Week 9 - Protozoans part 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Infective stage
Refers to the stage of the parasite that enters the host or the stage that is present in the parasite’s source of infection
Pathogenic stage
Refers to the stage of the parasite that is responsible for producing the organ damage in the host leading to the clinical manifestation
Encystation
Process by which trophozoites differentiate into cyst forms
Excystation
process by which cysts differentiate into trophozoite forms
Kingdom Protozoa
single-celled eukaryotic organisms
Spherical or elongated in shape
Classification is based on the organ of locomotion
Not all protozoan are parasitic
Amoeba - pseudopods (false feet)
Flagellates - Flagella
Ciliates - Cilia
Sporozoans - non-motile (obligate parasites)
Some are facultative parasites - capable of free-living state
Examples : Acanthamoeba and Naegleria
>Normally reside in the soil or water but can cause severe illness when they gain entrance in the central nervous system or the eyes.
Binary fission (Asexual reproduction)
Reproduction of Protozoa (e.g. flagellates, ciliates, and amebae)
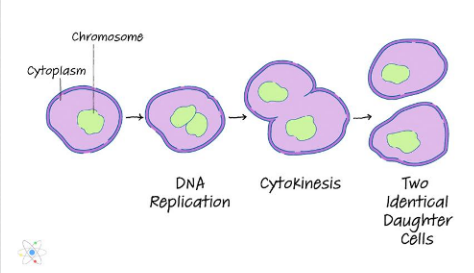
Sexual and asexual reproduction
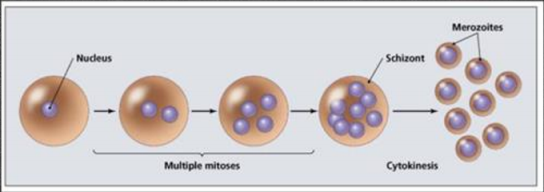
Reproduction of sporozoan
Trophozoite
Motile, feeding, dividing stage of the parasite
Pathogenic stage
Cyst
dormant non-motile form
infective stage
Trichomonas vaginalis
A parasite where cysts forms are not found
Entamoeba histolytica
Is an intestinal and tissue amoeba and is the only known pathogenic intestinal amoeba
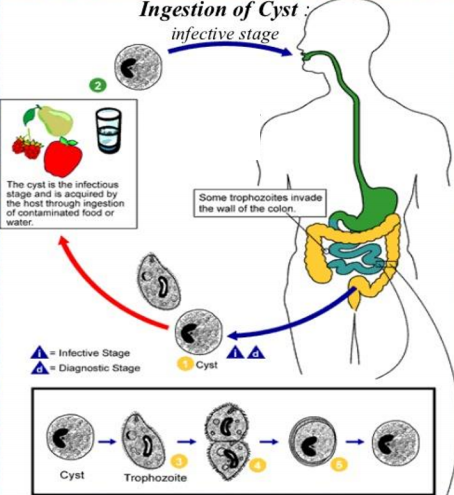
Consists of two stages: the non-motile cyst (infective stage) and the motile trophozoite (pathogenic stage).
the trophozoite is found within the intestinal and extraintestinal lesions and in diarrheal stools:
cysts are found in non-diarrheal formed stools
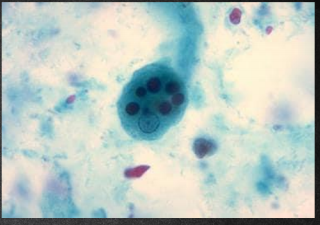
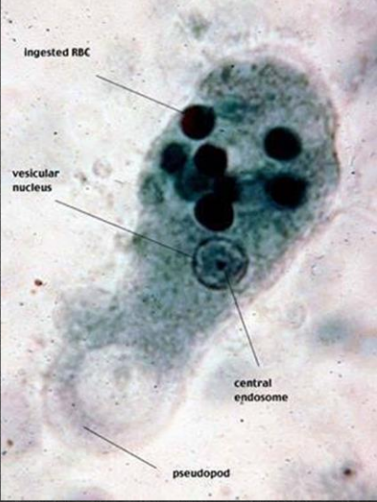
E. histolytica trophozoite forms
Size range: 8-65 um (micro meter)
Shape: irregular
Motility: Yes (with finger-like pseudopodia)
Number of nuclei: One
Karyosome: Small and Central
Peripheral chromatin: Fine and evenly distributed
Cytoplasm: Finely granular
Cytoplasmic inclusions: Ingested red blood cells
E. histolytica cysts forms
Size range: 8-22 um (micro meter)
Shape: Spherical to round
Motility: No
Number of nuclei: One to four
Karyosome: Small and Central
Peripheral chromatin: Fine and evenly distributed
Cytoplasm: Finely granular
Cytoplasmic inclusions: Chromatoid bars and diffuse glycogen mass in young cysts
Pathogeneis of cyst
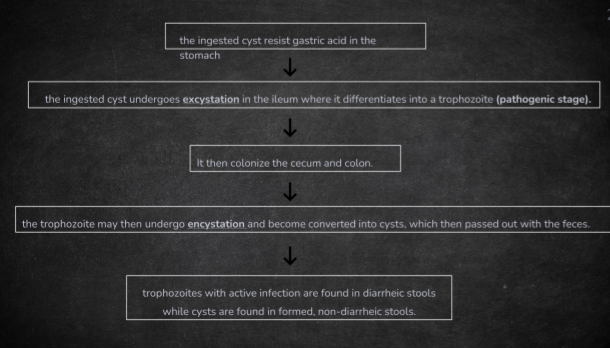
Life Cycle of Entamoeba Histolytica
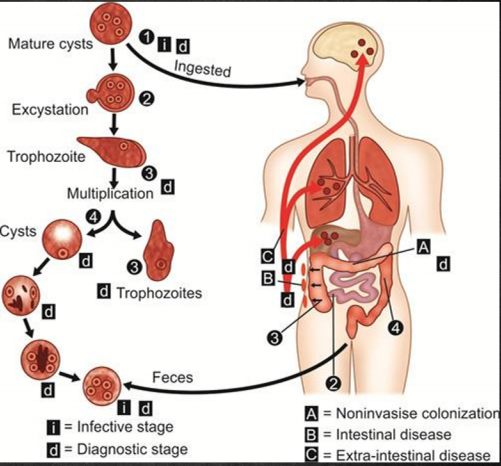
local necrosis
The trophozoites of E. histolytica secrete enzymes that cause ___ producing the typical “flask-shaped” ulcer associated with the parasites
Note: Invasion of the portal circulation may occure leading to the development of abscess in the liver,lungs, and the brain
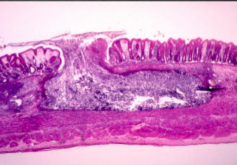
Acute intestinal amoebiasis
Presents a blood; mucus-containing diarrhea (dysentery) accompanied by lower abdominal discomfort, flatulence (release of gas) and tenesmus (feeling of incomplete defecation)
Chronic inflammation may occure, with symptoms such as occasional diarrhea, weight loss and fatigue
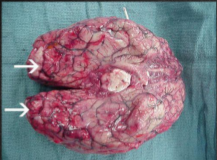
In some patients. a lesion called an amoeboma may form in the cecum or in the rectosigmoid area of the colon, which may be mistaken for a malignant tumor in the colon
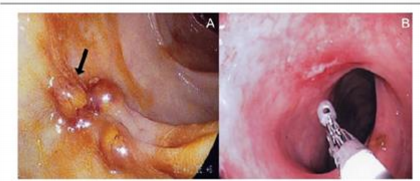
Extraintestinal Amoebiasis
Occurs when the parasite enters the circulatory system
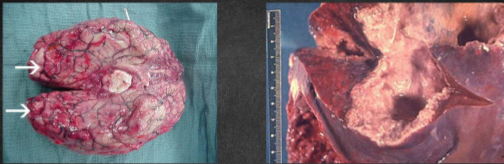
Most common extraintestinal form is the amoebic liver abscess
Characterized by right upper quadrant pain, weight loss, fever, and a tender and enlarged liver
Abscess found on the right lobe of the liver may penetrate the diaphragm and cause lung disease (Amoebic pneuomonitis)
Other organs that may become infected include the pericardium, spleen, skin, and brain (Meningoencephalitis)
Amoeboma
In some patients. a lesion called an___ may form in the cecum or in the rectosigmoid area of the colon, which may be mistaken for a malignant tumor in the colon
Amoebic Pneumonitis
Abscess found on the right lobe of the liver may penetrate the diaphragm and cause lung disease
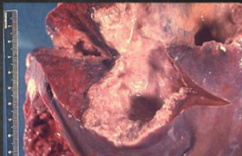
Meningoencephalitis
Other organs that may become infected include the pericardium, spleen, skin, and brain
Asymptomatic carrier state
Occurs under the ff conditions:
(a) if the parasite involved is a low-virulence strain:
(b) if the parasite is low;
(C) if the patient’s immune system is intact
In these cases, patient presents no symptoms but the parasite reproduces and is passed out with the patient’s feces
diarrheic stools
Diagnostic of intestinal amoebiasis is confirmed by:
E. histolyitca Trophozoites > in a __ or;
E. histolyitca Cysts > in formed stools
formed stools
Diagnostic of intestinal amoebiasis is confirmed by:
E. histolyitca Trophozoites > in a diarrheic stools or;
E. histolyitca Cysts > in ___
Ingested red blood cells
E. histolyitca Trophozoites characteristically contain ___ during diagnostic test
hour of collection
the stool specimen should be examined within an ___ to see the motility of the E. histolyitca trophozoites
Serologic testing
Another test that may be useful for the diagnosis of invasive amoebiasis
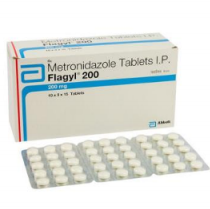
metronidazole
Treatment of choice for symptomatic intestinal amoebiasis or hepatic abscess
Tinidazole
alternative drug for both intestinal and extraintestinal amoebiasis
Diloxanide furoate, metronidazole, or paromomycin
treatment for asymptomatic carrier with E. histolytica
Good personal hygiene: by washing of hands, especially for food handlers
Proper waste disposal to avoid fecal contamination of water sources
Avoid the use of '“night soil“ (human feces) for fertilization of crops
Adequate washing and cookig of vegetable should be observed
Prevention and control for E.histolytica
Gardia Lamblia (Giardia Intestinalis)
Iinitially known as Cercomonas intestinalis. Another name used is Giardia duodenale
The parasite also exists in a cyst form and a trophozoite form
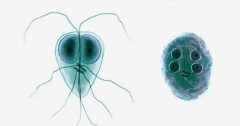
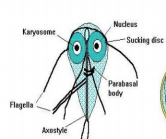
Giardia Intestinalis trophozoite form
Pear-shaped or teardrop-shaped with 4 pairs of flagella and has a motility likened to a falling leaf
Resembling to an old man with whiskers (“old man facies”)
It also possess a sucking disc which the parasite uses to attach itself to the intestinal villi of the infected human
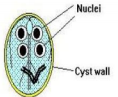
Giardia Intestinalis cysts form
Oval and thick-walled with 4 nuclei. It divides through binary fission. Each cyst gives rise to two trophozoites during excystation in the intestinal tract
Pathogenesis of Giardia Intestinalis

Life Cycle of Giardia Intestinalis
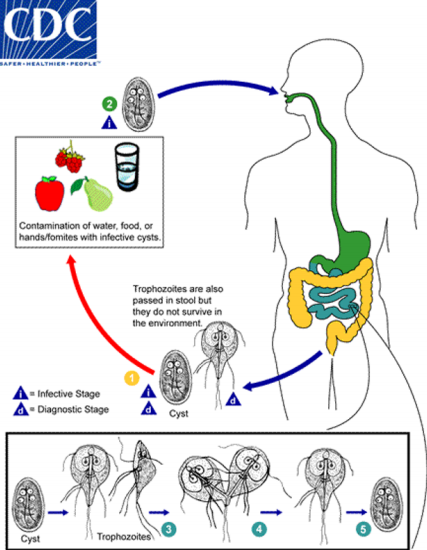
Asymptomatic carrier state (Giardiasis)
Infection with the parasite is usally completely asymptomatic. The infected individual unknowingly passes out the parasite with the feces which can contaminate water
Giardiasis (Traveler’s diarrhea)
The infection is characterized by a non-bloody foul smelling diarrhea accompanied by nausea, loss of appetite, flatulence, and abdominal clamps
The symptoms may persist for week or montjs
Malabsorption of fat may lead to the presence of fat in the stool (steatorrhea)
Patients are usually afebrile
Manifestation resulting to malabsorption may include deficient in fat-soluble vitamins, folic acid, and proteins
Self-limiting infection, lasting one to two weeks. Relapse may occur, esp in patients with Iga deficiency
A
D
E
K
Fat soluble vitamins
Vitamin A
Vision, Reproduction, Bone Health, Immune System, Skin
Vitamin D
Strengthens Bones, Calcium Absorption, Immune System
Vitamin E
Immune System, Flushes toxins
Vitamin K
Blood clotting, Bone health
diarrheic stools
diagnosis is made by demonstration of the giardia intestinalis cyst or trophozoite (or both) in ___
Cysts
Only giardia intestinalis ___ are isolated from the stools of asymptomatic carriers
String test
If microscopic examination of stool is negative for giardia intestinalis. ___ may be performed
Metronidazole, tinidazole, and nitazoxanide
treatment of Choice for G. lamblia are ____
Avoidance of fecal contamination of water supplies through proper waste disposal
Drinking water should be boiled, filtered or iodine-treated especially in endemic areas
Proper hand washing is recommended
Prevention and Control (Giardia intentestinalis)
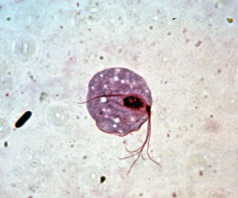
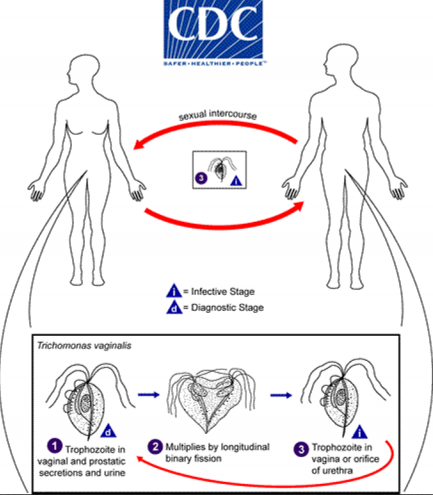
Trichomonas Vaginalis
Parasite is pear-shaped organism; central nucleus, four anterior flagella, and an undulating membrane
It exisrs only in the trophozoite form (infective and pathogenic)
It is not an intestinal pathogen. It causes urogenital infections and transmitted through sexual intercourse
Isolated form the urethra and vagina>in infected women; Isolated in the urethra and prostate gland>in infected men
Infection is highest among sexually-active women in their thirties and lowest in postmenopausal women.
Occasionally, the parasite may be transmitted through toilet articles and clothing of infected individuals
Infants may be infected as they pass through the infected birth canal during delivery
the parasite invades the vaginal mucosa of infected women, where they multiply through binary fission
the trophozoites feed on local bacteria and leukocytes
In men, most common infection site is the prostate gland and the urethral epithelium
Life cycle of Trichomonas Vaginalis
Trichomoniasis (Infection in men)
Usually asymptomatic; men serve as the resevoir for infection in women.
In men who develops symptoms, manifestations are related to prostatits (inflammation of the prostate), urethritis (manifests as discharge), and other urinary tract involvement.
Persistent or recurring urethritis is the common symptomatic form of infection
Trichomoniasis (Infection in women)
Also asymptomatic; some women may present with scant, water vaginal discharge
More sever cases: discharge may be foul smelling and greenish-yellow in color; accompanied by itching (pruritus), and burning sensation in the vagina. Cervix may appear red, with small punctuate hemorrhage, giving rise to a strawberry cervix
Other symptoms include dysuria and increased frequency of urination
Trichomoniasis (Infection in infants)
Occurs as the infant passes through the infected birth canal of the mother during vaginal delivery.
the infected infants may manifest conjunctivits or respiratory infection
Wet mount
Findings of the trophozoites in a ___ of vaginal or prostatic secretions, urine, and urethral discharges
Metronidazole
drug choice for trichomoniasis. All sexual partners of an individual with the infection must be simultaneously treated to prevent “ping pong” infections
Practice safe sex; use of condoms can limit the transmission of the parasite
Health and sex education is important
Maintenance of the acidic pH of the vagina may also be helpful
prevention and control (Trichomoniasis)
Balantidium Coli
is morphologically more complex than E. histolytica
it has a primitive mouth called a cystome, a nucleus, food vacuoles, and a pair of contractile vacuoles.
The infective stage is the cyst and the pathogenic stage is the trophozoite, which invades the mucosal lining of the terminal ileum, cecum and colon.
It is the largest protozoan to infect humans
the trophozoites exhibit a rotary, boring motility (through cilia) and contain two nuclei (a small dot-like micronucleus adjacent to a kidney bean-shaped macronucleus
The cyst also contains two nuclei although micronucleus may not be readily observable
Parasite has a worldwide distribution. The most common and important resevoir is the pig.
Monkeys may occasionally act as resevoirs of the parasite.
The main source of infection is water contaminated by pig feces and the mode of transmission is through the fecal-oral route.
Person-to-person transmission via food handlers has been implicated in outbreaks.
The cysts are found in contaminated water, which when ingested, undergoes excystation in the small intestines.
From there, the trophozoites travel to the large intestines where they produce ulcers similar to those seen in amoebiasis
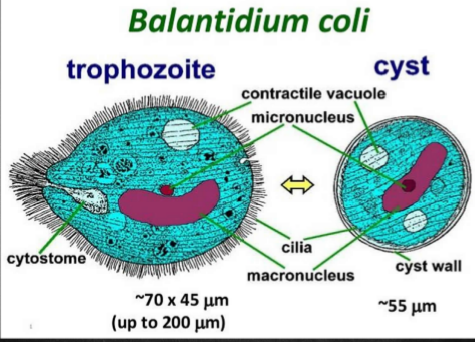
Life Cycle of Balantidium Coli
Balantidiasis
Most infected individuals are asymptomatic.
a dystenteric type of diarrhea resembling amoebic dysentery may occure in patients with high parasite load
Acute infections may manifest with liquid stools containing pus, blood, and mucus
Chronic infections may manifest with a tender colon, anemia, wasting (cachexia), and alternating diarrhea and constipation.
Extraintestinal infection is rare and may involve the liver, lungs, mesenteric nodes, and urogenital tract.
fresh, wet microscopic preparations
based on finding Trichomonas vaginalis trophozoites and cysts in the stool specimen
Due to its large size, the parasite can be readily detected in _____
oxytetracycline and iodoquinol
the treatment of choice for trochonomas vaginalis involves two drugs: ____
Metronidazole
it may also be used as alternative to treat infected patient with Trochonomas vaginalis
Sanitary hygiene
Proper disposal of pig feces
Boiling of drinking water
Prevention and control of Trochonomas vaginalis