11th grade Protein & Enzyme Revie
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Proteins
Made up of amino acids.
Condensation Reactions
Anabolic reaction that removes HOH (water) from 2 monomers to create a polymer
Hydrolysis Reactions
Catabolic reaction that adds HOH (water) into the location where 2 monomers are linked together, breaking them apart
Enzymes
All metabolic processes in the body use _____________ because they speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy (energy needed to get the reaction started)
Hydrogen Bonding
Forms between polar R groups during the tertiary level of protein folding
Ionic Bonding
Forms between positively charged (basic) amino acid R groups and negatively charged (acids) amino acid R groups
Hydrophobic R groups
R groups that stay away from the outside of a protein structure during tertiary structure
Tertiary Protein Structure
The 3-D shape of the protein that is stabilized by interactions between R groups
Primary Protein Structure
The sequence of amino acids that determines all the other levels of protein structure (polypeptide chain of amino acids)
Competitive Inhibition
When a molecule other than the substrate binds to the active site on an enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding
Noncompetitive Inhibition
When a molecule binds to a location of the enzyme separate from the active site and changes the shape of the active site, preventing the substrate from binding to the enzyme
Secondary protein structure
Alpha helices and Beta-pleated sheets are the localized folding that is found in this level of protein structure
Quaternary protein structure
When more than 1 polypeptide chain combine to form a large, functional protein
Active Site
Where the substrate binds to the enzyme
Substrate
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction
Denaturation
Loss of shape of a protein / enzyme
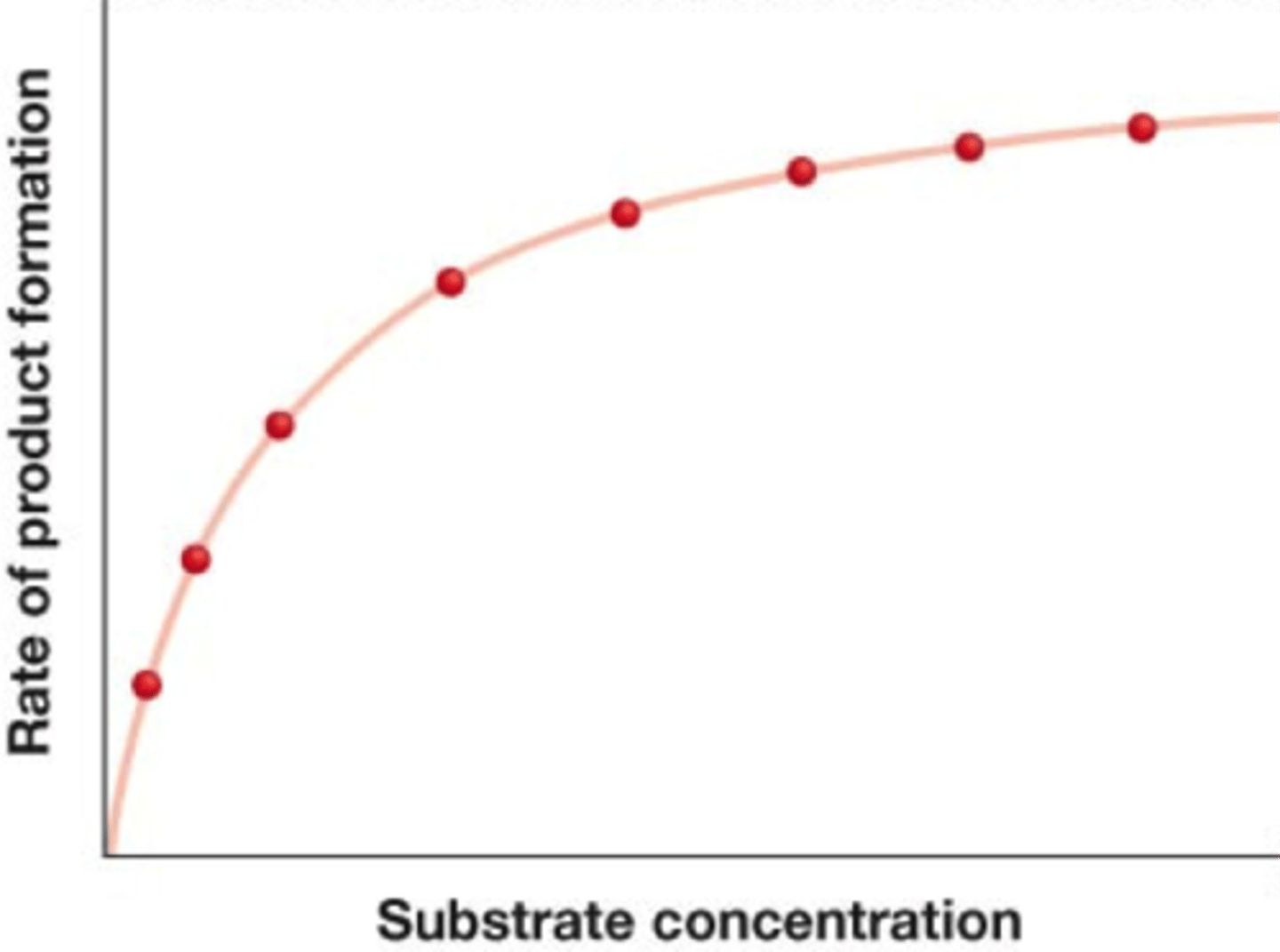
Effect of increasing substrate on enzyme activity
There is so much substrate that the enzyme active sites become saturated - all occupied so that they cannot bind to further substrate / create more product
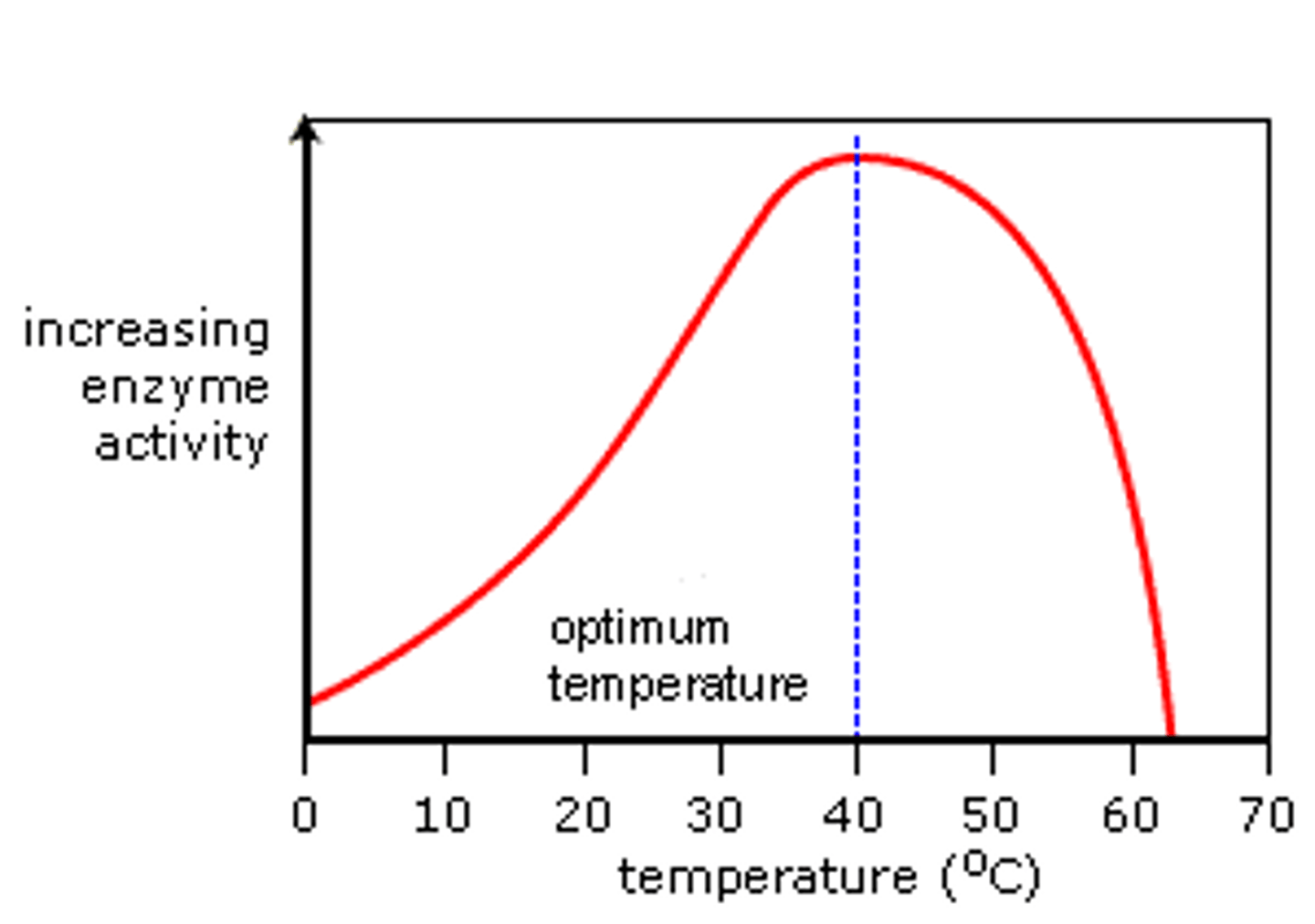
Effect of increasing temp on enzyme activity
At first, increasing molecular movement increases the chance that a substrate and enzyme will interact but after the optimum temp, the enzyme becomes denatured and unable to bind to substrate
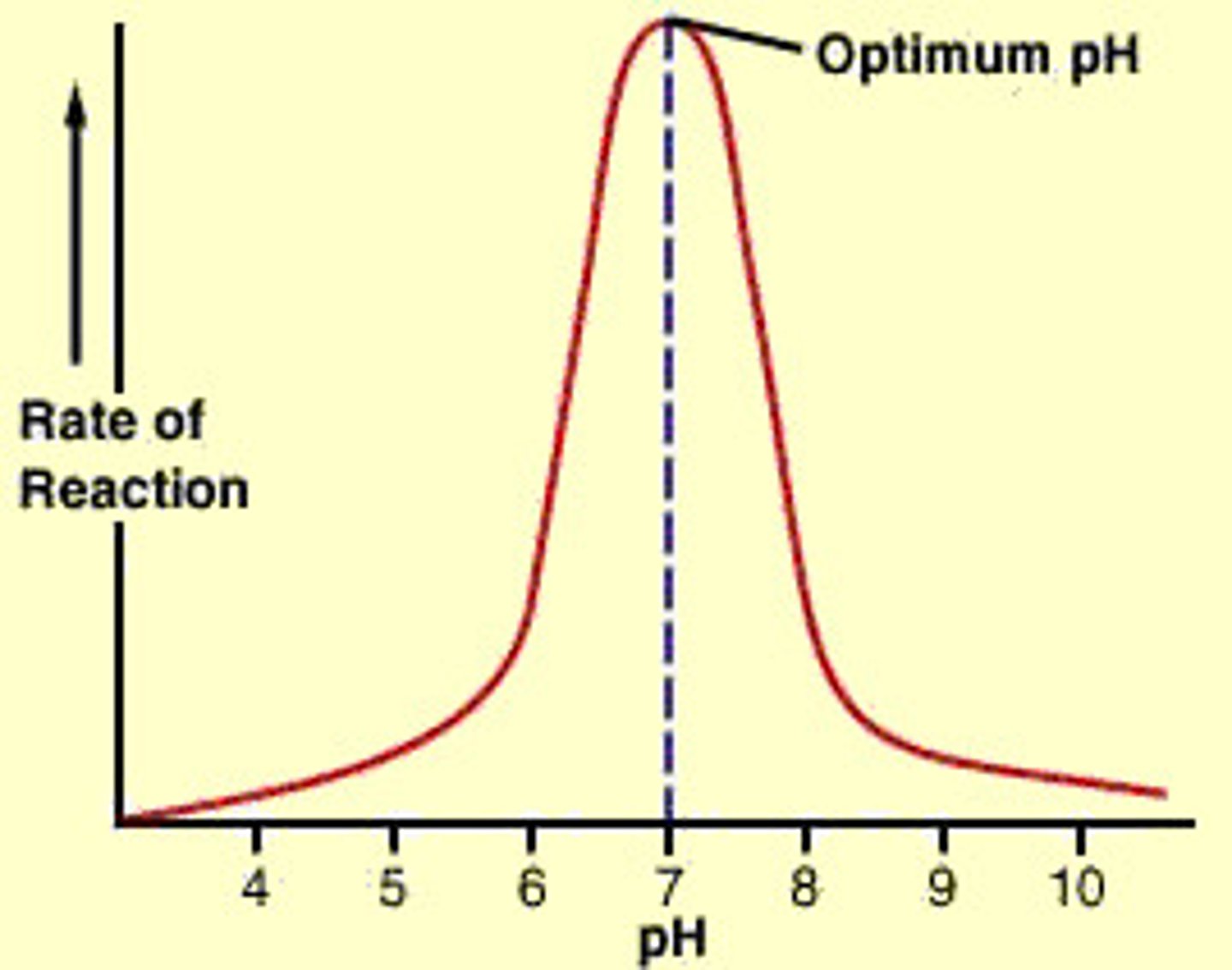
Effect of increasing pH on enzyme activity
Enzymes have an optimum pH that they work BEST at. If you go too far below or above this optimum pH, the enzyme becomes denatured and unable to bind to substrate