Biology Exam #1 - Chapters 1-3
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What is inductive reasoning?
Bottom-Up reasoning, moves from specific observations to a broader generalization or theory
What is deductive reasoning?
Beginning with a generalized principle and moving to specifics (Top-Down)
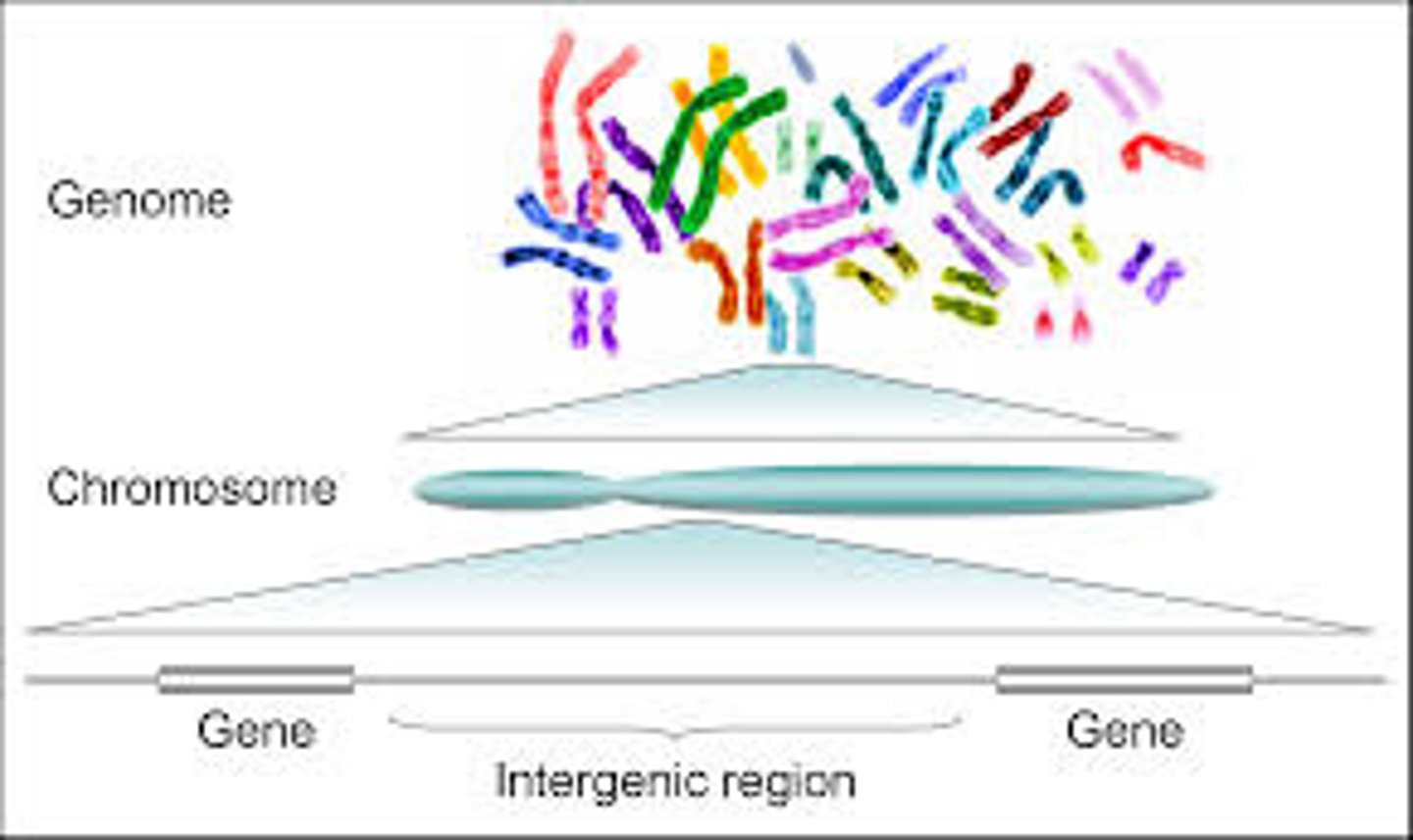
What is a genome?
The entire set of genetic material in an organism
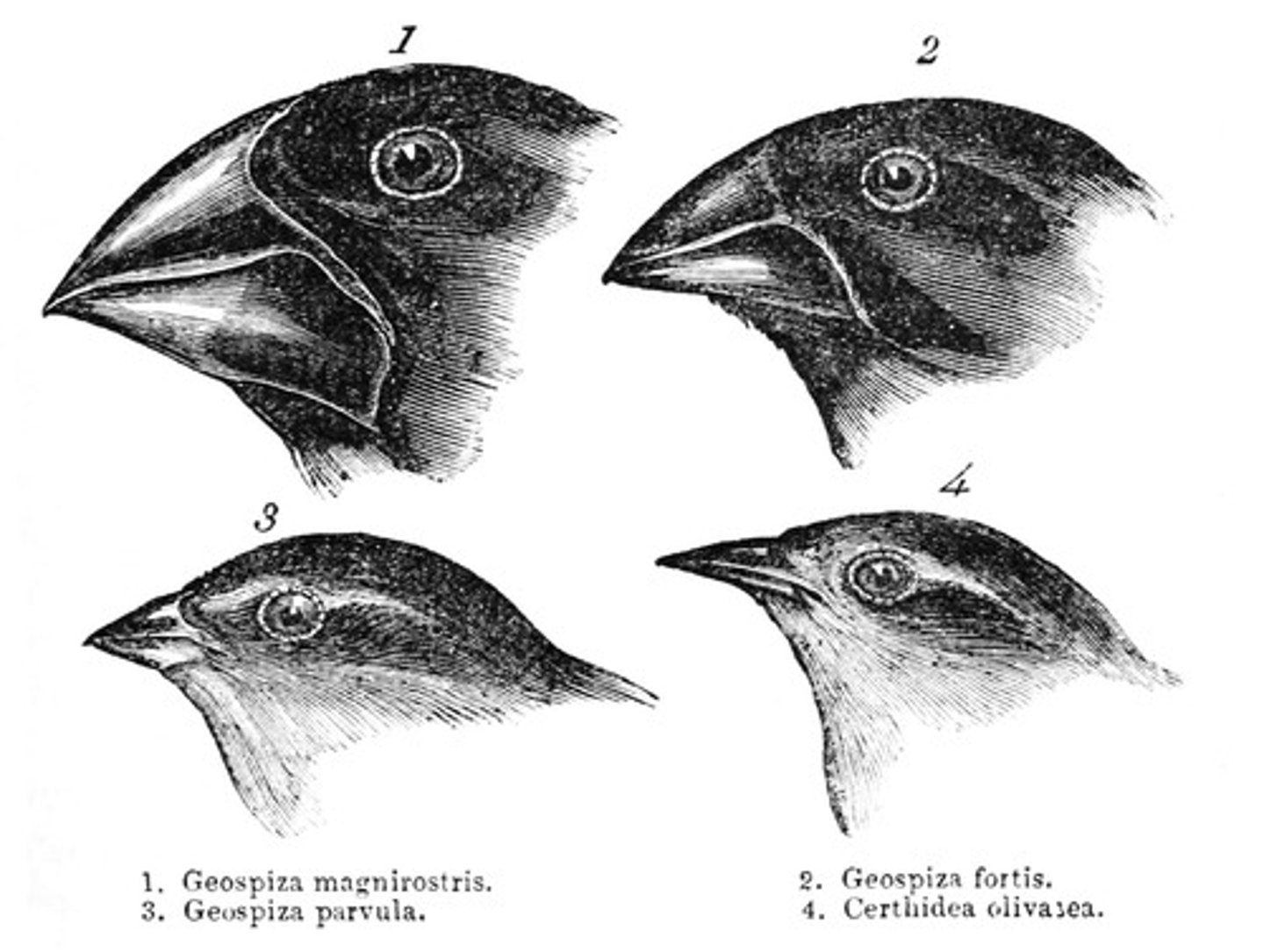
What did Charles Darwin discover?
Natural selection drives evolution
What is an acid?
a source of hydrogen ions, H⁺
What is a base?
less concentration of H+ ions; >7
Carbon's importance in biology
"Backbone" of macromolecules
What is an organic molecule?
a molecule that contains carbon
What is a macromolecule?
a molecule containing a very large number of atoms; proteins, lipids, carbs, nucleic acids, etc.
What is a eukaryote
cell with a nucleus

What is a prokaryote
A cell without a nucleus; "pro" = no. Usually bacteria

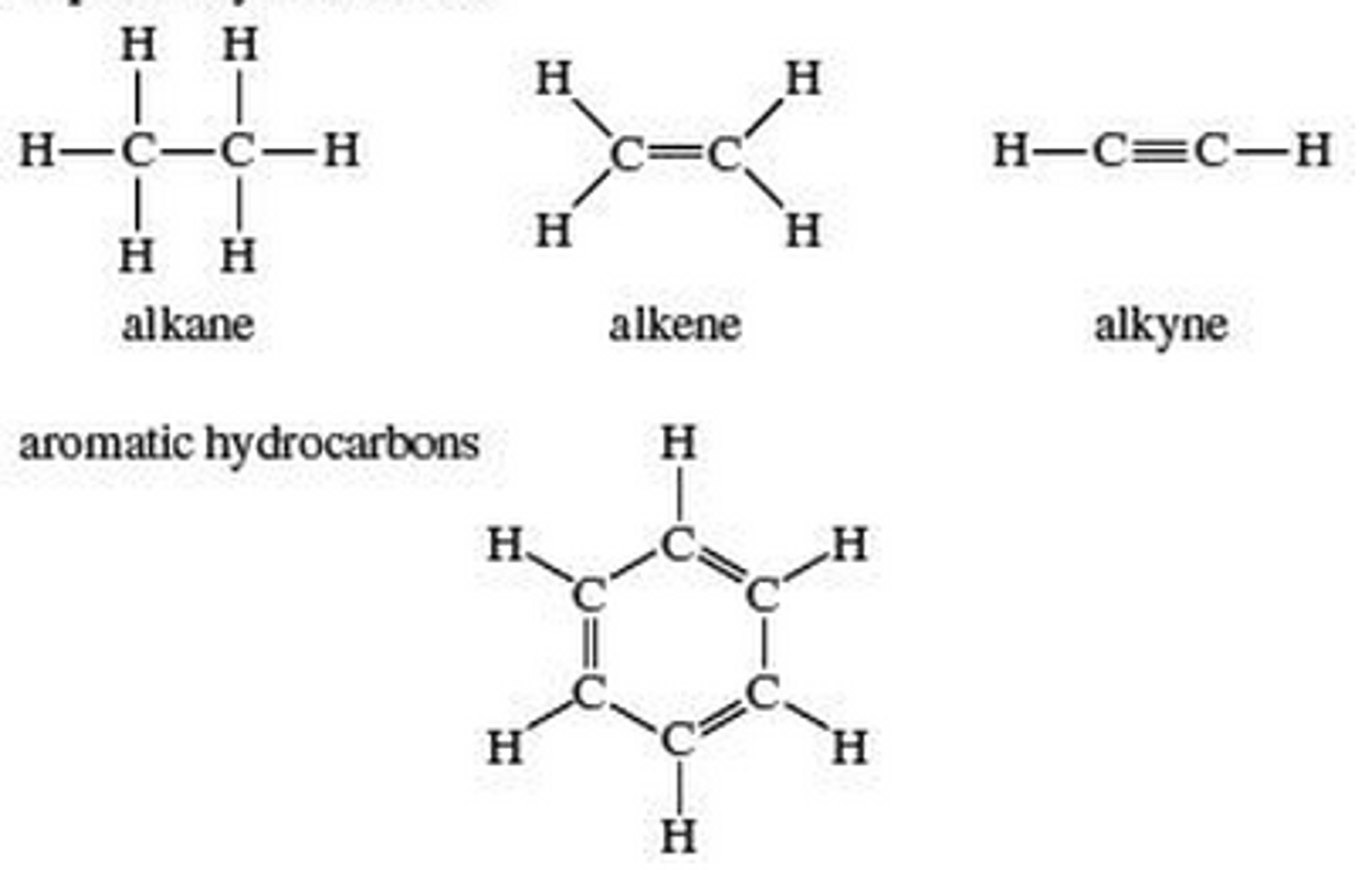
What is a hydrocarbon?
a compound made of hydrogen and carbon atoms; used as fuel.
What is an isomer?
Compound with the same atoms, but arranged differently
What is a geometrical isomer?
Compounds that have the same atoms, but have a different arrangement of atoms around a double bond
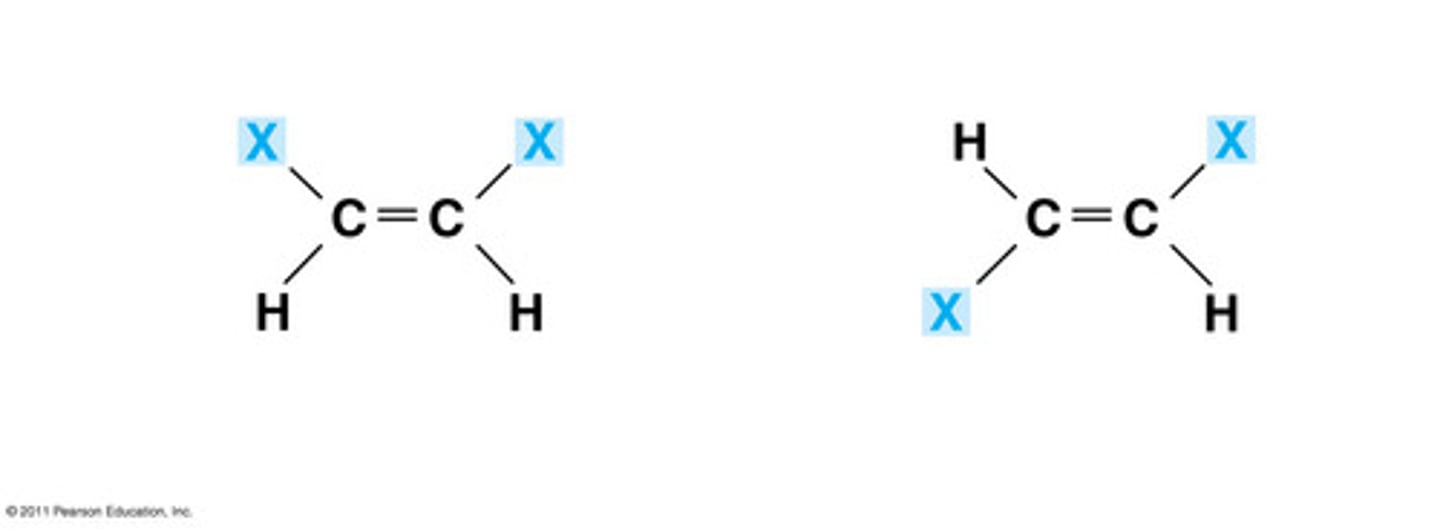
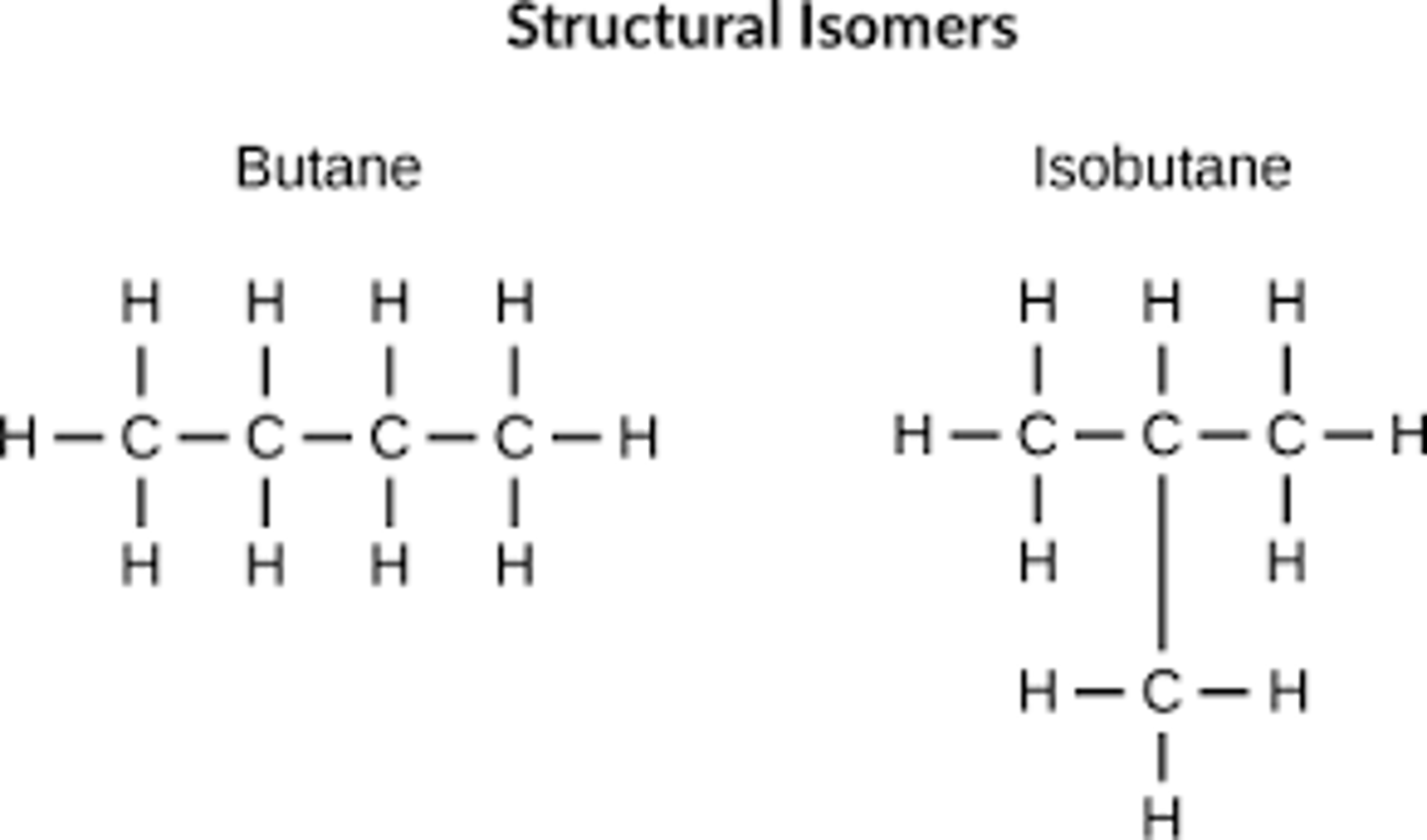
What is a structural isomer?
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
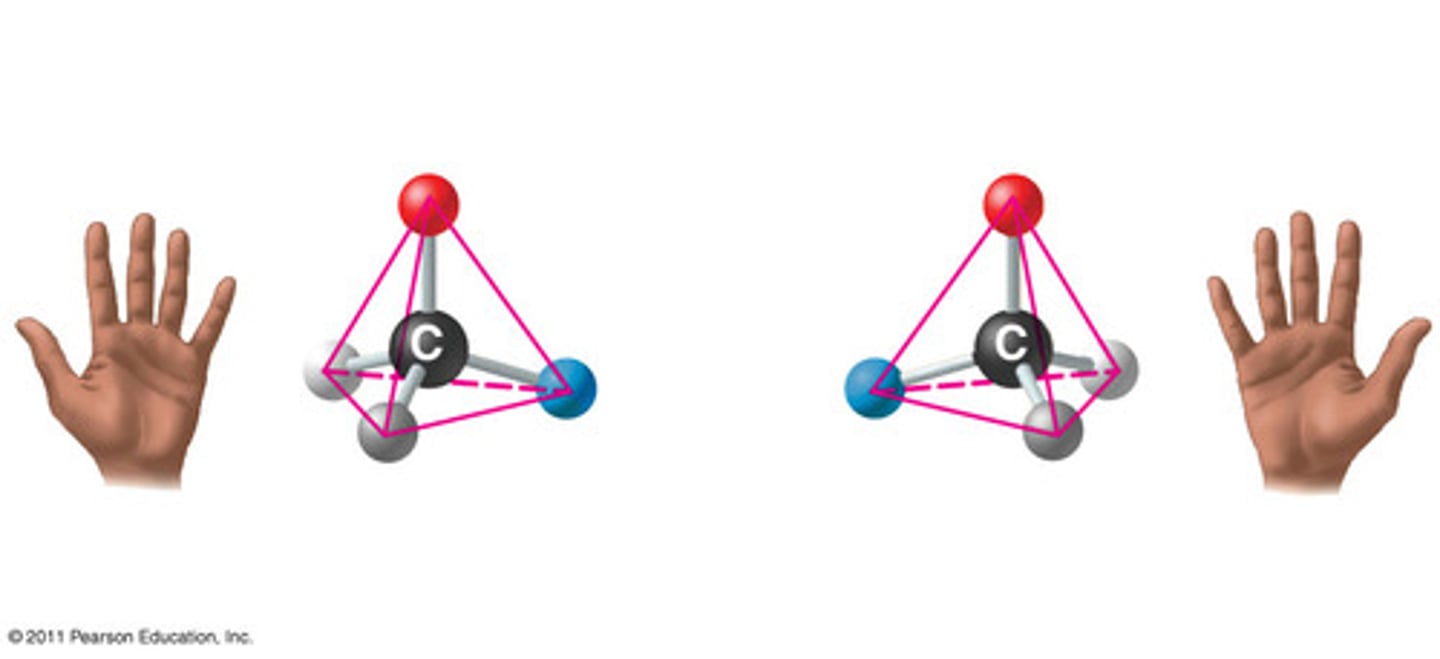
What is an enantiomer?
Non-superimposable mirror image
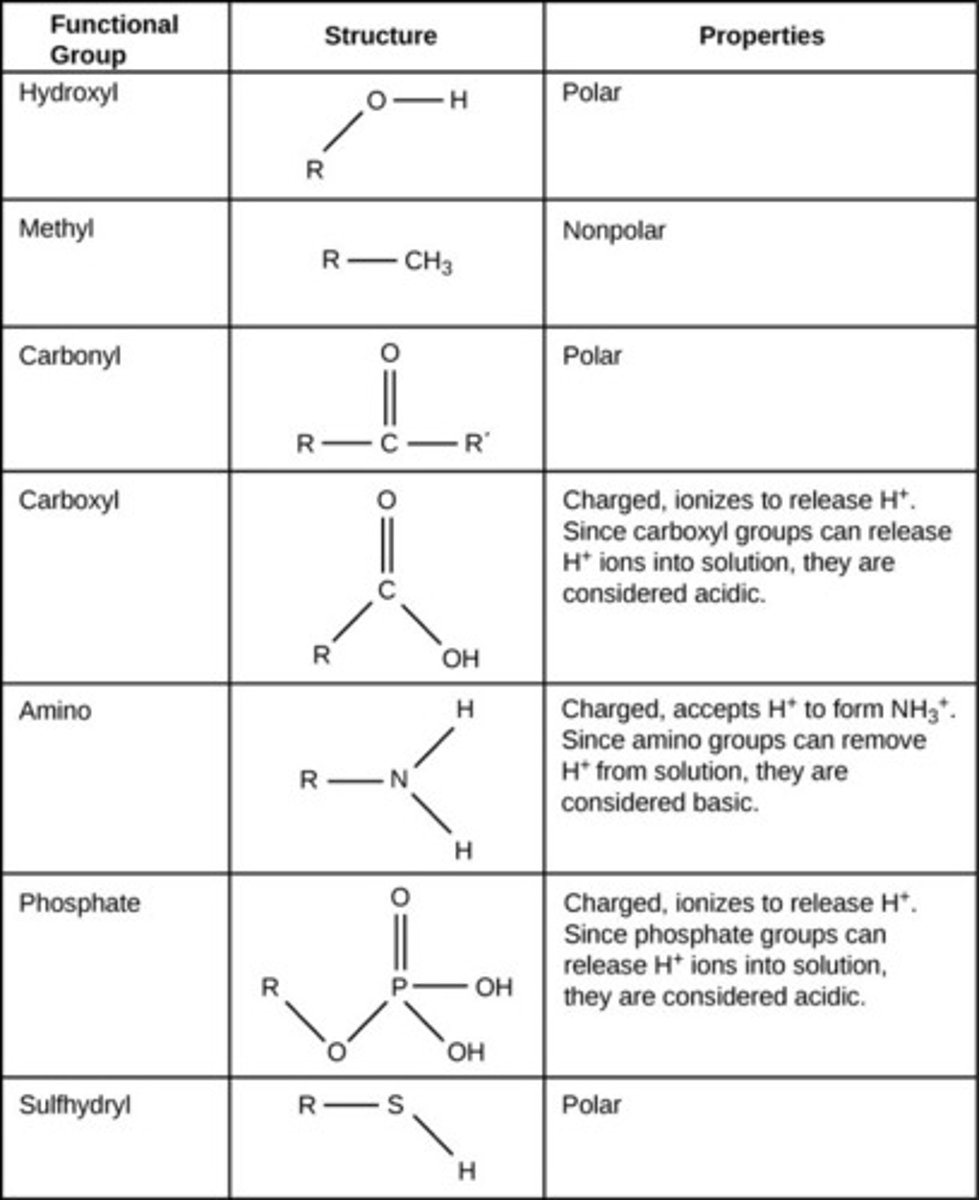
What are functional groups?
hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate, methyl. Found in the backbones of macromolecules. Helps maintain shape/folding
What does a buffer do for pH?
Neutralizes the pH.
What is a dehydration synthesis?
removal of one H2O molecule to combine two monosaccharides
What is hydrolysis?
The separation of two macromolecules by adding water.

What are monomers?
what most macromolecules are made up of; building blocks of polymers
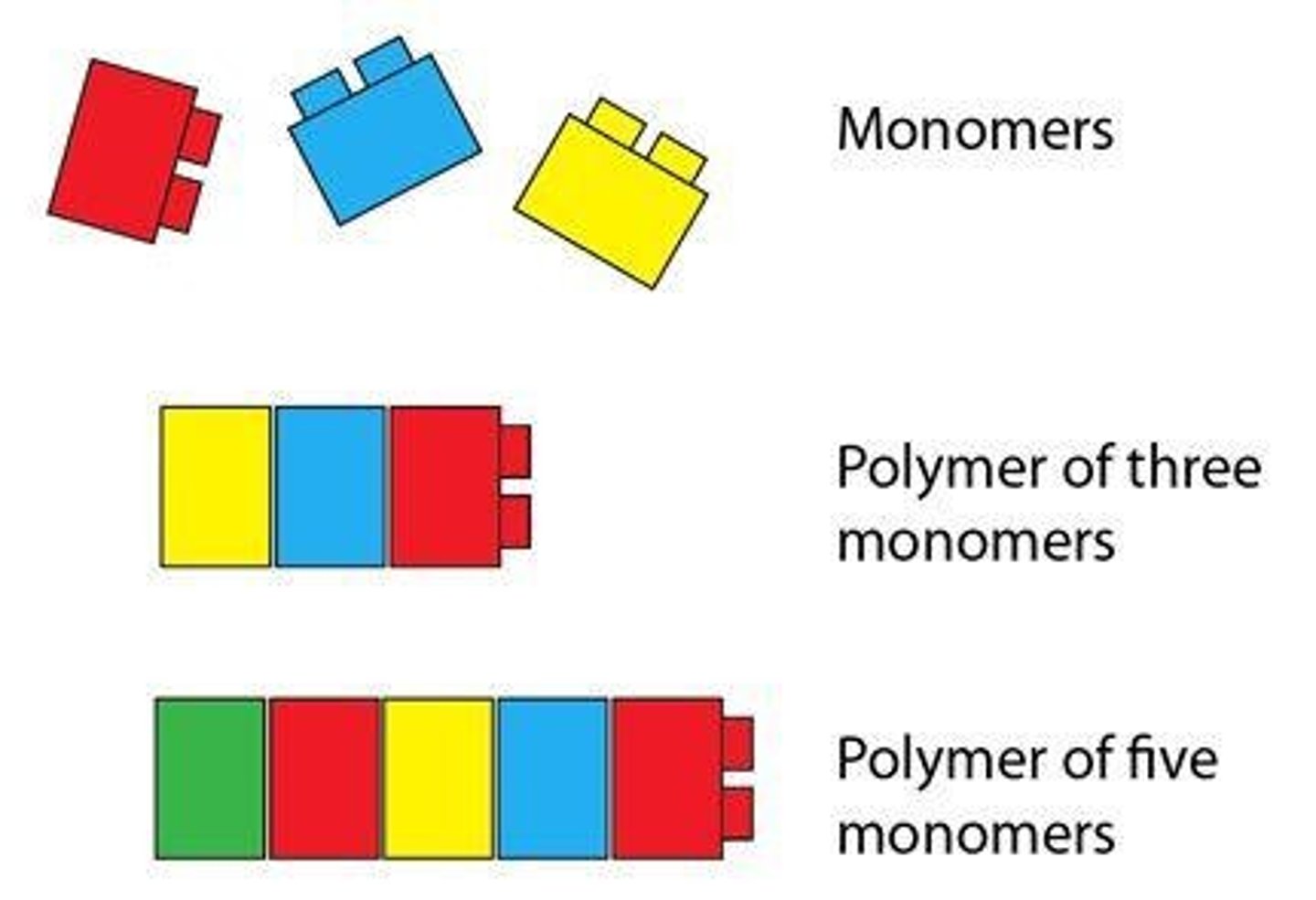
What is a polymer?
long chain of monomers
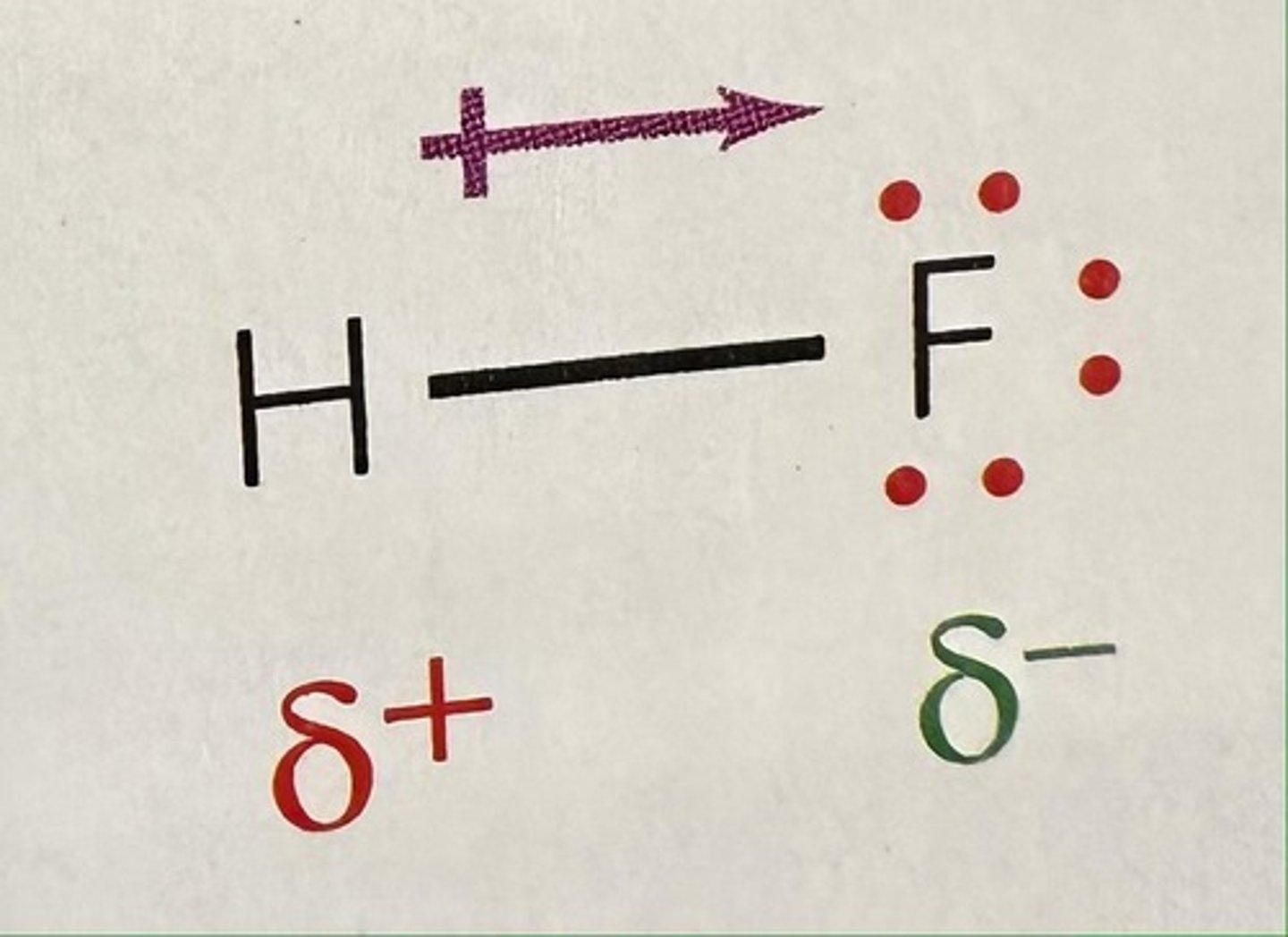
What is polarity?
a molecule in which the charges are unevenly distributed.
What is an aldehyde?
A carbonyl is bonded to at least one hydrogen; O=C-H. At the end of the chain.

What is a ketone?
carbonyl group bonded to 2 carbons; C=O. Located within the chain.
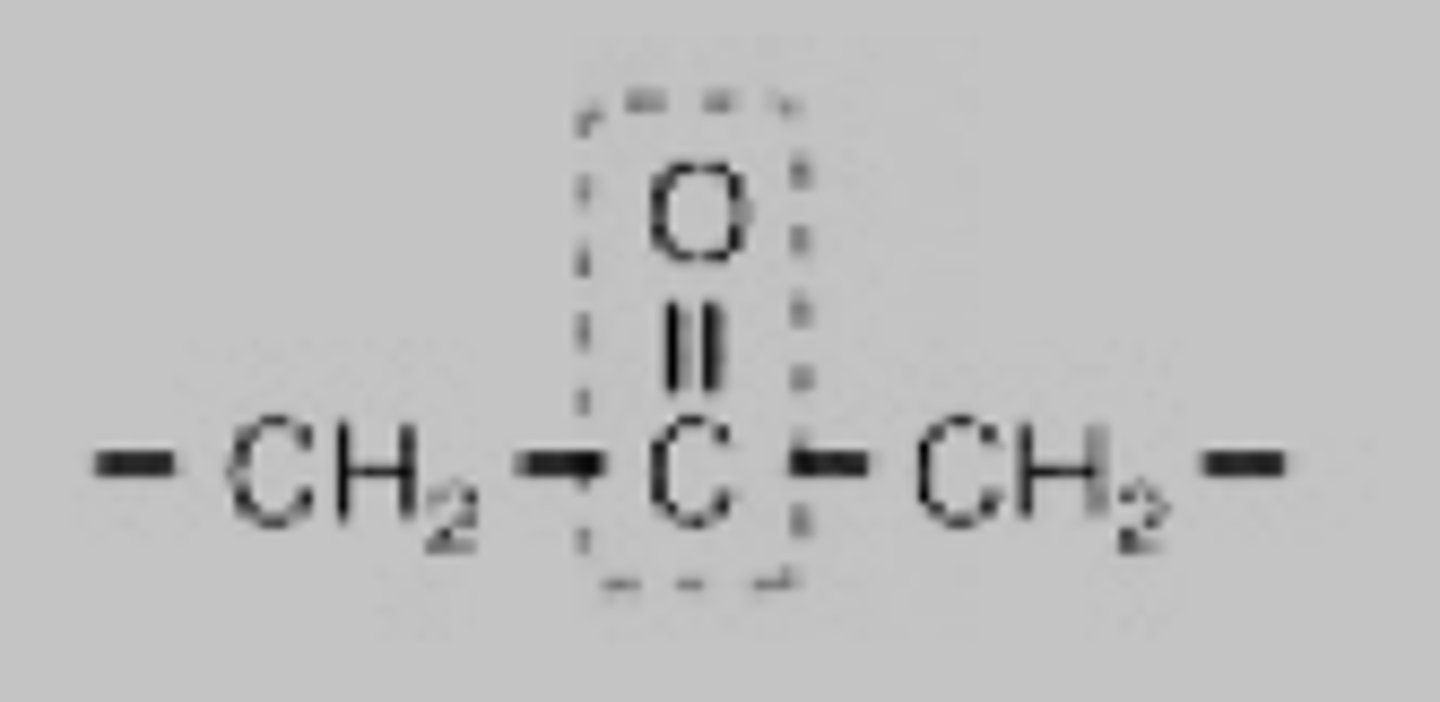
What is a carbohydrate?
compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; major source of energy for the human body
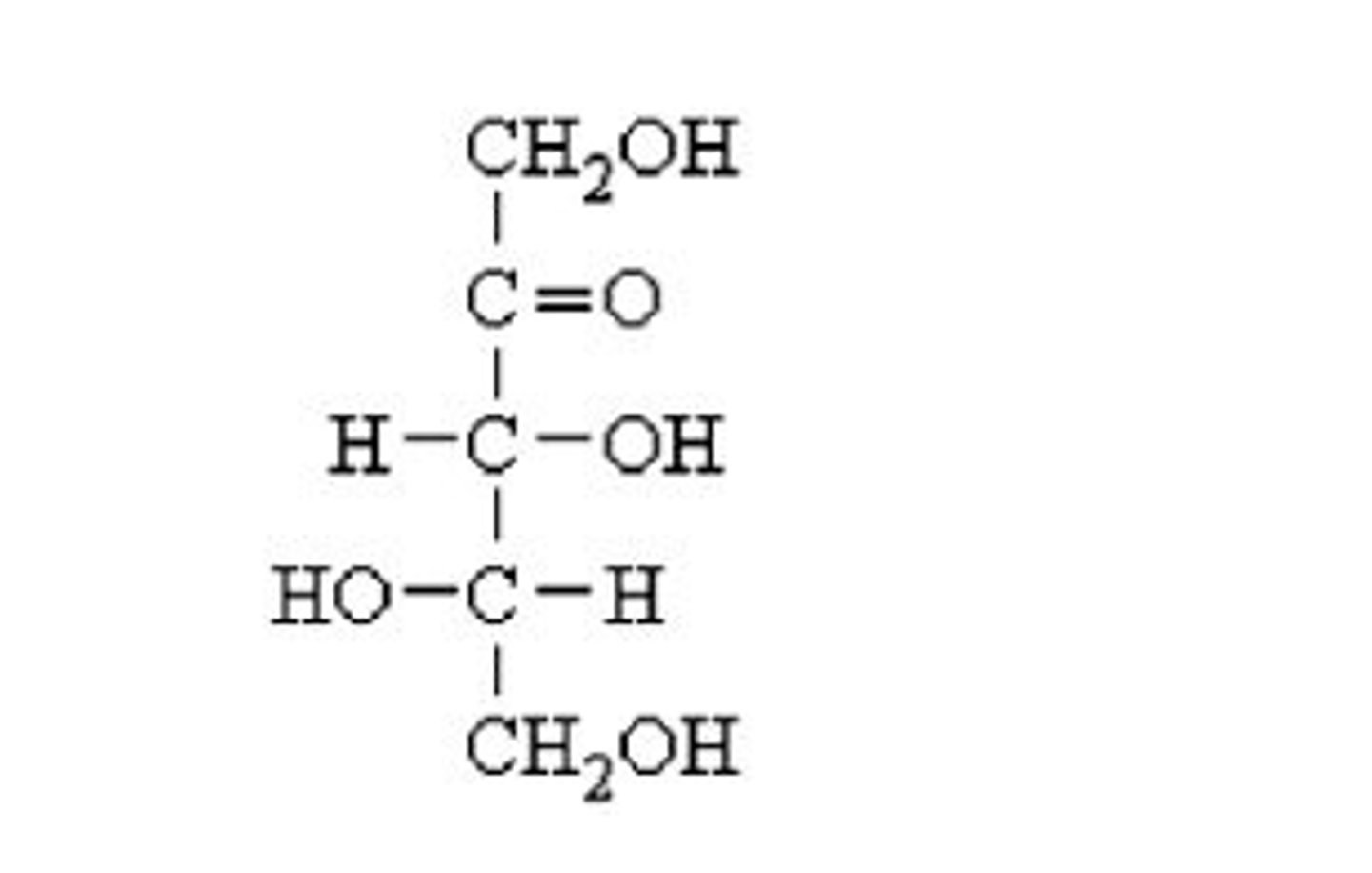
What is a monosaccharide?
simple sugar

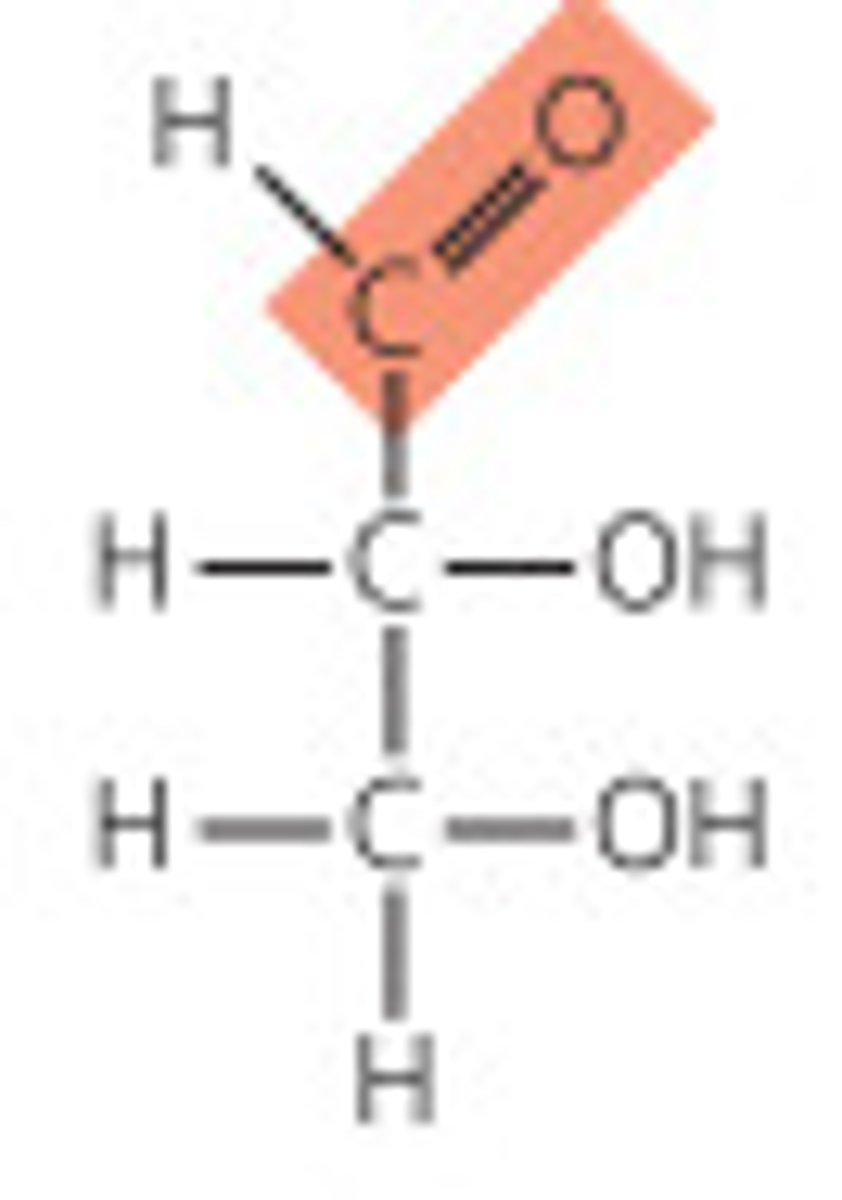
What is aldose?
Monosaccharide with an aldehyde functional group.
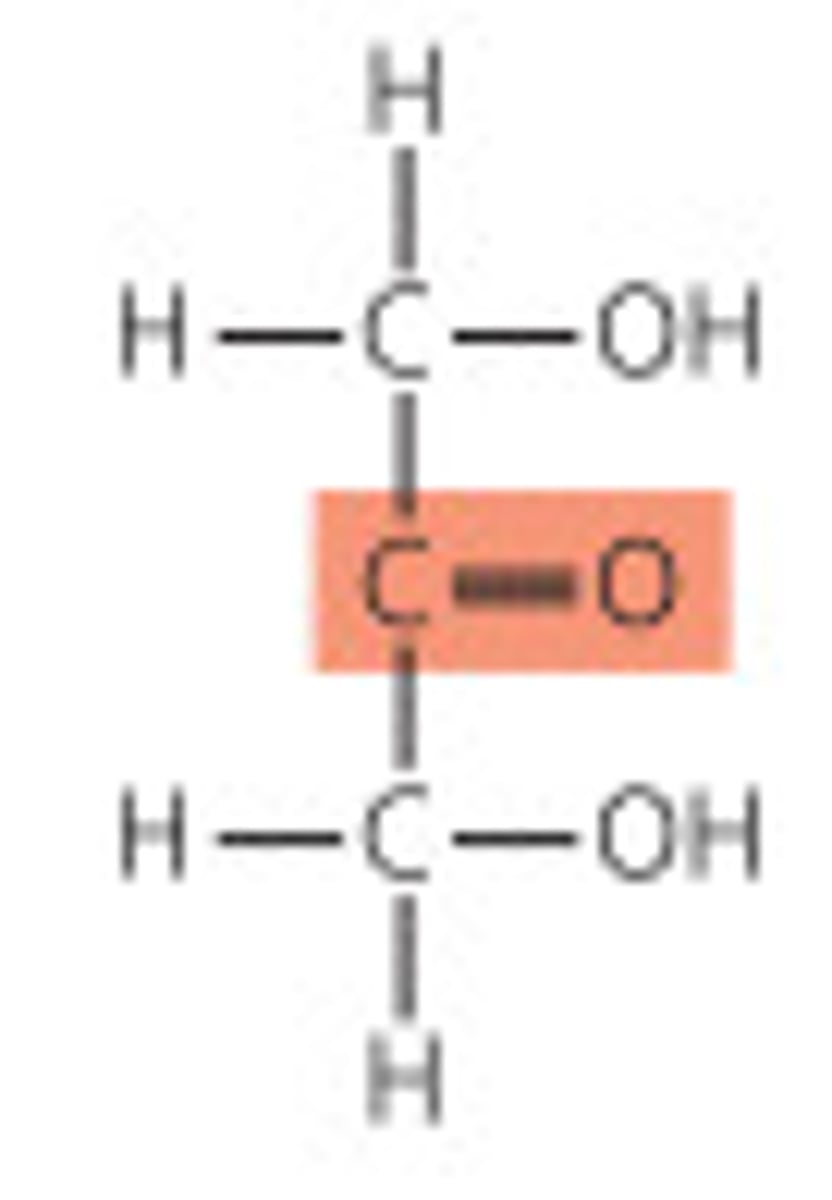
What is a ketose?
Monosaccharide with a ketone group.
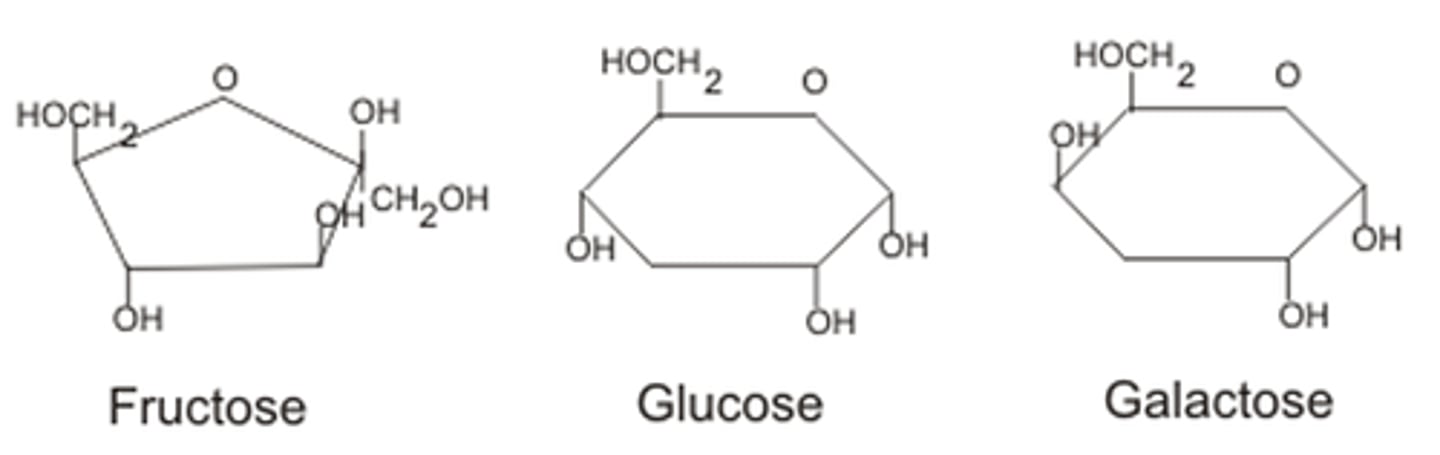
Examples of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
What is a disaccharide?
Two monosaccharides joined together
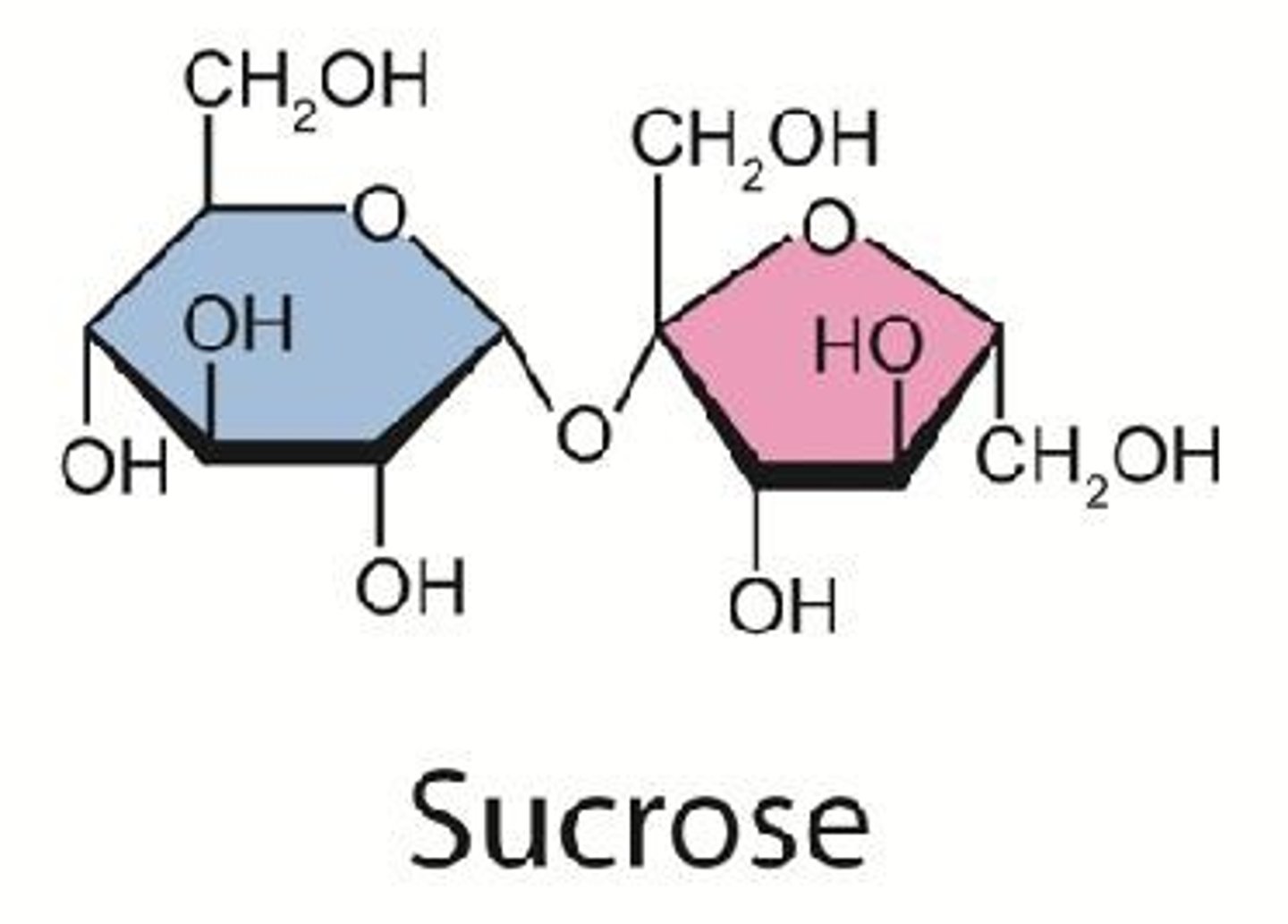
What is a glycosidic bond?
a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
What are polysaccharides?
large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides
What is glycogen?
Storage form of glucose
What is cellulose?
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
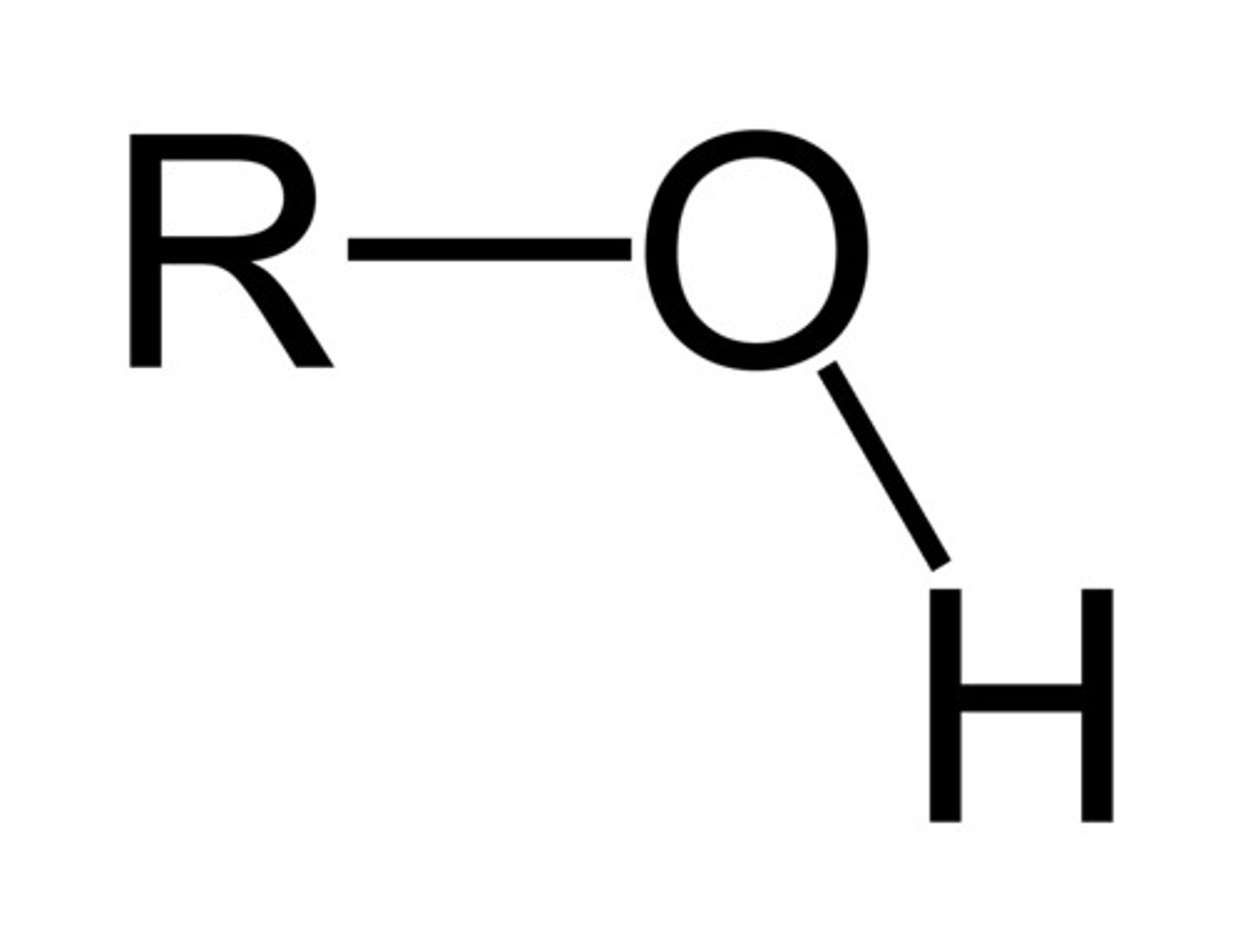
hydroxyl
OH-; polar
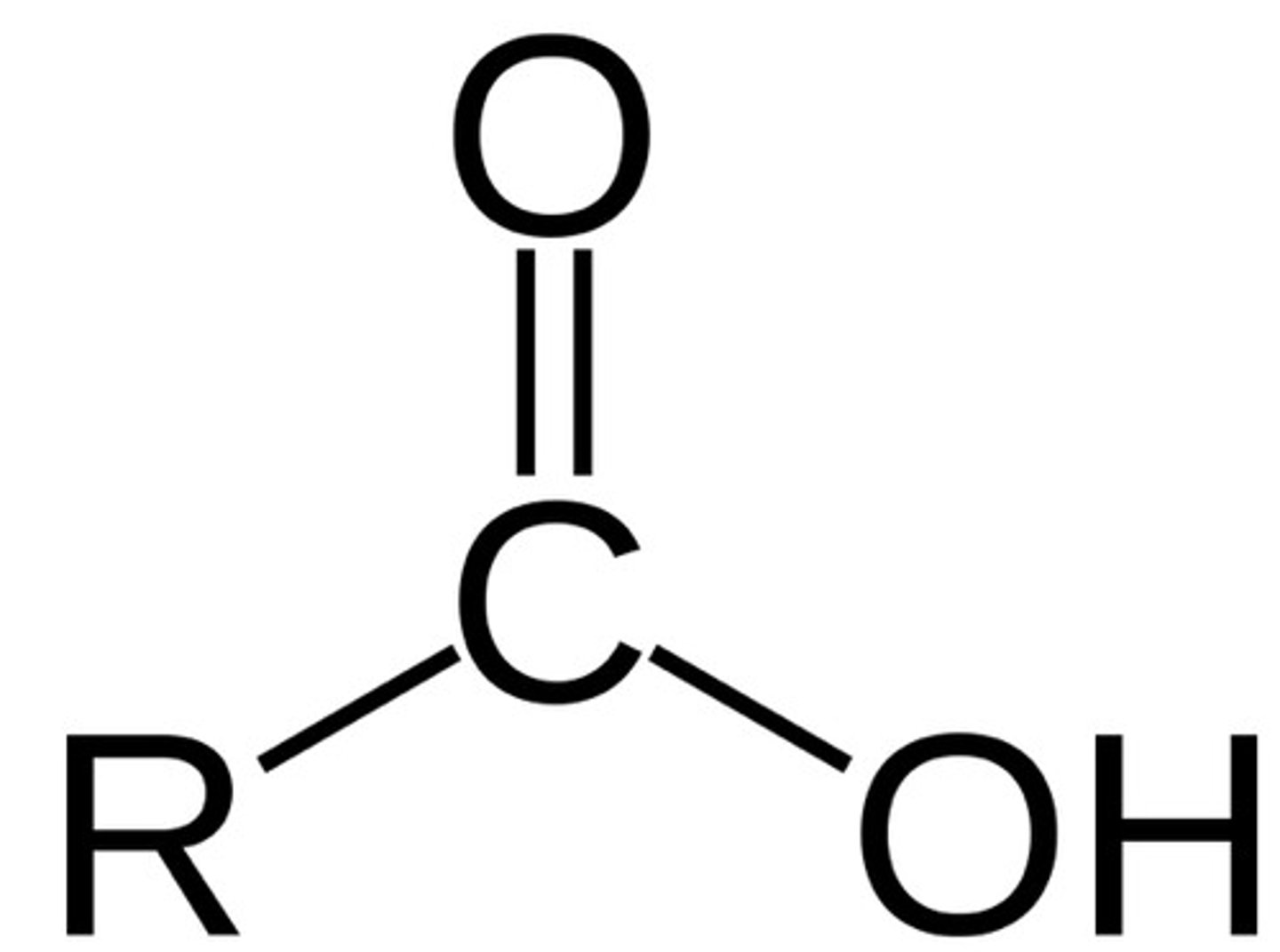
carboxyl
O=C-OH; polar
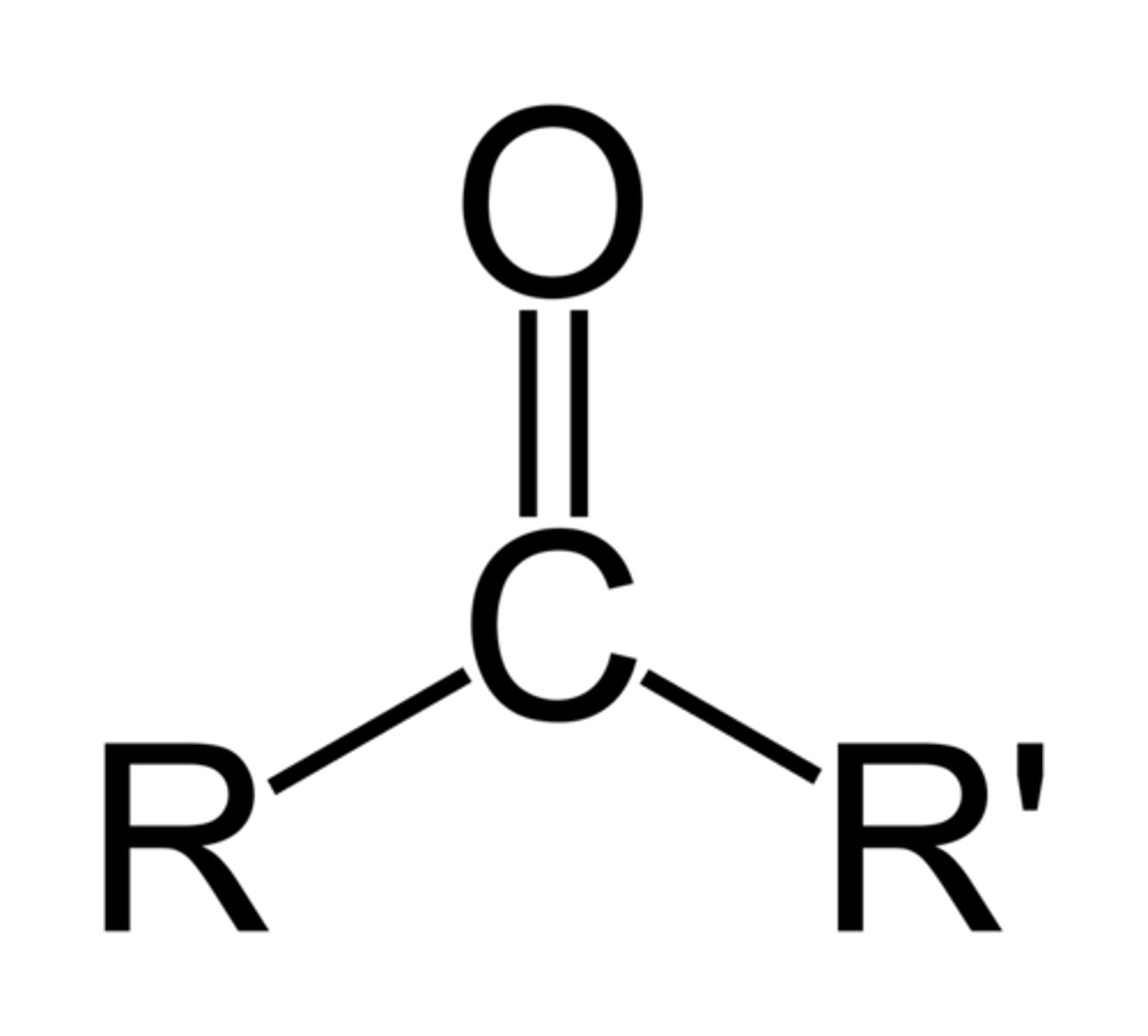
carbonyl
C=O; polar
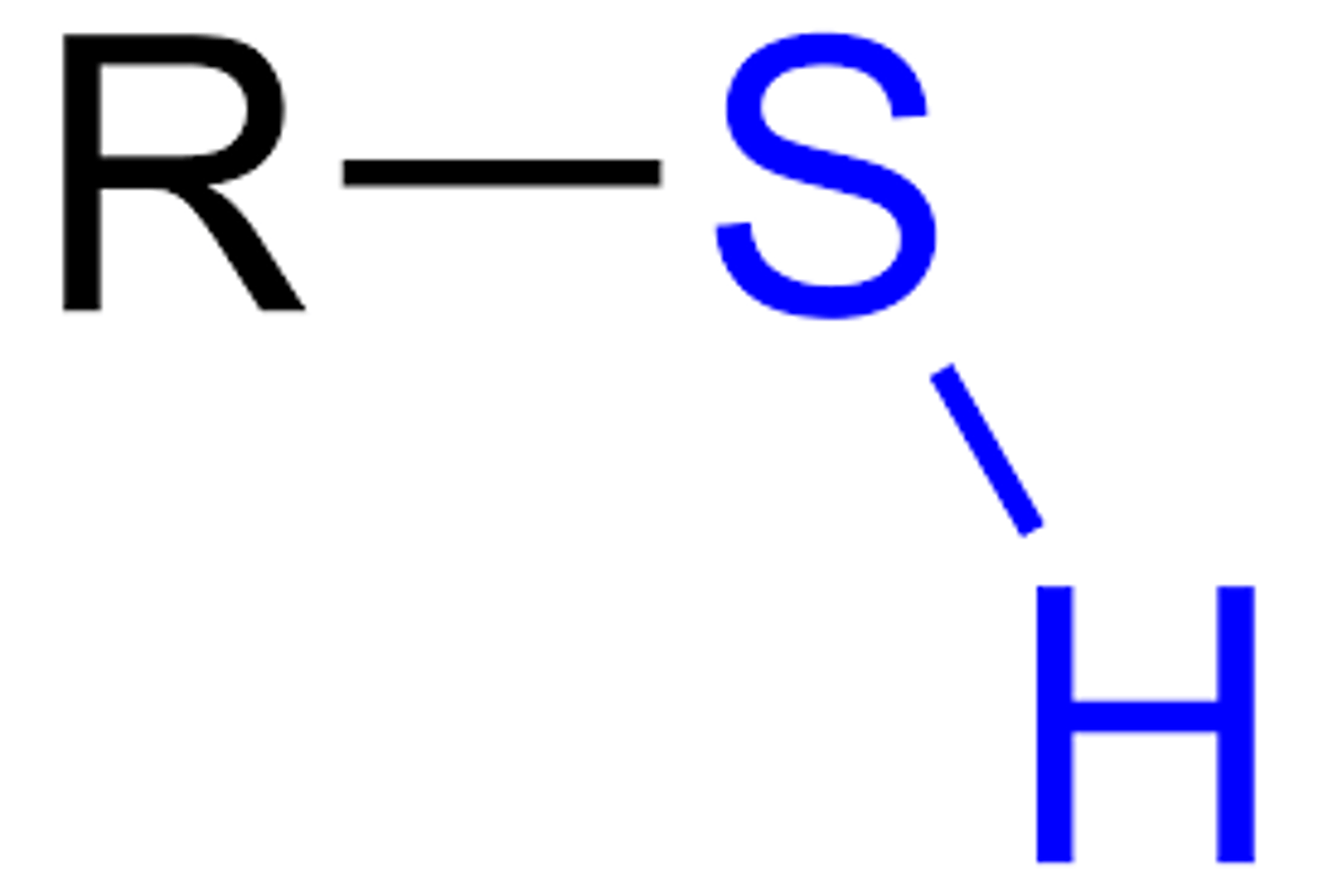
sulfhydrl
R-SH; polar
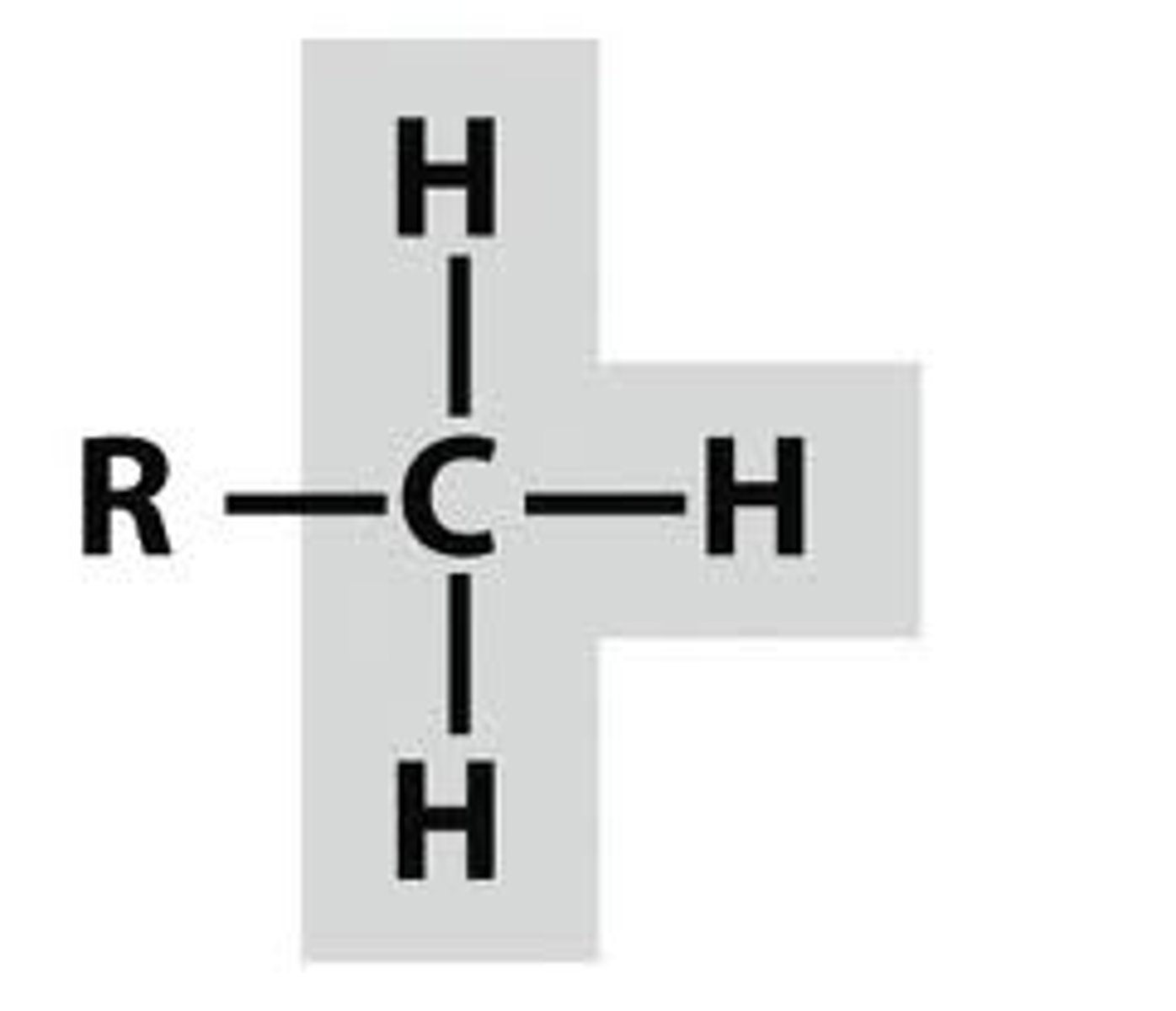
methyl
R-CH3; non-polar
Polarity
More soluble in water
Nonpolar
Less soluble in water
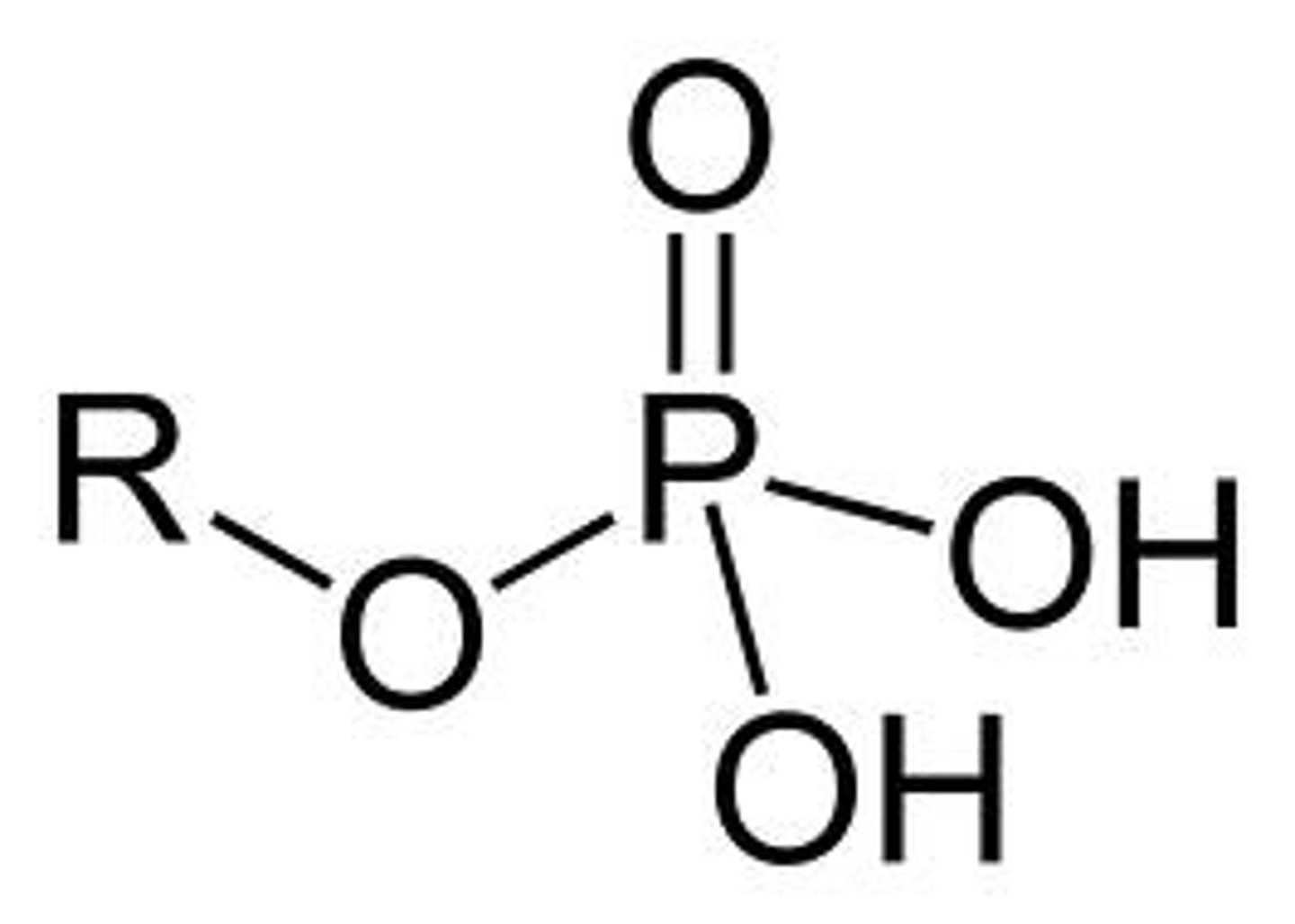
Phosphate group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms
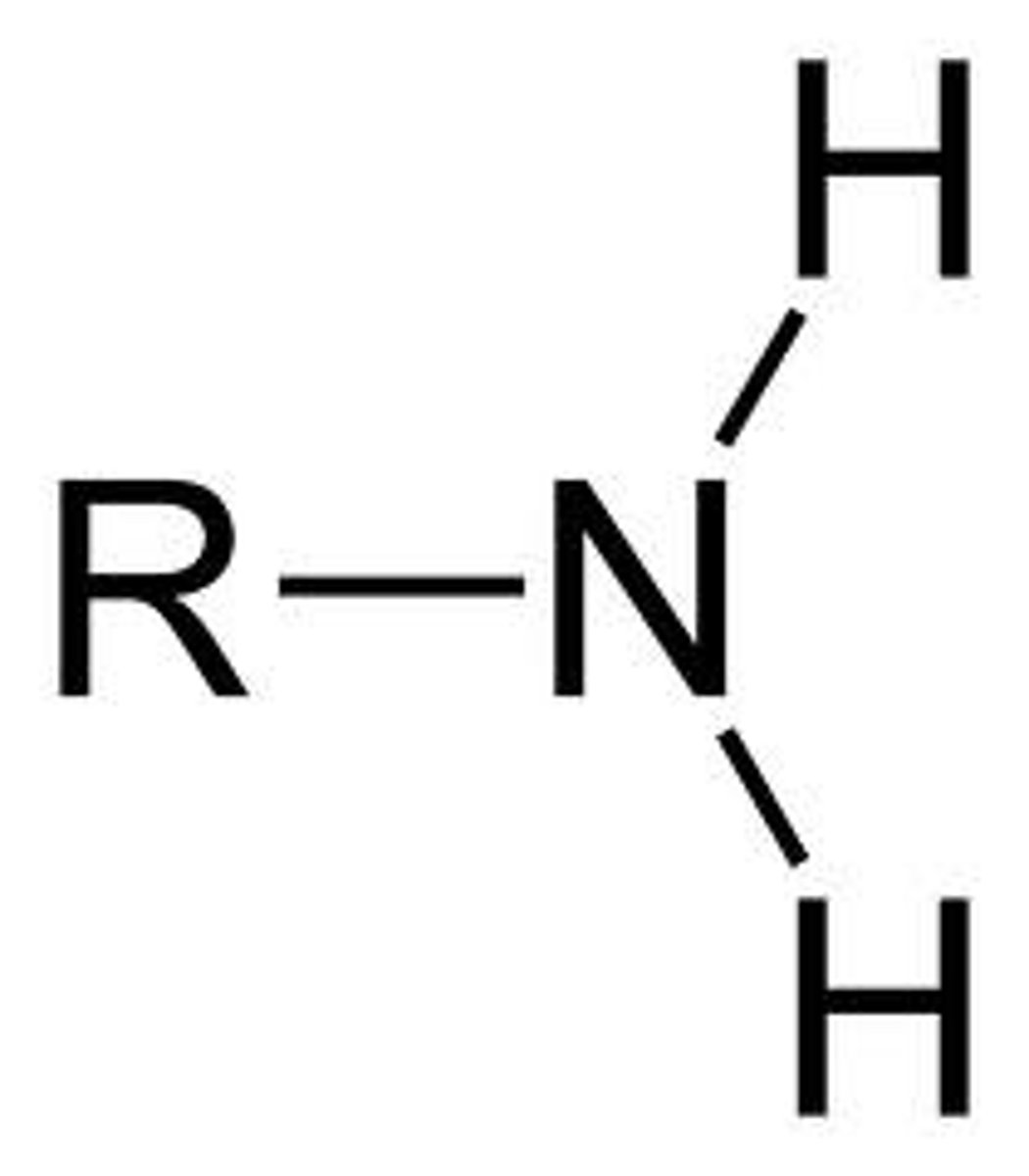
Amino group
NH2
What is a lipid?
fats and oils
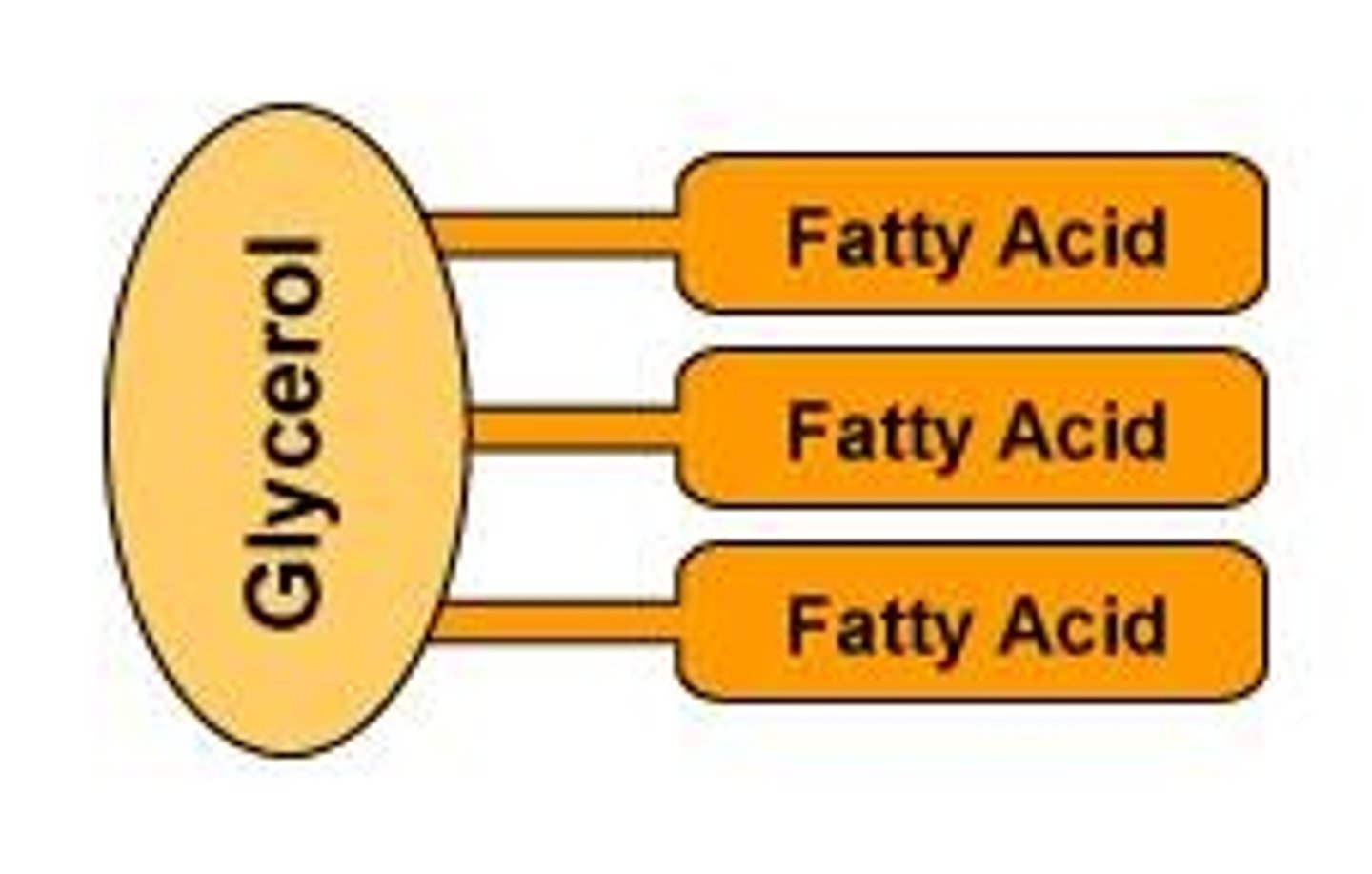
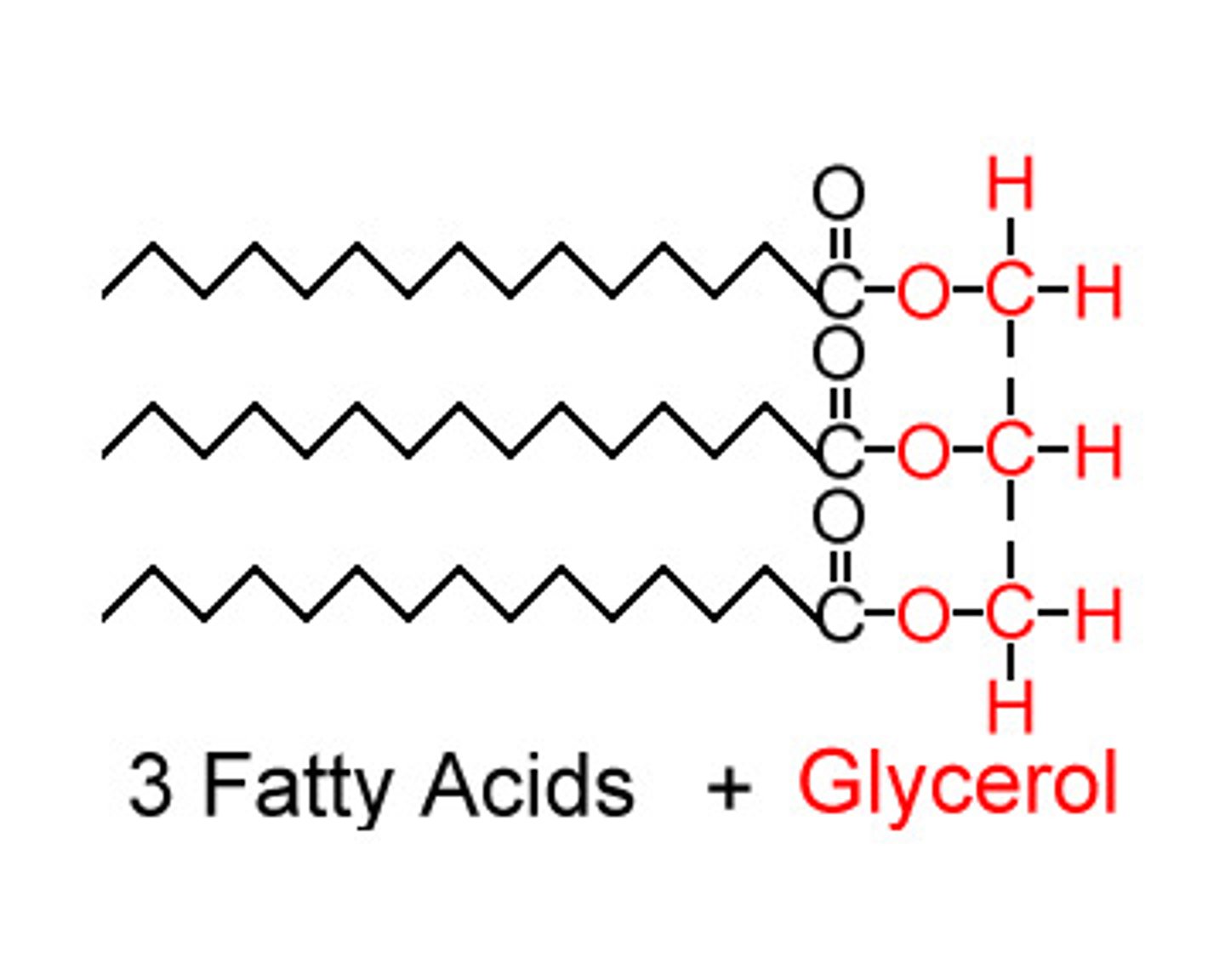
What is a fat molecule?
consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids
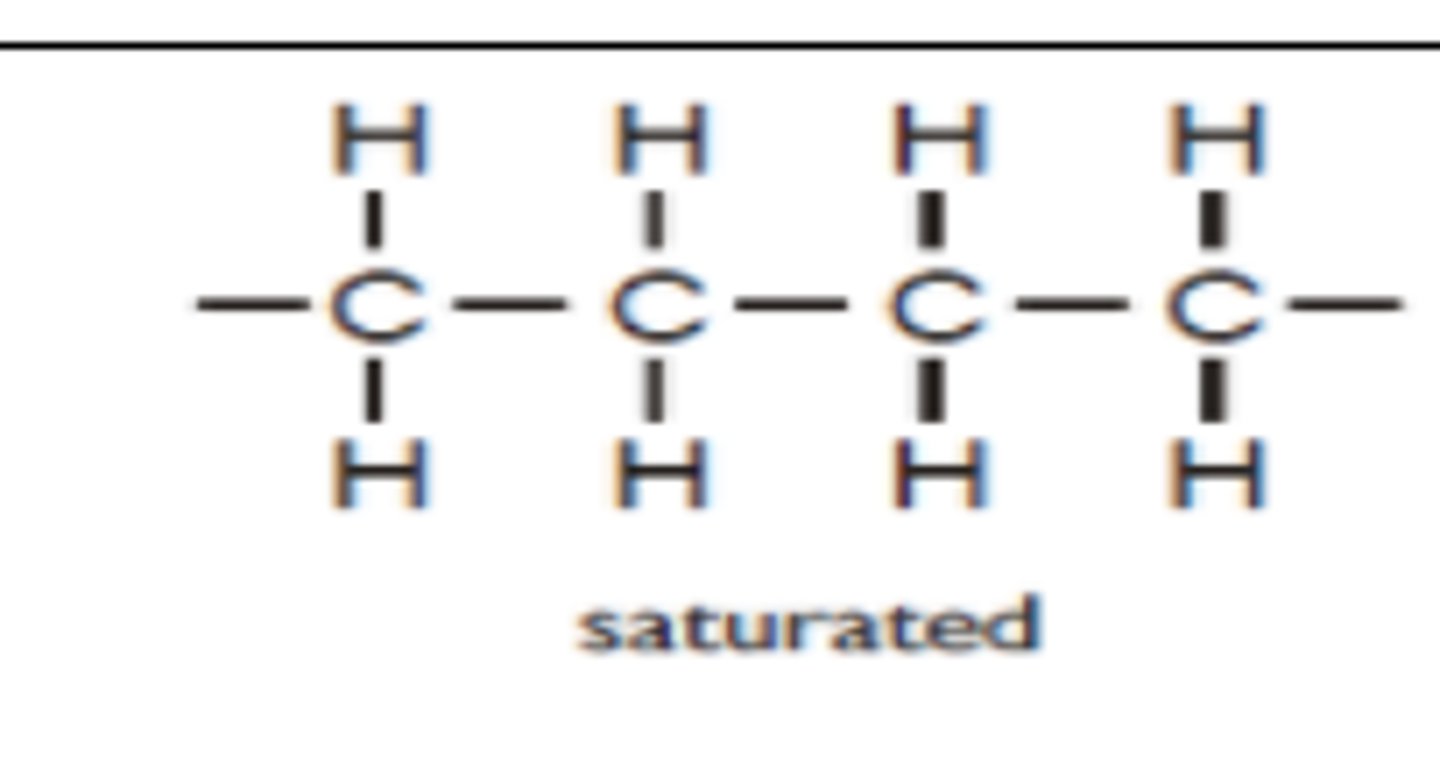
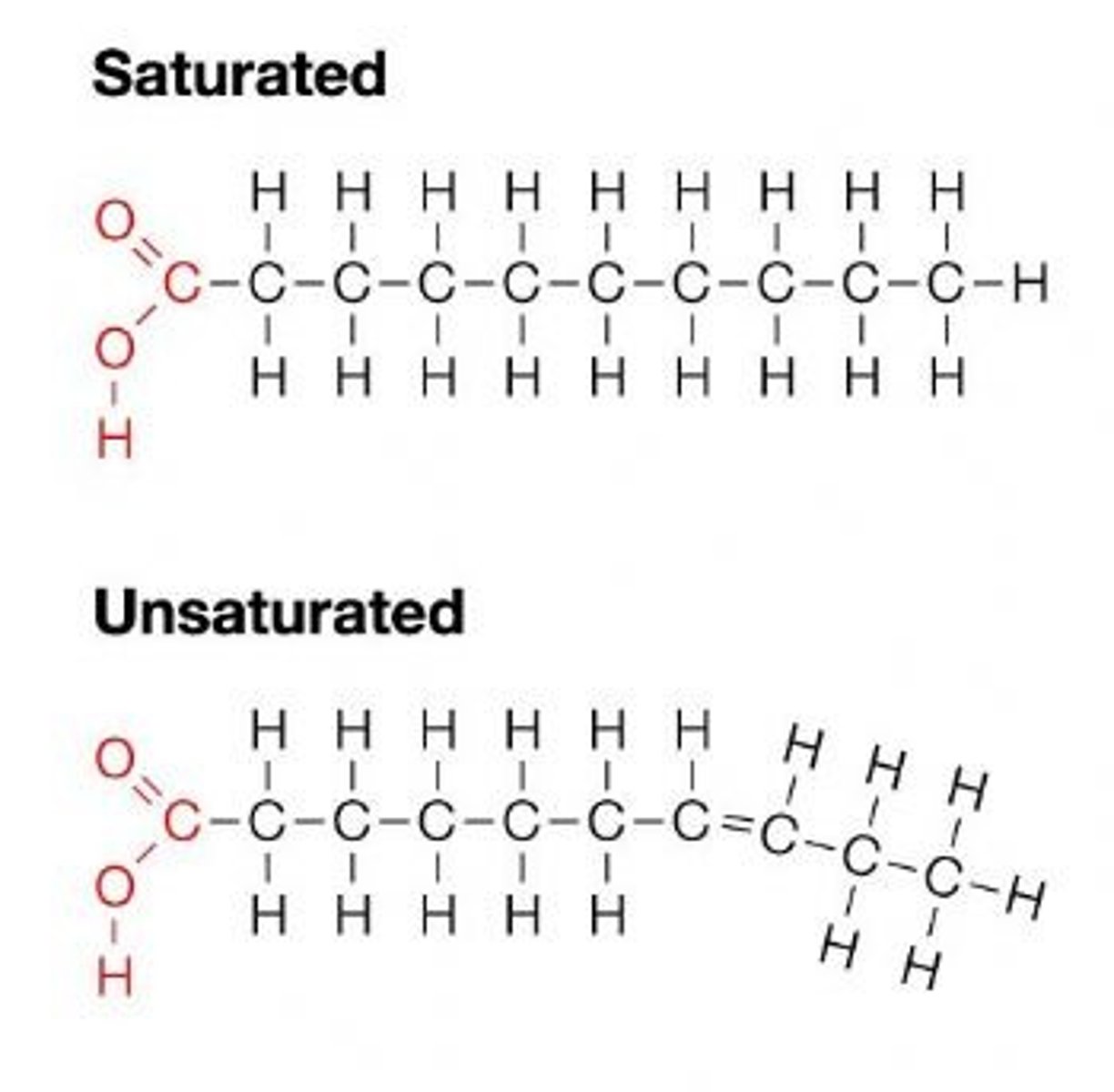
What is a saturated fatty acid?
it doesnt contain any double bond
What is an unsaturated fatty acid?
One with double bonds.
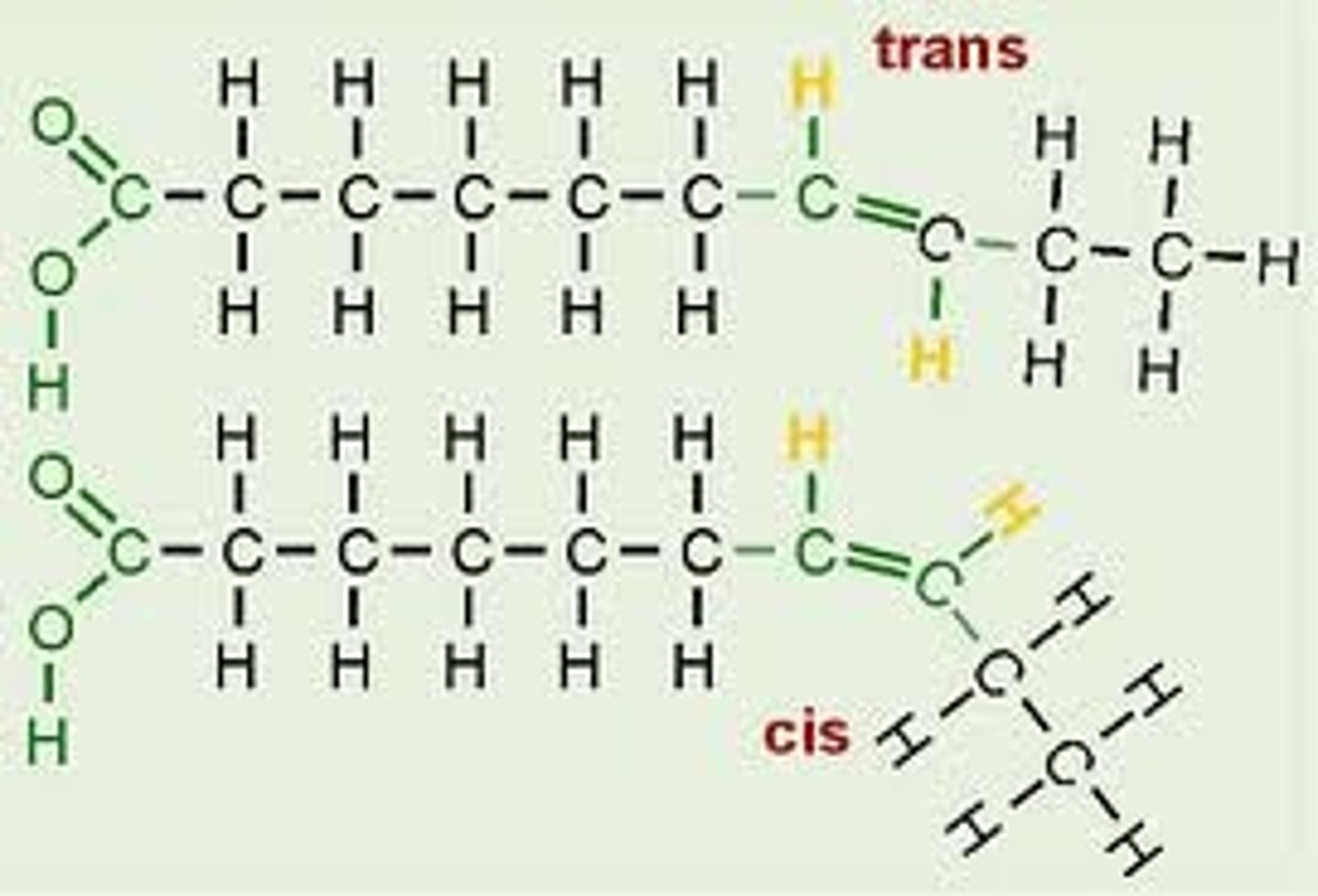
Cis fat
Hydrogens on the same side of the double bond; Examples: most natural fats and oils
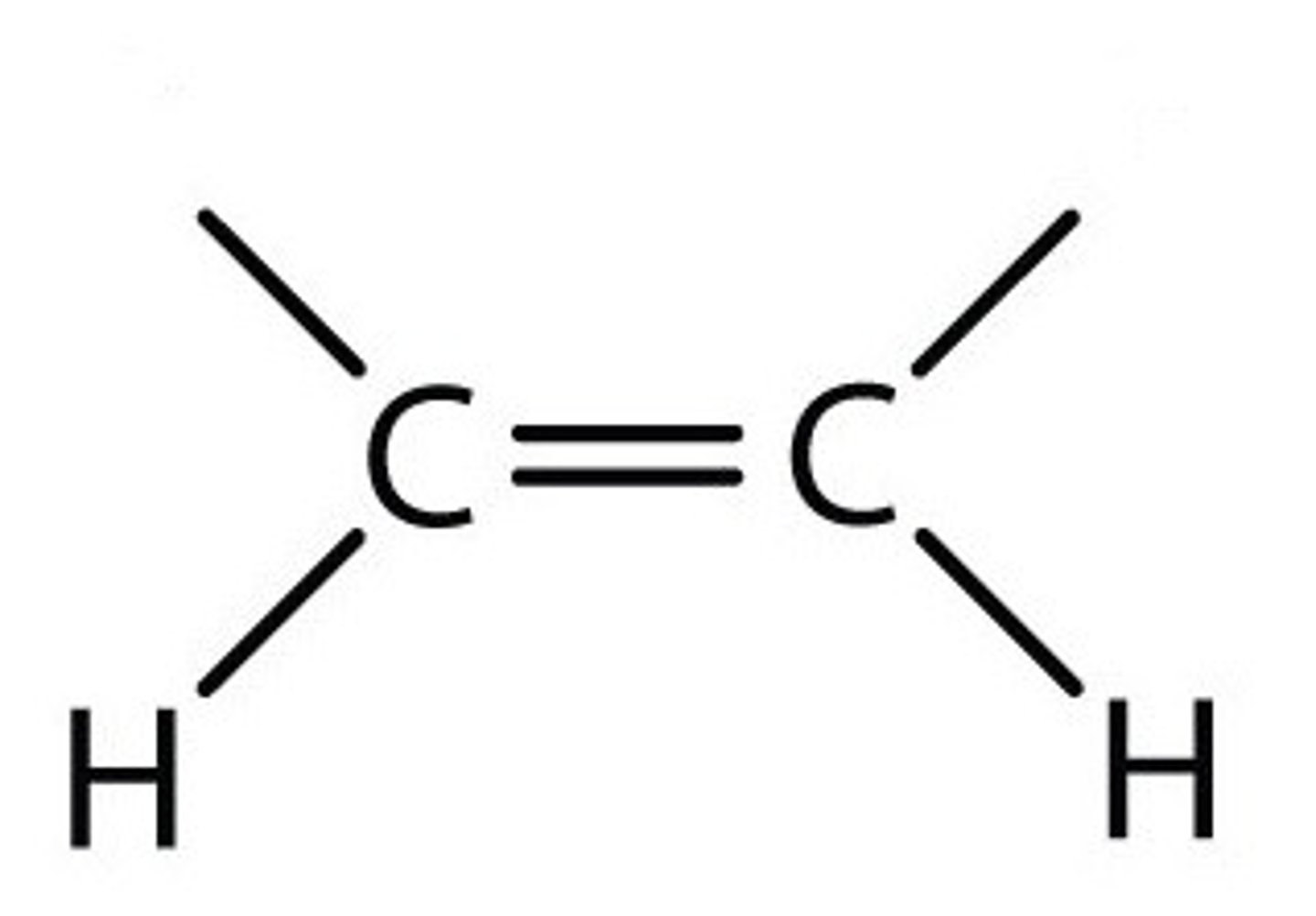
Trans fat
An unsaturated fat, formed artificially during hydrogenation of oils, containing one or more trans double bonds.
Omega fatty acids
A family of unsaturated fats that have several beneficial health effects; omega fatty acids are found in fish, nuts, flaxseed, fruits, and vegetables.
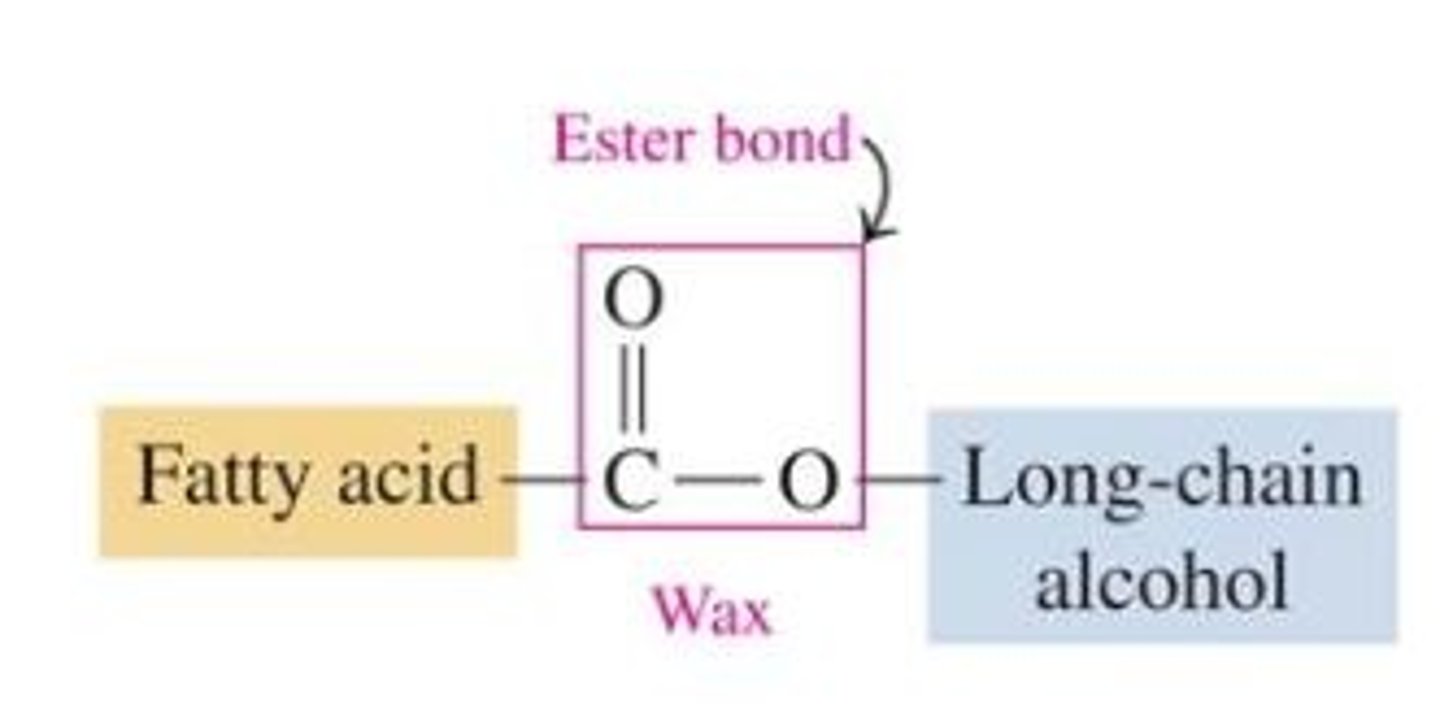
Waxes
type of structural lipid; long fatty acids chain bonded to long alcohol chain; highly waterproof; in plants and animals. hydrophobic
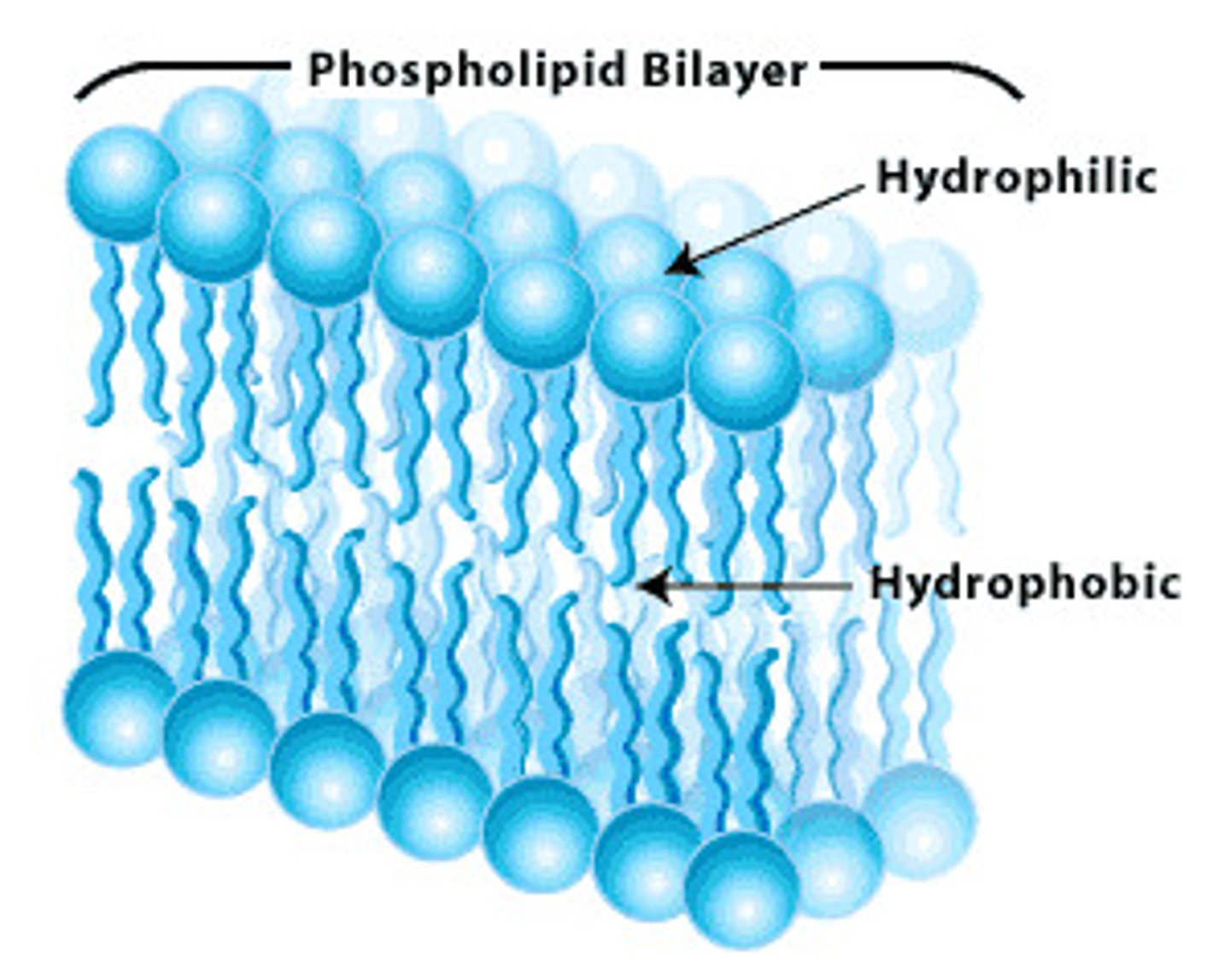
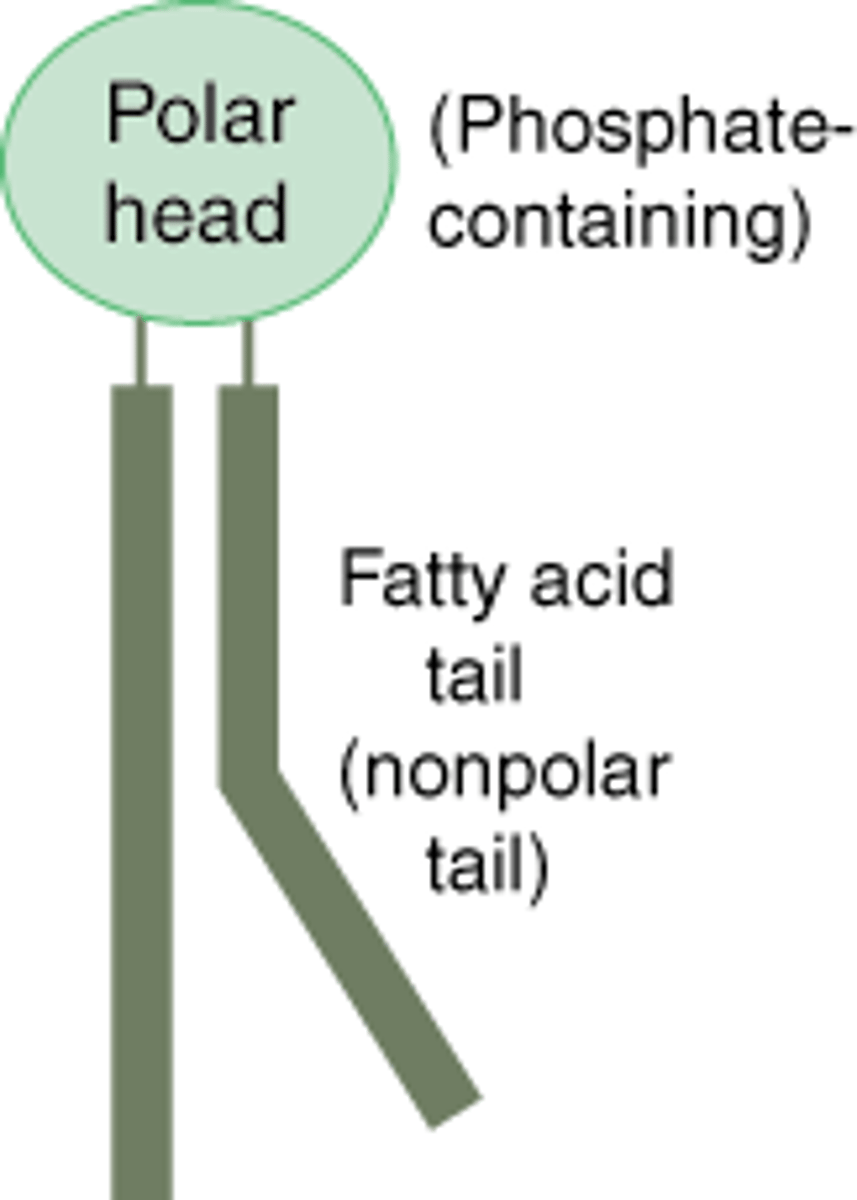
Phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
Steroids
A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of FOUR rings with various functional groups attached.
What are proteins?
most abundant organic molecules; polymers of amino acids
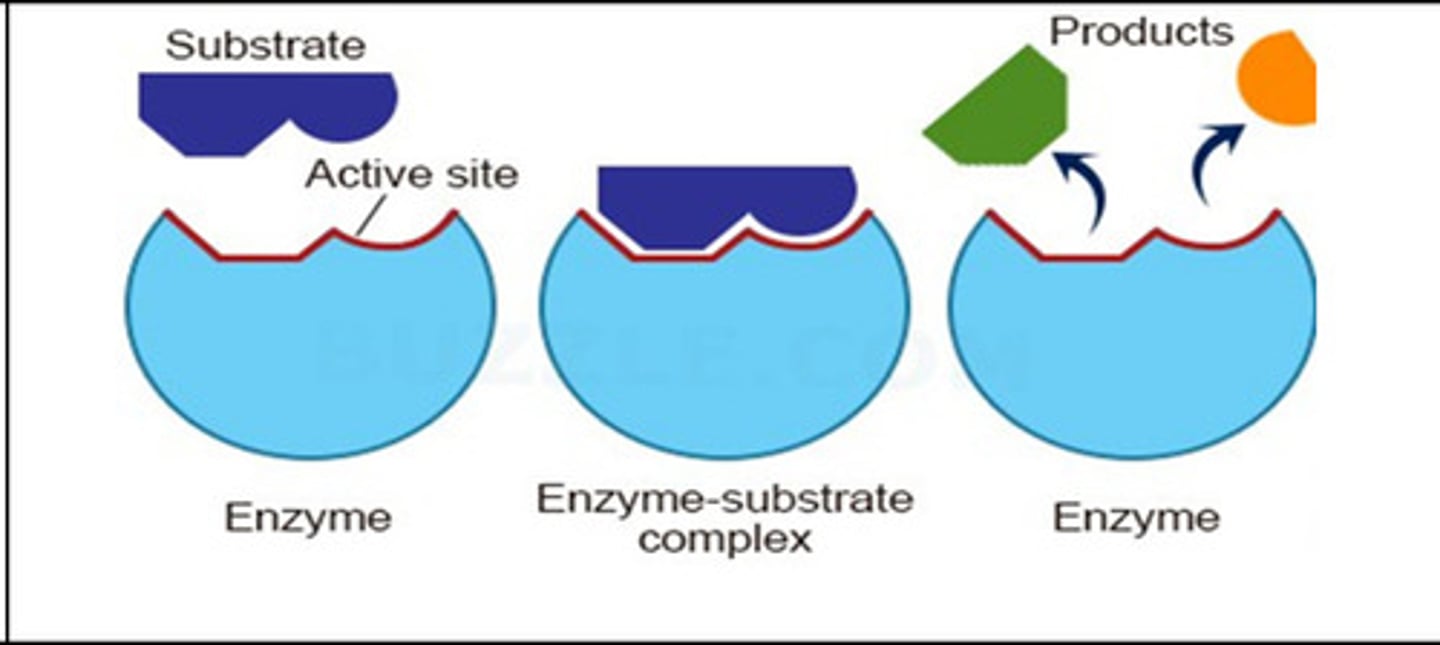
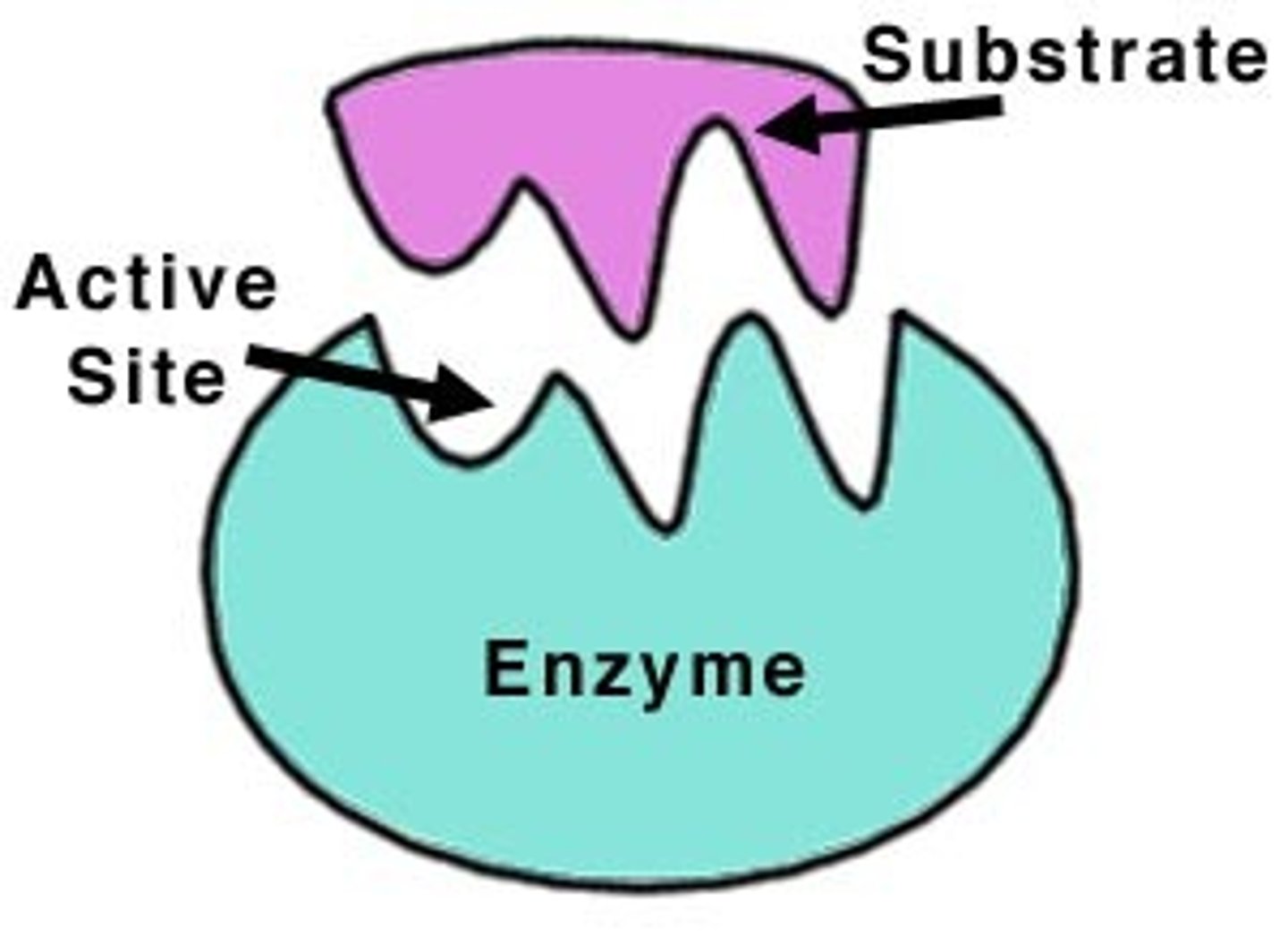
What are enzymes?
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
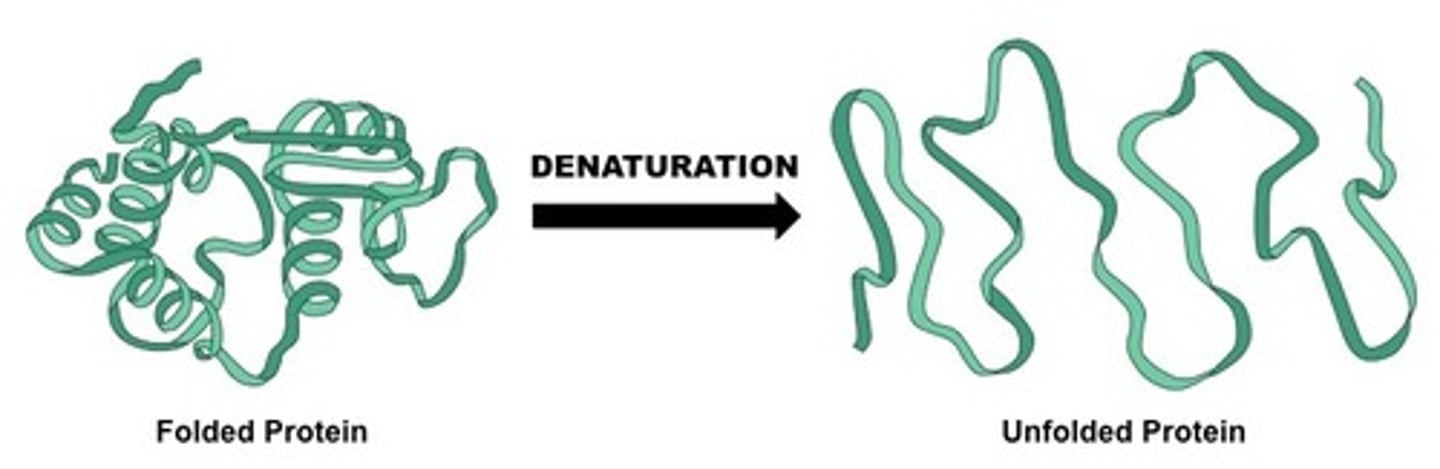
What is denaturation?
loss of a protein's native structure
What are hormones?
chemical messengers
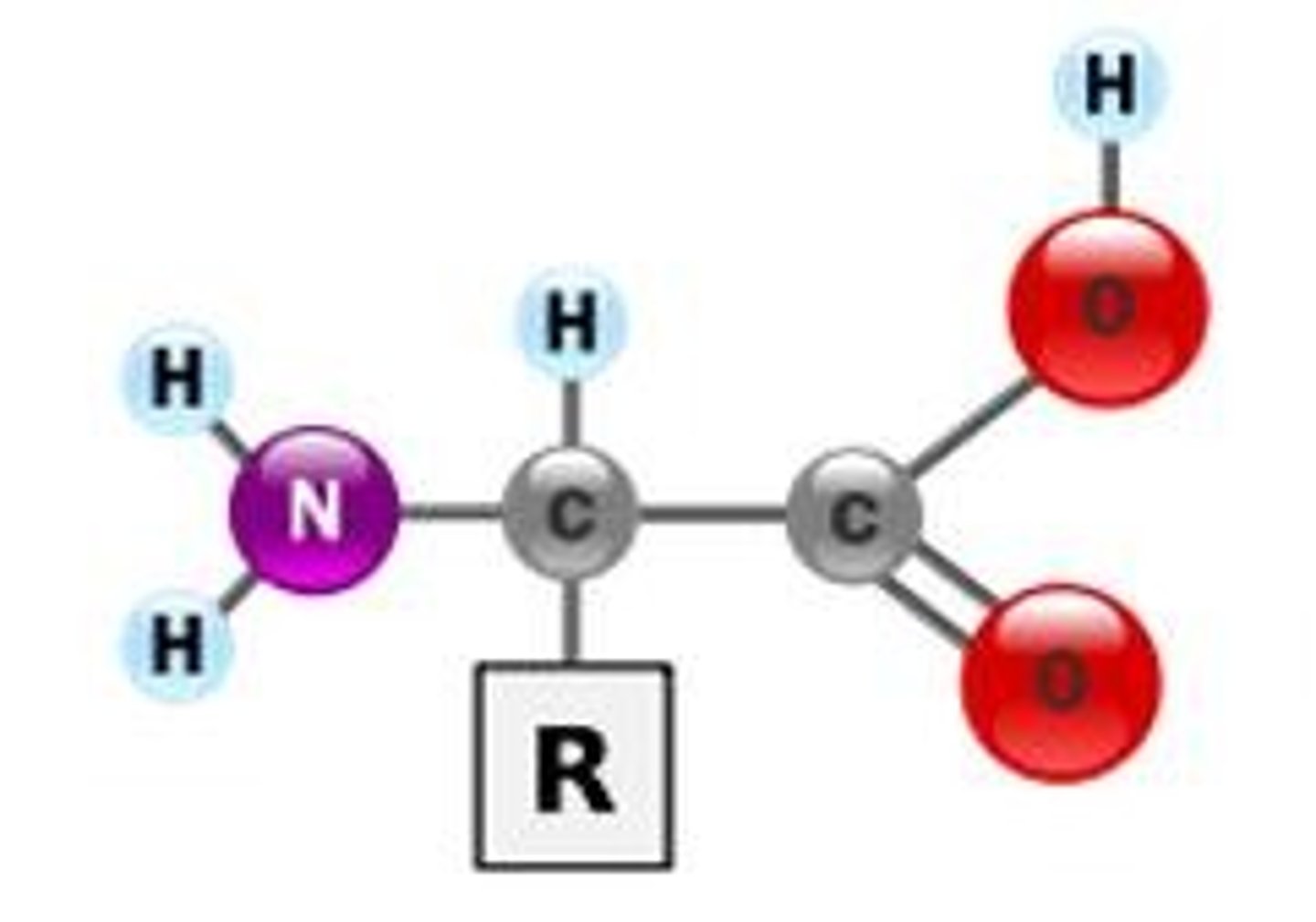
What are amino acids?
building blocks of proteins
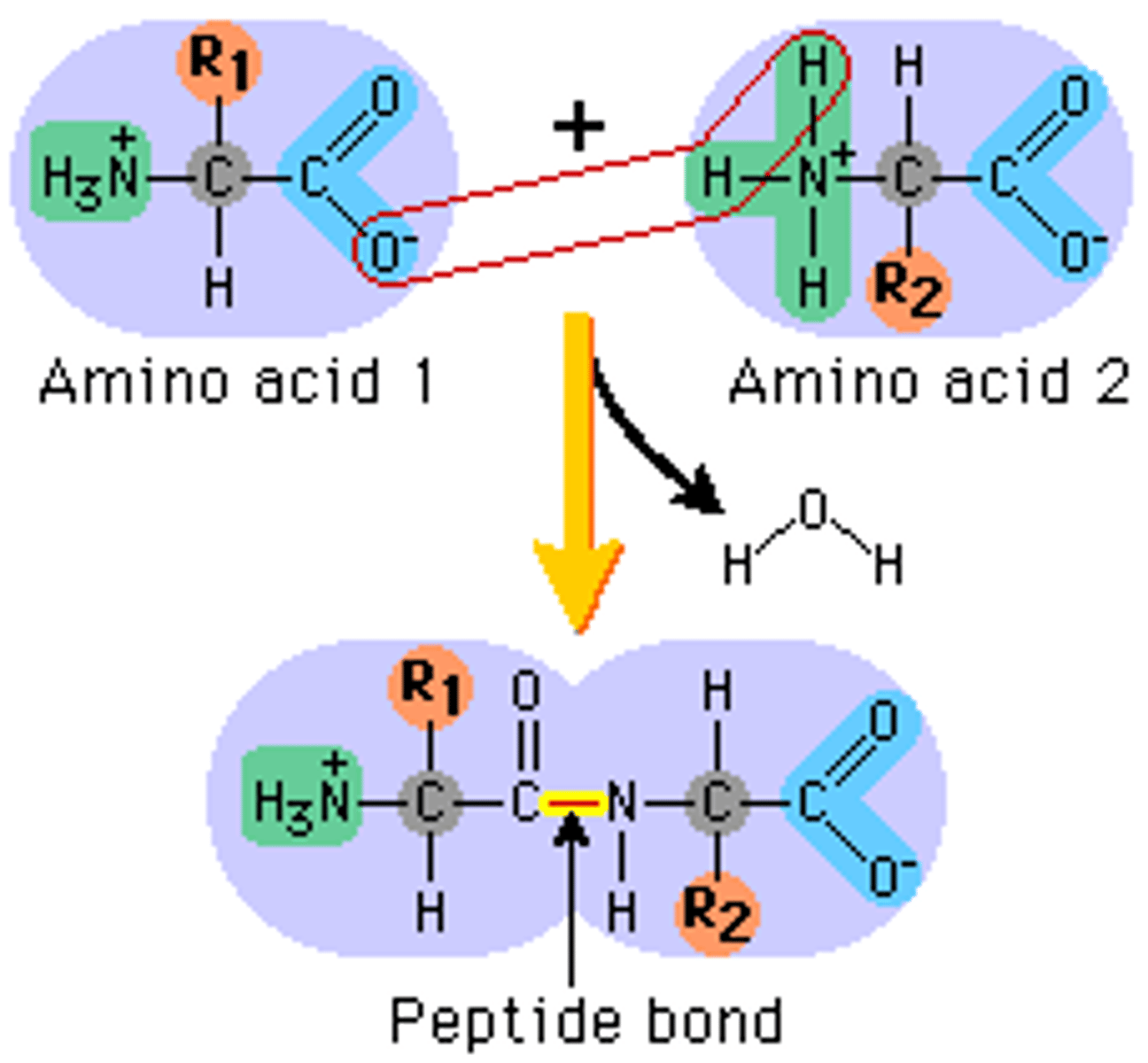
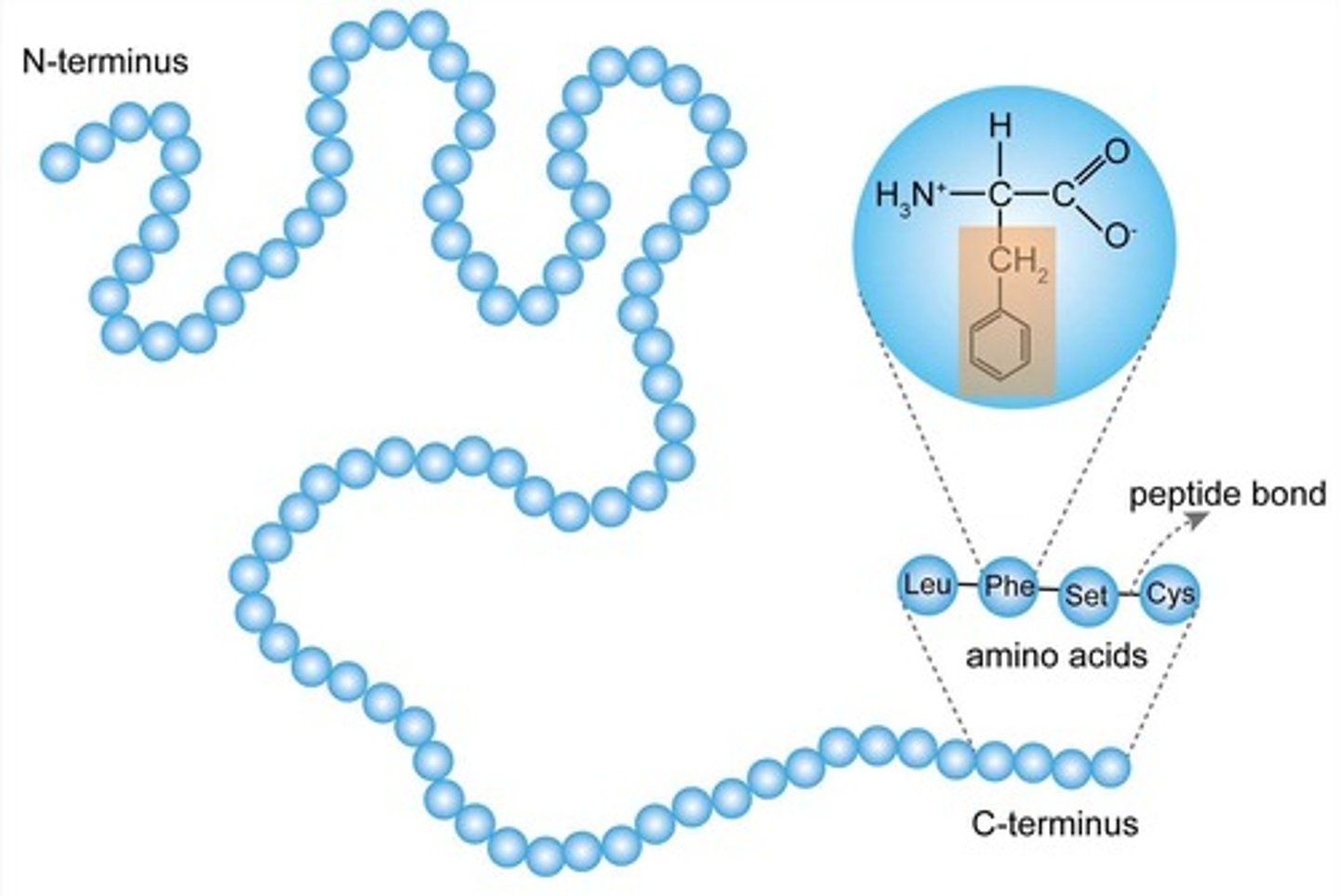
What is a peptide bond?
bond between amino acids
What is a polypeptide?
long chain of amino acids
Active site of a protein
site of interaction (binding)
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure is the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
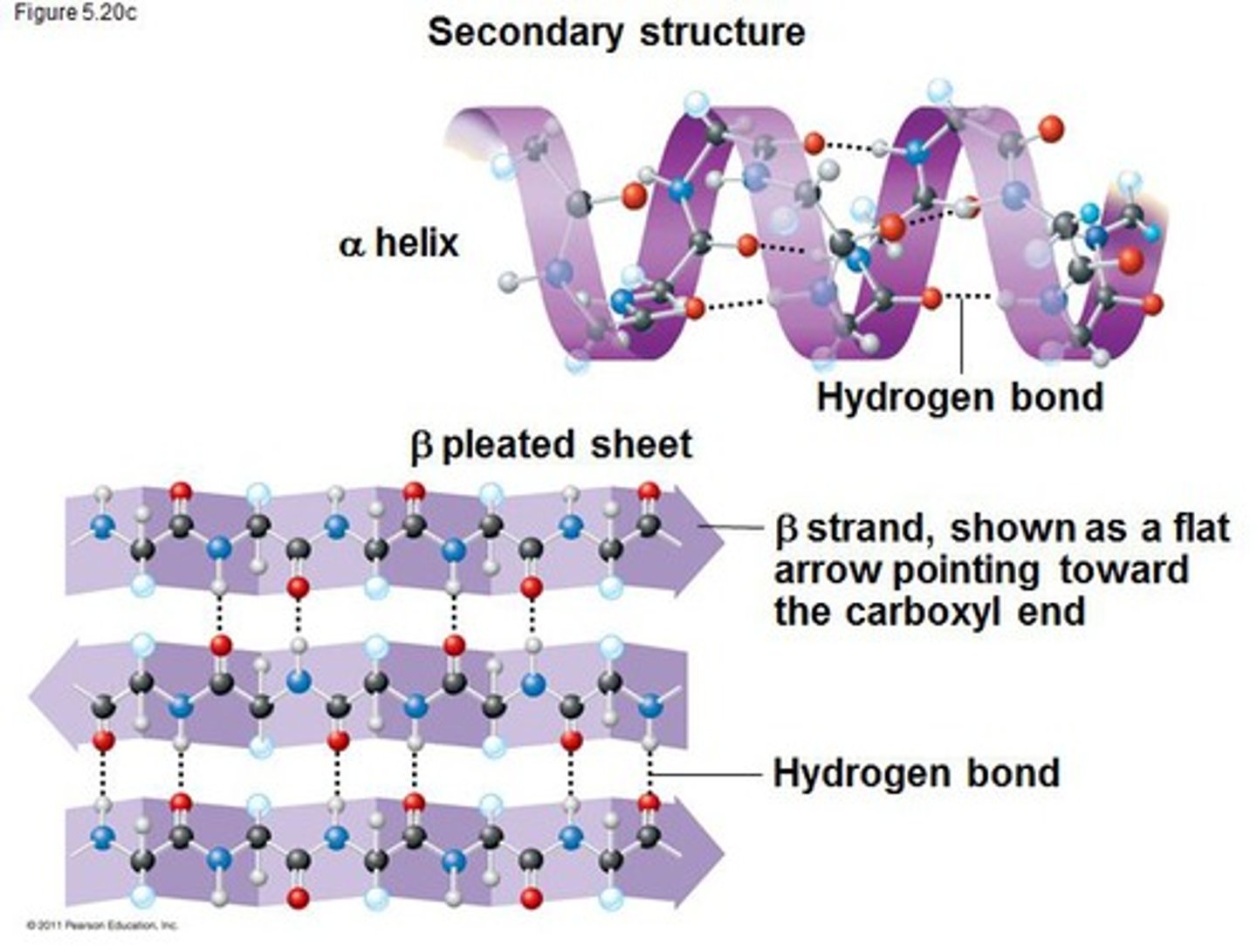
Secondary structure
The second level of protein structure is the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain. Contains A-helix and B-pleated sheets.
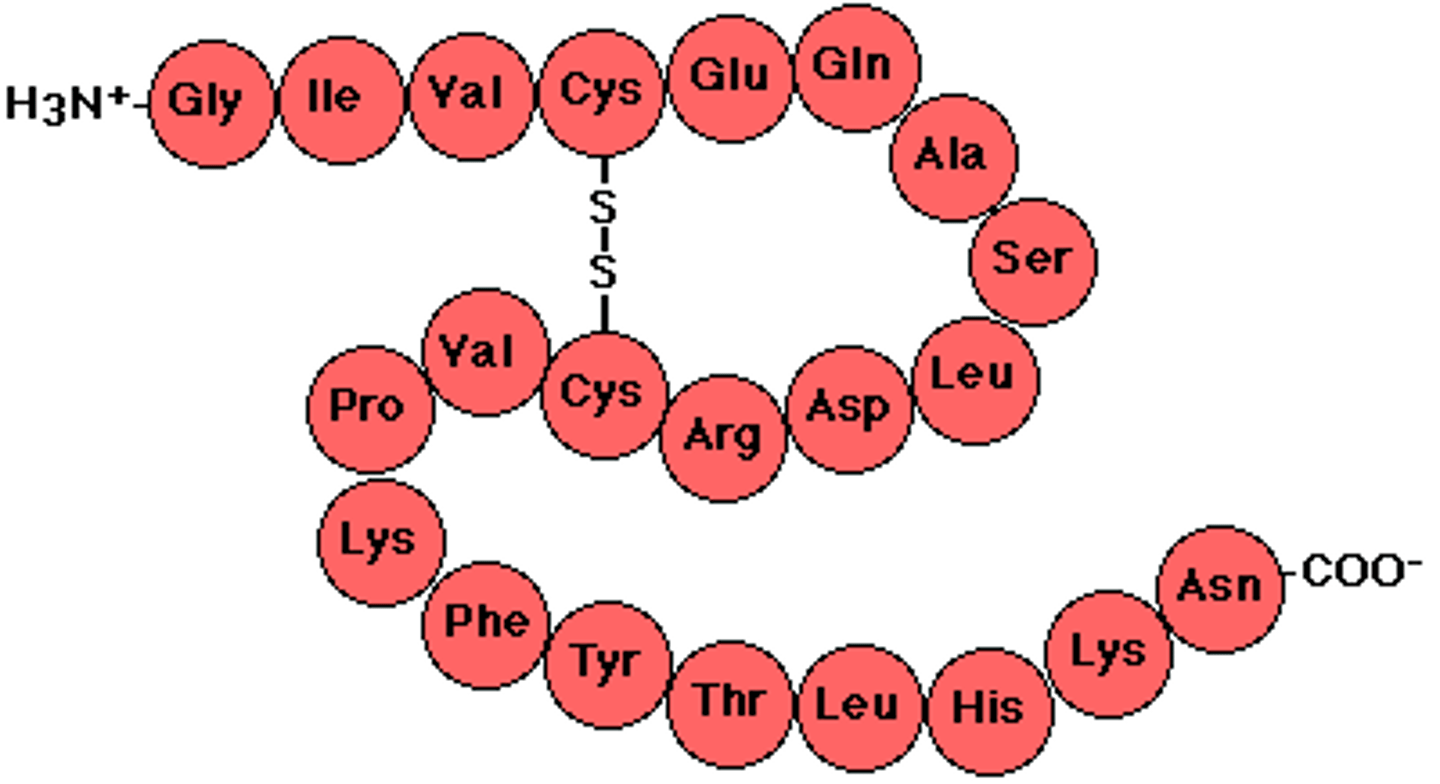
Tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure is the three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
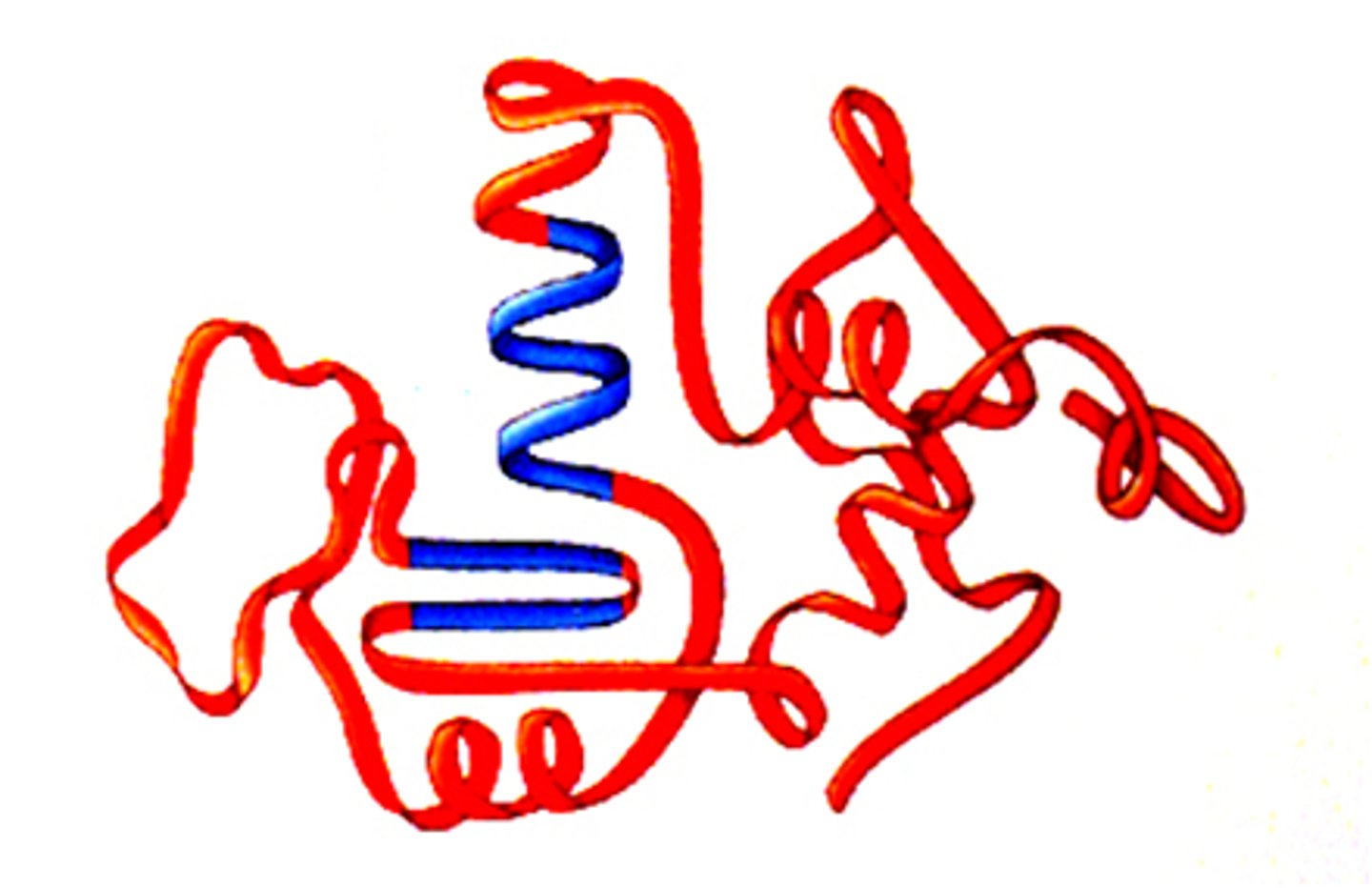
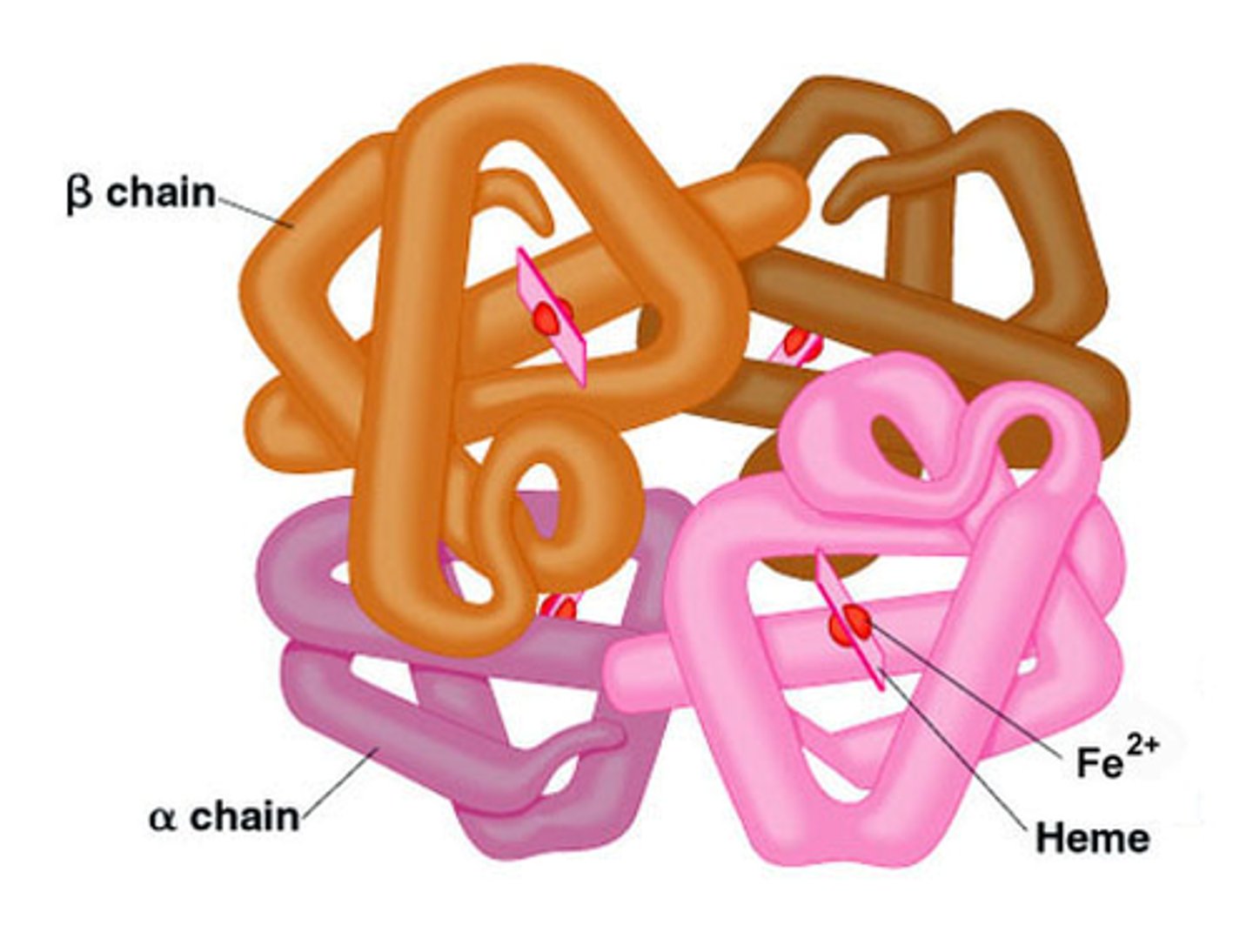
Quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure is the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
Nucleic Acids
DNA & RNA

What is DNA?
Genetic material for all living organisms.
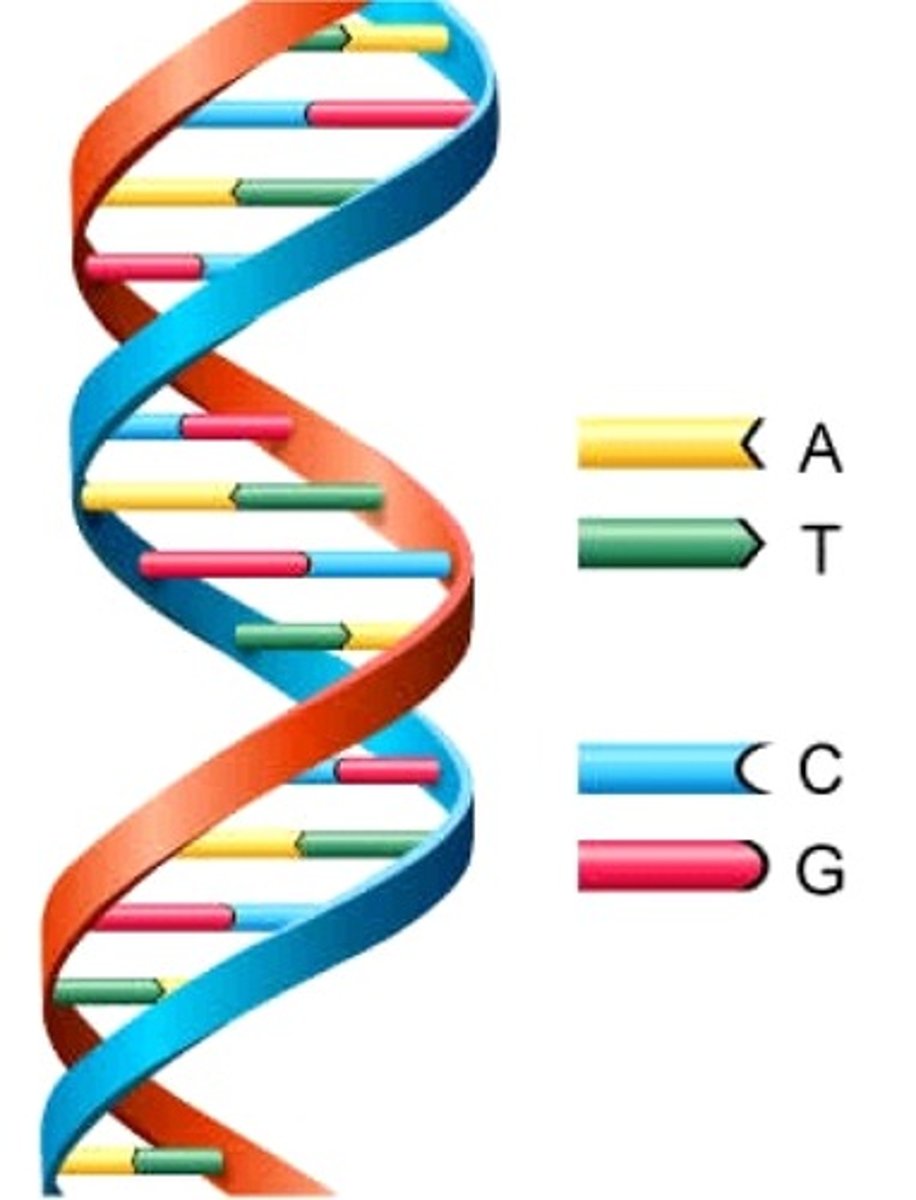
DNA structure
DNA forms a complex with histone (condenses DNA into chromatin) proteins.
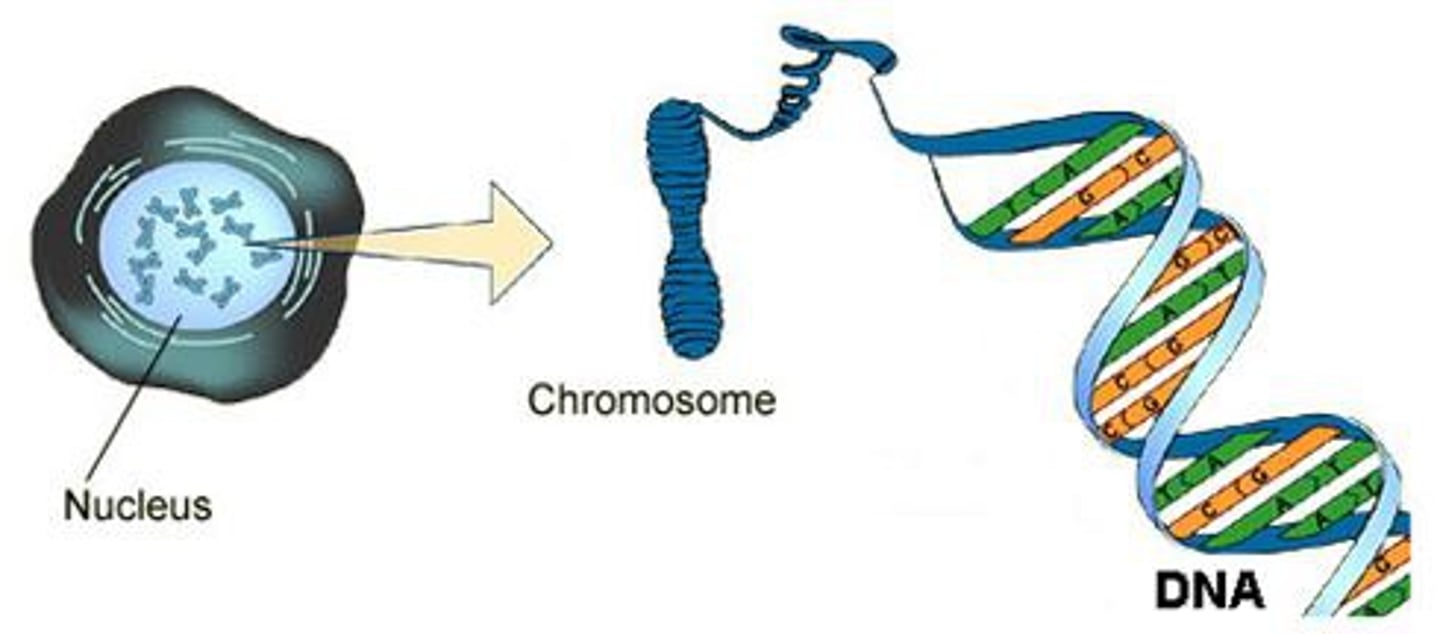
What are chromosomes?
Coiled up lengths of DNA molecules are found in the nuclei. Some codes for protein.
What is RNA?
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose. information for making proteins
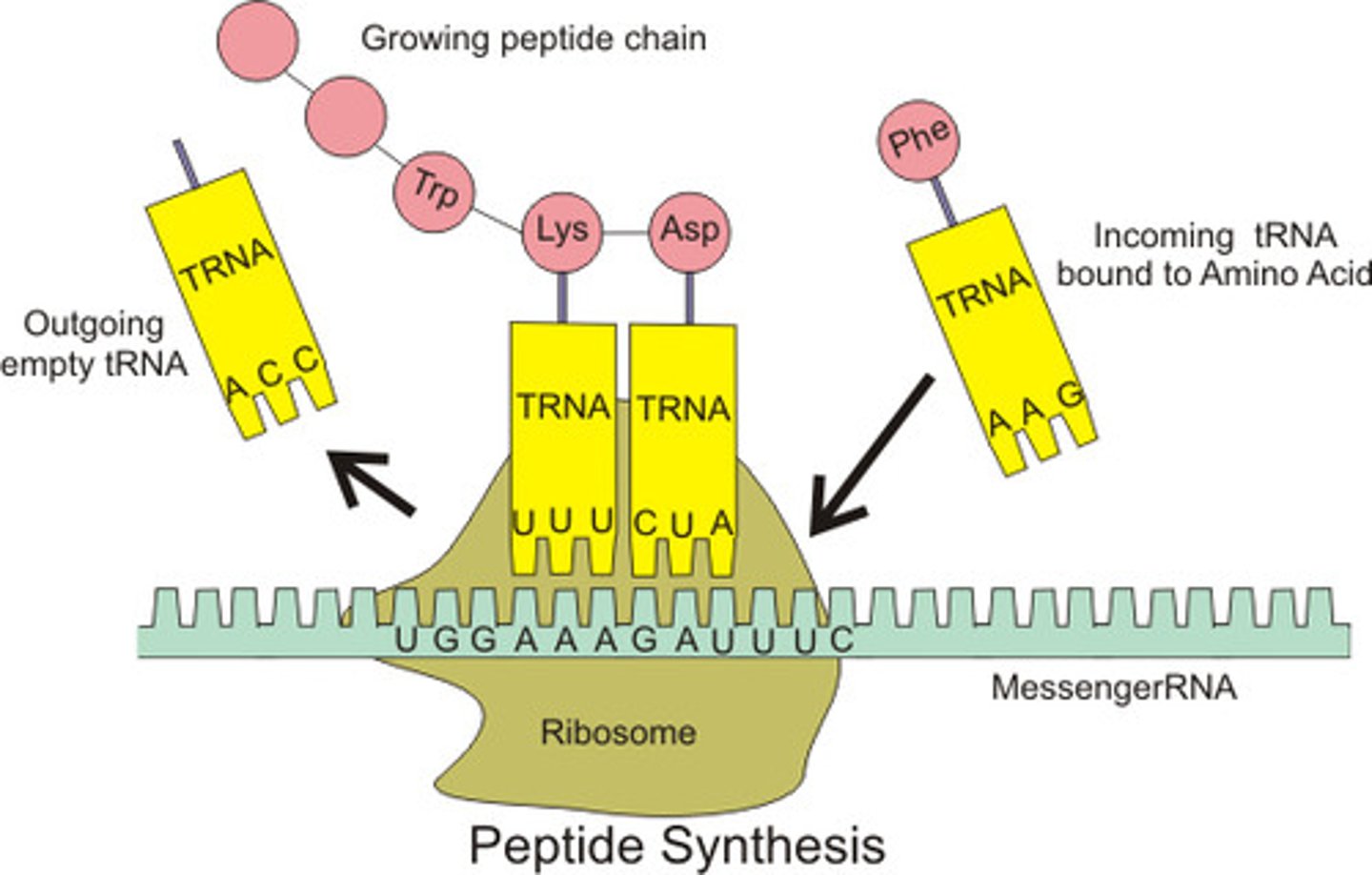
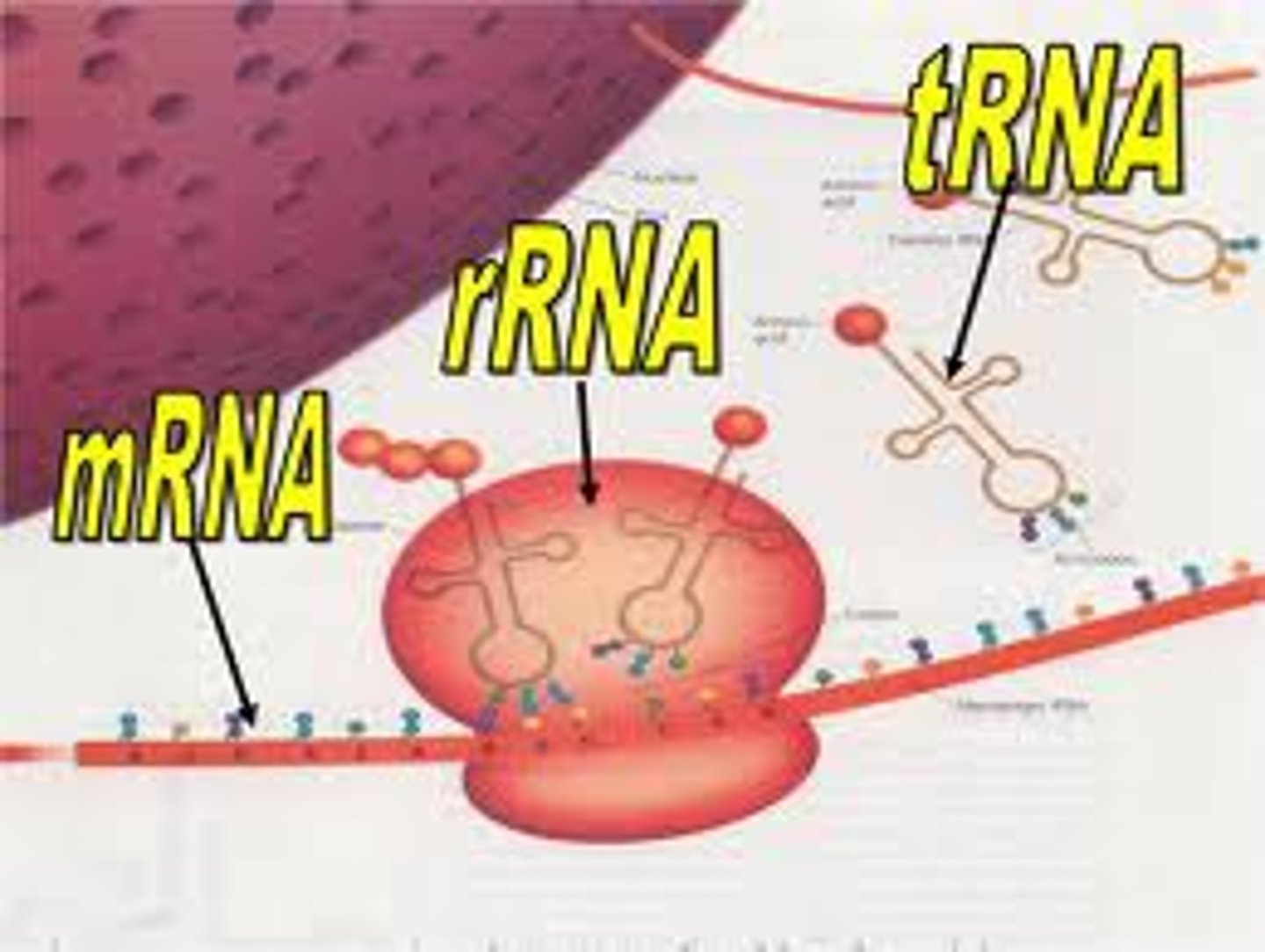
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
microRNA
small single stranded RNA molecules that bind to mRNA and can degrade mRNA or block its translation.
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
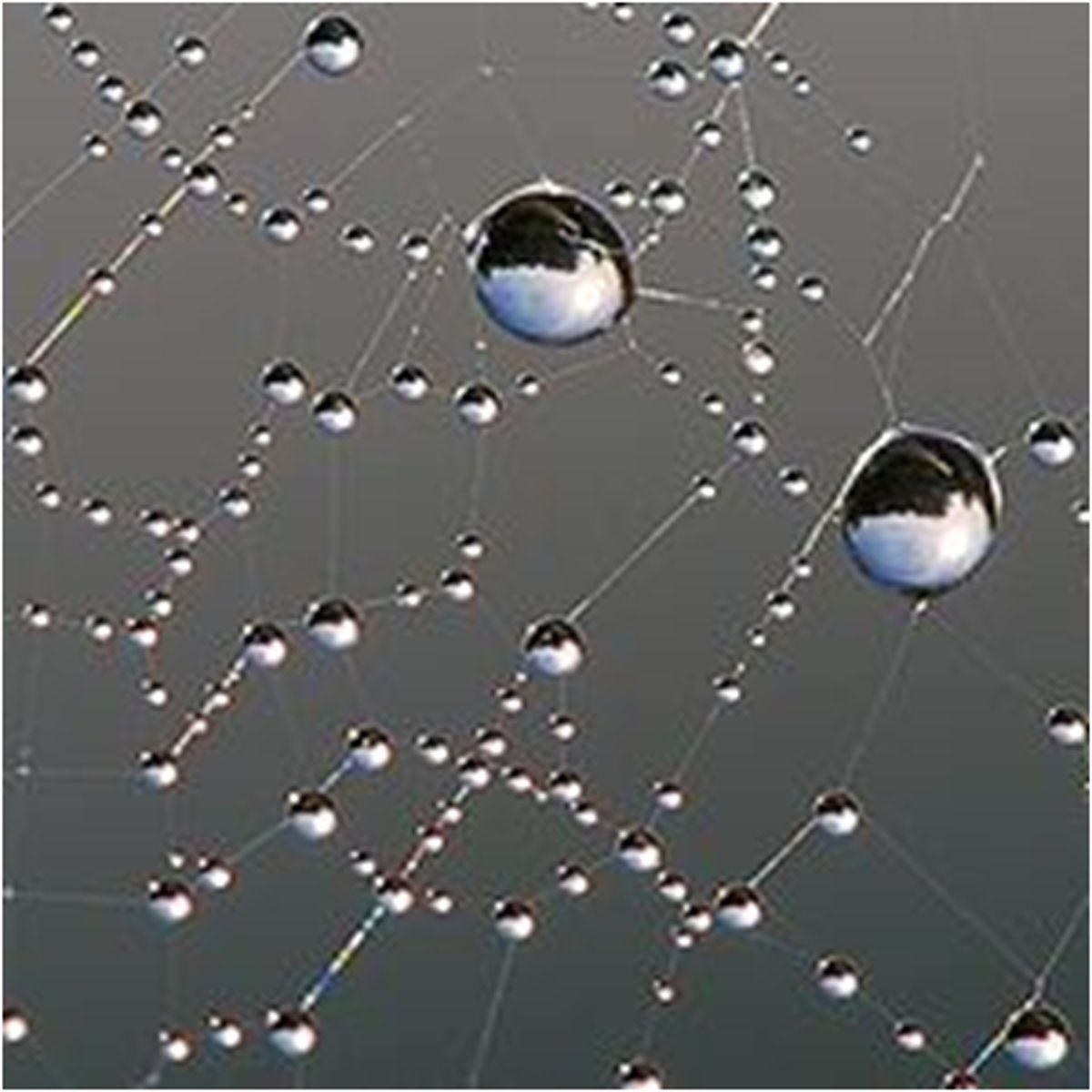

Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Four of water's properties that facilitate anenvironment for life are
Cohesive Behavior, Ability to moderate temperature, Expansion upon freezing, and Versatility as a solvent.
3 multiple choice options
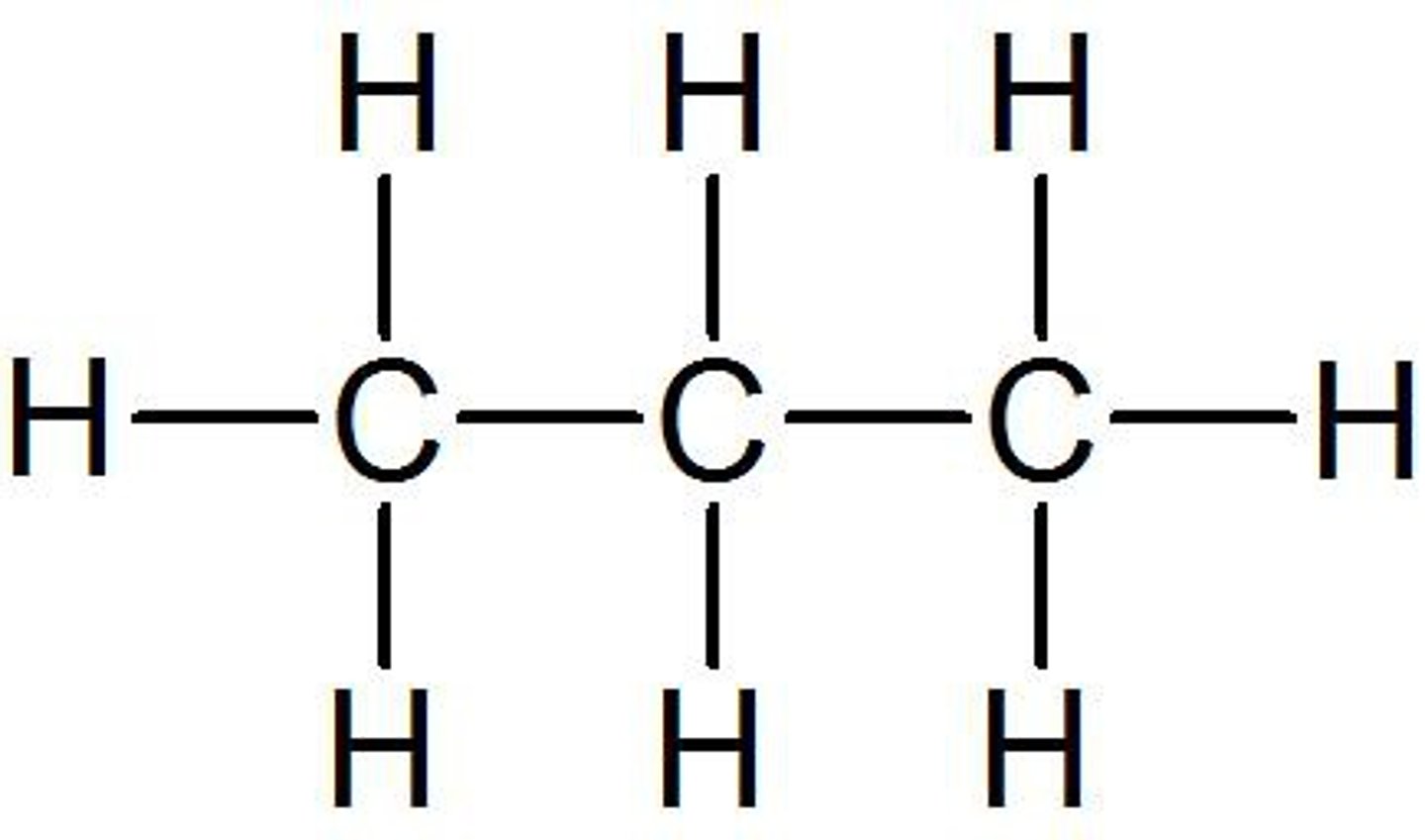
Ethane
C2H6

Propane
C3H8
What are examples of prokaryotes?
Bacteria and Archaea
2 multiple choice options
Not a domain of life
Fungi
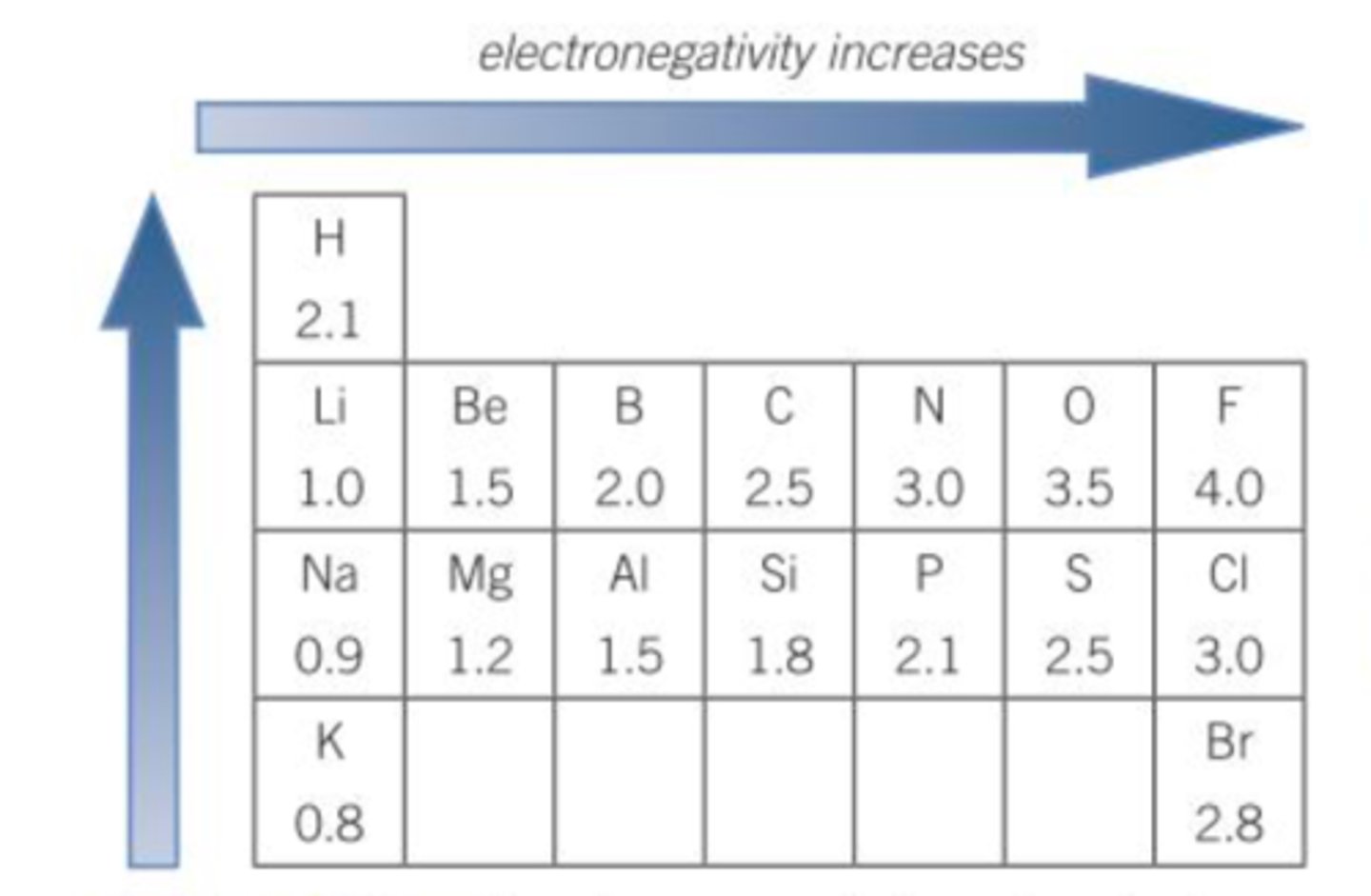
Electronegativity scale
0-4; 0 being the lowest and 4 being the highest.
What is a dependent variable?
variable that is measured
What is an independent variable?
variable that is manipulated
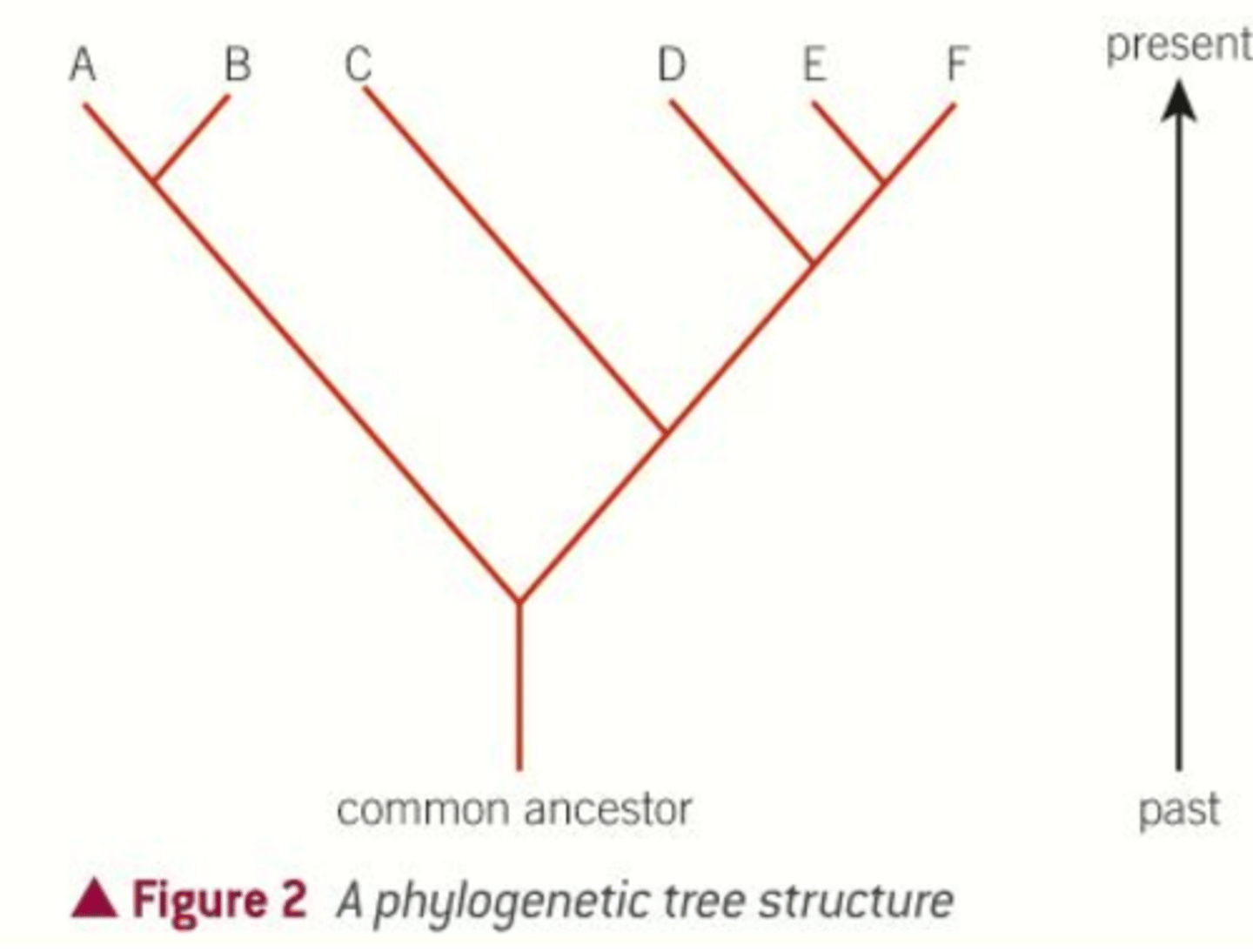
What is a phylogenetic tree?
A diagram that shows how species are related to each other through common ancestors
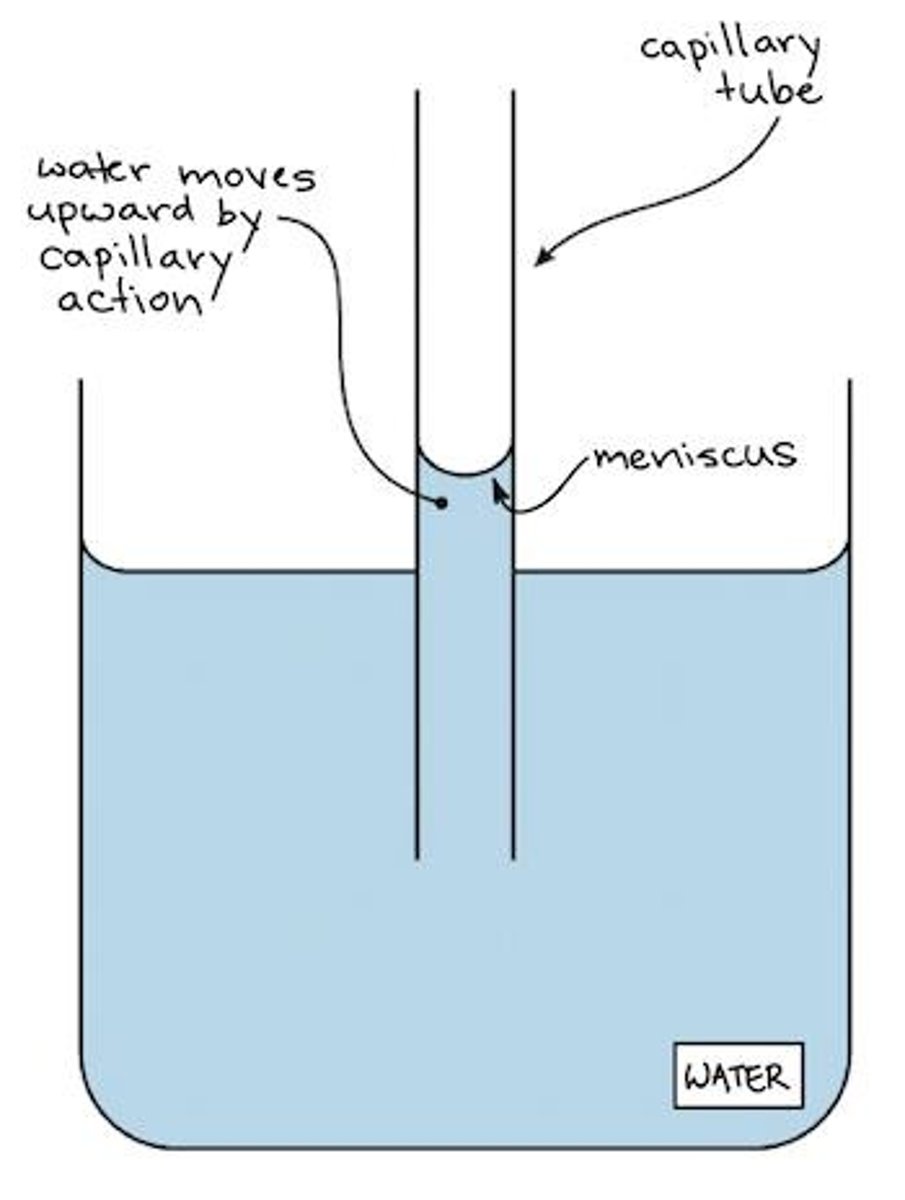
What is capillary action?
The attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
What is a hydrogen bond?
a weak bond between two partially charged atoms
What is chitin?
a fibrous substance consisting of polysaccharides and forming the major constituent in the exoskeleton of arthropods and the cell walls of fungi.
What is triglycerol?
a lipid made with three fatty acids and glycerol
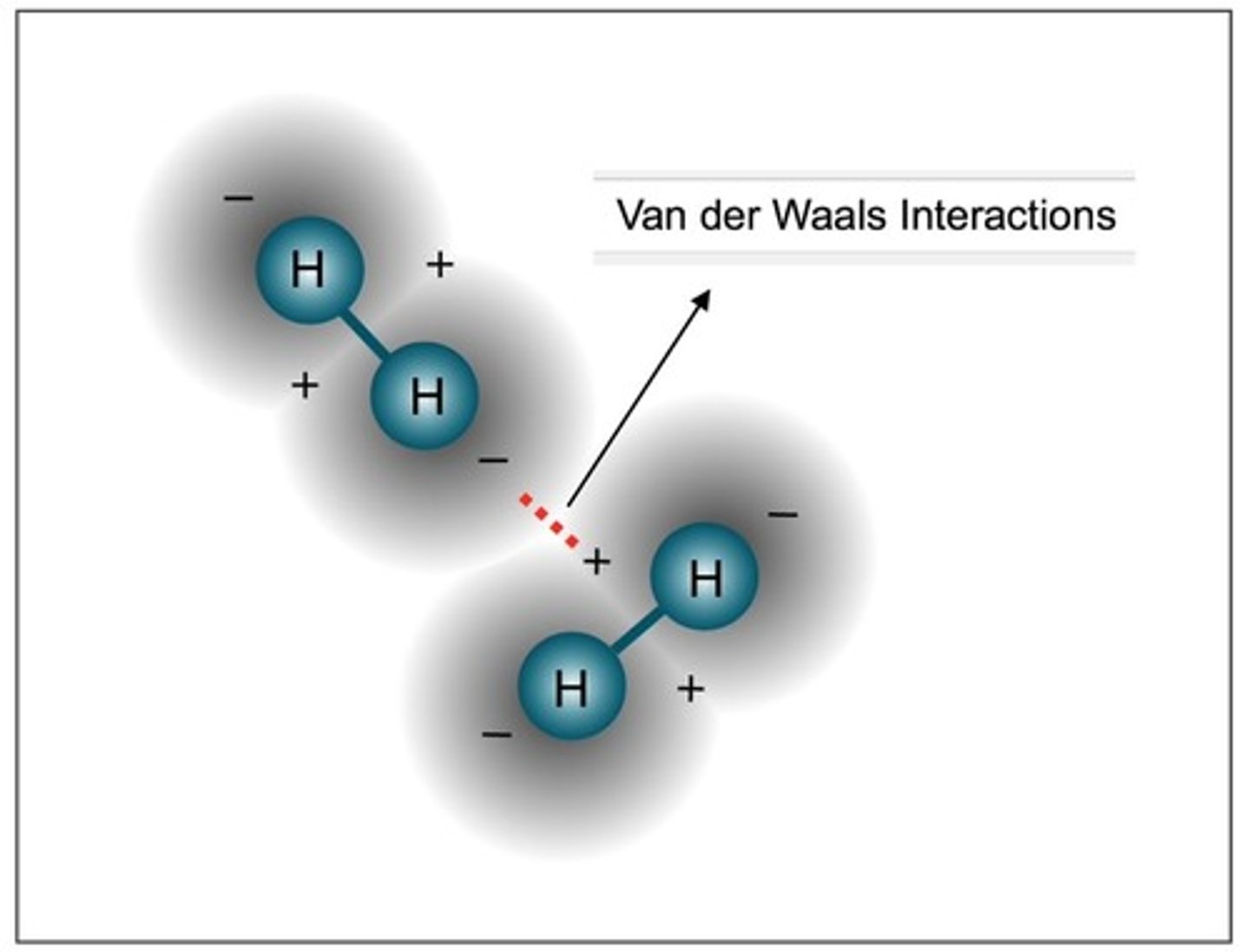
Van Der Waals Interactions are...
Weak bonds that occur between nonpolar molecules
What is chaperonin?
protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins
What is a purine?
a double-ringed nitrogenous base; Adenine and Guanine
What is a pyrimidine?
single-ringed nitrogenous base; cytosine, uracil, and thymine. CUT