Nutrition Endocrine 2025 SA lipid disorders and obesity
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Common causes in dogs and cats with lipid disorders is
Post prandial hyperlipidemia
Lipid disorders are more common in
dogs
less common in cats
Secondary hyperlipidemias are most common form in dogs and usually a result of
hypothyroid, diabetes mellitus, or cushing’s disease
basically an endocrinopathy
Primary Hyperlipidemias are typically seen in what dog breed?
Mini Schnauzer
other breeds: collies, beagles, rotties, dobermans
increased age = increase severity and prevalence
Primary hyperlipidemias present on bloodwork as:
HTG - from abnormal accumulation of VLDLs or VLDLs + chylomicrons
HCH may or not be present
pathogenesis is unknown
Name some canine clinical signs of hyperlipidemia

Cats with hyperlipidemia have what type of deficiency?
LPL lipoprotein lipase deficiency
What are feline clinical signs of hyperlipidemia
typically noticed after 6-9months of age
peripheral neuropathies, cutaneous xanthomas, formation of lipid granulomas.
Most affected kittens do not show clinical signs OTHER THAN LIPEMIA RETINALIS
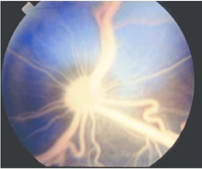
How does the LPL deficiency seen in cats work?
LPL is on capillary epithelium of many tissues
responsible for breaking down triglycerides (TAG) in circulating lipoproteins when activated by insulin: called fatty acid oxidation (catabolic phase)
also facilitates TAG reassembly and storage in adipose tissue (anabolic phase)
this is a naturally occurring mutation causing HTG and HCH
can be homozygous or heterozygous for the mutation
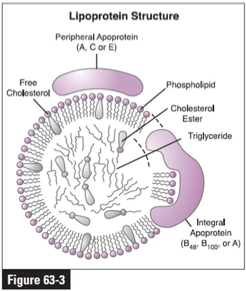
What is a chylomicron test?
A chylomicron test in dogs is a simple diagnostic method used to detect elevated levels of chylomicrons in the blood, a type of lipoprotein primarily responsible for transporting fats from the digestive system to the body's tissues. It helps diagnose hyperlipidemia, a condition where there's an abnormal increase of fat in the blood.
Refrigerate serum sample for 12 hours. The top will have a froth that are the chylomicrons. The bottom layer is the infranatant.

What are treatment goals for persistent secondary hyperlipidemia and primary hyperlipidemia
Both conditions are treated using the same principles
It is better to start treatment when severity of HTG is low to decrease risk of complications

Treatment approach for secondary hyperlipidemia should be approached by
treating primary disease process (endocrinopathy)
confirm with laboratory testing 4-6 weeks post initiation of treatment.
What is the importance of dietary fat?
energy source
source of essential fatty acids
vehicle for fat soluble vitamin absorption
palatability
What is considered low fat per 1000 kcal for dogs? What about ultra low fat?
low fat = 25-35 grams
ultra low fat = <20 grams
What are some instances where ultra low fat diet should be considered for a canine patient?

What are some instances where low far should be considered for a canine patient?

What is considered low fat per 1000kcal in cat patients?
<30 grams
In what instances should cats be placed in a low fat diet?

Once you start a canine low fat diet when should recheck be assessed? What is assessed at the recheck?
recheck in 3-6 weeks
if <500mg/dL with dietary intervention, continue nutrition support plan long term
if serum TG>500 mg/dL, drug therapy is recommended
What are some risks of utilizing a weight loss commercial food in cats (unfortunately that is the only low-fat option)
contraindicated for underconditioned patients, volume intolerant patients, hepatic lipidosis (acute)
may be better to create a complete and balanced formulation by a board-certified veterinary nutritionist.
When should a patient with a feline low fat diet be rechecked? Reassessed for what?
Recheck in 3-6 weeks
if serum <500mg/dL with dietary intervention, continue support plan long term
if serum TG > 500mg/dL, drug therapy is recommended
(diets depicted here are < or = to 35g/1000 kcal of fat)

Medical management option(s) for patients with HTG and nonresponsive to diet alone?
Omega 3- Fatty Acids
Chitin or Chitosan
Fibrates
Niacin (Nicotinic acid, Vit B3)

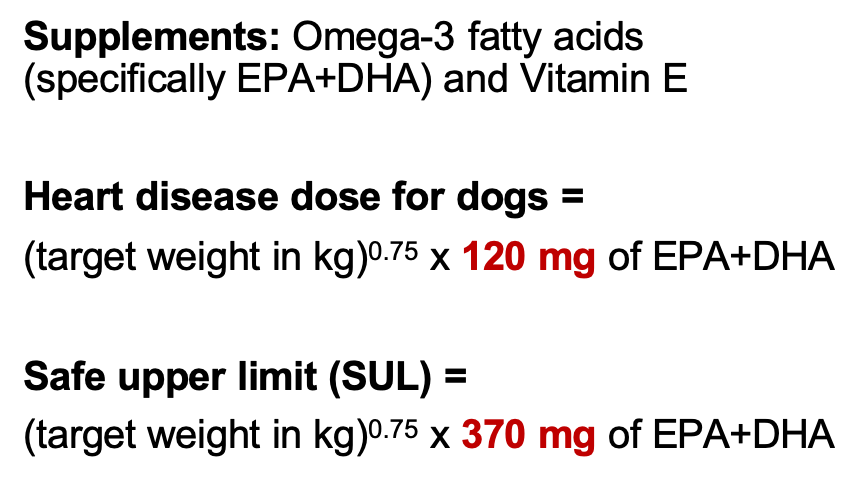
How do you calculate dosage for Omega 3 fatty acids in dogs? What if they have heart disease?
What is the purpose of chitin/chitosan supplementation?
Chitin or Chitosan
proposed MOA: fiber supplement derived from shellfish exoskeleton, binds dietary lipids and decreases their absorption into the body
anecdotal only, with no notable adverse effects
DO NOT USE if known shellfish allergy
Epikatin is not recommended given low chitosan concentration
given 30 min prior to meal
What is the purpose of Omega 3 FAs?
Omega 3- Fatty Acids:
●Proposed mechanism of action:
○Regulation of transcription factors ⇒ ↓lipogenesis, ↑ β-oxidation and activation of lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
○↓ serum TG and cholesterol via ↓ VLDL + LDL
●CHALLENGE: May develop worsening hyperlipidemia
How do fibrates help?
Fibrates:
●Proposed MOA:
○ ↑ oxidation of fatty acids from liver ⇒ diverted from TG synthesis ⇒ ↓ VLDL
○↑ lipoprotein lipase gene & HDL production
●Potential adverse effects:
○GI upset, hepatotoxicity,
abdominal pain, creatinine elevation, myopathy/myalgia
○Caution if renal, liver, and/or gallbladder disease
○May increase ALP and ALT
○Questionable efficacy
How does niacin help?
Niacin (Nicotinic Acid, Vit B3):
-Proposed MOA: Inhibits hormone sensitive lipase and diacylglycerol acyltransferase reduced hepatic TG synthesis + VLDL production
-Adverse effects: Potentially erythema and pruritus
-Questionable efficacy: especially on a complete and balanced diet

What is the generic dosage for cats consuming omega-3 fatty acids?
Generic dose for cats =
(target weight in kg)0.67 x 100-130 mg of EPA+DHA
What are some concerns you should keep in mind when recommending omega-3 fatty acid supplementation?
potential side effects due to Vitamin A and D overload due to the fish oils
When recommending vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) supplementation what are the dosing calculations?
•Use (mg of EPA + DHA) / (kg of target body weight) for calculations:
•If below 80 mg/kg à give 200 IU
•If above 80 mg/kg à give 400 IU
remember that ONLY alpha-tocopherol has biological activity.
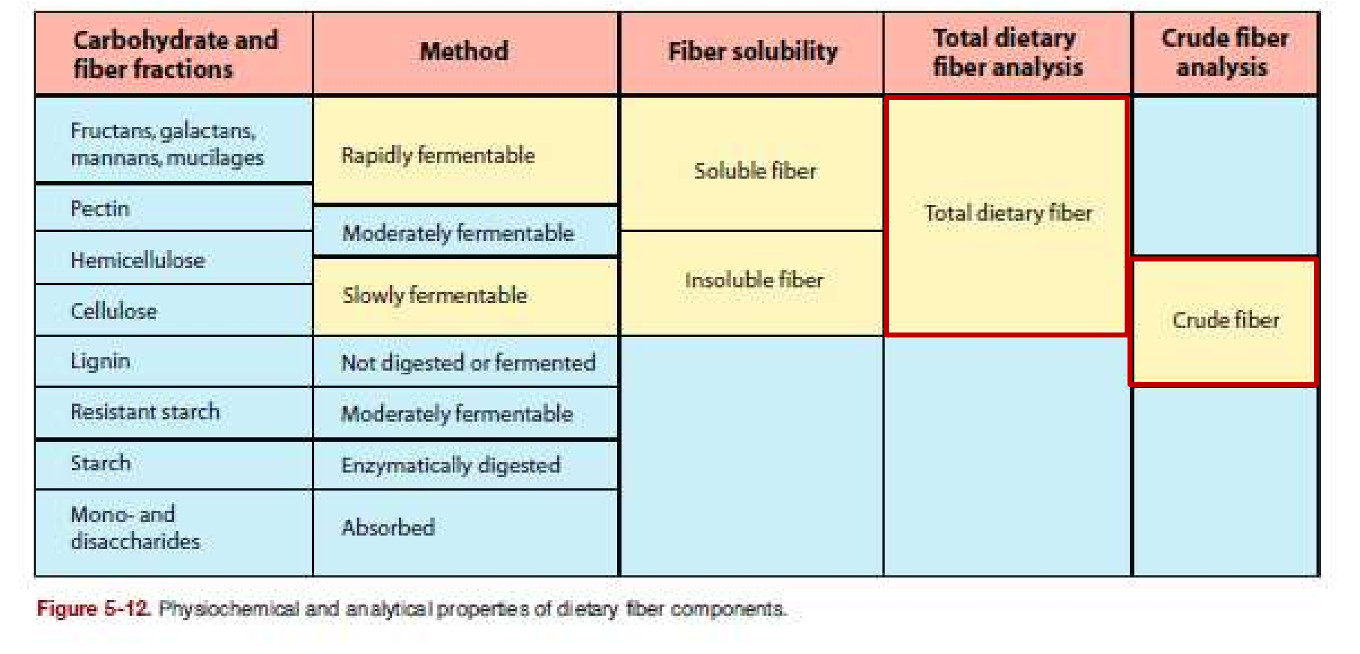
What are differences between rapidly fermentable and slowly fermentable fibers?

What are some effects of proper consumption of dietary fibers?
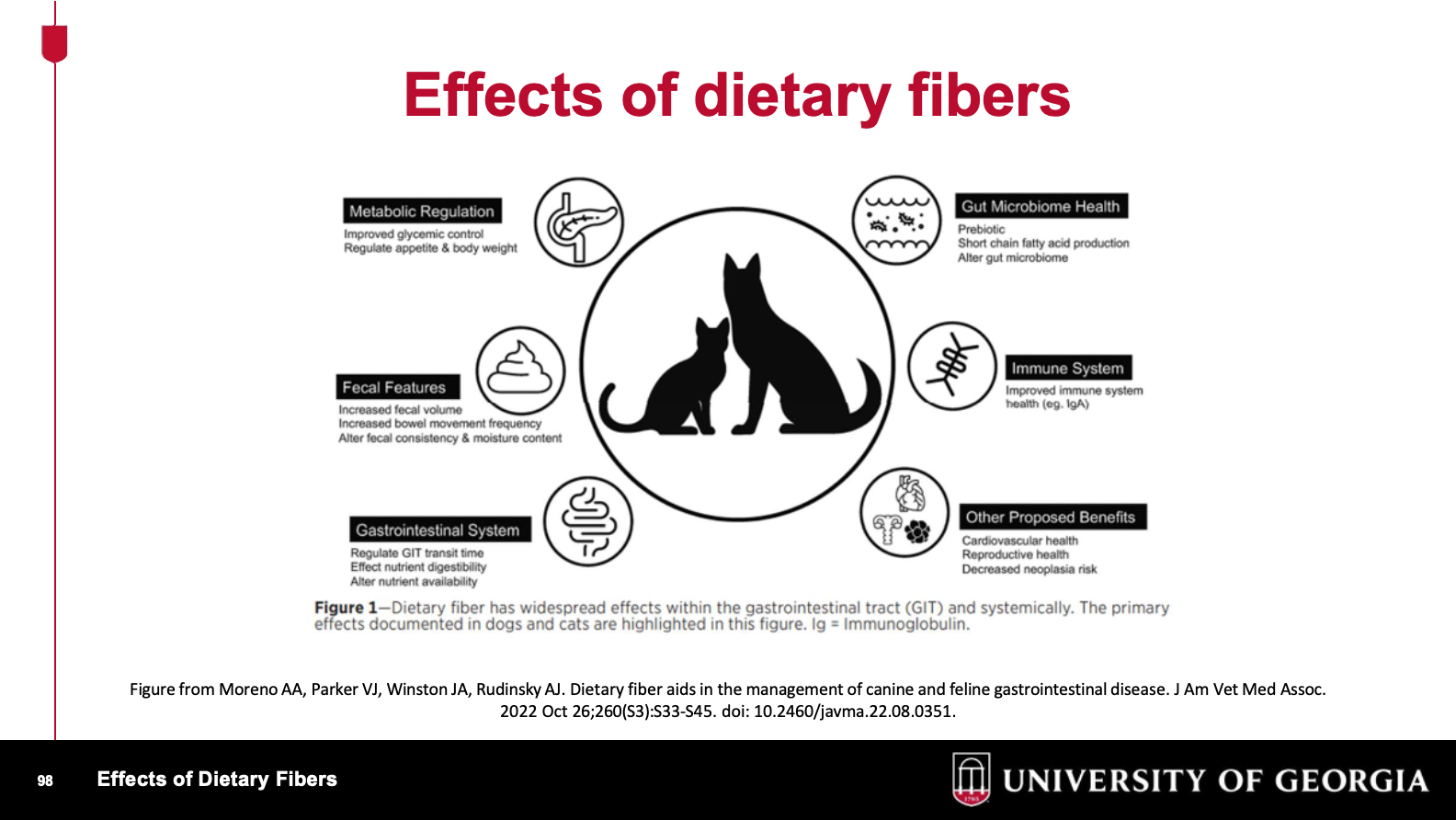
What are some examples of total dietary fiber and crude fiber?
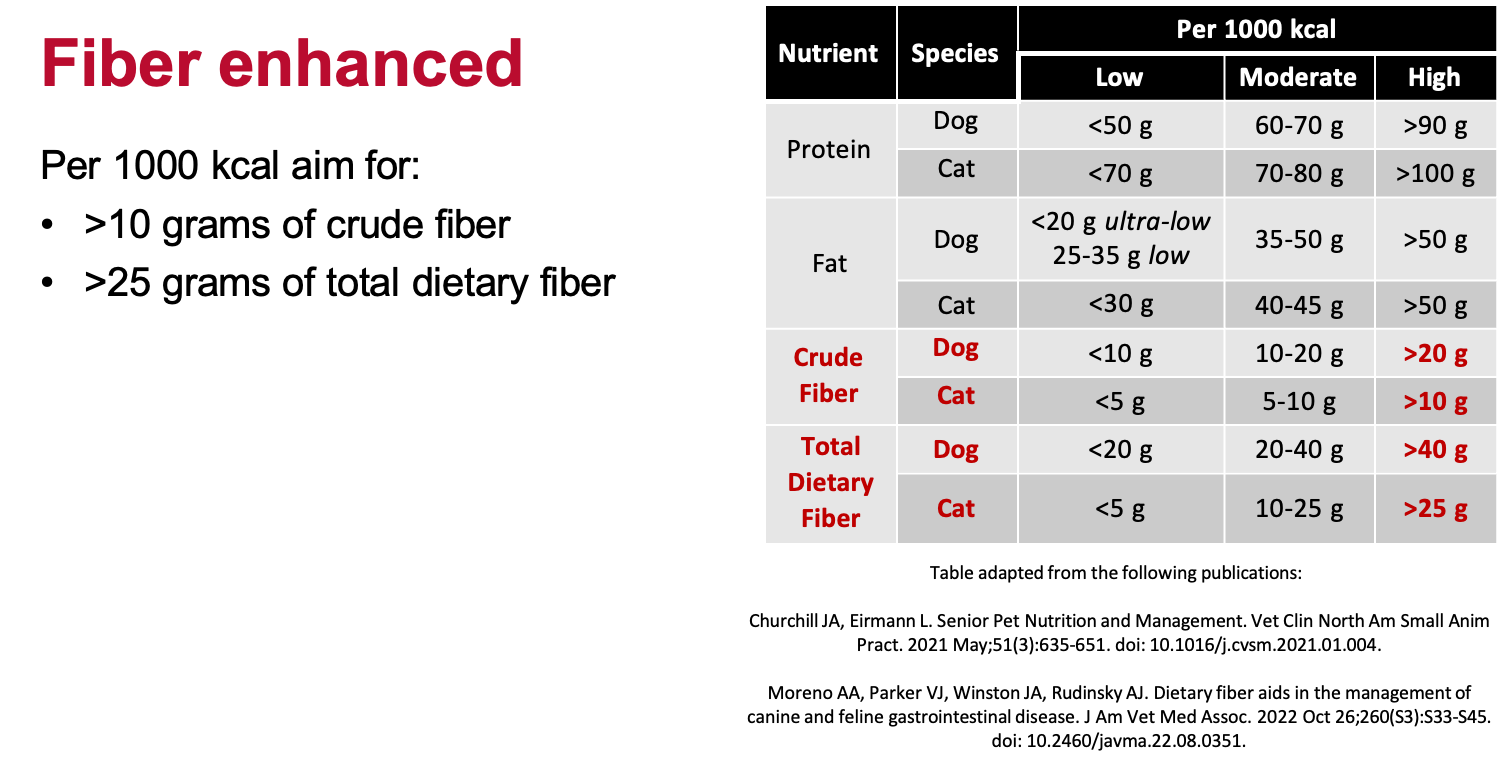
To build a fiber enhanced diet, how many grams of crude and total dietary fiber should we aim for?
In what cases should a fiber enhanced diet be considered?
Acute enteritis, including dietary indiscretion
Stress colitis Chronic colitis Constipation
REFRESHER: Weight loss plans for over- conditioned patients
Satiety for begging
In what cases is a fiber enhanced diet contraindicated?
Megacolon/obstipation (loss of motility)
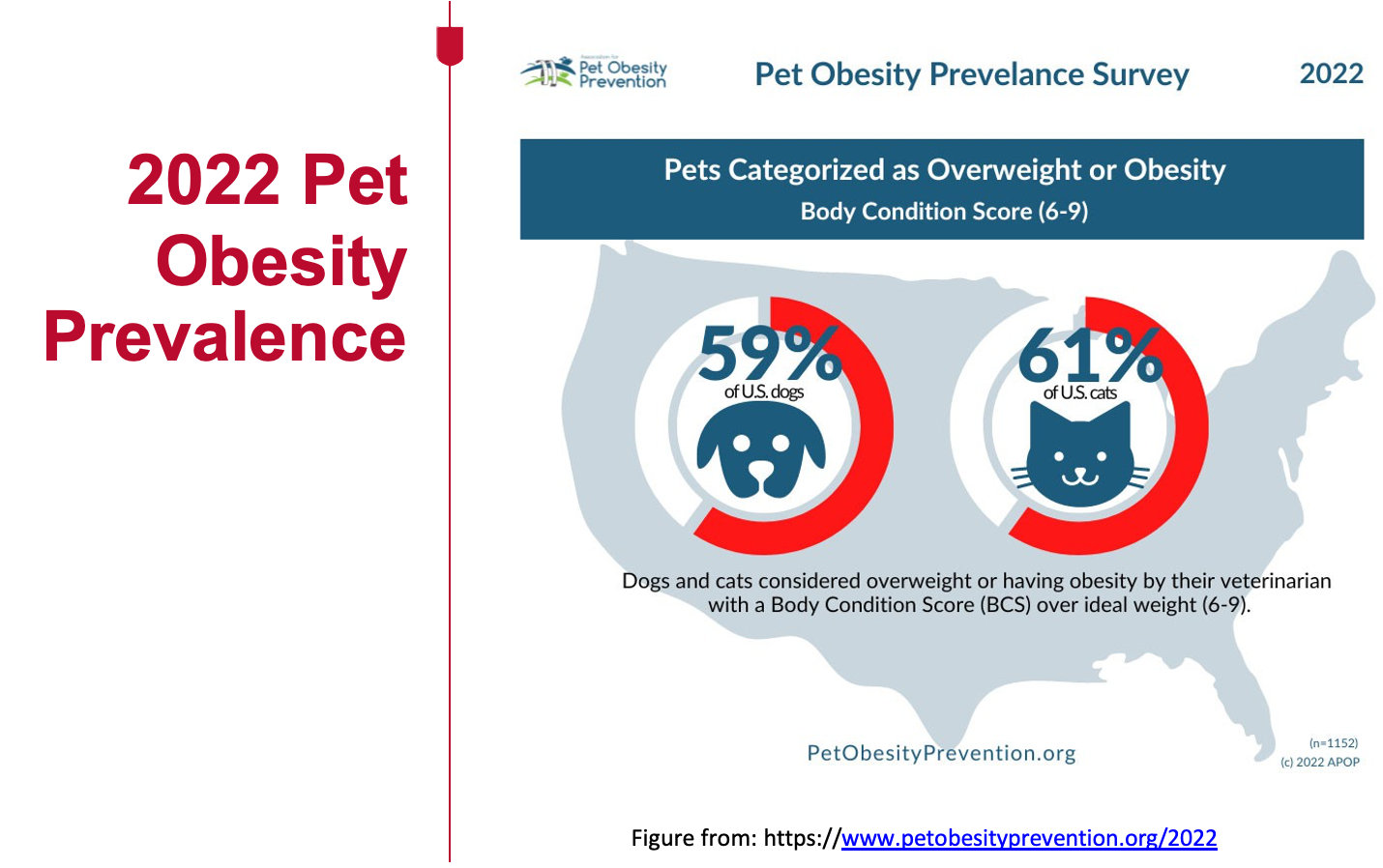
What is the prevalence of over-conditioned dogs in the US?
59%
a 158% increase in overweight dogs!
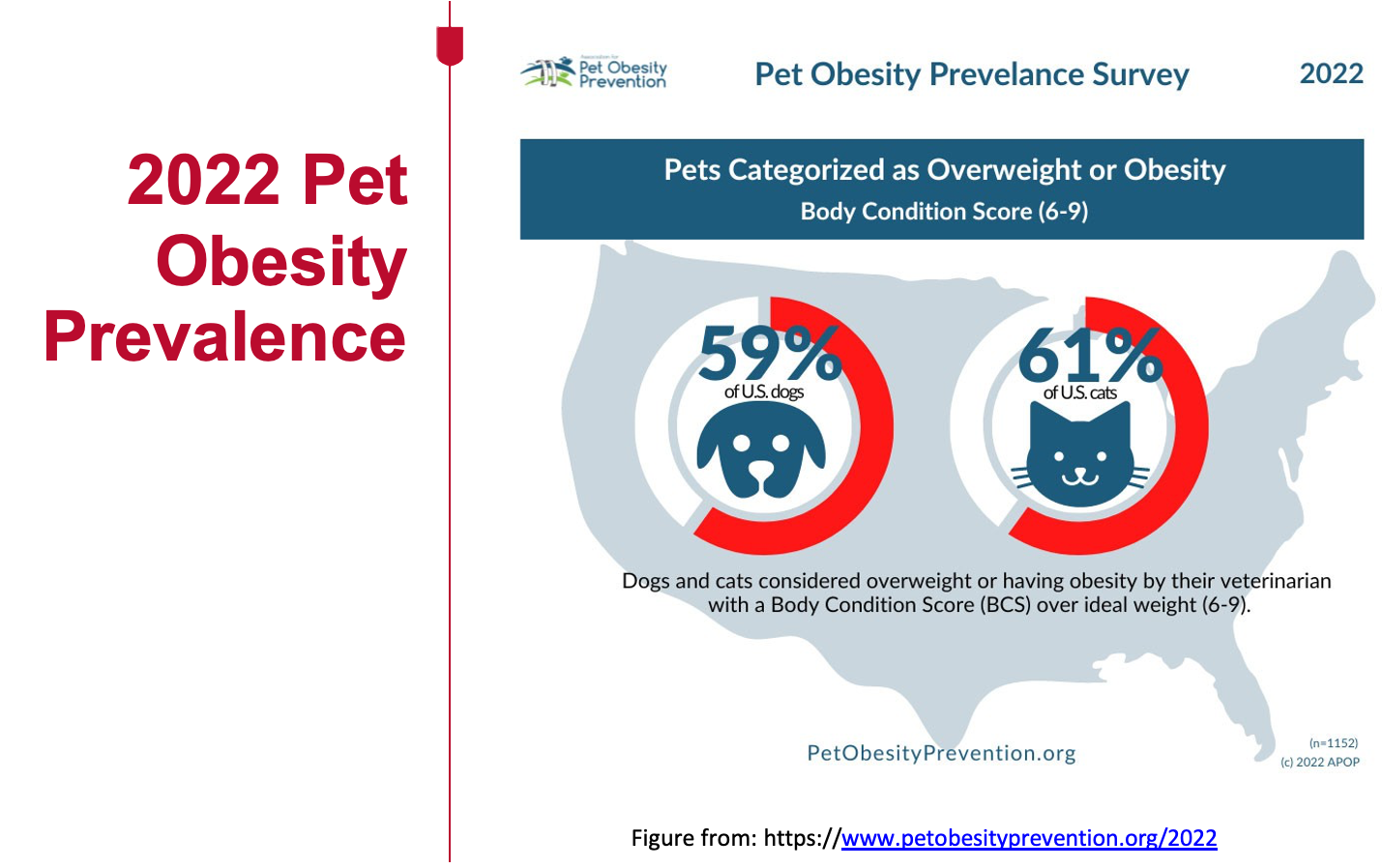
What is the prevalence of over-conditioned cats in the US?
61%
this is an 169% increase in overweight cats!
Based on the Pet Obesity Initiative what is defined as obesity?
30% above ideal weight which is started at 8/9 on the BCS
What are the 3 Global Pet Obesity Initiatives?
Obesity = disease
Use standardized BCS scale
8/9 or 9/9 is considered obese = 30% above ideal weight
Which dog breeds are predisposed to obesity?
What are some predisposing factors to obesity? (Age, sex, environment)
Age: Peak prevalence
•Cats: 5-11 years
•Dogs: 6-9 years
Sex: Neutering increases prevalence; alterations in sex hormones
•Occurs in both dogs/cats
Environment: Living indoors increases prevalence
•Occurs in both dogs/cats
Which disease states predispose dogs/cats to weight gain?

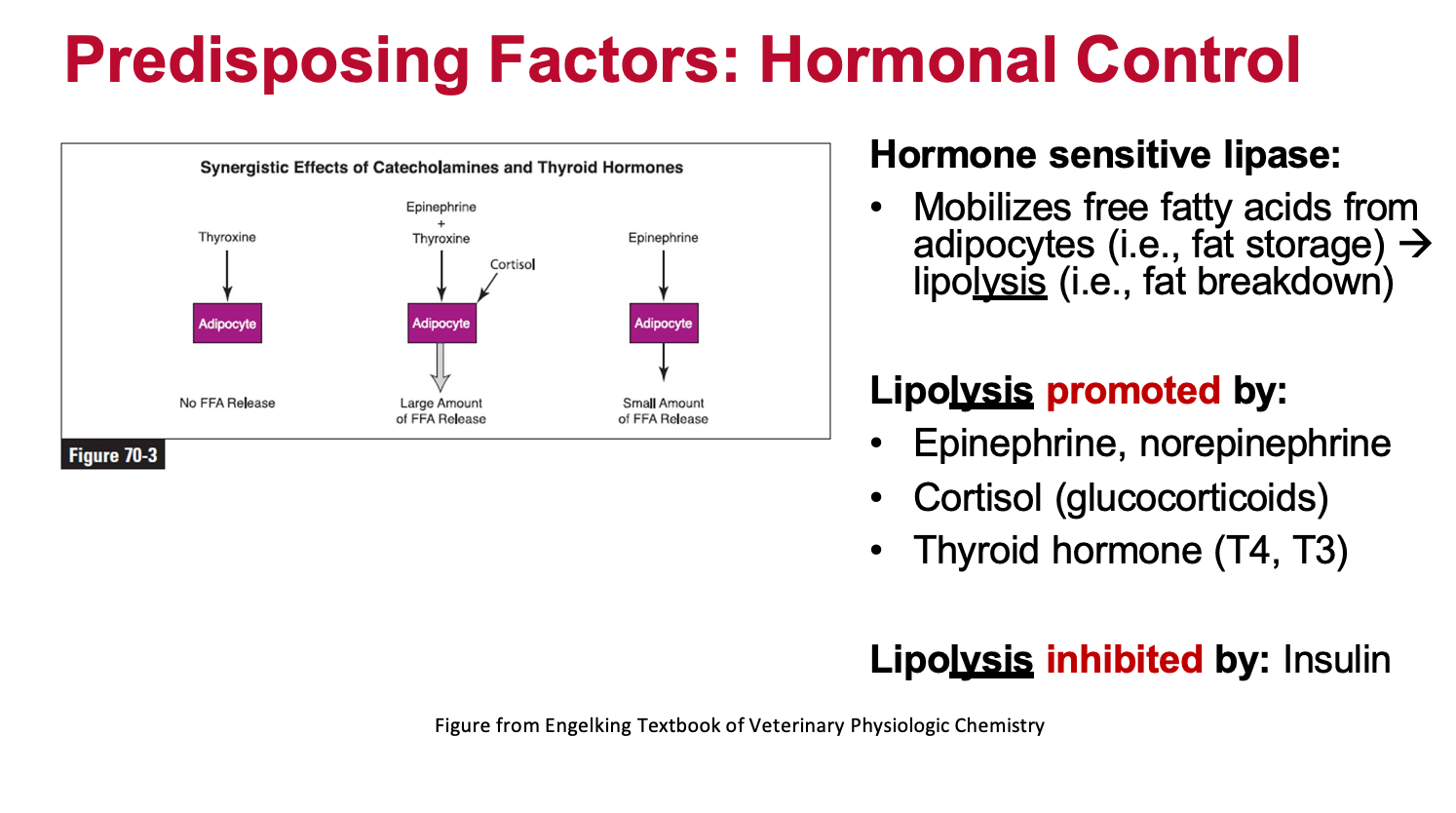
What mobilizes free fatty acids from adipocytes and causes lipolysis? What are other factors that promote or inhibit lipolysis?
How does leptin affect obesity?
In animals, obesity is associated with elevated leptin concentrations, but often with a phenomenon called "leptin resistance." This means that while leptin levels are high, the body's response to them is blunted, leading to continued weight gain despite the presence of this satiety hormone. Leptin, primarily released from fat cells, signals to the brain to regulate appetite and energy expenditure. In obese animals, this signaling is disrupted, and the body becomes less sensitive to the effects of leptin

What does Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) do? How does this affect obesity?
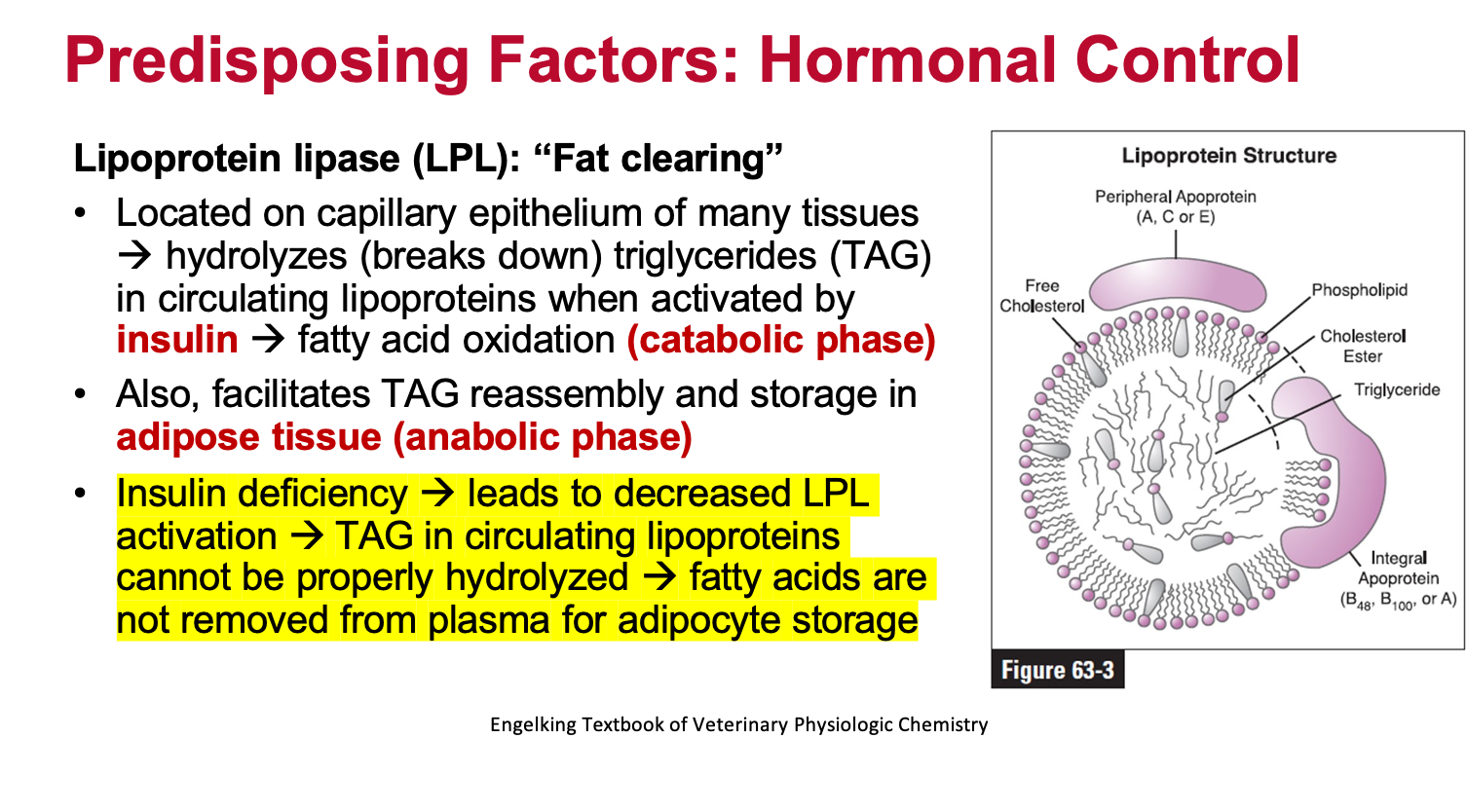
What are some dietary factors associated with overweight or obesity in dogs and cats?

What are some owner factors implicated in the development of overweight and obesity in DOGS?

What are relative risk of conditions for an obese or overweight cat?
top two are arthritis and dermatopathy

What is the prevalence of disease in overweight or obese dogs?

Patients with an ideal BCS of 4-5/9 throughout life have
•Increased median life span
•Delayed the onset of aging
•Delayed the onset of chronic disease
What is the average reduction in lifespan for overweight dogs?
about 1-2 years
Patients on a weight management diet should:
be maintained in their weight management diet
following weight loss, weight management should be: increase calories by 2.5-5%
requires weigh in rechecks to assess if patient is still losing weight or has gained weight, goal is to reach a consistent stable weight