Synovial Fluid
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Synovial Fluid
formed by ultrafiltration of plasma
synovial membrane
secretion by synoviocytes
Synovial Fluid functions
viscous fluid to lubricate joints
nutrient source for articular cartilage
absorbent material for joint compression
Type A Synovial Fluid
more predominant
actively phagocytic
synthesizes degradative enzymes (Collagenases)
removes waste and debris
Type B synovial fluid
synthesizes hyaluronate, a mucopolysaccharide
makes fluid viscous
What are the 4 joint disorder classifications
Noninflammatory
Inflammatory
Septic
Hemorrhagic
Noninflammatory Joint Disorder
degenerative, osteoarthritis
Inflammatory Joint Disorder
immunologic, SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, lyme disease, gout and pseudogout
Septic Joint Disorder
microbial infection
Hemorrhagic Joint Disorder
trauma, tumors, coagulation deficiencies
Normal Synovial Fluid
volume: <3.5 ml
color: pale yellow
viscosity: high
WBC : <200
neutrophils: <25%
glucose: approx. equal to plasma
glucose P-SF : <10 mg/dL
culture: negative
Noninflammatory Synovial FLuid
volume: >3.5 ml
color: yellow
viscosity: high
WBC : <3000
neutrophils: <25%
glucose: approx. equal to plasma
glucose P-SF : <20 mg/dL
culture: negative
Inflammatory Synovial Fluid
volume: >3.5 ml
color: yellow-white
viscosity: low
WBC : 2000-100,000
neutrophils: >50%
glucose: less than plasma
glucose P-SF : >20 mg/dL
culture: negative
Septic Synovial Fluid
volume: >3.5 ml
color: yellow-green
viscosity: low
WBC : 10,000-100,000
neutrophils: >75%
glucose: less than plasma
glucose P-SF : >40 mg/dL
culture: positive
Hemorrhagic Synovial Fluid
volume: >3.5 ml
color: red-brown
viscosity: decreased
WBC : >5,000
neutrophils: >25%
glucose: approx. equal to plasma
glucose P-SF : <20 mg/dL
culture: negative
Arthrocentesis
aspiration from a joint
requirements for arthrocentesis collection
patient should be fasting a min 4-6 hrs
blood sample should be collected at same time
formal volume: -.1-3.5 ml
transport and analyze at room temp
a fluid volume of what means an inflamed joint?
>25 ml
dry tap
arthrocentesis of a joint with no fluid build up
What are the three collection tubes used for synovial fluid collection
no anticoagulant
chemical/immunologic
anticoagulant
microscopic, cell counts
sterile anticoagulate
microbiology
What is used in synovial fluid formation to prevent crystal formation?
sodium heparin or EDTA
Normal color for synovial fluid
pale yellow or colorless and clear
what could red/brown synovial fluid mean?
trauma during collection
disorders that disrupt synovial membrane allowing blood to enter joint cavity
Greenish or purulent synovial fluid could mean…
infectious
milky synovial fluid could indicate what?
tuberculous arthritis
SLE
What could cause synovial fluid to be cloudy
WBC, RBC, synoviocytes
crystals, fat droplets
fibrin, cell debris, rice bodies
Rice bodies
white, free floating substances made of collagen covered by fibrinous tissue
where are rice bodies most commonly seen?
rheumatoid arthritis
Normal viscosity of synovial fluid
normally very high due to high concentration of mucoprotein hyaluronate
What happens to viscosity during inflammatory conditions
hyaluronate can become depolymerized by enzyme hyaluronidase
what should normal synovial fluid look like in a collection syringe
should show string formation when expelled
at least 4 cm long
what can change the viscosity of synovial fluid
enzyme hyaluronidase (inflammatory conditions)
diseases that inhibit production/secretion of hyaluronate by synoviocytes
What can cause a spontaneous clot to form in synovial fluid?
abnormal presence of fibrinogen
T/F normal synovial fluid does not clot
true
What would cause fibrinogen to be present in synovial fluid
pathologic process that damage synovial membrane
traumatic arthrocentesis with blood contamination
What is used for microscopic examination of synovial fluid
hemocytometer
What is used as a diluent for the hemocytometer?
saline
hyaluronidase buffer can also be used to reduce viscosity for more efficient county
why would hyaluronidase buffer be used as a diluent for the hemacytometer?
reduce viscosity for more efficient counting
what is not used as a buffer when using a hemacytometer for microscopic evaluation of synovial fluid?
acetic acid
What is normal RBC count for synovial fluid
less than 2000/ul
What can increased RBC indicate
traumatic tap
hemorrhagic effusions
What is the normal WBC in synovial fluid
less than 200/ul
What can increased WBC indicate
bacterial arthritis
what are normal centrifugation amounts of WBC
60% monocytes/macrophages
30% lymphocytes
10% neutrophils
what does it mean if over 80% are neutrophils
bacterial arthritis
urate gout
What can WBC differentiate
disease process and stage of disease
How should crystals be identified in synovial fluid?
maintain sample at room temp/examine immediately
use wet preparations or cytospin slides
what method is used to identify crystals
polarized microscopy
What are the two main crystaled identified using polarized microscopy
monosodium urate (MSU)
calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)
Monosodium Urate (MSU) Crystals
needle-like with pointed ends
seen in intra/extra cellularly
what do MSU crystals look like in polarized microscopy?
strongly birefringent
bright against a black background
What do MSU crystals look like with a red compensator?
appear yellow when longitudinal axes are parallel
appear blue when perpendicular
What conditions have MSU Crystals?
gouty arthritis
impaired purine metabolism
high purine foods
leukemia chemotherapy
decreased renal excretion of uric acid
Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate (CPPD) Crystals
smaller/blunter
rodlike, rhomboid, or square
what do CPPD crystals look like in polarized microscopy?
weak positive birefringence with colors opposite MSU
What do CPPD crystals look like with a red compesator
blue when longitude axis is parallel
yellow when perpendicular
What conditions have CPPD crystals
degenerative arthritis
arthritis accompanying metabolic diseases
disorders causing elevated calcium levels
pseudogout
Cholesterol Crystals
observed via wet preparation or unstained cytospin slide
flat, rectangular plates
what conditions have cholesterol crystals
chronic inflammation
systemic autoimmune disease
SLE and RA
Other possible crystals
corticosteroid injections
look like glass shards
calcium oxalate
renal dialysis patients
artifacts
starch, powered anticoagulants, dust, scratches
Glucose levels in synovial fluid
should have same levels as plasma
difference should be less than 10 mg/dl of plasma level
When should plasma be drawn
same time as synovial fluid
what conditions can cause a significant decrease glucose in fluid
inflammatory (>20 mg/dl)
septic (>40 mg/dl)
Total protein in synovial fluid
normally > 3 g/dl
typically ½ to ¼ that of plasma
what causes increased total protein
joint diseases
indicates an inflammatory process
Uric acid
levels should be that same as plasma
what can happen if there are increased levels of uric acid?
MSU crystal formation
what causes lactate to be increased
anaerobic glycolysis
severe inflammatory processes
Normal Synovial Fluid
Vol: <3.5 ml
color: pale yellow/colorless
clarity: clear
viscosity: able to form string 4-6 cm long
leukocyte: <200 cells/ul
neutrophils: <25% of differential
crystals: none
glucose: <10 mg/dl lower than blood glucose plasma
total protein: 3 g/dl
Why is gram stain useful?
may offer useful diagnostic information when positive
most infectious agents are bacterial and come from blood
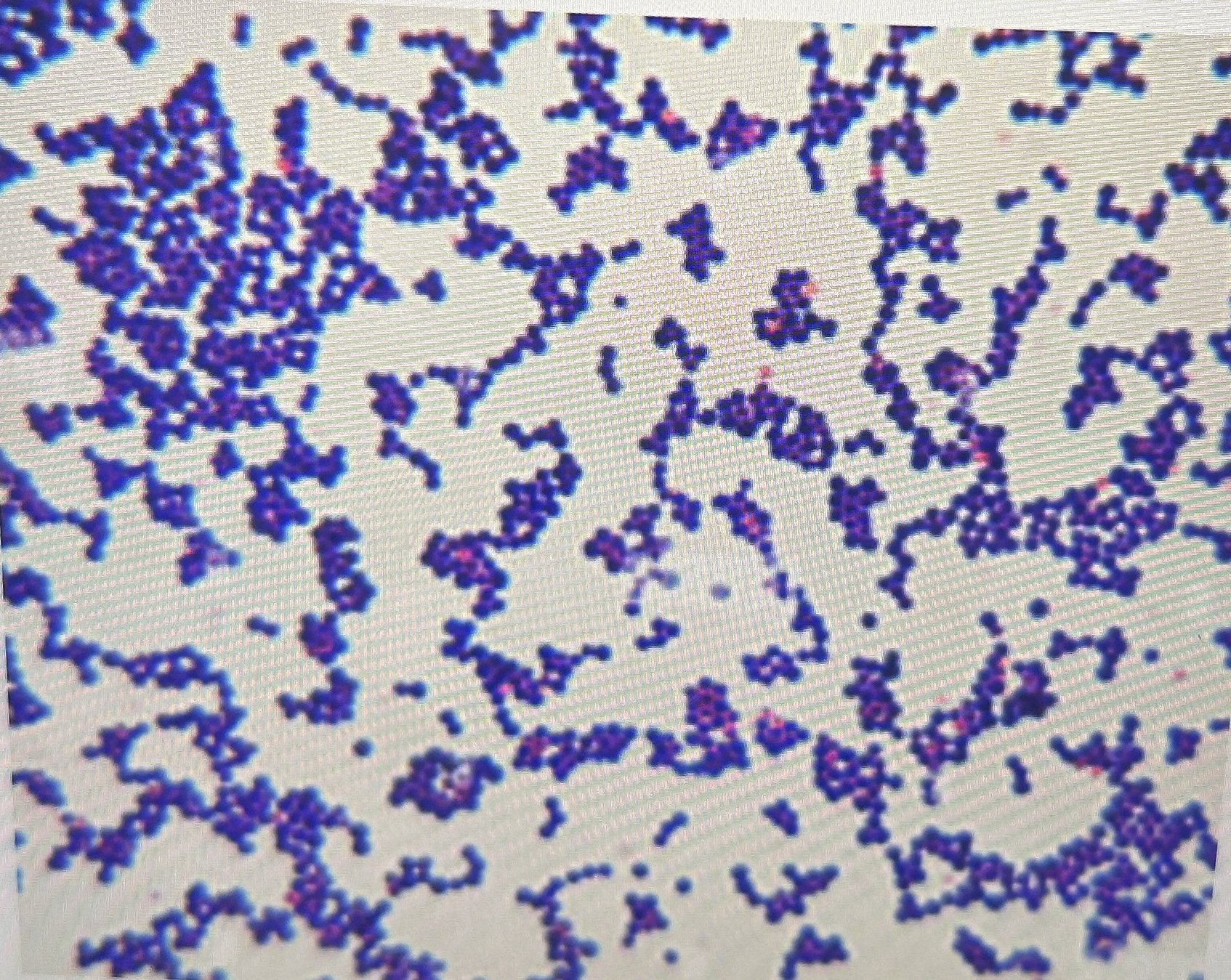
75% of patents with staphylococcal infections identified as positive by gram stain
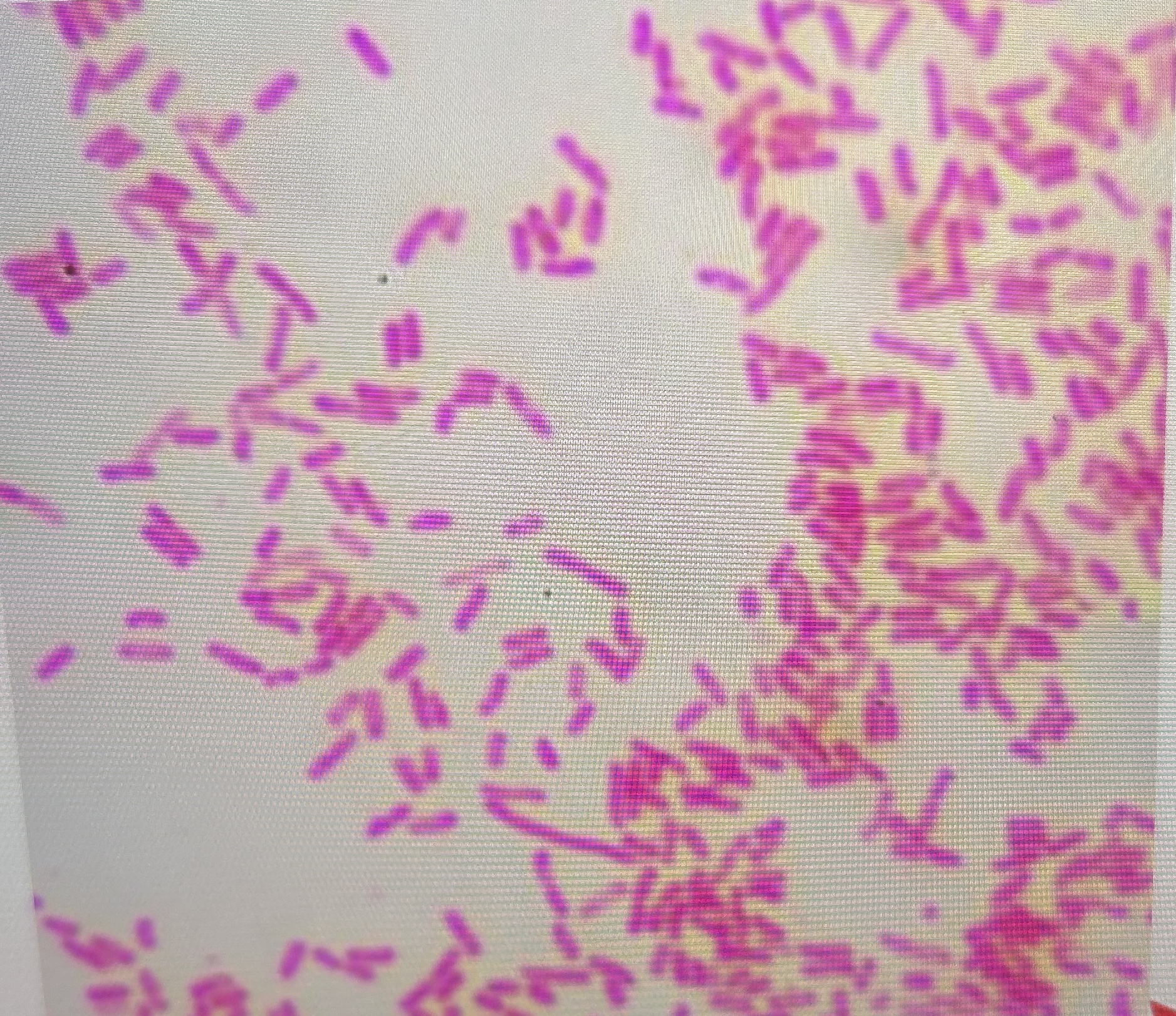
50% of gram negative organisms
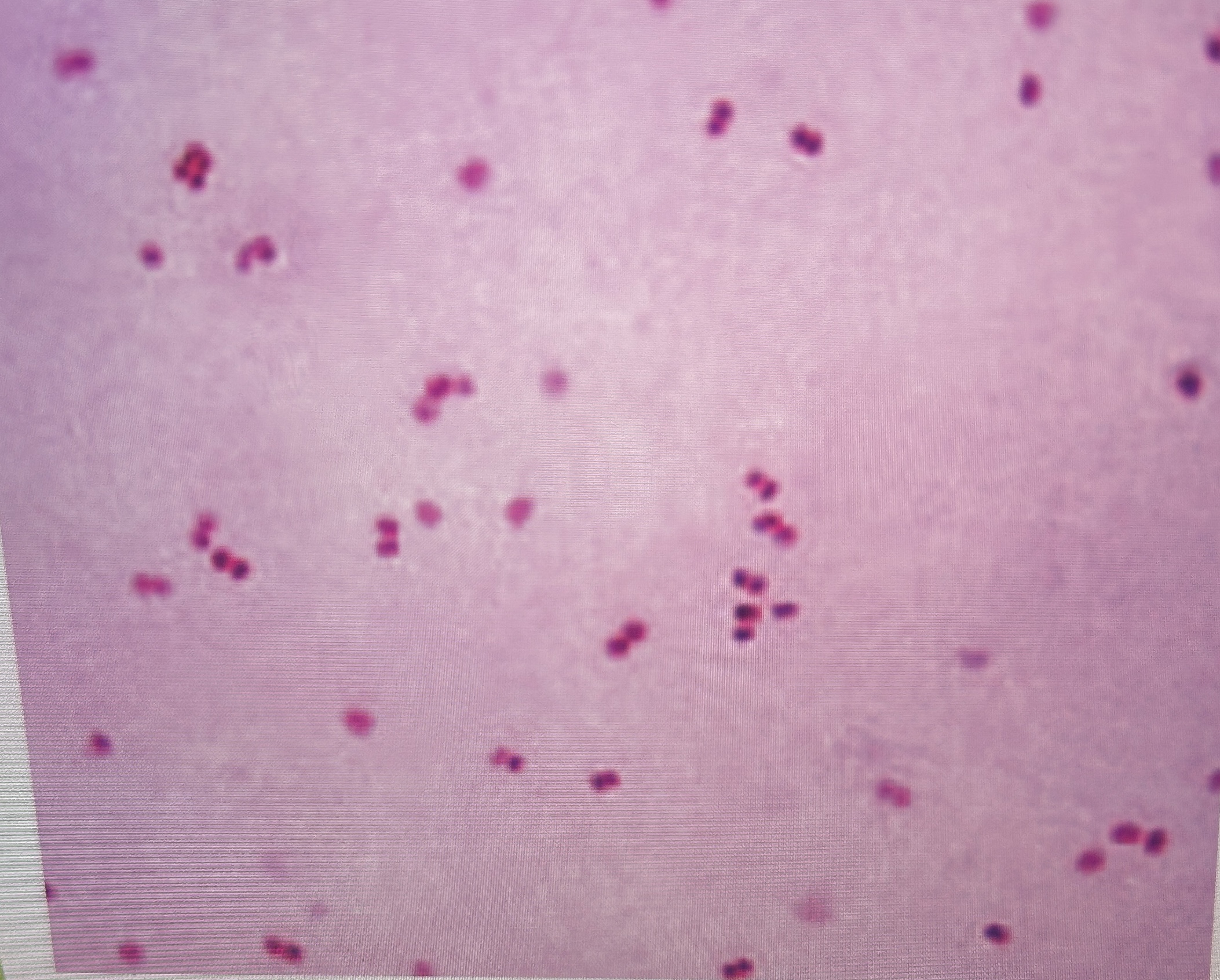
40% gonococcal infections
when should synovial samples be cultured?
when bacterial or septic arthritis is suspected
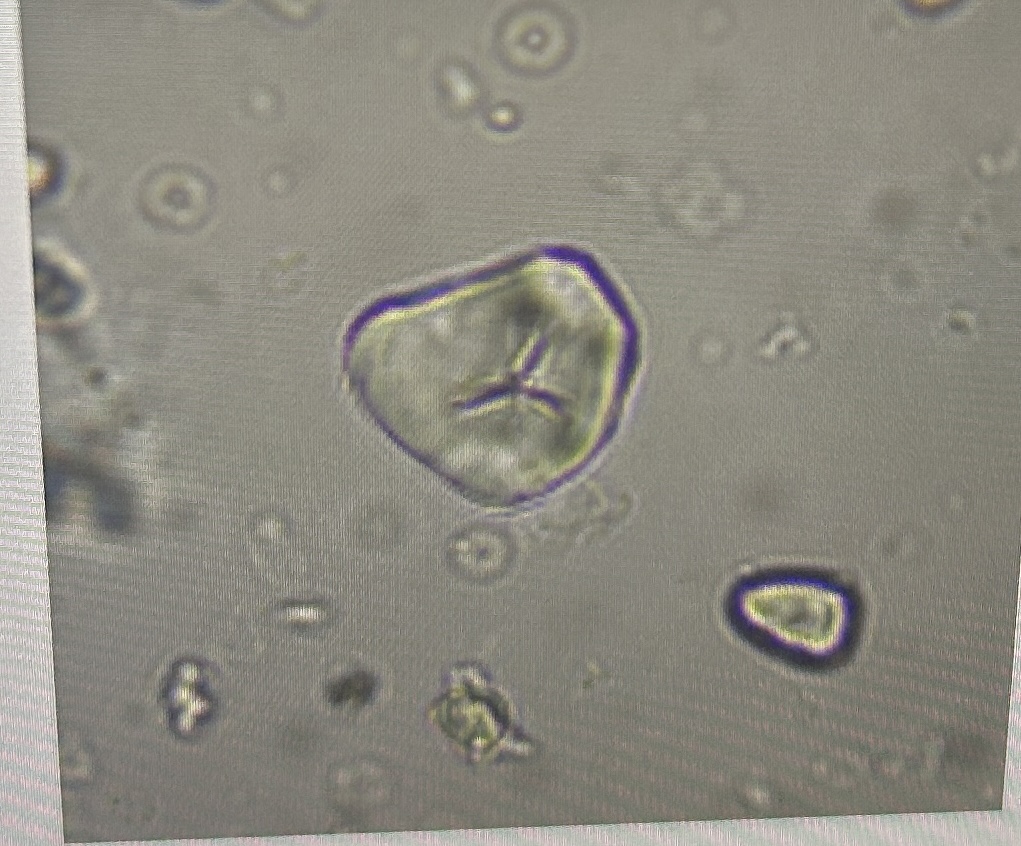
artifacts
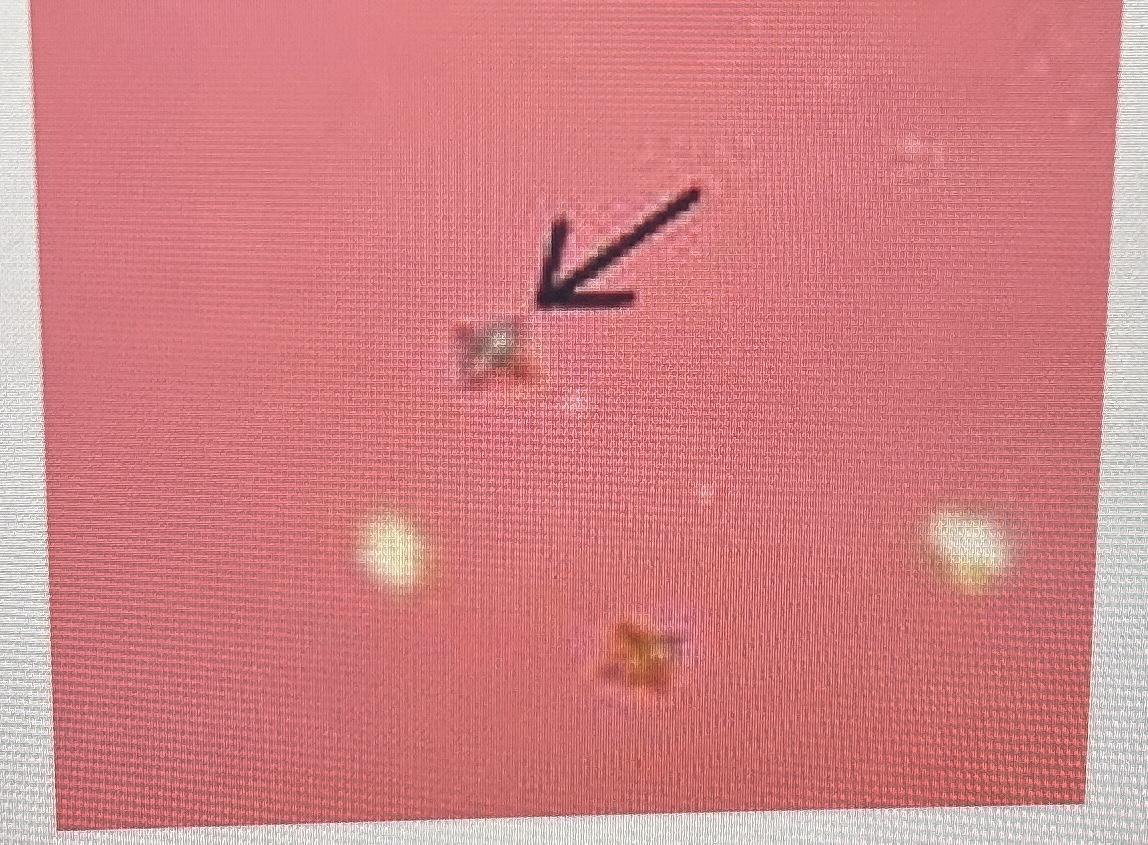

Calcium Oxalate
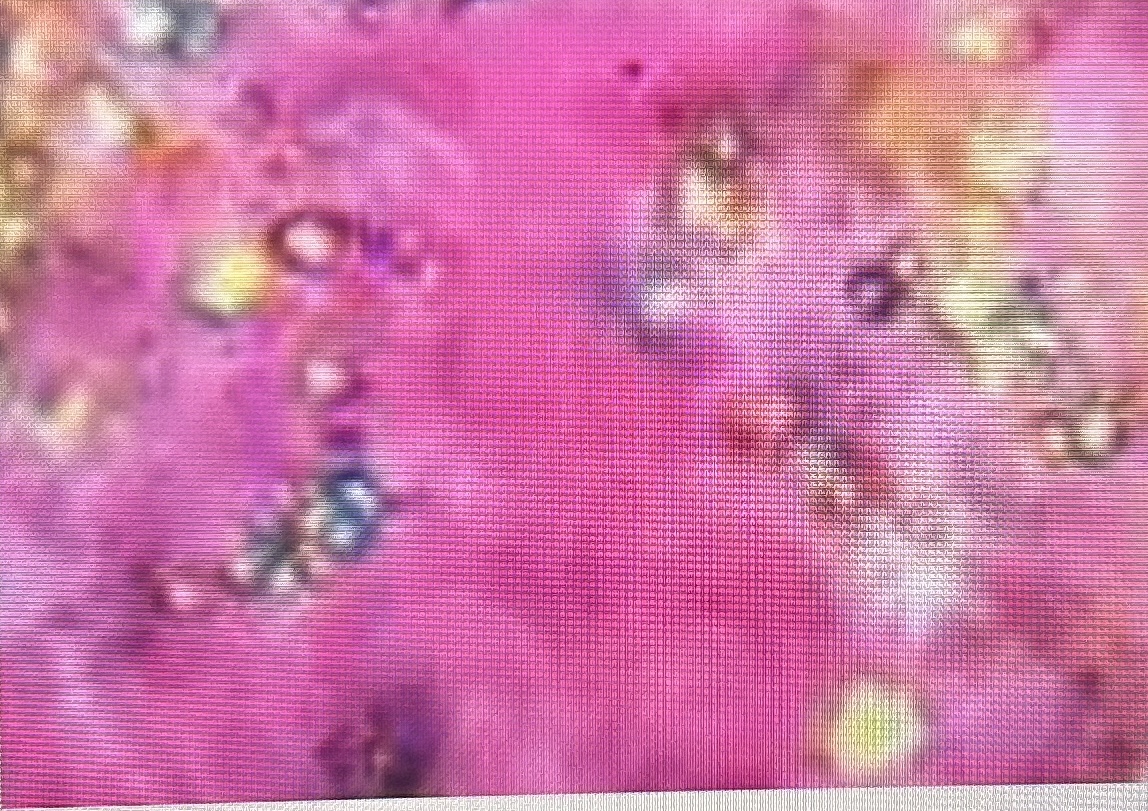

corticosteroid injections
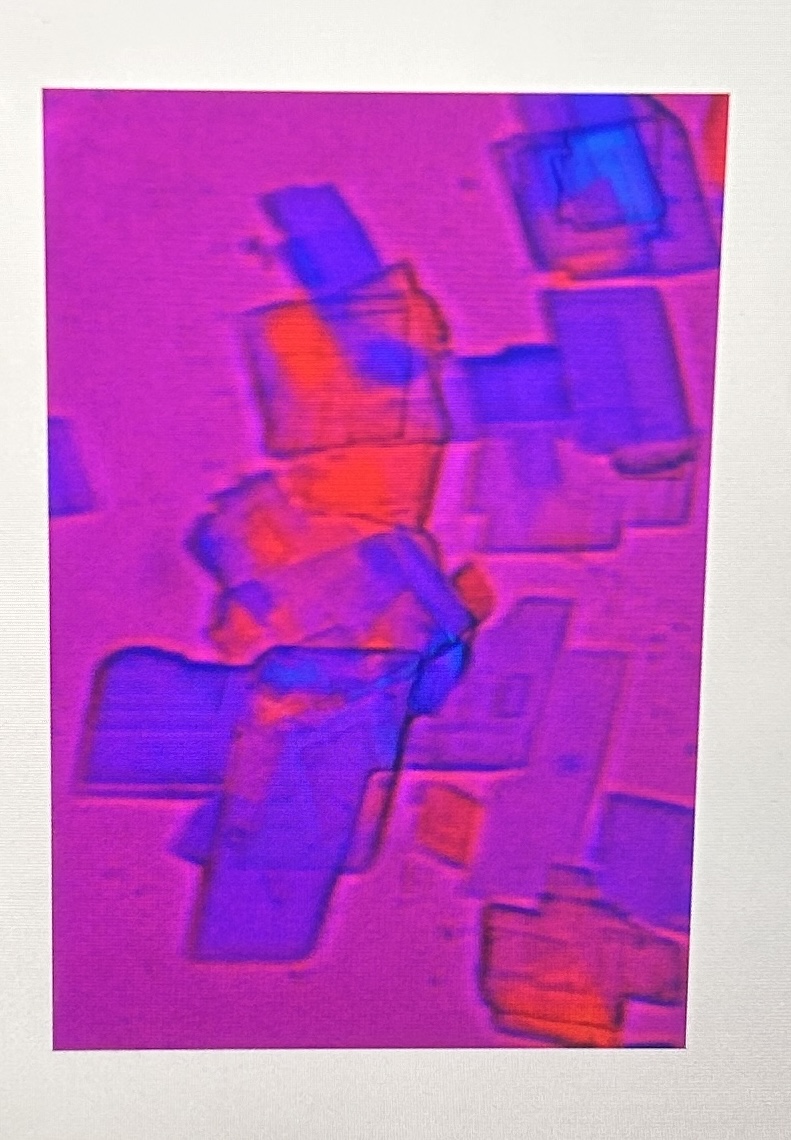

cholesterol
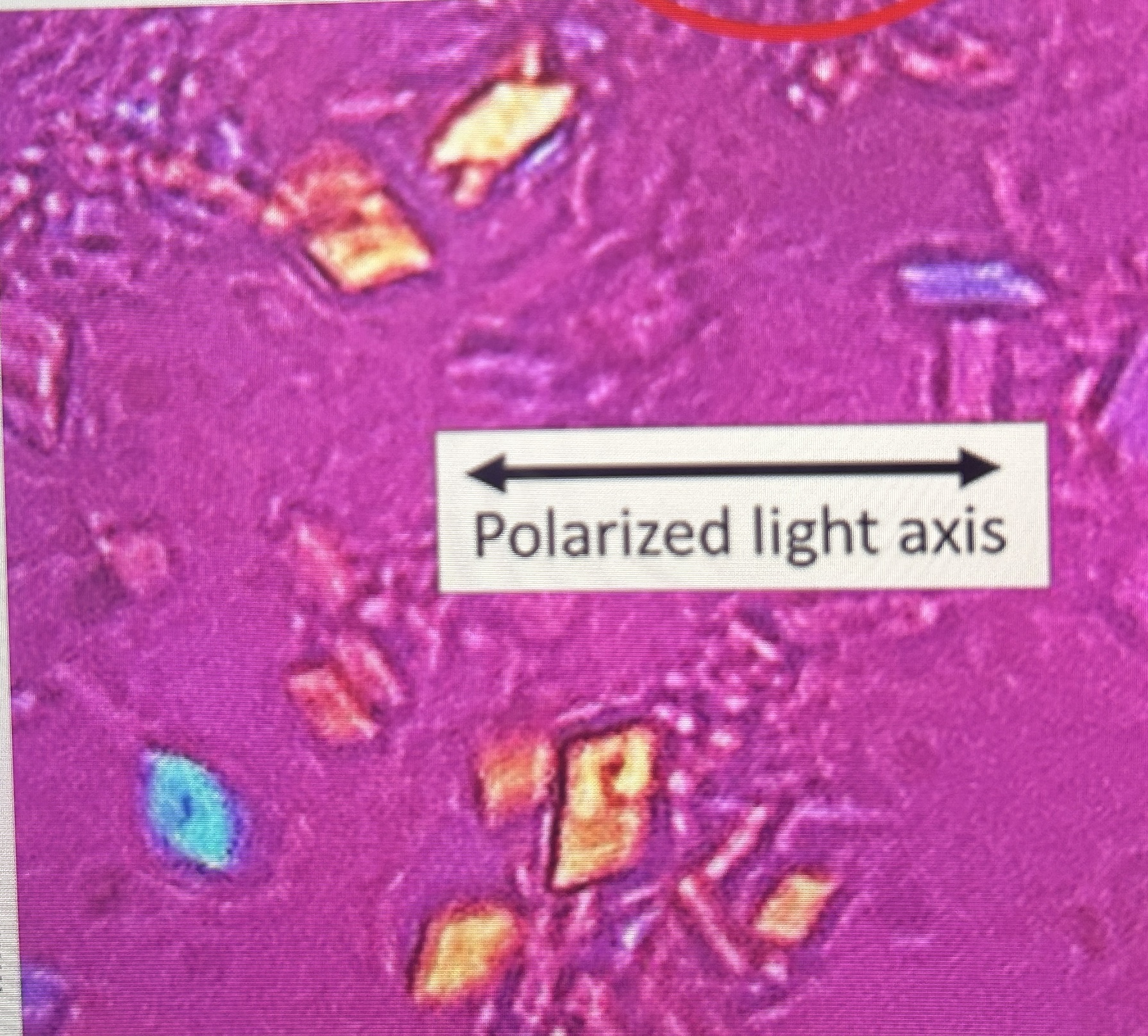
CPPD crystals with red compensator
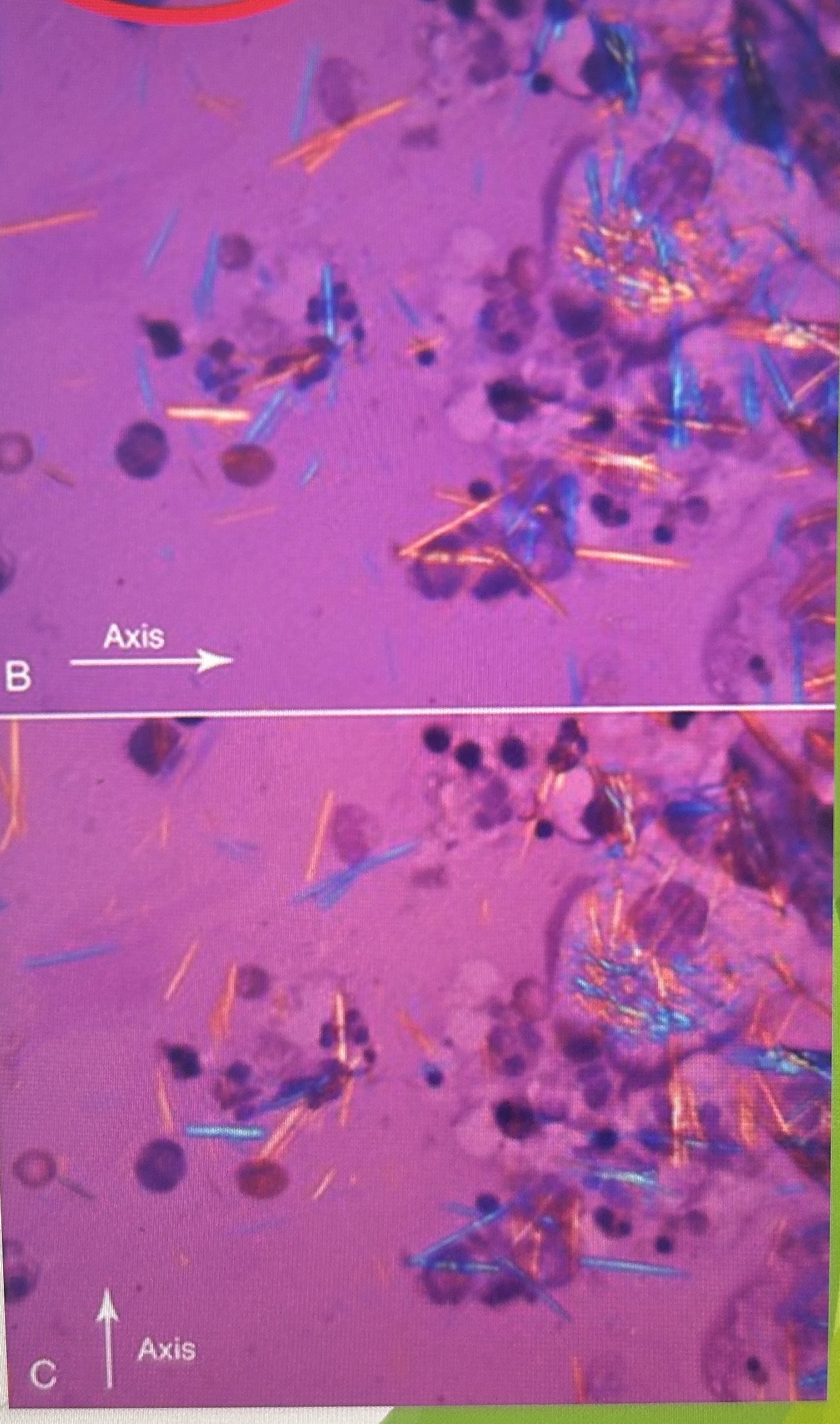
MSU Crystals with red compensator
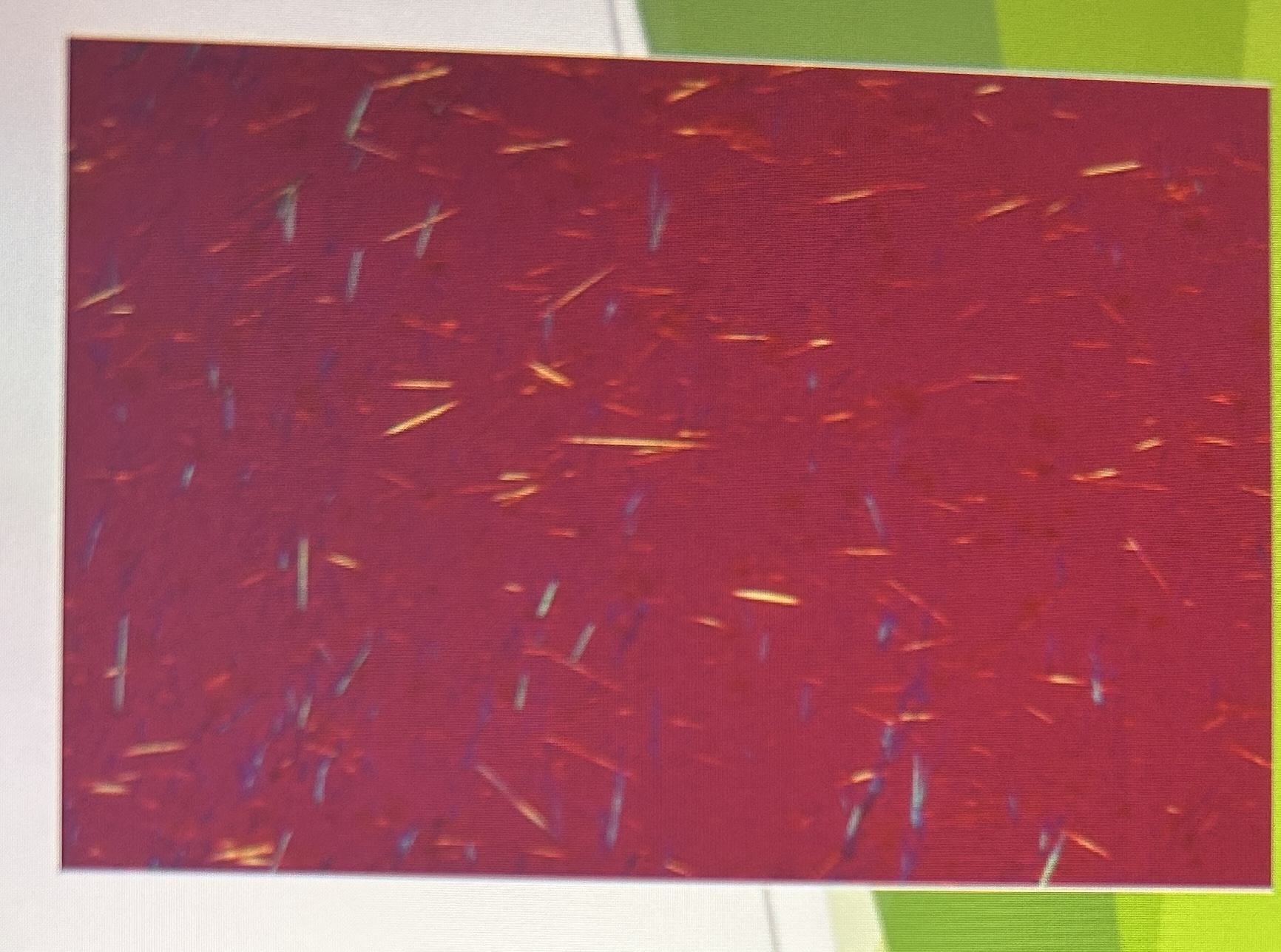

MSU Crystals
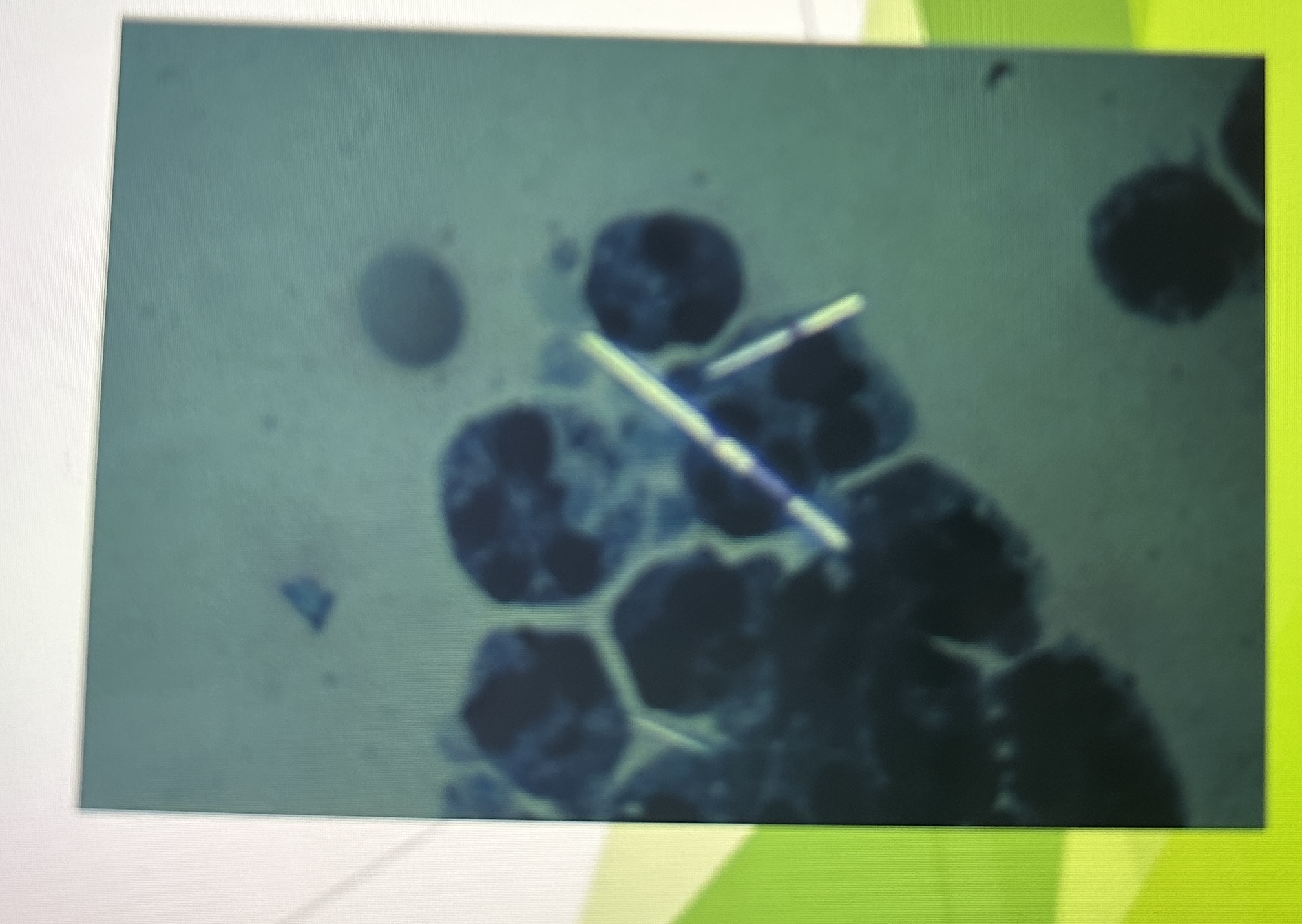
MSU Crystals in polarized microscopy