Surgery - Final Exam - Study Tips
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Immediate post-anesthesia monitoring includes...
initial postop TPR taken at least every 15 minutes, Pulse oximetry, ECG, Blood pressure, untie ET tube for ease in extubation, deflate ET cuff
To minimize problems during recovery, the patient should be positioned in the ____________________ so that mucous membranes and respiration can be easily observed.
recovery cage
When animals are placed in a recovery cage, how should they be positioned?
animal's head is toward the front of the cage and is uncovered to aid observation, NEVER tightly curl their bodies
What are the potential complications seen during post-operative monitoring
hypoxemia/hypoventilation, hypotension, hypothermia, hyperthermia, emergence delirium, cardiac arrhythmias, hemorrhage, uncontrolled pain, prolonged recovery
When is the ET tube removed?
once the animal is awake blinking, once they have had at least 2-3 good strong swallows meaning you can see the contraction clearly
the recovery period starts with the...
cessation of anesthesia to the time the patient's vital signs and level of consciousness return to normal
the length of the recovery period depends on...
length of anesthetic period, condition of the patient, type of anesthetic agent used and route of administration, patient's body temp, breed of the patient
What breeds are prone to developing complications while recovering from anesthesia?
Brachycephalic breeds of dogs like English bulldogs, pugs, and Pekingese
When managing a brachycephalic dog under anesthesia, what is the best course of action regarding ET tube extubation?
delay extubating as long as possible, then closely monitor for any dyspnea or cyanosis
When do we remove ET tube in brachycephalic patients, since we want to wait as long as possible till doing so?
only after they can lift their heads by themselves
When removing the ET tube, what do you for look at the end of tube?
should come out clear, check for any blood or regurgitant
decreased oxygen in blood/tissues
hypoxemia
What are some common causes of hypoxemia during post-op recovery?
Atelectasis, pain/hypoventilation, upper airway obstruction
- collapsed lung
- often due to prolonged recumbency
- propping animal sternal may help
Atalectasis
- low blood pressure
- caused by Hypovolemia (from blood loss or dehydration) and vasodilation (related to severe hypothermia, septic patients, or drugs)
- treatment includes: IV fluid bolus or rate increase, patient warming, and pressors
hypotension
Mild hypothermia is considered a temperature of between __________ degrees F
96-99
A patient temp below ______ degrees F is a CONCERN, since the body will shut off their temp. regulation system
93
What are some examples of things that can drop temperature?
drugs, surgery, cold oxygen in gas line, cold IV fluids, cold lavage fluids, cold table
Regarding hypothermia,
most heat loss occurs within the first ___________ of anesthesia.
20 minutes
Rewarming should be considered when hypothermic patients have a temperature less than ___________ degrees F.
97.6
Once the temperature has reached ___________ degrees F. rewarming efforts can be discontinued
100
What are the 3 techniques for rewarming patients?
passive external rewarming, active external rewarming, active core rewarming
Methods of providing heat...
Snugglesafe, hot dog warmer, sacks of rice or lentils heated in a microwave oven, warm water bottles or bags, expired fluid bags heated in microwave oven
When microwaving 1 L heating units for lavage or IV fluids, how long do you put it in for?
**shake it up too avoid hot spots!
2-3 minutes
What should NEVER be used as a method of providing heat to a patient?
electric heating pads
T/F:
The patient, including their head, can be placed under a tend of blankets and warming objects. The air under the blankets is warmer than room air.
true
Fluids administered subcutaneously or intravenously should be warmed to approximately _____________ degrees F.
98-99
fluids, when testing the temp. on your wrist, should be...
baby-bottle warm
Hyperthermia is a patient with a temp. over __________ degrees F
103.5
Hyperthermia can be seen often in cats and can be related to drug use such as...
ketamine, opioids (hydromorphone)
A body temp of over _________ degrees F is associated with risk of cellular damage and death!!
106
- when a patient recovering of general anesthesia experiences signs of excitement, possibly with exaggerated and uncontrollable movements
- animal may thrash around in the cage, cry out, or paddle on all 4 legs
*hyperthermia can be associated with this
emergence delirium
What are a few methods of treating hyperthermia?
remove bedding, fan, alcohol on pads and ears, cool or room temp IV fluids
- abnormal ECG reading, i.e. irregular pulse
- reasons: pain, electrolyte abnormalities, heart disease, drugs
- some, not all require treatment
cardiac arrhythmias
What should you do in response to superficial hemorrhage?
direct pressure for 5-10 minutes, bandage if needed
What are some signs of internal bleeding?
pale MM, rapid HR, rapid RR, abdominal distension, swelling around surgical site, hypotension, shock
Naloxone and/or butorphanol are reversal agents for what?
opioids such as hydromorphone, fentanyl, and morphine
Flumazenil is the reversal agent for what?
diazepam, midazolam
Antisedan is the reversal agent for what?
Dexdomitor
- premature loss of sutures and opening of the surgical sight
- occurs with any or all layers of incisions
-can be serious and/or fatal!!
- caused by licking, playing, rubbing, scratching, falling, infection, and weak or inappropriate sutures
Dehiscence
procedure to aseptically collect blood pooling in the abdomen or thorax, pass it through a blood transfusion micropore filter, and then readminister it to the patient
autotransfusion
fluid pocket under the skin
- can be the result of overactive patient postop or dead space from surgery
- can delay healing and lead to infection
seroma
- fluid pocked filled with bacteria and neutrophils
- straw-colored light red fluid
- draining purulent fluid
- hard and infected
abscess
- fluid pocket filled with blood
- can resolve it if it is just blood
hematoma
- aspiration will be empty or fall filled from omentum
- may be reducible, may need surgical repair
hernia
Shivering in patient recovering from anesthesia indicates...
the patient's body attempting to produce heat
Which of these is a patient-related cause of prolonged recovery from anesthesia?
Answer choices:
- Hypotension
- hyperthermia
- hypertension
- hyperglycemia
hypotension
Which breed of dog is more likely to have postoperative bleeding related to Von Willebrand disease?
Doberman pinscher
forceful rinsing of a wound is called...
lavage
Which material is an example of occlusive dressing?
Answer choices:
- natural cellulose
- cotton gauze pads
- petroleum jelly-coated gauze pads
- antibiotic ointment-coated polyethylene sponges
natural cellulose
A catheter placed in which vein allows monitoring of central venous pressure?
Answer choices:
- cephalic
- jugular
- medial saphenous
- lateral saphenous
jugular
What type of physical therapy limits swelling by causing vasoconstriction?
Answer choices:
- Petrissage
- Cryotherapy
- Thermotherapy
- Passive ROM exercises
cryotherapy
Intervention for nutritional support should be provided when a patient has been completely anorexic for:
Answer choices:
- 2 days
- 4 days
- 3 days
- 5 days
3 days
the formation of a hematoma within the auricular cartilage on the concave surface of the ear
- forms when the cartilage in the ear pinna fractures, usually from violent head shaking or scratching at the ears
Aural hematoma
Aural hematomas occur most commonly in...
but also in cats and erect eared dogs
pendulous-eared dogs
What is the goal of Aural Hematoma surgery?
to alleviate the hematoma and prevent recurrence
What kind of incision do you make to drain the aural hematoma, to remove clot and scar tissue
'S' or linear incision on the concave surface of pinna
What is the conservative management options for Aural Hematomas?*note: this doesn't always work.
treat underlying disease, trocharization/needle decompression, local steroid injection, a wrap for at least two weeks
How long do you leave the Aural Hematoma surgery sutures and bandage in place for?
3 weeks
what is the tip of the ear called?
pinna
inside of the pinna is __________.
concave
outside of the pinna is __________.
convex
what is the medical abbreviation for the right ear?
AD
what is the medical abbreviation for the left ear?
AS
what is the medical abbreviation for the both ears?
AU
What are some indicators of facial nerve damage?
inability to blink eye, pupil sizes different, lip dropping, eyelid drooping
- resection of the lateral ear canal that involves lateralization of the horizontal ear canal
- create 2 vertical incisions along vertical ear canal; cartilage flipped down; skin sutured to cartilage
*indicated for animals with chronic otitis externa or neoplasia
lateral ear canal resection
What is used post-op for lateral ear canal resections, to protect the surgical site?
bandage over the ear, E-collar to be sent home with owner to avoid self-mutilation complications, analgesics sent home with owner
Although complications post-op for lateral ear canal resections are uncommon,
WHAT are potential complications we can see?
insufficient drainage, sustained ear infections
For lateral ear canal resections,
HOW soon can the suture be removed after surgery
10-14 days post-op
What is the medical abbreviation for the right eye?
OD
What is the medical abbreviation for the left eye?
OS
What is the medical abbreviation for the both eyes?
OU
ocular term for tear production...
lacrimation
ocular term for squinting, blinking excessively...
blepharospasm
ocular term for light sensitivity...
photophobia
ocular term for pulling back eye, which causes third eyelid protrusion...
enophthalmos
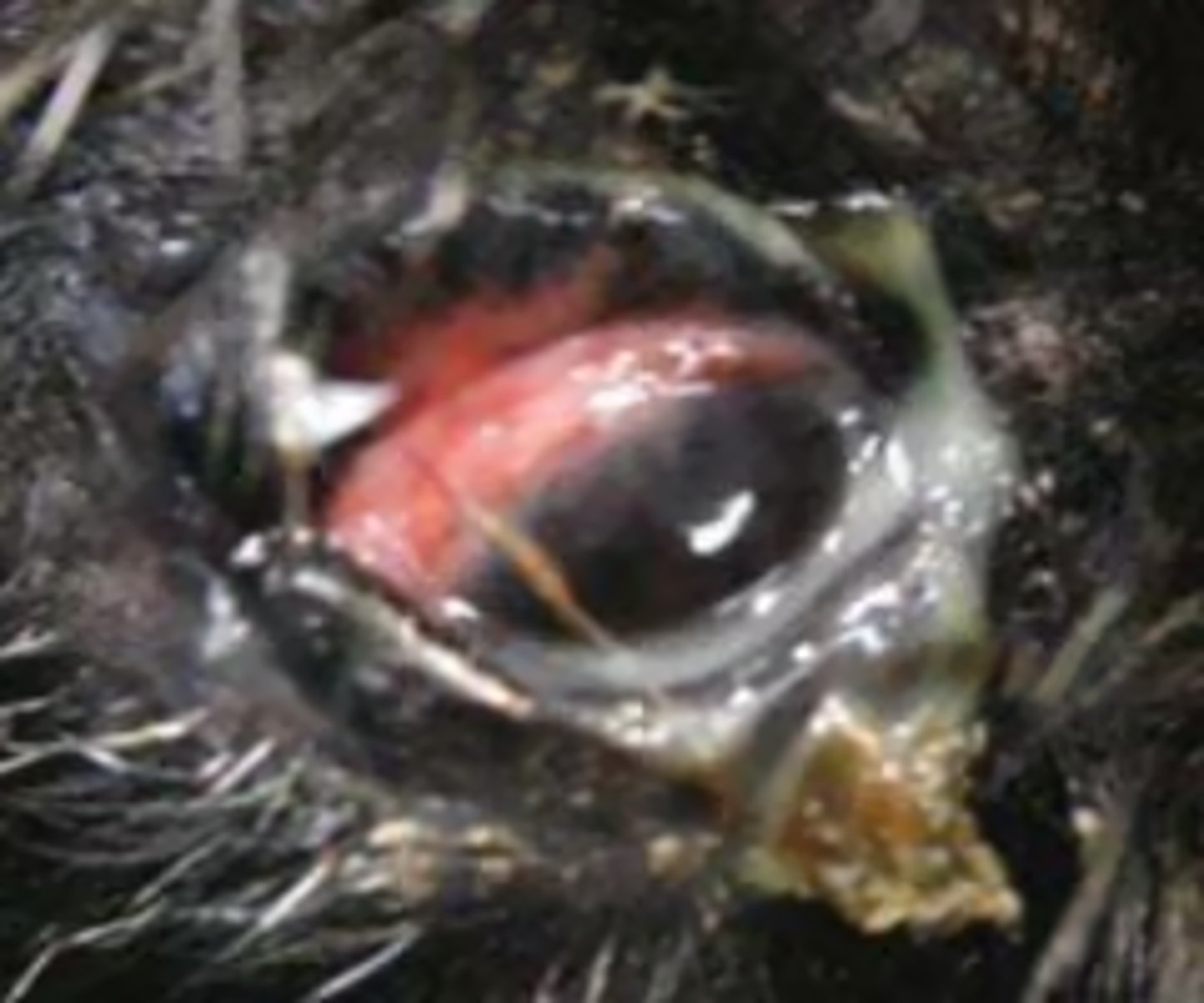
medical term for inflamed conjunctiva...
conjunctivitis
medical term for inflamed cornea...
keratitis
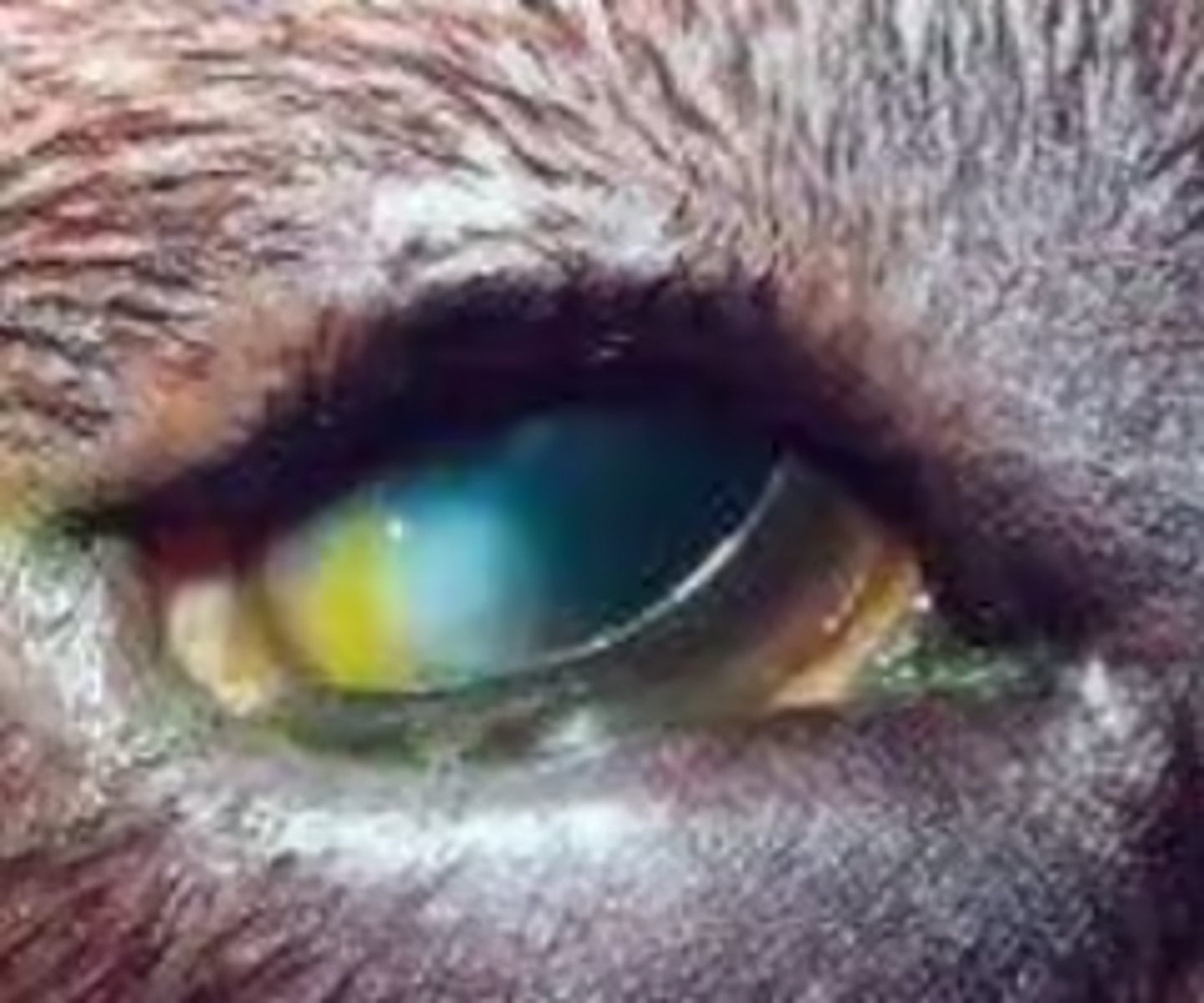

rolling in/inward of the eyelid...
entropion

rolling out/outward of the eyelid...*drooping of eyelid
ectropion
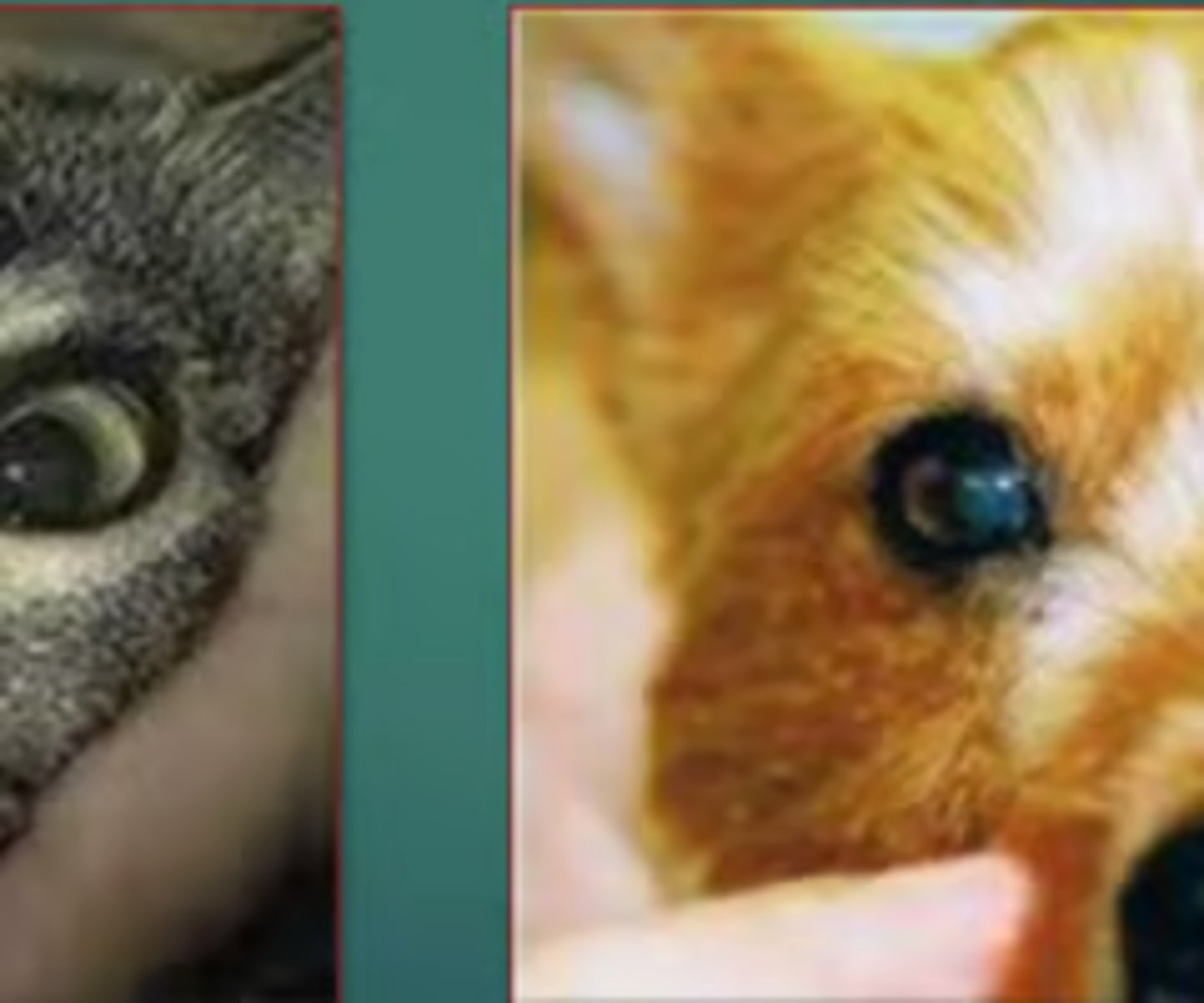

ocular term for when the pupils are different sizes
anisocoria
prolapse of the third eyelid gland
*seen in puppies
breeds predisposed: English bulldog, Boston terrier, Great Dane, pug
cherry eye
What can NEVER be used in or around the eye (for a scrub during ophthalmic surgery)?
*it causes ulcers (very painful!)
Chlorhexidine
What should you use around the eye as a scrub during ophthalmic surgery, to aseptically prepare the area?
*to protect delicate structures
very dilute 1:50 povidone-iodine/Betadine solution
Post-op care of eyelid surgery includes...
e-collar until sutures are removed, restriction of activity, pain meds, ocular antibiotics ointment or drops, warm compresses, recheck in 10-14 days
When should you start warm compresses after eyelid surgery?
2 days after
When should re-checks take place after eyelid surgery?
10-14 days, sooner if there are any problems
For eyelid masses in dogs, are they are usually benign or malignant?
usually benign, malignant may occur
For eyelid masses in cats, are they are usually benign or malignant?
usually malignant
Regarding eyelid masses in dogs, what is the most common mass type?
Meibomian/sebaceous adenoma
Regarding eyelid masses in cats, what is the most common mass type?
squamous cell carcinoma
Eyelid masses are more common with cats who have...
white or pink eyelids
What breeds of dogs are more predisposed to eyelid masses?
poodles, Labrador retrievers, mixed breeds
How are patients for eyelid mass removal (and most other ophthalmic procedures) positions?
In other words, what is the recumbency for surgery?
sternal or lateral, sandbags used to help position the head
What is the indication for a patient to undergo a Zepp/Lateral ear resection procedure?
Answer choices:
- dystocia
- cystic calculi
- urethral obstruction
- chronic ear infection
chronic ear infection
Removal of the gland of the third eyelid can lead to...
Answer choices:
- entropion
- cherry eye
- photophobia
- keratoconjunctivitis sicca
keratoconjunctivitis sicca/dry eye
What does LASER stand for?
light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
What kind of lasers are most commonly used for laser surgey?
CO2 and diode
- these layers DO NOT contact tissue
- intensity is controlled by distance and length of exposure
- highly absorbed by water
- operated through photothermal laser-tissue interaction
CO2 lasers