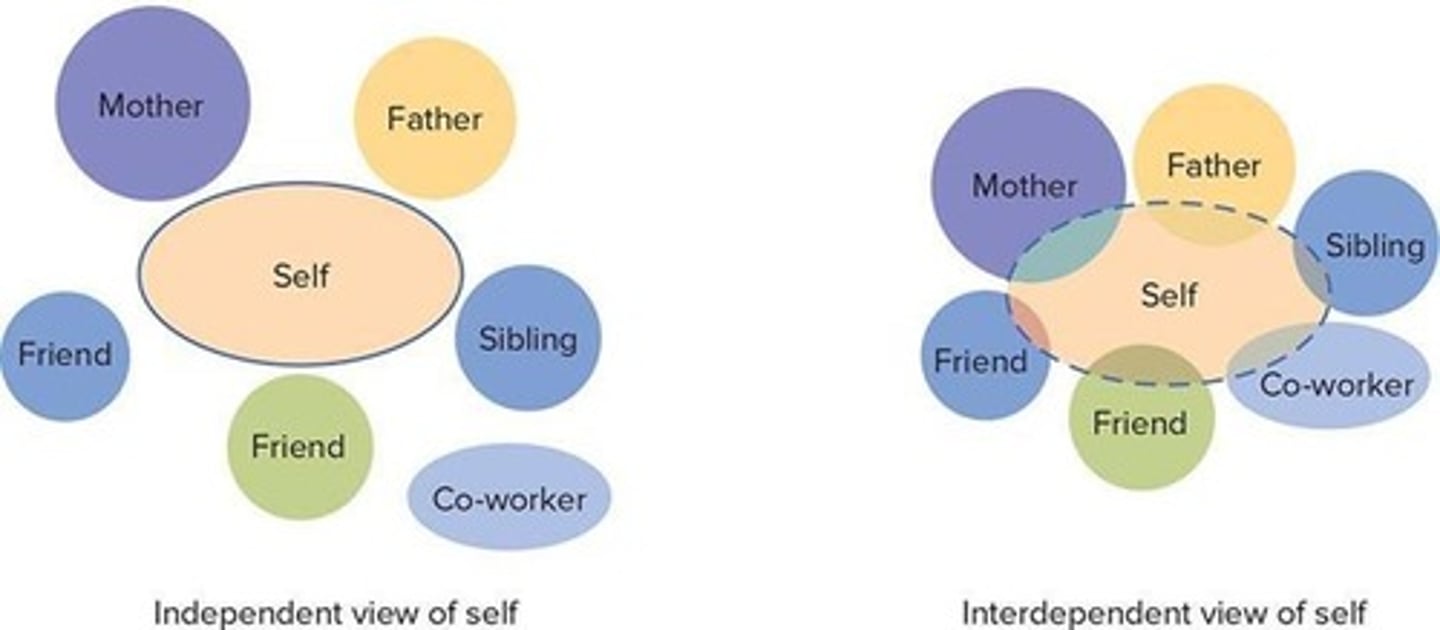
What is collectivism?
Collectivism prioritizes the goals of the group and defines identity in terms of group membership.
What does the term 'independent self' refer to?
The independent self is viewed as an autonomous individual with unique abilities, traits, values, and dreams.
What does the term 'interdependent self' refer to?
The interdependent self is defined by relationships and social contexts, emphasizing group identity.
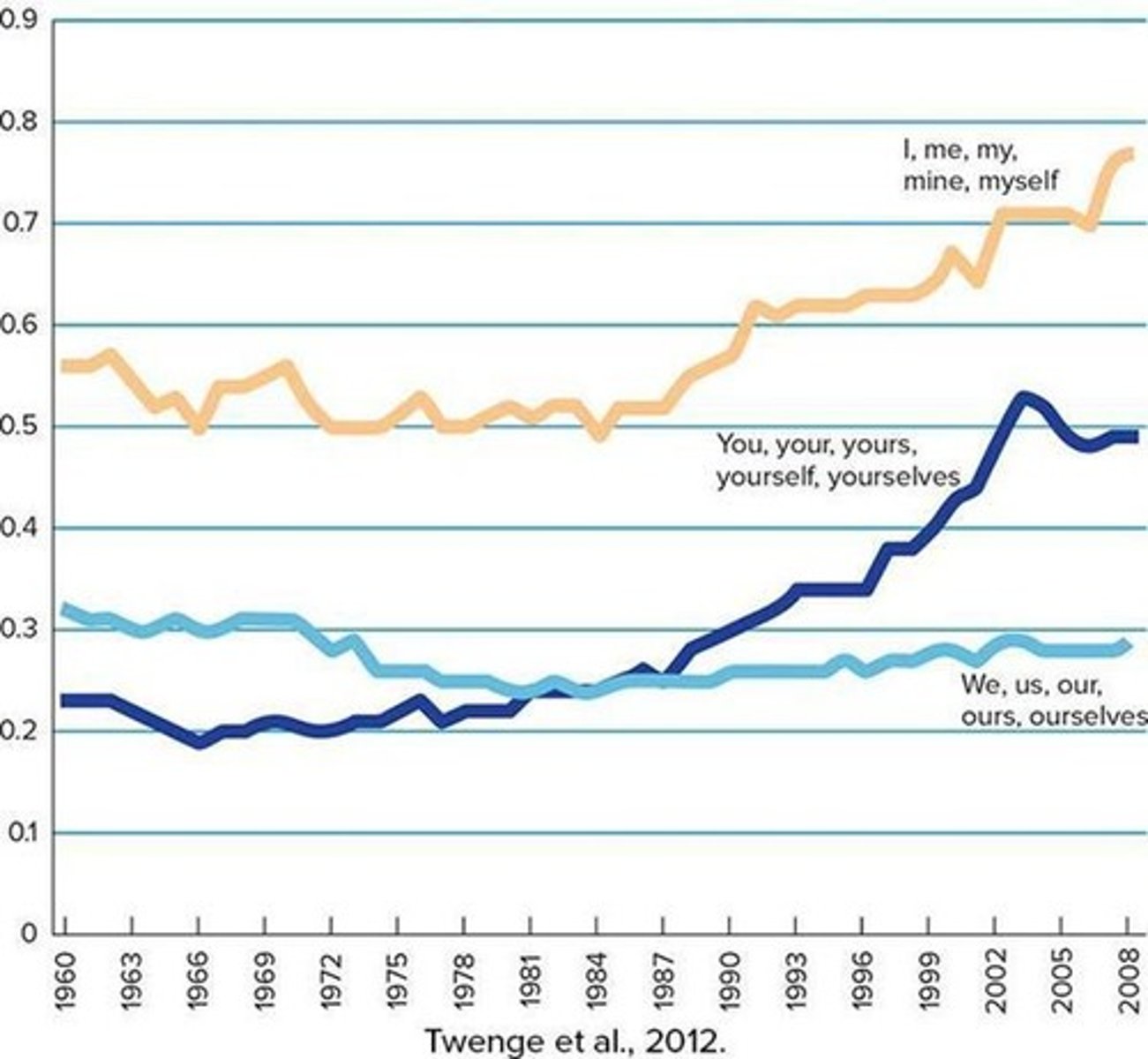
What trend in pronoun usage was observed in American books from the 2000s compared to the 1960s and 1970s?
There was an increase in the use of first-person pronouns (I, me, my) relative to second-person pronouns (you, your).
What is the significance of the study by Chou & Edge (2012)?
The study examines social comparison in college students, particularly in the context of social media.
What is the Geography of Thought by Richard Nisbett about?
It explores the relationship between culture, thinking, and perception, highlighting differences between collectivistic and individualistic cultures.
What is the primary research question in reading a research article activity?
The primary research question typically focuses on the hypothesis being tested in the study.
What are some limitations of social comparison?
Limitations include the use of incomplete information and the potential for negative self-evaluation.
How does culture influence cognition according to the text?
Culture influences cognition by affecting how individuals perceive their surroundings and the relationships between objects and context.
What is the main takeaway from the discussion about media and culture?
Media can reflect characteristics of individualism or collectivism, influencing how identities are portrayed.
What is the primary focus of individualistic cultures?
Individual achievements, personal fulfillment, and abilities.
What is the primary focus of collectivistic cultures?
Group goals, solidarity, relationships, and responsibilities.
What is affective forecasting?
The attempt to predict future feelings when making significant decisions.
What is the planning fallacy?
The tendency to underestimate how long it will take to complete a task.
What is impact bias?
The tendency to overestimate the enduring impact of emotion-causing events.
What are contingencies of self-worth?
Different domains that vary in importance to an individual's overall self-esteem.
What is the bottom-up view of self-esteem?
High self-esteem in important domains leads to a high impact on overall self-esteem.
What is the top-down view of self-esteem?
High overall self-esteem leads to higher self-esteem in specific domains.
What is self-efficacy?
A sense of competence and effectiveness in performing tasks.
What is the difference between self-efficacy and self-esteem?
Self-efficacy is about believing in one's ability to perform tasks, while self-esteem is about liking oneself overall.
What are self-serving attributions?
Attributing positive outcomes to oneself and negative outcomes to external factors.
What is unrealistic optimism?
The predisposition to approach life positively, often leading to vulnerability.
What is defensive pessimism?
The strategy of anticipating problems to motivate effective action.
What is the false consensus effect?
The tendency to overestimate the commonality of one's opinions and undesirable behaviors.
What is the false uniqueness effect?
The tendency to underestimate the commonality of one's abilities and desirable behaviors.
What is self-handicapping?
Creating excuses for potential failure by engaging in behaviors that hinder performance.
What is self-monitoring?
Being attuned to and adjusting one's behavior in social situations to achieve desired impressions.